Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Guide Data Communication Assessment
Загружено:
isaachariИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Guide Data Communication Assessment
Загружено:
isaachariАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
NATIONAL CERTIFICATES (VOCATIONAL)
ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES
DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING NQF Level 4
September 2007
DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING LEVEL 4 CONTENTS
SECTION A: PURPOSE OF THE SUBJECT ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES SECTION B: ASSESSMENT IN THE NATIONAL CERTIFICATES (VOCATIONAL) 1 2 Assessment in the National Certificates (Vocational) Assessment framework for vocational qualifications 2.1 Internal continuous assessment (ICASS) 2.2 External summative assessment (ESASS) Moderation of assessment 3.1 Internal moderation 3.2 External moderation Period of validity of internal continuous assessment (ICASS) Assessor requirements Types of assessment 6.1 Baseline assessment 6.2 Diagnostic assessment 6.3 Formative assessment 6.4 Summative assessment Planning assessment 7.1 Collecting evidence 7.2 Recording 7.3 Reporting Methods of assessment Instruments and tools for collecting evidence Tools for assessing student performance Selecting and/or designing recording and reporting systems Competence descriptions Strategies for collecting evidence 13.1 Record sheets 13.2 Checklists
4 5 6
8 9 10 11 12 13
SECTION C: ASSESSMENT IN DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING 1 2 3 4 Schedule of assessment Recording and reporting Internal assessment of Subject Outcomes in Data Communication and Networking Level 4 Specifications for external assessment in Data Communication and Networking Level 4 4.1 Integrated summative assessment task (ISAT) 4.2 National Examination
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
SECTION A: PURPOSE OF THE SUBJECT ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES
This document provides the lecturer with guidelines to develop and implement a coherent, integrated assessment system for Data Communication and Networking in the National Certificates (Vocational). It must be read with the National Policy Regarding Further Education and Training Programmes: Approval of the Documents, Policy for the National Certificates (Vocational) Qualifications at Levels 2 to 4 on the National Qualifications Framework (NQF). This assessment guideline will be used for National Qualifications Framework Levels 2-4. This document explains the requirements for the internal and external subject assessment. The lecturer must use this document with the Subject Guidelines: Data Communications and Networking to prepare for and deliver Data Communications ad Networking. Lecturers should use a variety of resources and apply a range of assessment skills in the setting, marking and recording of assessment tasks.
SECTION B: ASSESSMENT IN THE NATIONAL CERTIFICATES (VOCATIONAL)
1 ASSESSMENT IN THE NATIONAL CERTIFICATES (VOCATIONAL)
Assessment in the National Certificates (Vocational) is underpinned by the objectives of the National Qualifications Framework (NQF). These objectives are to:
Create an integrated national framework for learning achievements. Facilitate access to and progression within education, training and career paths. Enhance the quality of education and training. Redress unfair discrimination and past imbalances and thereby accelerate employment opportunities. Contribute to the holistic development of the student by addressing: � social adjustment and responsibility; � moral accountability and ethical work orientation; � economic participation; and � nation-building.
The principles that drive these objectives are:
Integration
To adopt a unified approach to education and training that will strengthen the human resources development capacity of the nation.
Relevance
To be dynamic and responsive to national development needs.
Credibility
To demonstrate national and international value and recognition of qualification and acquired competencies and skills.
Coherence
To work within a consistent framework of principles and certification.
Flexibility
To allow for creativity and resourcefulness when achieving Learning Outcomes, to cater for different learning styles and use a range of assessment methods, instruments and techniques.
Participation
To enable stakeholders to participate in setting standards and co-ordinating the achievement of the qualification.
Access
To address barriers to learning at each level to facilitate students progress.
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
Progression
To ensure that the qualification framework permits individuals to move through the levels of the national qualification via different, appropriate combinations of the components of the delivery system.
Portability
To enable students to transfer credits of qualifications from one learning institution and/or employer to another institution or employer.
Articulation
To allow for vertical and horizontal mobility in the education system when accredited pre-requisites have been successfully completed.
Recognition of Prior Learning
To grant credits for a unit of learning following an assessment or if a student possesses the capabilities specified in the outcomes statement.
Validity of assessments
To ensure assessment covers a broad range of knowledge, skills, values and attitudes (SKVAs) needed to demonstrate applied competency. This is achieved through: � � � � clearly stating the outcome to be assessed; selecting the appropriate or suitable evidence; matching the evidence with a compatible or appropriate method of assessment; and selecting and constructing an instrument(s) of assessment.
Reliability
To assure assessment practices are consistent so that the same result or judgment is arrived at if the assessment is replicated in the same context. This demands consistency in the interpretation of evidence; therefore, careful monitoring of assessment is vital.
Fairness and transparency
To verify that no assessment process or method(s) hinders or unfairly advantages any student. The following could constitute unfairness in assessment: � � � � Inequality of opportunities, resources or teaching and learning approaches Bias based on ethnicity, race, gender, age, disability or social class Lack of clarity regarding Learning Outcome being assessed Comparison of students work with other students, based on learning styles and language
Practicability and cost-effectiveness
To integrate assessment practices within an outcomes-based education and training system and strive for cost and time-effective assessment. 2 ASSESSMENT FRAMEWORK FOR VOCATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS
The assessment structure for the National Certificates (Vocational) qualification is as follows: 2.1 Internal continuous assessment (ICASS) Knowledge, skills values, and attitudes (SKVAs) are assessed throughout the year using assessment instruments such as projects, tests, assignments, investigations, role-play and case studies. The internal continuous assessment (ICASS) practical component is undertaken in a real workplace, a workshop or a Structured Environment. This component is moderated internally and externally quality assured by Umalusi. All internal continuous assessment (ICASS) evidence is kept in a Portfolio of Evidence (PoE) and must be readily available for monitoring, moderation and verification purposes. 2.2 External summative assessment (ESASS) The external summative assessment is either a single or a set of written papers set to the requirements of the Subject Learning Outcomes. The Department of Education administers the theoretical component according to relevant assessment policies.
