Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Osmosis&diffusion 3N
Загружено:
ms_m_tanИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Osmosis&diffusion 3N
Загружено:
ms_m_tanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name:_____________________( ) Class:__________ Date:__________
Diffusion and Osmosis Chapter 2
At the end of the chapter, students should be able to:
1. Define diffusion and describe its role in nutrient uptake and gaseous exchange in
plants and humans.
2. Define osmosis and describe the effects of osmosis on plant and animal tissues.
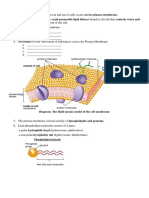
The plasma membrane is partially permeable only allows certain substances to
pass through
Substances cross the plasma membrane, leaving or entering cell by diffusion,
osmosis and active transport.
Diffusion and osmosis 1
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Why are most cells microscopic?
Why are all large organisms made up of many cells but not just one cell?
Total surface area
(height x width x 6 250 750
number of sides x
number of boxes)
Total volume 1 125 125
(height x width x
length x number of
boxes)
Surface-area-to- 6 1.2 6
volume ratio (area ÷
volume)
In the diagram, cells are represented as boxes
As the size of cell increases to 5 units of length per side in (b), the ratio of
surface area to volume ratio decreases compared to the smaller cell (a)
In a large cell (b), rates of movement of materials across cell membranes are
needed to meet the needs of cell may not be enough because most of the
cytoplasm is far away from the cell membrane
By dividing large cell to many small cells in (c), a high surface area to volume
ratio can be restored. This can serve each cell’s need for getting nutrients and
remove waste products
That is why larger organisms do not generally have larger cells than smaller
organisms, but more cells.
Diffusion and osmosis 2
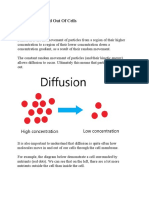
Diffusion
Molecules of oxygen are moving about all the time. Molecules of a liquid, or a
substance like sugar dissolved in water also move around.
The movement cause molecules to spread themselves out evenly to fill all the
available space
Diffusion movement of molecules from a region of _______________
concentration to a region of _________________ concentration, down a
concentration gradient.
Concentration gradient difference between high concentration and low
concentration
Diffusion ________________________________.
Diffusion also occurs in liquids.
o When you add a drop of red ink to a beaker of water, the ink spread slowly
throughout the water without stirring.
o Water in beaker becomes evenly red
Diffusion and osmosis 3
Rate of diffusion depends on:
o Concentration gradient
The greater the difference in concentrations between two regions of a
substance, the faster the rate of diffusion __________________
diffusion gradient, faster diffusion
o Distance over which diffusion takes place
Shorter distance between the 2 regions of concentration,
__________________ rate of diffusion
o Area over which diffusion takes place
Larger surface area, ___________________ rate of diffusion.
Diffusion surfaces have structures for increasing surface area where
they exchange material. Eg. Microvilli on cells lining the intestine.
o Size and nature of diffusion molecules
Small molecules dissolve ____________________
Molecules that dissolve in fats diffuse _____________________
through cell membranes than molecules that dissolve in water.
Diffusion and osmosis 4
Importance of diffusion
Diffusion an important way which substances move in and out of cells. In booth plant
and animal cells, gases are exchanged through diffusion
Examples:
o Presence of millions of alveoli in the lungs provides very large surface area
for gaseous exchange
o In plants, carbon dioxide diffuses in through the stomata during
photosynthesis and oxygen diffuses out
o In a one-celled organism called Amoeba, _________________ diffuses in
and __________________ diffuses out of it.
Osmosis
The figure shows a concentrated sugar solution, separated from a dilute sugar
solution by a partially permeable membrane.
o This membrane only allows _________________ molecules but not the larger
sugar molecules to pass through
Diffusion and osmosis 5
Water then diffuses from _____________ solution (more water molecules) into more
____________________ solution (less water molecules) through partially permeable
membrane.
Process osmosis
o Definition: movement of ____________________________ from region of their
_______________ concentration to a region of their _______________
concentration, through a partially permeable membrane.
Water potential
Water potential of solution whether the solution lose water molecules or gain
water molecules from another solution
Pure water has highest water potential
Another way of defining osmosis movement of water molecules from a region of
__________________ water potential to a region of _________________ water
potential, through a partially permeable membrane.
Importance of osmosis in the uptake of water by plants
Plants absorb water from soil through root hairs.
