Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Communication Systems II Formula Sheet
Загружено:
GreenThumb100%(5)100% нашли этот документ полезным (5 голосов)
2K просмотров2 страницыFormula Sheet
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документFormula Sheet
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(5)100% нашли этот документ полезным (5 голосов)
2K просмотров2 страницыCommunication Systems II Formula Sheet
Загружено:
GreenThumbFormula Sheet
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
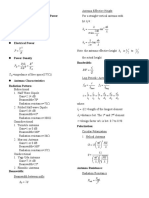
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS II TEST I
Characteristic Impedance Vr Vi Vt Vr Vi
L L L
ZO = T
C v p vfC
- Coaxial Cable Length of Line/Wavelength/Phase Shift
D = inside diameter of outer conductor wavelength
d = diameter of inner conductor L length
ε r = relative permittivity of the dielectric phase shift
138 D
ZO= log C Speed of Light 300 106 m / s
εr d
d (m) v
- Air Dielectric Parallel Line v( m / s ) 1. v p 2. p
t (s) T f
D = spacingbetween center of conductors
v v C
r = conductor radius 3. L o
g f
D 360 f f
Z O =276log 1 L v
r f 360 d
1/4 Wave Shorted Stub T t
C 1 Length of line in deg rees
Zo ZoZl g v f g
f 4 4 L
360
Velocity Factor and Propagation Velocity Im pedance looking int o line
v p propagation.velocity.of .line(m / s) Z jZo tan
Z Zo L
v f velocity. factor ( decimal. fraction) Zo jZl tan
C speed .of .light 300 106 m / s SWR
1 Vmax
r dielectric.cons tan t SWR
1 Vmin
v 1
vf p vf vp f v f C SWR ZO / ZL if ZO ZL
C r
SWR ZL / ZO if ZL ZO
vp Vmax Vi Vr Vmax Vi Vr
T
Response of Line Power Reflection
L(2( reflected back ?) PL load power
T
vp Pr power reflected from load
Gamma and Voltage Reflection Pi incident power at load
Coefficient Pr 2 Pi
PL Pi 1 2
vr reflected voltage
Attenuation(dB)=L Loss(ratio)
v incident voltage
Loss (dB )
Gamma voltage reflection coefficient Voltage(ratio)=antilog
20
V Zl Zo SWR 1 cm=m×100
r
Vi Zl Zo SWR 1 m=cm÷100
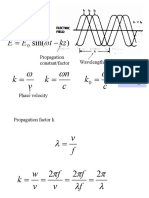
Radio-Wave Propagation
- Electric and Magnetic Fields
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS II TEST I
L impedance of medium in ohms PD power density in W / m 2
E electric field strength in v / m Pt total power in watts
H magnetic field strength in A / m r dis tan ce from antenna in meters
Z Im pedancein ohms V2 E2
V electromotive forcein volts P PD PD H 2 L
R L
I current in apmeres PD EH
propagation velocity in medium Free Space Propagation
c propagation velocity in free space P E2
PD t 2 PD
300 106 m / s 4 r L
2
permeability of medium H / m E P PL Pt L
t 2 E2 t 2 E
permittivity of medium F / m L 4 r 4 r 4 r 2
377 Pt 30 Pt
r relative permittivity in medium E
4r 2
r
dielectric cons tan t
GT gain of Tx antenna
0 permittivity of free space
PT total Tx power in watts
vacuum permittivity
Aeff effective area of antenna in m2
c V E
Z L PR power delivered to Rx in watts
r I H
GR antenna gain as power ratio
GT
- For a lossless medium
anti log 10
L PR 2GR
EIRP PT GT Aeff Aeff
Free Space PD 4
0 4 107 H / m Aeff PT GT 2GR PT GT 2GR PT GT
PR Aeff PD
0 8.854 1012 F / m 4 r 2 (4 )(4 r 2 ) (16 2 r 2 )
o
LO 377
o
0
r L
0 r 0
o 1 377
0 r r
Power Density
P power in watts
V voltage in volts
R resis tan ce in ohms
Вам также может понравиться
- Lec1-Transmission Line TheoryДокумент35 страницLec1-Transmission Line TheoryKamar Abou MuharamОценок пока нет
- Hand Book Formulas Communication TeliДокумент3 страницыHand Book Formulas Communication TeliJet'sОценок пока нет
- Useful Formulae GuideДокумент6 страницUseful Formulae GuidehelloОценок пока нет