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
A compulsory component of external summative assessment (ESASS) is the integrated summative assessment task (ISAT). This assessment task draws on the students cumulative learning throughout the year. The task requires integrated application of competence and is executed under strict assessment conditions. The task should take place in a simulated or Structured Environment. The integrated summative assessment task (ISAT) is the most significant test of students ability to apply acquired knowledge. The integrated assessment approach allows students to be assessed in more than one subject with the same integrated summative assessment task (ISAT). External summative assessments will be conducted annually between October and December, with provision made for supplementary sittings. 3 MODERATION OF ASSESSMENT
3.1 Internal moderation Assessment must be moderated according to the internal moderation policy of the Further Education and Training (FET) college. Internal college moderation is a continuous process. The moderators involvement starts with the planning of assessment methods and instruments and follows with continuous collaboration with and support to the assessors. Internal moderation creates common understanding of Assessment Standards and maintains these across vocational programmes. 3.2 External moderation External moderation is conducted by the Department of Education, Umalusi and, where relevant, an Education and Training Quality Assurance (ETQA) body according to South African Qualifications Authority (SAQA) and Umalusi standards and requirements. The external moderator:
monitors and evaluates the standard of all summative assessments; maintains standards by exercising appropriate influence and control over assessors; ensures proper procedures are followed; ensures summative integrated assessments are correctly administered; observes a minimum sample of ten (10) to twenty-five (25) percent of summative assessments; gives written feedback to the relevant quality assuror; and moderates in case of a dispute between an assessor and a student.
Policy on inclusive education requires that assessment procedures be customised for students who experience barriers to learning, and supported to enable these students to achieve their maximum potential. 4 PERIOD OF VALIDITY OF INTERNAL CONTINUOUS ASSESSMENT (ICASS)
The period of validity of the internal continuous assessment mark is determined by the National Policy on the Conduct, Administration and Management of the Assessment of the National Certificates (Vocational). The internal continuous assessment (ICASS) must be re-submitted with each examination enrolment for which it constitutes a component. 5 ASSESSOR REQUIREMENTS
Assessors must be subject specialists and should ideally be declared competent against the standards set by the ETDP SETA. If the lecturer conducting the assessments has not been declared a competent assessor, an assessor who has been declared competent may be appointed to oversee the assessment process to ensure the quality and integrity of assessments. 6 TYPES OF ASSESSMENT
Assessment benefits the student and the lecturer. It informs students about their progress and helps lecturers make informed decisions at different stages of the learning process. Depending on the intended purpose, different types of assessment can be used.
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
6.1 Baseline assessment At the beginning of a level or learning experience, baseline assessment establishes the knowledge, skills, values and attitudes (SKVAs) that students bring to the classroom. This knowledge assists lecturers to plan learning programmes and learning activities. 6.2 Diagnostic assessment This assessment diagnoses the nature and causes of learning barriers experienced by specific students. It is followed by guidance, appropriate support and intervention strategies. This type of assessment is useful to make referrals for students requiring specialist help. 6.3 Formative assessment This assessment monitors and supports teaching and learning. It determines student strengths and weaknesses and provides feedback on progress. It determines if a student is ready for summative assessment. 6.4 Summative assessment This type of assessment gives an overall picture of student progress at a given time. It determines whether the student is sufficiently competent to progress to the next level. 7 PLANNING ASSESSMENT
An assessment plan should cover three main processes: 7.1 Collecting evidence The assessment plan indicates which Subject Outcomes and Assessment Standards will be assessed, what assessment method or activity will be used and when this assessment will be conducted. 7.2 Recording Recording refers to the assessment instruments or tools with which the assessment will be captured or recorded. Therefore, appropriate assessment instruments must be developed or adapted. 7.3 Reporting All the evidence is put together in a report to deliver a decision for the subject. 8 METHODS OF ASSESSMENT
Methods of assessment refer to who carries out the assessment and includes lecturer assessment, selfassessment, peer assessment and group assessment.
LECTURER ASSESSMENT SELF-ASSESSMENT PEER ASSESSMENT GROUP ASSESSMENT The lecturer assesses students performance against given criteria in different contexts, such as individual work, group work, etc. Students assess their own performance against given criteria in different contexts, such as individual work, group work, etc. Students assess another students or group of students performance against given criteria in different contexts, such as individual work, group work, etc. Students assess the individual performance of other students within a group or the overall performance of a group of students against given criteria.
INSTRUMENTS AND TOOLS FOR COLLECTING EVIDENCE
All evidence collected for assessment purposes is kept or recorded in the students PoE. The following table summarises a variety of methods and instruments for collecting evidence. A method and instrument is chosen to give students ample opportunity to demonstrate the Subject Outcome has been attained. This will only be possible if the chosen methods and instruments are appropriate for the target group and the Specific Outcome being assessed.
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
METHODS FOR COLLECTING EVIDENCE Observation-based (Less structured) Observation Class questions Lecturer, student, parent discussions Assessment instruments Task-based (Structured) Assignments or tasks Projects Investigations or research Case studies Practical exercises Demonstrations Role-play Interviews Checklists Rating scales Rubrics Open middle: Students produce the same evidence but in different ways. Open end: Students use same process to achieve different results. Test-based (More structured) Examinations Class tests Practical examinations Oral tests Open-book tests
Assessment tools
Evidence
Observation sheets Lecturers notes Comments Focus on individual students Subjective evidence based on lecturer observations and impressions
Marks (e.g. %) Rating scales (1-7) Students answer the same questions in the same way, within the same time.
10 TOOLS FOR ASSESSING STUDENT PERFORMANCE Rating scales are marking systems where a symbol (such as 1 to 7) or a mark (such as 5/10 or 50%) is defined in detail. The detail is as important as the coded score. Traditional marking, assessment and evaluation mostly used rating scales without details such as what was right or wrong, weak or strong, etc. Task lists and checklists show the student what needs to be done. These consist of short statements describing the expected performance in a particular task. The statements on the checklist can be ticked off when the student has adequately achieved the criterion. Checklists and task lists are useful in peer or group assessment activities. Rubrics are a hierarchy (graded levels) of criteria with benchmarks that describe the minimum level of acceptable performance or achievement for each criterion. Using rubrics is a different way of assessing and cannot be compared to tests. Each criterion described in the rubric must be assessed separately. Mainly two types of rubrics, namely holistic and analytical, are used. 11 SELECTING AND/OR DESIGNING RECORDING AND REPORTING SYSTEMS The selection or design of recording and reporting systems depends on the purpose of recording and reporting student achievement. Why particular information is recorded and how it is recorded determine which instrument will be used. Computer-based systems, for example spreadsheets, are cost and time effective. The recording system should be user-friendly and information should be easily accessed and retrieved. 12 COMPETENCE DESCRIPTIONS All assessment should award marks to evaluate specific assessment tasks. However, marks should be awarded against rubrics and not be simply a total of ticks for right answers. Rubrics should explain the competence level descriptors for the skills, knowledge, values and attitudes (SKVAs) that a student must demonstrate to achieve each level of the rating scale. When lecturers or assessors prepare an assessment task or question, they must ensure that the task or question addresses an aspect of a Subject Outcome. The relevant Assessment Standard must be used to create the rubric to assess the task or question. The descriptions must clearly indicate the minimum level of attainment for each category on the rating scale.