The __________________ is usually less concentrated than ______________ in
vacuole of root hair cell
Water moves into root hair cell by _____________, from higher water potential to
lower water potential through partially permeable membrane (plasma membrane of
root hair cell.
Water passes from one cell to another by _______________ until it reaches the
xylem vessels.
Effect of Osmosis on Plant Cells
The effects of osmosis on plant cells can be observed by placing them in
a) Water
b) Concentrated sugar or salt solution (more concentrated than the cell sap in
the vacuole)
Diffusion and osmosis 6
In solution of high water potential or In solution with low water potential
pure distilled water
1. water _____________ cell by
1. water _______________ cell by osmosis
osmosis
2. vacuole ______________ in size
2. vacuole _______________ in size
3. cytoplasm shrinks away the
3. cell contents are pushed against the cellulose cell wall and it stops
cellulose cell wall pushing outwards on the cell wall
4. the cell wall prevents over expansion 4. the cell becomes ______________
of the cell by exerting an opposing
pressure preventing the entry of more 5. as more water is lost, the cytoplasm
water shrinks further into the centre of the
cell but the cell wall is too stiff to
5. the cell becomes ______________ shrink much
6. the plant cell does not _____________ 6. the cell membrane surrounding the
because the cell wall is tough cytoplasm tears away from the cell
wall. The cell is ________________
7. Plasmolysis occurs when a plant cell
is placed in a concentrated solution.
Diffusion and osmosis 7
Effect of Osmosis on Animal Cells
The effect of osmosis on animal cells can be shown by putting red blood cells in
a) Water
b) Strong salt solution (more concentrated than the cytoplasm)
Strong salt solution water
In water
Water ___________________ cell by osmosis
Cells become larger and burst
In strong salt solution
Water _________________ cell by osmosis
Cells shrink
Active Transport
Requires energy (from respiration)
Enables cell to transport substances from a region of __________________
concentration to a region of ___________________ concentration.
Example of active transport
o Root hair cells take in mineral salts from soil although the soil may not have a
lot of mineral salts
Diffusion and osmosis 8
Вам также может понравиться
- Cell Biology Worksheet Blank4Документ10 страницCell Biology Worksheet Blank4Loveena SteadmanОценок пока нет
- Cell City ProjectДокумент5 страницCell City ProjectRyan RosenzweigОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Notes With SpecДокумент66 страницO Level Biology Notes With Specshaayaa71% (7)
- Year 9 Science Revision BookletДокумент25 страницYear 9 Science Revision BookletLabeenaОценок пока нет
- 2.2.6 Diffusion & Osmosis Worksheet 1Документ6 страниц2.2.6 Diffusion & Osmosis Worksheet 1Vittada BadgeriОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes For OlevelДокумент45 страницBiology Notes For OlevelSaira Binte SalekОценок пока нет
- Mito-Meiosis Test AnswersДокумент11 страницMito-Meiosis Test Answersrosidin_551390Оценок пока нет
- Grade 11 Biology Midterm HLДокумент31 страницаGrade 11 Biology Midterm HLSaima SyedaОценок пока нет
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeДокумент40 страницMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuОценок пока нет
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetsДокумент8 страницCell Transport Review WorksheetsD50% (2)
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementДокумент5 страницCell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementMargie OpayОценок пока нет
- WORKSHEET 14.3 Sex Determination in OffspringДокумент3 страницыWORKSHEET 14.3 Sex Determination in OffspringafzalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 25: Lipid Metabolism: Multiple ChoiceДокумент7 страницChapter 25: Lipid Metabolism: Multiple ChoiceMaxinefgc Baculo100% (1)
- Uncariae Tomentosae Cortex ESCOP 2018Документ24 страницыUncariae Tomentosae Cortex ESCOP 2018Valentina MolinaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Документ4 страницыWorksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Kaung Myat SanОценок пока нет
