Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Impaired Gas - Cervical Cancer
Загружено:
mawel0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
103 просмотров1 страницаCues: "maglisud ko ug ginhawa maam" as verbalized by the patient. Objective After 6-8 hours of nursing intervention, the patient will be able to: a. Be able breathe on room air without shortness of breath by discharge. Research indicates that keep the head of the bed elevated between a 30 - 45 degree angle increases oxygenation and gas exchange.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Impaired Gas_cervical Cancer
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCues: "maglisud ko ug ginhawa maam" as verbalized by the patient. Objective After 6-8 hours of nursing intervention, the patient will be able to: a. Be able breathe on room air without shortness of breath by discharge. Research indicates that keep the head of the bed elevated between a 30 - 45 degree angle increases oxygenation and gas exchange.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
103 просмотров1 страницаImpaired Gas - Cervical Cancer
Загружено:
mawelCues: "maglisud ko ug ginhawa maam" as verbalized by the patient. Objective After 6-8 hours of nursing intervention, the patient will be able to: a. Be able breathe on room air without shortness of breath by discharge. Research indicates that keep the head of the bed elevated between a 30 - 45 degree angle increases oxygenation and gas exchange.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
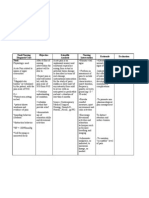
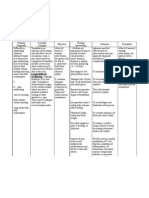
Need/Nursing Scientific Nursing Value
Objective Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis/Cues Analysis Intervention Integration
Need: After 6-8 Independent: After 6-8 Sense of
Physiologic need Due to fluid excess hours of hours of responsibility
volume in the lung nursing • Encouraged deep • Opening up all the way to the nursing and
Nursing Diagnosis: and intervention, breathing bases increases surface area intervention, accountability
Impaired gas exudates crosses the patient techniques to open for oxygen exchange. the patient in whatever
exchange related to the will be able up lung bases was able to: actions being
fluid overload as permeable to: increase oxygen done.
manifested by membrane exchange in blood. a. Patient
requirements of of the pleurae a. Patient • Taught patient the • It is important that patient be was able to Self-
oxygen causing will be able importance of deep involved in their return to breathe on confidence in
supplementation and it to accumulate in to breathe breathing. health and will increase room air interacting
shortness of breath this on room air compliance. without with the
with activity. membranous space. without • Auscultated breath • The presence of crackles or shortness of patient.
Instead of the lungs shortness of sounds, listening wheezes would indicate fluid breath by
Cues: being able to breath by for sounds of is filling her lungs: further discharge.
function discharge. crackles or exacerbation of fluid
Subjective cues: normally, these wheezes. overload.
“Maglisud ko ug fluids
ginhawa maam”, as inhibit the lungs to
verbalized by the expand • Positioned in semi- • Research indicates that keep
patient. anteroposteriorly fowler’s position. the head of the bed elevated
thus between a 30 – 45 degree
Objective cues: causing ineffective angle increases oxygenation
• Rapid, shallow breathing and gas exchange. (Ackley, B.
breathing & discomfort. J., Ladwig, G. B., 2008)
• Sodium restricted • Decreased amounts of sodium
• Adventitious diet. will reduce the amount of
breath sounds fluid retention which will help
noted (rhonchi, the underlying problem.
wheezes)
• Monitored intake • To see a negative balance to
• Restlessness and output confirm effectiveness of
volumes. diuretics and other therapies
• Dyspnea to reduce fluids.
• Weighted patient • This will show progress of
• Use of daily. fluid removal and help
accessory determine effectiveness of
muscles for treatments.