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
13 STRATEGIES FOR COLLECTING EVIDENCE A number of different assessment instruments may be used to collect and record evidence. Examples of instruments that can be (adapted and) used in the classroom include: 13.1 Record sheets The lecturer observes students working in a group. These observations are recorded in a summary table at the end of each project. The lecturer can design a record sheet to observe students interactive and problemsolving skills, attitudes towards group work and involvement in a group activity. 13.2 Checklists Checklists should have clear categories to ensure that the objectives are effectively met. The categories should describe how the activities are evaluated and against what criteria they are evaluated. Space for comments is essential.
SECTION C: ASSESSMENT IN DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING
1 SCHEDULE OF ASSESSMENT
At NQF levels 2, 3 and 4, lecturers will conduct assessments as well as develop a schedule of formal assessments that will be undertaken in the year. All three levels also have an external examination that accounts for 50 percent of the total mark. The marks allocated to assessment tasks completed during the year, kept or recorded in a PoE account for the other 50 percent. The PoE and the external assessment include practical and written components. The practical assessment in Data Communication and Networking must, where necessary, be subjected to external moderation by Umalusi or an appropriate Education and Training Quality Assurance (ETQA) body, appointed by the Umalusi Council in terms of Section 28(2) of the General and Further Education and Training Quality Assurance Act, 2001 (Act No. 58 of 2001). 2 RECORDING AND REPORTING
Data Communication and Networking, as is the case for all the other Vocational subjects, is assessed according to five levels of competence. The level descriptions are explained in the following table. Scale of Achievement for the Vocational component
RATING CODE 5 4 3 2 1 Outstanding Highly Competent Competent Not yet competent Not achieved RATING MARKS % 80-100 70-79 50-69 40-49 0-39
The programme of assessment should be recorded in the Lecturers Portfolio of Assessment for each subject. The following at least should be included in the Lecturers Assessment Portfolio:
A contents page The formal schedule of assessment The requirements for each assessment task The tools used for each assessment task Recording instrument(s) for each assessment task A mark sheet and report for each assessment task
The college must standardise these documents.
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
The students PoE must include at least:
A contents page The assessment tasks according to the assessment schedule The assessment tools or instruments for the task A record of the marks (and comments) achieved for each task
Where a task cannot be contained as evidence in the PoE, its exact location must be recorded and it must be readily available for moderation purposes. The following units of internal assessment must serve as a guide for Data Communication and Networking:
NO. OF UNITS 2 1 3 ASSESSMENT Formal written tests Internal written exam Practical assessments COVERAGE 1 or more completed topics All completed topics Must cover the related subject outcomes Install a LAN Install networked computer application software Support a LAN user/s Support Local Area computer Network
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
ASSESSMENT OF DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING LEVEL 4
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT OF SUBJECT OUTCOMES IN DATA COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING - LEVEL 4
Topic 1 Principles of computer network
SUBJECT OUTCOME 1.1 Describe data communication. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The roles of key elements in data communication are explained. The difference between LANs and WANs is explained. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain the roles of key elements in data communication. Explain the difference between local area and wide area networks (LANs and WANs).
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment. Projects.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 1.2 Demonstrate the knowledge of main features of Local Area Networks (LANs). ASSESSMENT STANDARD The uses of LANs is identified with respect to current practice. The main types of LAN media are identified. The main LAN configurations are described. LAN bandwidth s described. LAN protocols are described. LEARNING OUTCOME Identify the uses of LANs with respect to current practice. Identify the main types of LAN media. Describe the main LAN configurations. Describe LAN bandwidth. Describe LAN protocols. ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment. Projects.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 1.3 Demonstrate knowledge of main features of WANs ASSESSMENT STANDARD The uses of WANs s explained with respect to current practice. The uses, hardware requirements and advantages of WANs are described. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain the uses of WANs with respect of current practice. Explain the uses, hardware requirements and advantages of WANs.
10
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment. Projects.
Topic 2: Synchronous/asynchronous communication of computers
SUBJECT OUTCOME 2.1 Describe past, present and emerging developments in data communication. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The origin of current data communication is explained. The taxonomy of current systems is described. Trends from emerging developments in data communications are identified. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain the origin of current data communication. Describe taxonomy of current systems. Identify trends from emerging developments in data communications.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 2.2 Describe synchronous and asynchronous data communication. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The characteristics of each form of data communication are outlined. The features of data communications equipment is explained with respect to synchronous and asynchronous data communication. LEARNING OUTCOME Outline the characteristics of each form of data communication. Explain the features of data communications equipment with respect to synchronous and asynchronous data communication.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
Department of Education
11
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
SUBJECT OUTCOME 2.3 Describe communication with computers using telephone networks. ASSESSMENT STANDARD Types of telephone network services are distinguished, and their features and costs outlined. The functions of telephone network components are outlined. The types of problems encountered in digital transmission are explained. The options available as distance increases are described. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment. SUBJECT OUTCOME 2.4 Describe synchronous and asynchronous communication with computers. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The interface of the physical layer for synchronous and asynchronous communication is described. The application and operation of protocols are described. The delays incurred in transmissions are described. The operation of link control protocols is described. LEARNING OUTCOME Describe the interface of the physical layer for synchronous and asynchronous communication. Describe the application and operation of protocols. Describe the delays incurred in transmissions. Describe the operation of link control protocols. LEARNING OUTCOME Distinguish types of telephone network services and outline their features and costs. Outline the functions of telephone network components. Explain the types of problems encountered in digital transmission. Describe the options available as distance increases.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
Topic 3: Computer network architectures and standards
SUBJECT OUTCOME 3.1 Describe computer network types and standards. ASSESSMENT STANDARD Types of networks are distinguished. Network topologies are compared. Features of node addressing method are described and distinguished. The standards for industry network architectures are described. Demonstrations. Practical tests. LEARNING OUTCOME Distinguish types of networks. Compare network topologies. Describe and distinguish features of node addressing methods. Describe the standards for industry network architectures.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES
12
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
SUBJECT OUTCOME 3.2 Explain local and wide area network architectures. ASSESSMENT STANDARD Channel utilisation techniques and their features are described. The principles of access protocols are compared. The purpose of LAN components is identified. Network configurations and installation issues are described. Class tests. Assignment. SUBJECT OUTCOME 3.3 Explain WAN architectures. ASSESSMENT STANDARD Switching techniques are identified. Switching techniques are compared. WAN management issues are described. Class tests. Assignment. LEARNING OUTCOME Identify switching techniques. Compare switching techniques. Describe WAN management issues. LEARNING OUTCOME Describe channel utilisation techniques and their features. Compare the principles of access protocols. Identify the purpose of LAN components. Describe network configurations and installation issues.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES
Topic 4: Computer network communication
SUBJECT OUTCOME 4.1 Explain computer network transmission security and integrity problems and solutions. ASSESSMENT STANDARD Current problems are described. The requirements to address the problems are identified. The strategies to address the problems are explained and examples used in the industry provided. LEARNING OUTCOME Describe current problems. Identify the requirements to address the problems. Explain the strategies to address the problems and provide examples used in the industry.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
Department of Education
13
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
SUBJECT OUTCOME 4.2 Describe public switching computer network protocols. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The features of typical data link protocols are described. The features of a data link protocol are described. The features of a network layer protocol are described. LEARNING OUTCOME Describe the features of typical data link protocols. Describe the features of a data link protocol. Describe the features of a network layer protocol.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 4.3 Monitor a computer network. ASSESSMENT STANDARD Monitoring is performed by using computer network monitoring tools. Monitoring activities are described by means of a report. Common network problems are identified. LEARNING OUTCOME Describe monitoring of computer network using computer network monitoring tools. Describe activities by means of a report. Identify common network problems.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
Topic 5: Computer cabling
SUBJECT OUTCOME 5.1 Describe past, present and emerging developments in computer cabling. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The origin of current computer cabling systems is explained with an outline of past developments. The taxonomy of current cabling systems is described. Trends from emerging developments in computer cabling are identified and projected. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain the origin of current computer cabling systems with an outline of past developments. Describe the taxonomy of current cabling systems. Identify and project trends from emerging developments in computer cabling.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
14
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
SUBJECT OUTCOME 5.2 Describe termination methods for computer cabling. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The characteristics of each method are described. The features of each method are explained with respect to synchronous and asynchronous data communication. LEARNING OUTCOME Describe the characteristics of each method. Explain the features of each method with respect to synchronous and asynchronous data communication.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
Topic 6: Install a Local Area Network (LAN)
SUBJECT OUTCOME 6.1 Review the design and installation plan of a local area computer network. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The feasibility of the network design and installation plan is identified and explained. The procedures to ensure that the final outcome meets user requirements are explained. LEARNING OUTCOME Identify and explain the feasibility of the network design and installation plan. Explain the procedures to ensure that the final outcome meets user requirements.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 6.2 Install local area computer network devices. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The installation ensures that the device completes the manufacturers diagnostic tests free of errors. The installation ensures that the devices are located and interconnected according to the manufacturers specifications and network design. The installation ensures that the devices are configured and customised according to the network design and the manufacturers specifications. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to ensure that the device completes the manufacturers diagnostic tests free of errors. Explain how to ensure that the devices are located and interconnected according to the manufacturers specifications and network design. Explain how to ensure that the devices are configured and customised according to the network design and the manufacturers specifications.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
Department of Education
15
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
SUBJECT OUTCOME 6.3 Install local area computer network system and application software. ASSESSMENT STANDARD Installation ensures that the manufacturers guidelines are followed. Installation ensures that the software operates according to manufacturers specification. Installation ensures that software is configured and customised according to network designs. Installation ensures that the software performs according to the network design. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to ensure that the manufacturers guidelines are followed. Explain how to ensure that the software operates according to manufacturers specification. Explain how to ensure that the software is configured and customised according to network designs. Explain how to ensure that the software performs according to the network design.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 6.4 Test the installation of a local area computer network. ASSESSMENT STANDARD Testing ensures that the network operates according to manufacturers and installation specifications. Testing procedures meet the manufacturers guidelines. Testing results are recorded according to the installation specifications. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how testing will ensure that the network operates according to manufacturers and installation specifications. Explain how testing procedures meet the manufacturers guidelines. Explain how to record testing results according to the installation specifications.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 6.5 Gain user acceptance for the installation of a local area computer network. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The manner in which the manufacturers supplied operating procedures allow the user to begin operating the network is explained. The manner in which training and support options allow the user to obtain training and support is explained. The manner in which the installation and installation specifications allow the user to check that the installation has been completed is explained. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how the manufacturers supplied operating procedures will allow the user to begin operating the network. Explain how training and support options allow the user to obtain training and support. Explain how the installation and installation specifications allow the user to check that the installation has been completed.
16
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignment.
Topic 7 Install networked computer application software
SUBJECT OUTCOME 7.1. Plan the installation of networked computer application software. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The feasibility of the network application specification is identified and explained. Milestones are specified and the time and resources required for the installation estimated. The manner in which to ensure that the installation is scheduled to minimise disruption to the users is explained. The plan ensures that an analysis of risk identifies the tasks which are vulnerable to standard risks. The plan identifies measures to be taken to minimise risk, and the contingency measures to be adopted in the event of a risk manifesting. The plan adopts a review procedure that ensures that the final outcome meets user requirements. LEARNING OUTCOME Identify and explain the feasibility of the network application specification. Specify milestones and estimate the time and resources required for the installation. Explain how to ensure that the installation is scheduled to minimise disruption to the users. Explain how to ensure that a risk analysis identifies the tasks which are vulnerable to standard risks. Identify measures to be taken to minimise risk, and the contingency measures to be adopted in the event of a risk manifesting. Explain how a review procedure will be adopted to ensure that the final outcome meets the user requirements.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 7.2 Install networked computer application software. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The installation ensures that the software operates according to the publishers specifications. The installation ensures that the software is configured and customised according to the installation specification. The installation ensures that the software operates according to installation specification. The pre-installation environment is restored in the event of an unsuccessful installation LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to ensure that the software operates according to the publishers specifications. Explain how to ensure that the software is configured and customised according to the installation specification. Explain how to ensure that the software operates according to installation specifications Explain how to ensure that the pre-installation environment is restored in the event of an unsuccessful installation.