- Appendix C - Symbols and Constants - 2015 - Top Down Digital VLSI DesignДокумент9 страницAppendix C - Symbols and Constants - 2015 - Top Down Digital VLSI DesignsuperpapozzoloОценок пока нет
- Trans LineДокумент102 страницыTrans LineprashantОценок пока нет
- Basic Formulas AcousticsДокумент16 страницBasic Formulas Acousticssmani170100% (1)
- XII Chemistry Project on Alternating CurrentДокумент26 страницXII Chemistry Project on Alternating CurrentAnand KОценок пока нет
- Unit 2newДокумент99 страницUnit 2newlaibaОценок пока нет
- The Output of Ac Generator Is:: E E Sinwt (E Nbaw) E - (D/DT) (Ø)Документ36 страницThe Output of Ac Generator Is:: E E Sinwt (E Nbaw) E - (D/DT) (Ø)Lasya notesОценок пока нет
- Transmission Lines (Complete)Документ14 страницTransmission Lines (Complete)Floyd SampianoОценок пока нет
- 1502957604lectrure 11 12 13 KUETДокумент35 страниц1502957604lectrure 11 12 13 KUETAnikaОценок пока нет
- EMFT TxLineДокумент71 страницаEMFT TxLineSurya Pratap Singh ShekhawatОценок пока нет
- chpt14 3Документ19 страницchpt14 3WESTLY JUCOОценок пока нет
- Notes BookДокумент81 страницаNotes BookJason JiaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To AntennasДокумент47 страницIntroduction To AntennasBalaKrishnaОценок пока нет
- Basic Electrical Theory FormulaДокумент4 страницыBasic Electrical Theory FormulaMohammad TammamОценок пока нет
- Alternating CurrentДокумент24 страницыAlternating CurrentAnand KОценок пока нет
- Basics of Microwave Measurements and Transmission Line TheoryДокумент20 страницBasics of Microwave Measurements and Transmission Line TheoryRamya SuriyaraniОценок пока нет
- Chapter No1.PropagationДокумент28 страницChapter No1.PropagationlifeОценок пока нет
- I. Introduction To Wave Propagation: July, 2003 © 2003 by H.L. Bertoni 1Документ71 страницаI. Introduction To Wave Propagation: July, 2003 © 2003 by H.L. Bertoni 1Ninni SinghОценок пока нет
- AC Circuits: Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsДокумент16 страницAC Circuits: Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsHiếu Dương100% (1)
- Physics Project: Topic: Alteernating CurrentДокумент25 страницPhysics Project: Topic: Alteernating CurrentAnand KОценок пока нет
- 7 AntennassssssssДокумент2 страницы7 AntennassssssssIan Neil LaenoОценок пока нет
- 1) Ground Reflection 2) Diffraction 3) Wave Propagation in Complex EnvironmentsДокумент37 страниц1) Ground Reflection 2) Diffraction 3) Wave Propagation in Complex EnvironmentsKarunya Vardana SОценок пока нет
- EE 321: Angle Modulation and DemodulationДокумент41 страницаEE 321: Angle Modulation and DemodulationIBRAHIM ALFARISОценок пока нет
- 6transmission LinesssssssssssssssДокумент2 страницы6transmission LinesssssssssssssssIan Neil LaenoОценок пока нет
- LMH Chapter7-Part2Документ70 страницLMH Chapter7-Part2Nguyen Son N NguyenОценок пока нет
- Utkarsh Physics Ac Project 2.0Документ21 страницаUtkarsh Physics Ac Project 2.0T VpОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ26 страницLecture 2Ano Ni MousОценок пока нет
- Esc201: Introducton To Electronics: Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurДокумент36 страницEsc201: Introducton To Electronics: Dept. of Electrical Engineering Iit KanpurAbhishek AryaОценок пока нет
- Ciciut Desing and AnalysДокумент37 страницCiciut Desing and AnalysMeriçin HikayesiОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ40 страницLecture 2NurulAnisAhmadОценок пока нет
- EE-211 Lecture on Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis and Phasor TransformationsДокумент23 страницыEE-211 Lecture on Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis and Phasor TransformationsBushra Azmat Qureshi Bushra AzmatОценок пока нет