- Biology Chapter 1Документ7 страницBiology Chapter 1Kuan LoongОценок пока нет
- 04 NotesДокумент6 страниц04 NotesAirus SamaОценок пока нет
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetДокумент5 страницCell Transport Review WorksheetЯн ЛомОценок пока нет
- Plasma Membrane Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementДокумент5 страницPlasma Membrane Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementCarlosОценок пока нет
- Botany Plant Water Relation Plasmolysis Answer WorksheetДокумент2 страницыBotany Plant Water Relation Plasmolysis Answer WorksheetKrisha Mae VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Lab 3 Cell Permeability 2013Документ14 страницLab 3 Cell Permeability 2013Andrew MartiniОценок пока нет
- Ch3 OL RevisionДокумент11 страницCh3 OL Revisionzuhra123coolОценок пока нет
- REVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellДокумент4 страницыREVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDavé TranОценок пока нет
- Worksheet: Passive Transport Diffusion and OsmosisДокумент8 страницWorksheet: Passive Transport Diffusion and OsmosisJake HagbergОценок пока нет
- Exercise1 DEMONSTRATION OF OSMOSISДокумент5 страницExercise1 DEMONSTRATION OF OSMOSISKristel Bliss RomanoОценок пока нет
- 1TheCellOsmosis - Diffusion 200825 123143 PDFДокумент5 страниц1TheCellOsmosis - Diffusion 200825 123143 PDFAlicia O CallaghanОценок пока нет
- Movement in and Out of CellsДокумент25 страницMovement in and Out of Cellsmajanga johnОценок пока нет
- Transport Across A MembraneДокумент8 страницTransport Across A MembraneAdah JoshiОценок пока нет
- Cellular Transport TestДокумент1 страницаCellular Transport TestAmyОценок пока нет
- LR Revision GuideДокумент19 страницLR Revision GuidelachippaОценок пока нет
- Bio OL Chapter 3 & 4Документ9 страницBio OL Chapter 3 & 4zuhra123coolОценок пока нет
- Osmosis and DiffusionДокумент3 страницыOsmosis and Diffusionsidra ahmadОценок пока нет
- Cell Summative ReviewДокумент5 страницCell Summative Reviewapi-422959755100% (1)
- Cell PhysiologyДокумент12 страницCell PhysiologyJaseme OtoyoОценок пока нет
- Cell Transport Notes (Unit 3.4-3.10) : - ConcentrationДокумент4 страницыCell Transport Notes (Unit 3.4-3.10) : - ConcentrationBrenda SchroederОценок пока нет
- 2 D Movement in and Out of CellsДокумент39 страниц2 D Movement in and Out of Cellsyippee.ndi13Оценок пока нет
- Diffusion and Osmosis Lab RealДокумент12 страницDiffusion and Osmosis Lab Realapi-319999783Оценок пока нет
- Bio3 TransiДокумент47 страницBio3 TransichemasuetОценок пока нет
- Diffusion and Osmosis LabДокумент13 страницDiffusion and Osmosis Labapi-233777623Оценок пока нет
- Osmosis: XCCC C CC CC CC CC CCCCДокумент9 страницOsmosis: XCCC C CC CC CC CC CCCCIwizpv DzimmieОценок пока нет
- NotesДокумент212 страницNotesmaatlabatshabileОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Biology Chapter 3: Movement in & Out of CellsДокумент7 страницIGCSE Biology Chapter 3: Movement in & Out of CellsNabil AhmedОценок пока нет
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesДокумент9 страницMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35Оценок пока нет
- 02 Cells Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Документ21 страница02 Cells Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Pablo CostaОценок пока нет
- 2015 Cell Transport WorksheetДокумент5 страниц2015 Cell Transport Worksheetpaigemk1988Оценок пока нет
- Chapter - 04 - The Cell in ActionДокумент22 страницыChapter - 04 - The Cell in ActionBily roriguesОценок пока нет
- Bio 1 Osmosis IIДокумент11 страницBio 1 Osmosis IIAsrar Ul-haqОценок пока нет
- Unit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFДокумент47 страницUnit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFanuksha aroraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellsДокумент6 страницChapter 3 Movement in and Out of CellsWezu heavenОценок пока нет
- Cell Classix Notes Session2 Made by Purnima SharmaДокумент4 страницыCell Classix Notes Session2 Made by Purnima Sharmajeetjyoti787Оценок пока нет
- Lab 1 - Osmosis & Diffusion - AU21Документ10 страницLab 1 - Osmosis & Diffusion - AU21Ava ChappellОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 3Документ5 страницLab Report 3Dunya FAОценок пока нет