Department of Education
17
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 7.3. Test the installation of networked computer application software. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The test ensures that the software operates according to the manufacturers and installation specification. The test procedures meet the manufacturers guidelines. Test results are recorded according to organisation specifications. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how testing will ensure that the network operates according to manufacturers and installation specifications. Explain how testing procedures meet the manufacturers guidelines. Explain how to record testing results according to the installation specifications.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 7.4. Accomplish user acceptance for the installation of networked computer application software. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The manner in which the manufacturers operating procedures allow the user to begin the network application is explained. The manner in which training and support options allow the user to obtain training and support is explained. The manner in which installation and installation specifications allow the user to check whether the installation has been completed, is explained. The manner in which to ensure that documentation is completed according to the publishers and organisation requirements is explained. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how the manufacturers supplied operating procedures will allow the user to begin the network application. Explain how training and support options allow the user to obtain training and support. Explain how the installation and installation specifications allows the user to check that the installation has been completed. Explain how to ensure that documentation is completed according to the publishers and organisation requirements.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignments.
18
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
Topic 8 Principles of supporting LAN users
SUBJECT OUTCOME 8.1. Demonstrate the use of LAN. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The demonstration illustrates how user utilities are operated to perform user tasks according to the manufacturers specifications. The structure of the network access security system is described. The manner in which print queues are managed according to the manufacturers specifications is explained and demonstrated. LEARNING OUTCOME Demonstrate how user utilities are operated to perform user tasks according to the manufacturers specifications. Describe the structure of the network access security system. Explain and demonstrate how print queues are managed according to manufacturers specifications.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 8.2. Install a single user computer application software package. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The installation is performed according to manufacturers specifications. The installation is configured according to specifications. Documentation is prepared according to industry recommended practice. The installation site is left clean and tidy according to industry recommended practice. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to perform installation according to manufacturers specifications. Explain how to configure installations according to specifications. Explain how to prepare documentation according to industry recommended practice. Explain how to ensure that the installation site is left clean and tidy according to industry recommended practice.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 8.3. Customise a local area network user interface. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The customisation includes preparation of a log in script. The customisation includes creation of a menu according to organisations specifications. Documentation is completed according to industry recommended practice. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to prepare a log in script. Explain how to create a menu according to organisations specifications. Explain how to ensure that documentation is completed according to industry recommended practice.
Department of Education
19
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 8.4. Connect a LAN workstation. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The workstation is linked to a LAN according to manufacturers specifications. The connection automates log in procedures in accordance with the manufacturers specifications. The connection resolves procedural problems encountered by users accessing the network. Documentation is completed according to industry recommended practice. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to ensure that the workstation is linked to a LAN according to manufacturers specifications. Explain how to ensure that connection automates log in procedures in accordance with the manufacturers specifications. Explain how to ensure that the connection resolves procedural problems encountered by users accessing the network. Explain how to ensure that the connection completes documentation according to industry recommended practice.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical tests. Interviews. Assignments.
Topic 9: Support a local area computer network
SUBJECT OUTCOME 9.1 Maintain the performance of a local area computer network. ASSESSMENT STANDARD Monitoring and tuning of the network ensures that operation and performance meet the manufacturers and organisation specifications. Network performance problems are resolved according to organisation specifications. Accurate and up-to-date documentation of network resource utilisation is maintained. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how monitoring and tuning of the network ensures operation and performance meet the manufacturer and organisation specifications. Explain how network performance problems are resolved according to organisation specifications. Explain how to ensure that accurate and up-to-date documentation of network resource utilisation is maintained.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical exercises. Interviews. Assignments.
20
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
SUBJECT OUTCOME 9.2. Execute procedures on a local area computer network. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The execution ensures that computer output is produced according to organisation specifications. Procedure messages are identified during execution, and actions are taken according to organisation specifications. Problems with procedures are identified, and action is taken according to organisation specifications. Potential improvements to procedures are identified, and action is taken according to organisation specifications. Start-up and shutdown of the network are in accordance with the manufacturers and organisation specifications. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to ensure that computer output is produced according to specifications. Identify procedure messages during execution, and the actions taken according to organisation specifications. Identify problems with procedures, and action taken according to organisation specifications. Identify potential improvements to procedures, and action taken according to organisation specifications. Explain how to start-up and shutdown the network in accordance with the manufacturers and organisation specifications.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical exercises. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 9.3 Administer security systems for a local area network. ASSESSMENT STANDARD Security exposures and violations are identified, and action is taken according to organisation policies, procedures and requirements. Back-ups are made according to the organisation policies, procedures and specifications. Access to the network is provided according to organisation policies, procedures and specifications. LEARNING OUTCOME Identify security exposures and violations and action taken according to organisation policies, procedures and requirements. Explain how to make back-ups according to the organisation policies, procedures and specifications. Explain how to provide access to the network according to organisation policies, procedures and specifications.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical exercises. Interviews. Assignments.
Department of Education
21
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
SUBJECT OUTCOME 9.4 Maintain the supply of consumables for a LAN. ASSESSMENT STANDARD A forecast of the rates of use of computer system consumables is justified using measurement of historical rates of use and anticipated events. Supply agreements are established and maintained so that the consumable supplies are available to meet demand. Stocks of consumable supplies meet forecasted demand. Overstock of consumable supplies are avoided. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to forecast the rate of use of computer system consumables, using measurement of historical rates of use and anticipated events. Explain how to establish and maintain supply agreements so that the consumable supplies are available to meet demand. Explain how forecasted demand meets stocks of consumable supplies. Explain how to avoid overstock of consumable supplies.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical exercises. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 9.5 Plan capacity for a LAN. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The plan includes a forecast based documentation of current network resource utilisation, historical growth and future plans. The plan includes recommendations for network changes that allow the network to meet the future capacity requirements. The feasibility of the recommendations is identified and explained and identified. Actual resource usage is compared with forecast usage according to organisation requirements. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to include a forecast based documentation of current network utilisation, historical growth and future plans. Explain how to include recommendations for network changes that allow the network to meet the future capacity requirements. Explain and identify the feasibility of the recommendations. Compare actual resource usage with forecast usage according to organisation requirements.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical exercises. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 9.6 Maintain the availability of a LAN. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The network is available and accessible according to organisation requirements. Network availability problems are resolved according to organisation specifications. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to ensure the availability and accessibility of the network according to organisation requirements. Explain how to resolve network availability problems according to organisation requirements.