- Module1 TransmissionLinesДокумент7 страницModule1 TransmissionLinesFrancis LebadesusОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Distance Measurement (Edm)Документ11 страницElectromagnetic Distance Measurement (Edm)Ismail Ben MabroukОценок пока нет
- Utkarsh Physics Ac Project 2.0OOOДокумент20 страницUtkarsh Physics Ac Project 2.0OOOT VpОценок пока нет
- 4 Transmission Lines An D Cables: Distributed Parameter ModelДокумент5 страниц4 Transmission Lines An D Cables: Distributed Parameter ModelYazid AbouchihabeddineОценок пока нет
- Lec 7Документ43 страницыLec 7Atiga EntОценок пока нет
- 6.013 Electromagnetics and Applications: Problem 1. (30/200 Points)Документ3 страницы6.013 Electromagnetics and Applications: Problem 1. (30/200 Points)Shahid HasanОценок пока нет
- Labwork1 - M1 EECS - PropagationCable - 2023-24Документ11 страницLabwork1 - M1 EECS - PropagationCable - 2023-24liamanalieva54Оценок пока нет
- Chap 14 Frequency Response AnalysisДокумент20 страницChap 14 Frequency Response AnalysisEngr. Afshan ishaq Electronics ABTОценок пока нет
- Solved Problems in Electrical & Safety Engineering 2014Документ28 страницSolved Problems in Electrical & Safety Engineering 2014hshshdhdОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER VII Direct Current Circuits NEWДокумент21 страницаCHAPTER VII Direct Current Circuits NEWIhza Fikry Aryaditama ArroziОценок пока нет
- SCP Lab BookДокумент38 страницSCP Lab BookGhoulОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ36 страницChapter 3Md Jahirul IslamОценок пока нет
- RF&MW Unit IV MaterialДокумент64 страницыRF&MW Unit IV MaterialMaheshwaranОценок пока нет
- Phyics HandbookДокумент8 страницPhyics HandbookStephen HillОценок пока нет
- Facts About SWR, Reflected Power, and Power Transfer on Real LinesДокумент62 страницыFacts About SWR, Reflected Power, and Power Transfer on Real Linessebastian nasiОценок пока нет
- AC CircuitsДокумент56 страницAC CircuitsAdrian PrinceОценок пока нет
- 2009 Ifcs Power DetectorsДокумент4 страницы2009 Ifcs Power DetectorsGabriel ManoelОценок пока нет
- Transmission Lines: Electronic Systems and TechnologiesДокумент73 страницыTransmission Lines: Electronic Systems and TechnologiesKier SinghОценок пока нет
- Alexander CH 14 Final R1Документ20 страницAlexander CH 14 Final R1utpОценок пока нет
- EEN330-ElectromagneticsI-Chapter2-Transmission LinesДокумент103 страницыEEN330-ElectromagneticsI-Chapter2-Transmission LinesjulioОценок пока нет
- RLC Lab Manual on Series and Parallel ResonanceДокумент59 страницRLC Lab Manual on Series and Parallel ResonancepragatinareshОценок пока нет
- Small-Signal Analysis of Open-Loop PWM Flyback DCDC Converter For CCMДокумент8 страницSmall-Signal Analysis of Open-Loop PWM Flyback DCDC Converter For CCMAshok KumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14Документ20 страницChapter 14TarikuОценок пока нет
- Transmission Lines ExplainedДокумент25 страницTransmission Lines Explainedmarthia perezОценок пока нет
- Transmission LinesДокумент114 страницTransmission LinesRad Sison LagoОценок пока нет
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3От EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1От EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- Assignment # 2 ME - 615 Last Date of Submission: 01-03-2013 Rotor Dynamics Marks: 20Документ1 страницаAssignment # 2 ME - 615 Last Date of Submission: 01-03-2013 Rotor Dynamics Marks: 20Nishant PatilОценок пока нет