respiration Dependent:
• Administration of • This will help remove some
Вам также может понравиться
- Special SensesДокумент29 страницSpecial Sensesmawel100% (2)
- PRC-Assisted Delivery 2010Документ1 страницаPRC-Assisted Delivery 2010mawelОценок пока нет
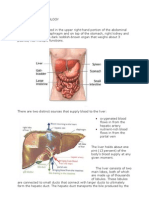
- Anatomy and Physiology-LiverДокумент2 страницыAnatomy and Physiology-Livermawel100% (1)
- NCP Acute PainДокумент1 страницаNCP Acute Painmawel93% (30)
- NCP FractureДокумент2 страницыNCP Fracturemawel50% (2)
- Nutrition Imbalance NCPДокумент1 страницаNutrition Imbalance NCPmawelОценок пока нет
- DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT SubjectiveДокумент1 страницаDIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT Subjectivemawel100% (1)
- Hematologic DisorderДокумент7 страницHematologic Disordermawel100% (2)
- NCP - Acute Pain - FractureДокумент1 страницаNCP - Acute Pain - Fracturemawel73% (22)
- Hexetidine (Latin: Hexetidinum) Is An Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Fungal Agent CommonlyДокумент1 страницаHexetidine (Latin: Hexetidinum) Is An Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Fungal Agent CommonlymawelОценок пока нет
- Need/Nursing Diagnosis/Cues Need: Physiologic Need Nursing Diagnosis: - Nutrition ImbalancedДокумент1 страницаNeed/Nursing Diagnosis/Cues Need: Physiologic Need Nursing Diagnosis: - Nutrition ImbalancedmawelОценок пока нет
- Molar PregnancyДокумент1 страницаMolar Pregnancymawel100% (1)
- LacerationsДокумент8 страницLacerationsmawelОценок пока нет
- Disturbed SleepДокумент1 страницаDisturbed Sleepmawel100% (1)
- Nutrition Imbalance NCPДокумент1 страницаNutrition Imbalance NCPmawelОценок пока нет
- Constipation LeukemiaДокумент1 страницаConstipation LeukemiamawelОценок пока нет
- PRC Form (Minor Operation)Документ1 страницаPRC Form (Minor Operation)mawelОценок пока нет
- Difficulty in SwallowingДокумент1 страницаDifficulty in SwallowingmawelОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology-LiverДокумент2 страницыAnatomy and Physiology-Livermawel100% (1)
- Mechanism of HealingДокумент1 страницаMechanism of HealingmawelОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Catalogue Mp200Документ33 страницыCatalogue Mp200Adrian TudorОценок пока нет
- 6RA80 Quick Commissioning Without TachoДокумент7 страниц6RA80 Quick Commissioning Without TachoBaldev SinghОценок пока нет
- Book 1Документ1 страницаBook 1PES SAFETYОценок пока нет
- Annual Syllabus Class 7 1Документ3 страницыAnnual Syllabus Class 7 1Ni shОценок пока нет
- Reservoir Rock PropertiesДокумент148 страницReservoir Rock Propertiesiscribdusername100% (7)
- Silo Dryers: Mepu - Farmer S First Choice Mepu To Suit Every UserДокумент2 страницыSilo Dryers: Mepu - Farmer S First Choice Mepu To Suit Every UserTahir Güçlü100% (1)
- BHS Inggris 2021Документ6 страницBHS Inggris 2021Muhammad FirmanОценок пока нет
- Idlers: TRF Limited TRF LimitedДокумент10 страницIdlers: TRF Limited TRF LimitedAjit SarukОценок пока нет
- The Fat CatsДокумент7 страницThe Fat CatsMarilo Jimenez AlgabaОценок пока нет
- ANG Coupe Coco Mangue PassionДокумент1 страницаANG Coupe Coco Mangue PassionRicardo Rovira ChalerОценок пока нет
- Dragons and Winged SerpentsДокумент5 страницDragons and Winged SerpentsYuna Raven100% (1)
- History of Costa RicaДокумент2 страницыHistory of Costa Ricakrishnan MishraОценок пока нет
- Brochure ISДокумент4 страницыBrochure ISJAYESH VIKRAM RastogiОценок пока нет
- MC 1Документ109 страницMC 1ricogamingОценок пока нет
- Acc05 SCG116Документ42 страницыAcc05 SCG116Hilal HazaaОценок пока нет
- CH Six Global Transportation Planning and ExecutionДокумент41 страницаCH Six Global Transportation Planning and ExecutionDsh ShОценок пока нет
- E11133 MB Pin Definition v2 Print Vendor Only PDFДокумент18 страницE11133 MB Pin Definition v2 Print Vendor Only PDFLuciano MalancaОценок пока нет
- Free-Field Equivalent Localization of Virtual AudioДокумент9 страницFree-Field Equivalent Localization of Virtual AudiojulianpalacinoОценок пока нет
- Modeling Plastics in ANSYS (Compatibility Mode) PDFДокумент14 страницModeling Plastics in ANSYS (Compatibility Mode) PDFashutosh.srvОценок пока нет
- MalachiteДокумент2 страницыMalachiteAkhil KumarОценок пока нет
- Environmental and Sustainability Issues - 1Документ21 страницаEnvironmental and Sustainability Issues - 121. PLT PAGALILAUAN, EDITHA MОценок пока нет
- (Js-Umum) Daftar Harga 01 Maret '23Документ1 страница(Js-Umum) Daftar Harga 01 Maret '23Kristin NataliaОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Jaime Alvarado (Jaime Alvarado)Документ3 страницыCurriculum Jaime Alvarado (Jaime Alvarado)yuly aldanaОценок пока нет
- Neoliberalism and Altered State Developmentalism in The Twenty First Century Extractive Regime of IndonesiaДокумент26 страницNeoliberalism and Altered State Developmentalism in The Twenty First Century Extractive Regime of IndonesiaErwin SuryanaОценок пока нет
- Origami Undergrad ThesisДокумент63 страницыOrigami Undergrad ThesisEduardo MullerОценок пока нет
- Proposal Form NagДокумент1 страницаProposal Form Nagnitheesh kumarОценок пока нет
- RestrictedДокумент51 страницаRestrictedsridharpalledaОценок пока нет
- Load ScheduleДокумент8 страницLoad SchedulemerebookОценок пока нет
- CST STUDIO SUITE - High Frequency Simulation PDFДокумент128 страницCST STUDIO SUITE - High Frequency Simulation PDFGenik Podunay100% (2)
- Stock+List 6ct8.3g2 Esn#30549237 Cpl#2218 GeneradorДокумент34 страницыStock+List 6ct8.3g2 Esn#30549237 Cpl#2218 GeneradorAlexis SanchezОценок пока нет