22
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical exercises. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 9.7 Manage changes to a LAN. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The impact and risks to the organisation of a proposed change are predicted. The timing of the proposed change minimises the impacts and risks. The contingency plan that allows the network to be restored to a status acceptable to the user in the event of problems with the change. Testing establishes the success of the installation and of the changes according to user and organisation requirements. The people affected by the change are notified to minimise disruption to their activity. LEARNING OUTCOME Explain how to ensure that the management plan of a proposed change predicts the impact and risks to the organisation associated with the change. Explain how the management plan ensures that the proposed change establishes when the change should occur to minimise the impacts and risks. Explain how the contingency plan will allow the network to be restored to a status acceptable to the user in the event of the problems with the change. Explain how testing will establish the success of installation and of the changes according to user and organisation requirements. Explain how to notify people affected by the change to minimise disruption to their activity.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical exercises. Interviews. Assignments.
Topic 10: Compare WAN with LAN
SUBJECT OUTCOME 10.1 Explain wide area computer networks. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The components of a WAN are identified and their purpose outlined. The purpose of a WAN is identified WAN configurations are identified and compared. WAN protocols are identified and compared. WAN transport media are identified and compared. LEARNING OUTCOME Identify the components of a WAN and outline their purpose. Identify the purpose of a WAN. Identify and compare WAN configurations. Identify and compare WAN protocols. Identify and compare WAN transport media.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical exercises. Interviews. Assignments.
Department of Education
23
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
SUBJECT OUTCOME 10.2. Evaluate a wide area computer network. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The method of implementation of the WAN is identified. Categories of the network components, the functions and examples are distinguished. The features and constraints of the network are identified and explained from a functional perspective. The alternative network designs are proposed and compared. LEARNING OUTCOME Identify the method of implementation of a WAN. Distinguish categories of the network components, the functions and examples. Identify and explain the features and constraints of the network from a functional perspective. Propose and compare alternative network designs.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical exercises. Interviews. Assignments.
SUBJECT OUTCOME 10.3. Explain network administration. ASSESSMENT STANDARD The tasks involved in network administration are identified and their requirements outlined. The explanation outlines, for a range of factors, how response times are affected. The explanation outlines the principles of network interconnections. Network security administration procedures are outlined and explained. Network administration documentation is completed. LEARNING OUTCOME Identify the tasks involved in network administration and outline their requirements. Explain how response times are affected for a range of factors. Outline the principles of network interconnections. Outline and explain network security administration procedures. Describe how to complete network administration documentation.
ASSESSMENT TASKS OR ACTIVITIES Observations. Class tests. Demonstrations. Practical exercises. Interviews. Assignments.
24
Department of Education
Data Communication and Networking National Certificates (Vocational)
SPECIFICATIONS FOR EXTERNAL NETWORKING - LEVEL 4
ASSESSMENT
IN
DATA
COMMUNICATION
AND
4.1 Integrated summative assessment task (ISAT) A compulsory component of the external assessment (ESASS) is the integrated summative assessment task (ISAT). The integrated summative assessment task (ISAT) draws on the students cumulative learning achieved throughout the year. The task requires integrated application of competence and is executed and recorded in compliance with assessment conditions. Two approaches to the integrated summative assessment task (ISAT) may be as follows: The students are assigned a task at the beginning of the year which they will have to complete in phases during the year to obtain an assessment mark. A final assessment is made at the end of the year when the task is completed. OR Students achieve the competencies during the year but the competencies are assessed cumulatively in a single assessment or examination session at the end of the year. The integrated summative assessment task (ISAT) is set by an externally appointed examiner and is conveyed to colleges in the first quarter of the year. The integrated assessment approach enables students to be assessed in more than one subject with the same integrated summative assessment task (ISAT). 4.2. National Examination A national examination is conducted annually in October or November by means of a paper(s) set and moderated externally. The following distribution of cognitive application is suggested:
LEVEL 4 KNOWLEDGE AND COMPREHENSION 50% APPLICATION 25% ANALYSIS, SYNTHESIS AND EVALUATION 25%
Department of Education
25
Вам также может понравиться
- Communication Networks Lesson PlanДокумент9 страницCommunication Networks Lesson Planramarajan100% (2)
- Ms Powerpoint Quiz2016Документ2 страницыMs Powerpoint Quiz2016api-2610280400% (2)
- Cse - 7th - Sem - Proposal and Synopsis For Mior Project 2021-22Документ5 страницCse - 7th - Sem - Proposal and Synopsis For Mior Project 2021-22Divin KurupОценок пока нет
- Data Structure-Module 1 PDFДокумент18 страницData Structure-Module 1 PDFKushОценок пока нет
- Used To Manage and Monitor The NetworkДокумент35 страницUsed To Manage and Monitor The NetworkFikru TesefayeОценок пока нет