- Chap 6 SteelДокумент18 страницChap 6 SteelDaniel VasquezОценок пока нет
- CRE NotesДокумент103 страницыCRE NotesShagun DahiyaОценок пока нет
- Ranpelen PP Random Copolymer: DescriptionДокумент2 страницыRanpelen PP Random Copolymer: DescriptionVu Thanh ThuongОценок пока нет
- 2021 A Review of Methods and Experimental StudiesДокумент28 страниц2021 A Review of Methods and Experimental Studiesrl leeОценок пока нет
- Atomic and Nuclear PhenomenaДокумент3 страницыAtomic and Nuclear PhenomenababaОценок пока нет
- Torsion Shaft DesignДокумент24 страницыTorsion Shaft DesignHARSHWARDHAN SINGH SENGARОценок пока нет
- Problems On DiffractionДокумент2 страницыProblems On DiffractionBrajesh Kumar67% (3)
- Gas Pressure Regulators For Inlet Pressures Up To 100 Bar: British Standard Bs en 334:2005+A1:2009Документ108 страницGas Pressure Regulators For Inlet Pressures Up To 100 Bar: British Standard Bs en 334:2005+A1:2009vinay1999Оценок пока нет
- PSA Cast-In Plates - Technical Data SheetДокумент7 страницPSA Cast-In Plates - Technical Data SheetGnansabesan JathurschanОценок пока нет
- 185hr DatasheetДокумент3 страницы185hr DatasheetAsh VigilОценок пока нет
- Thermo 2Документ9 страницThermo 2Drake William ParkerОценок пока нет
- Machinery fault diagnosis guide to vibration analysisДокумент42 страницыMachinery fault diagnosis guide to vibration analysisAbdurrhman AlzhraniОценок пока нет
- IIT JAM Physics Sample Theory for Entrance ExamsДокумент20 страницIIT JAM Physics Sample Theory for Entrance ExamsVikram KumarОценок пока нет
- ProjectДокумент16 страницProjectEhmida PofjraОценок пока нет
- Part - I: Subjective QuestionsДокумент11 страницPart - I: Subjective Questionspankaj agarwalОценок пока нет
- EN 1991-1-4:2005 (E) Eurocode 1: Actions On Structures Part 1-4: General Actions - Wind ActionsДокумент18 страницEN 1991-1-4:2005 (E) Eurocode 1: Actions On Structures Part 1-4: General Actions - Wind ActionsManuel ValenteОценок пока нет
- BS Iso 16063-1-1998+a1-2016 - (2018-01-19 - 01-28-23 PM) PDFДокумент30 страницBS Iso 16063-1-1998+a1-2016 - (2018-01-19 - 01-28-23 PM) PDFKrit JiamjirochОценок пока нет
- F1 Chapter 5 MatterДокумент13 страницF1 Chapter 5 Matteralya sophiaОценок пока нет
- Wessington Catalogue June 2015Документ46 страницWessington Catalogue June 2015ritesh kumarОценок пока нет
- Flare - Reduced Purge Rates in StacksДокумент13 страницFlare - Reduced Purge Rates in StacksGary JonesОценок пока нет
- BSC Physics 2019Документ189 страницBSC Physics 2019kab28Оценок пока нет
- Optical Leak Testing of Hermetic DevicesДокумент9 страницOptical Leak Testing of Hermetic DevicesTueОценок пока нет
- M 236 ContentДокумент103 страницыM 236 ContentgeetanandnОценок пока нет
- 4-Transfer Function and Modeling of Mechanical SystemДокумент35 страниц4-Transfer Function and Modeling of Mechanical SystemUsama KaleemОценок пока нет
- Technical Datasheet: Engineering SteelДокумент1 страницаTechnical Datasheet: Engineering SteelDhanu goswamiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 02Документ199 страницChapter 02351brendan83% (6)
- M11 Bor Pile Load Lateral 15257 0Документ28 страницM11 Bor Pile Load Lateral 15257 0Yusril RamadhanОценок пока нет
- Hydrolysis Ethyl Silicate PDFДокумент8 страницHydrolysis Ethyl Silicate PDFKUKUОценок пока нет
- B62 0030 (Rev. B 2003.05) EN - THERMOPLASTIC, THERMOSETTING MATERIALS AND THERMOPLASTIC ELASTOMERS SPECIFICATIONS - SYMBOLSДокумент10 страницB62 0030 (Rev. B 2003.05) EN - THERMOPLASTIC, THERMOSETTING MATERIALS AND THERMOPLASTIC ELASTOMERS SPECIFICATIONS - SYMBOLSDiego CamargoОценок пока нет