- Movement Across The Cell MembraneДокумент3 страницыMovement Across The Cell MembraneUmi Zaheera AzharОценок пока нет
- Movement of SubstancesДокумент39 страницMovement of Substancesapi-260151425Оценок пока нет
- Movement in and Out of CellsДокумент10 страницMovement in and Out of CellsarhampracticeОценок пока нет
- Cellular Structure and FunctionДокумент6 страницCellular Structure and FunctiondonnaОценок пока нет
- Notes Cell Structure and FunctionsДокумент11 страницNotes Cell Structure and FunctionsBishwajit PandeyОценок пока нет
- Cell Transport: Match The Definition On The Left With The Term On The RightДокумент5 страницCell Transport: Match The Definition On The Left With The Term On The RightJESUS EDUARDO CARBONO NIEBLESОценок пока нет
- Topic 3: Diffusion AND Osmosis: ObjectivesДокумент9 страницTopic 3: Diffusion AND Osmosis: ObjectivesAidah JasniОценок пока нет
- Module 3 - Transport Through Cell MembraneДокумент6 страницModule 3 - Transport Through Cell Membrane10. Briol AlvinОценок пока нет
- Bio NotasДокумент34 страницыBio NotasDhuhaa YusufОценок пока нет
- Cellular Transport WORKSHEETДокумент2 страницыCellular Transport WORKSHEETDr-Qussai ZuriegatОценок пока нет
- AbcДокумент3 страницыAbcAnnedi ZonОценок пока нет
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisДокумент6 страницActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanОценок пока нет
- General Biology 2Документ4 страницыGeneral Biology 2Sean LestherОценок пока нет
- Progress in PD-1 - PD-L1 Pathway Inhibitors - From Biomacromolecules To Small MoleculesДокумент30 страницProgress in PD-1 - PD-L1 Pathway Inhibitors - From Biomacromolecules To Small MoleculesMario Andres JuradoОценок пока нет
- CMH IДокумент48 страницCMH IFatima AddaОценок пока нет
- Grade 12 Biology: The Nervous System: NeuronsДокумент11 страницGrade 12 Biology: The Nervous System: NeuronsmiketutorОценок пока нет
- (1997) - (De Las Rivas) - Structure and Thermal Stability of Photosystem II ReactionДокумент7 страниц(1997) - (De Las Rivas) - Structure and Thermal Stability of Photosystem II ReactionamensetОценок пока нет
- Histology SummaryДокумент24 страницыHistology SummaryaelsehamyОценок пока нет
- Atherosclerosis PathophysiologyДокумент12 страницAtherosclerosis PathophysiologyHuman ResourcesОценок пока нет
- DPN - Biochem 1-Exam 2 - 2022Документ9 страницDPN - Biochem 1-Exam 2 - 2022chienyu2002Оценок пока нет
- Glucose Metabolism in Cancer and The Role of Ketogenic DietДокумент9 страницGlucose Metabolism in Cancer and The Role of Ketogenic DietЛилия ПоляковаОценок пока нет
- RetinaДокумент12 страницRetinagdudex118811Оценок пока нет
- SCOP and CATH DatabaseДокумент22 страницыSCOP and CATH DatabaseAishwarya Dharan100% (3)
- Unit 2 Module 2 Combined-1Документ14 страницUnit 2 Module 2 Combined-1api-2930012170% (2)
- Free RadicalsДокумент18 страницFree Radicalsswetha ramОценок пока нет
- Biozone, DNA ReplicationДокумент1 страницаBiozone, DNA ReplicationNick BaderОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules and Chon SynthesisДокумент88 страницBiomolecules and Chon SynthesisChristian Mar MeraizОценок пока нет
- Cell Organelle Study Guide 2022Документ3 страницыCell Organelle Study Guide 2022Munahail FatimaОценок пока нет
- Immune System (Non-Specific & Specific Defences) - ANSWERДокумент23 страницыImmune System (Non-Specific & Specific Defences) - ANSWERincognitus94Оценок пока нет
- ImmunosuppressionДокумент1 страницаImmunosuppressionabc007200Оценок пока нет
- Muscarinic and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonists: Current Scenario in Alzheimer's Disease TherapyДокумент48 страницMuscarinic and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonists: Current Scenario in Alzheimer's Disease Therapyanadil fidaОценок пока нет
- Microbiology & Parasitology MIC 2052 The Microorganism: Shuganti MayilvahanamДокумент70 страницMicrobiology & Parasitology MIC 2052 The Microorganism: Shuganti Mayilvahanamnorlina hazierahОценок пока нет
- Osmosis: 1 MechanismДокумент6 страницOsmosis: 1 MechanismsnowflomanОценок пока нет
- Ospe HistologyДокумент17 страницOspe Histologyaimi BatrisyiaОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 MicrobiologyДокумент77 страницUnit 3 Microbiologykrishkodal0020Оценок пока нет