- Course-Syllabus - Sia 101Документ7 страницCourse-Syllabus - Sia 101Richard CoronelОценок пока нет
- C++ Computer Programming RubricДокумент2 страницыC++ Computer Programming RubricCristy Balubayan NazarenoОценок пока нет
- Python Programming Lesson 03 - Control Structures in Python: 3.1 Decision MakingДокумент6 страницPython Programming Lesson 03 - Control Structures in Python: 3.1 Decision MakingAndrjstne SalesОценок пока нет
- Types of NetworksДокумент13 страницTypes of NetworksharmangahirОценок пока нет
- IT Systems Policies, Procedures and Risk AssessmentДокумент10 страницIT Systems Policies, Procedures and Risk AssessmentCkreedlyf de los Santos100% (1)
- DBMS Lesson PlanДокумент8 страницDBMS Lesson PlanGautam DemattiОценок пока нет
- Selected Topics in Computer Science CHДокумент24 страницыSelected Topics in Computer Science CHMehari TemesgenОценок пока нет
- Jimma Institute of Technology: Chapter 1 Introduction To OOPДокумент24 страницыJimma Institute of Technology: Chapter 1 Introduction To OOPbersufekad yetera100% (1)
- Question Paper SetДокумент6 страницQuestion Paper Setsugumar durai0% (1)
- Java Programming: PolymorphismДокумент30 страницJava Programming: PolymorphismNics BalanayОценок пока нет
- DCN Question BankДокумент5 страницDCN Question Bankushapetchi18Оценок пока нет
- Case Study of Various Routing AlgorithmДокумент25 страницCase Study of Various Routing AlgorithmVijendra SolankiОценок пока нет
- IP Address Fundamentals ExplainedДокумент18 страницIP Address Fundamentals ExplainedHan NiefОценок пока нет
- College ERP System FinalДокумент19 страницCollege ERP System FinalShubham SinghОценок пока нет
- Data Communication Network and Internet PDFДокумент20 страницData Communication Network and Internet PDFpooja guptaОценок пока нет
- Exp.1 Lab Manual (Peer To Peer Network)Документ5 страницExp.1 Lab Manual (Peer To Peer Network)Mau Dimapilis100% (1)
- OOPS in C++ PDFДокумент7 страницOOPS in C++ PDFVyomОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To ComputerДокумент61 страницаChapter 1 - Introduction To ComputerdugsicodeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Simple Sorting and SearchingДокумент18 страницChapter 3 - Simple Sorting and SearchingShemsedinShukre100% (1)
- Iot DefinitionДокумент6 страницIot DefinitionlijethaОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Offline and Online Learning Mode in The Performance of Student During Corona Virus Pandemic Era Using Machine Learning in PythonДокумент8 страницAssessment of Offline and Online Learning Mode in The Performance of Student During Corona Virus Pandemic Era Using Machine Learning in PythonInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Systems Planning and SelectionДокумент11 страницSystems Planning and SelectionNATI NT100% (1)
- Web-Based Document Tracking and Management System of The Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH), Laguna Ii District Engineering Office, Los Baños, LagunaДокумент1 страницаWeb-Based Document Tracking and Management System of The Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH), Laguna Ii District Engineering Office, Los Baños, LagunaKelly FrederickОценок пока нет
- Week 2 Assignment OOP C++Документ7 страницWeek 2 Assignment OOP C++Sanjog Pradhan Edits100% (1)
- Mobile Transport LayerДокумент18 страницMobile Transport LayervalansterОценок пока нет
- Grid and Cloud Computing NotesДокумент20 страницGrid and Cloud Computing NotesSherril Vincent100% (3)
- Mobile Computing Lab Manual Updated On 20th March 2018Документ96 страницMobile Computing Lab Manual Updated On 20th March 2018Niviya Dahiya100% (1)
- Making Ethernet Cables - Simple and Easy: How To Make An Ethernet CableДокумент14 страницMaking Ethernet Cables - Simple and Easy: How To Make An Ethernet CableJohn YohansОценок пока нет
- Bluetooth Protocol StackДокумент3 страницыBluetooth Protocol StackKrishanu Modak100% (2)
- Cisco Packet Tracer Keyboard Shortcuts GuideДокумент4 страницыCisco Packet Tracer Keyboard Shortcuts GuideHamami InkaZoОценок пока нет
- Module 08 - Basic Network ConfigurationДокумент12 страницModule 08 - Basic Network ConfigurationĐặng Đức100% (1)
- Overview of Expert System ToolsДокумент8 страницOverview of Expert System ToolsRanbir SinghОценок пока нет
- Assignment On Java InheritanceДокумент3 страницыAssignment On Java InheritancesalonyОценок пока нет
- Topic 1 Introduction TojavaДокумент15 страницTopic 1 Introduction TojavasmcmasaiОценок пока нет
- Vtu Computer Network Lab ManualДокумент61 страницаVtu Computer Network Lab ManualMayank Kushal100% (1)
- Course Plan HCIДокумент9 страницCourse Plan HCISathyanarayananОценок пока нет
- Lec 02 - Network ModelДокумент28 страницLec 02 - Network ModelAmirul AminОценок пока нет
- GTU VIDEO PROCESSING COURSEДокумент4 страницыGTU VIDEO PROCESSING COURSEChandan PurohitОценок пока нет
- 2 Marks With AnswerДокумент30 страниц2 Marks With AnswernarmathaОценок пока нет
- Wireless and Mobile Communication Course OverviewДокумент1 страницаWireless and Mobile Communication Course OverviewvinothОценок пока нет
- Network Topology - Computer System ServicingДокумент39 страницNetwork Topology - Computer System ServicingVhon Xander [Personal Channel]Оценок пока нет
- ISIS - Integrated Student Information System Project PlanДокумент16 страницISIS - Integrated Student Information System Project PlanArslОценок пока нет
- Cebu Technological University - Main Campus Bachelor of Science in Mechatronics (MX)Документ20 страницCebu Technological University - Main Campus Bachelor of Science in Mechatronics (MX)Engr. Jeremiah Badana100% (1)
- Lecture Note - Top Level View of ComputerДокумент6 страницLecture Note - Top Level View of Computertesfu zewduОценок пока нет
- Feedback FormsДокумент3 страницыFeedback FormsVenkata Rao NekkantiОценок пока нет
- Ambo University Woliso CampusДокумент10 страницAmbo University Woliso CampusTolosa TafeseОценок пока нет
- The Double Transposition CipherДокумент2 страницыThe Double Transposition CipherBenjie Sabado VasquezОценок пока нет
- Systems Analysis Phase Evaluation Software AlternativesДокумент54 страницыSystems Analysis Phase Evaluation Software AlternativesGagan Chandel0% (1)
- Introduction To Computer SystemДокумент4 страницыIntroduction To Computer SystemRegineDagumanFuellasОценок пока нет
- Net-Centric Past Questions AnswersДокумент7 страницNet-Centric Past Questions Answersaltair001Оценок пока нет
- JSD: Jackson System Development ProcessДокумент18 страницJSD: Jackson System Development ProcessArun SaxenaОценок пока нет
- IT 2352-Unit 2Документ32 страницыIT 2352-Unit 2ShankarОценок пока нет
- LAW OF PROCEDURES AND EVIDENCE - Assessment - PlanДокумент16 страницLAW OF PROCEDURES AND EVIDENCE - Assessment - PlanDreana MarshallОценок пока нет
- FOOD PREPARATION - Assessment - PlanДокумент17 страницFOOD PREPARATION - Assessment - Planddmarshall2838Оценок пока нет
- National Certificates (Vocational) : Mathematics NQF Level 3Документ24 страницыNational Certificates (Vocational) : Mathematics NQF Level 322nd ERA NandosОценок пока нет
- Underground Legal SteroidsДокумент86 страницUnderground Legal Steroidsbigpapaprause100% (11)
- Krav Maga GroundfightingДокумент15 страницKrav Maga Groundfightingbrogan100% (39)
- Chi Kung - Qigong Program Five AnimalsДокумент137 страницChi Kung - Qigong Program Five AnimalsGarbanzoNegro100% (12)
- Qi Gong (Chi Kung) 2Документ81 страницаQi Gong (Chi Kung) 2Jose Ivo Sampaio100% (6)
- Et - ncv.1.2.1 NCV Poa Pack r001 2013Документ6 страницEt - ncv.1.2.1 NCV Poa Pack r001 2013isaachariОценок пока нет
- Bas Rutten's MMA Workout Booklet PDFДокумент0 страницBas Rutten's MMA Workout Booklet PDFwpd2688100% (4)
- New Text DocumentДокумент1 страницаNew Text DocumentisaachariОценок пока нет
- Student Study Guide: Networking FundamentalsДокумент59 страницStudent Study Guide: Networking FundamentalsDanielaMuhajОценок пока нет
- Isat L2Документ36 страницIsat L2isaachari46% (13)
- Krav Maga GroundfightingДокумент15 страницKrav Maga Groundfightingbrogan100% (39)
- Isat L2Документ36 страницIsat L2isaachari46% (13)
- Isat L2Документ36 страницIsat L2isaachari46% (13)
- Isat L2Документ36 страницIsat L2isaachari46% (13)
- ISAT L3 - IT Computer Science 2011Документ26 страницISAT L3 - IT Computer Science 2011isaachari100% (1)
- Nc790 - Introduction To Systems Development l2 Sup QP 2009Документ10 страницNc790 - Introduction To Systems Development l2 Sup QP 2009isaachari100% (1)
- Isat L2Документ36 страницIsat L2isaachari46% (13)
- Bas Rutten's MMA Workout Booklet PDFДокумент0 страницBas Rutten's MMA Workout Booklet PDFwpd2688100% (4)
- ISAT L3 - IT Computer Science 2011Документ26 страницISAT L3 - IT Computer Science 2011isaachari100% (1)
- SKMBT C20313020611120Документ1 страницаSKMBT C20313020611120isaachariОценок пока нет
- Isat L2Документ36 страницIsat L2isaachari46% (13)
- MCS Syllabus for GTU's MBA 4th SemДокумент2 страницыMCS Syllabus for GTU's MBA 4th Semjitendra patoliyaОценок пока нет
- A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers 13Th Edition Full ChapterДокумент42 страницыA Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers 13Th Edition Full Chapterchristopher.hess142100% (23)
- AP Statistics Teacher GuideДокумент260 страницAP Statistics Teacher Guideharesh100% (2)
- COGNITIVE PSY Unit 1-2 Notes ShivaniДокумент56 страницCOGNITIVE PSY Unit 1-2 Notes ShivaniShivani MaratheОценок пока нет
- Developing Individuals, Teams and OrganizationsДокумент28 страницDeveloping Individuals, Teams and OrganizationsShaji Viswanathan. Mcom, MBA (U.K)94% (17)
- 03 Conversational MasteryДокумент38 страниц03 Conversational MasteryIomah Massiah100% (7)
- Active ListeningДокумент11 страницActive ListeningJorge Verdejo100% (2)
- Federal Ethiopia Education Policy Outlines ObjectivesДокумент7 страницFederal Ethiopia Education Policy Outlines ObjectivesFendishe AbdujebarОценок пока нет
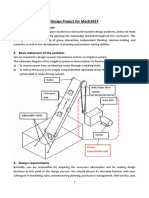
- MECH3427 Design Project 2017Документ8 страницMECH3427 Design Project 2017Genesis Norbert AlconabaОценок пока нет
- The interface between dementia and mental health: An evidence reviewДокумент52 страницыThe interface between dementia and mental health: An evidence reviewHisyamAngahLaaОценок пока нет
- Superpower!Документ10 страницSuperpower!vvvasimmmОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Artificial Intelligence and Expert SystemsДокумент14 страницIntroduction To Artificial Intelligence and Expert SystemsCristianBaesuОценок пока нет
- 5 Teaching Strategies to Improve Math LearningДокумент4 страницы5 Teaching Strategies to Improve Math LearningDoejejejОценок пока нет
- Itl Research 2012 - Innovative Teaching and Learning Research, 2011 Findings and Implications (Report)Документ40 страницItl Research 2012 - Innovative Teaching and Learning Research, 2011 Findings and Implications (Report)luiz carvalhoОценок пока нет
- Joint Staff Officer Handbook 2012Документ379 страницJoint Staff Officer Handbook 2012El Aries Somar100% (1)
- Officer Like QualitiesДокумент13 страницOfficer Like QualitiesasteeshОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Computers and C++ Programming ChapterДокумент38 страницIntroduction to Computers and C++ Programming Chapterken lacedaОценок пока нет
- Lesson PlanningДокумент37 страницLesson PlanningMariae JalandoonОценок пока нет
- BusinessPlan BusinessSimulation 12-18-18Документ76 страницBusinessPlan BusinessSimulation 12-18-18Stephanie Ann Asuncion100% (2)
- Mock Test 1Документ22 страницыMock Test 1Ngan Le80% (5)
- PECS@AMYДокумент7 страницPECS@AMYmie_fernandez11Оценок пока нет
- Defining Productive PlayДокумент19 страницDefining Productive PlaySebastianTrellesОценок пока нет
- The Impact of Classroom Evaluation Practices On STДокумент46 страницThe Impact of Classroom Evaluation Practices On STKishor JhaОценок пока нет
- Narrative Report GUTIERREZДокумент2 страницыNarrative Report GUTIERREZRazel HijastroОценок пока нет
- Induction Program QPIДокумент67 страницInduction Program QPISoo Chong HuatОценок пока нет
- The Radical Transformation of HaierДокумент28 страницThe Radical Transformation of Haiersagar_chhadva100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Transportation Planning ProcessДокумент28 страницChapter 5 - Transportation Planning Processren100% (2)
- SFBT Treatment ManualДокумент16 страницSFBT Treatment ManualMervin Imhotep Accouche100% (1)
- Readiness To ChangeДокумент35 страницReadiness To ChangeSakshiMalhotraОценок пока нет
- P21 Framework Definitions New Logo 2015 PDFДокумент9 страницP21 Framework Definitions New Logo 2015 PDFIndarYantОценок пока нет