Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 7 Community Ecology
Загружено:
hcpsmurphyedАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 7 Community Ecology
Загружено:
hcpsmurphyedАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 7: Community Ecology What is a community?
- A community is all the different populations in an area (all the living organisms) What is the hierarchy right below community? - Population What is the hierarchy right above community? - Ecosystem Gator Hole - Something the gators create - Give fish places to go during drought - Gators swim through little passages over and over again which creates a way of transportation for other organisms in the water - Alligators are considered key stone species o Dont just effect their population, they effect everything Alligators - Protected by Endangered Species Act o Were over hunted at one point o Population has now rebounded - You can get their skins and their meat through farming o They are successfully farmed - Alligators and Crocodiles are different o They are never together except Florida where they coexist Niche- the role an organism plays in its ecosystem - Organisms with a very narrow niche (specialists): Panda, owl, koala, California condor, Palliate Wood Pecker o California condor looks for very large animals to eat Captive Breeding Program: raised the chicks with puppets that look like condors (so they imprint on them) and reproduce to increase the population (used to only be 14 birds in the world and now they are up to about 200) If we have 200 individuals in a population the problem is if there was any type of disease it could wipe out all of them o Palliate Wood Pecker requires dead standing pine trees to create nest o Koala bears require Eucalyptus o Northern Spotted Owls require old growth forest (red wood forest) o Panda requires bamboo - Organisms with a wide range/tolerance (Generalist): Possum, red fox, raccoon, roaches, and coyotes o Get along well especially in Urban areas
Keystone Species- Has an important ecological role in helping maintain the structure and function of the communities where they are found o Example: Oyster, wolves The Theory of Island Biogeography - According to Model: o Species diversity determined by the immigration rate of the species from other inhabited areas and the extinction rate of species established on the island o The rates of immigration and extinction will reach equilibrium determining the islands average number of different species- species diversity o Immigration and extinction are in turn affected by: size of island and distance from a mainland source of immigrant species Larger island serves as a bigger target Characteristics of a Community Structure - Species Diversity: the number of different species in a community (richness) and the number of individuals in each species (abundance or evenness) o A tropical rainforest has a greater richness of species than the Arctic tundra. o The Arctic tundra may have a greater abundance of individuals in each species. o Rainforest has a high richness because climate is very predictable (warm and wet year round) Vs. Arctic tundra which has a very unpredictable temperature o For populations and species found in the community, relates to: Relative sizes Stratification Distribution o A greater number of species and higher population density exist in an ecotone than in either adjacent ecosystems Because species from both adjacent ecosystems could come together and exist together in the ecotone Vocabulary Native species Nonnative/Exotic/Alien Species o Rapa whelk in Chesapeake Bay Eat oysters, invasive species Keystone species o Play a pivotal role in the structure and function of an ecosystem because they are critically linked to a large number of other species o Prairie dogs dig holes and other organisms use them as refuge because there are no trees in regions that they live o Flying fox bat o Dung beetle Rolls balls of manure around
Distributes nutrients, which increases productivity, which increases biodiversity o Sea otters Live in kelp forest in pacific ocean Feed on crustaceans which feed on the kelp beds When sea otters were almost extinct, other organisms were eating the entire kelp bed o Gopher tortoise Digs tunnels, provides shelter for other creatures (rodents, snakes, birds) o Elephant Strip trees (in the Savanna of Africa) Like Bison (mechanism for maintaining grasslands) o Beaver Make dams Affects water flow: converts land into water, converts flowing water into still water Increases the amount of organisms that can inhabit the area o Oyster Indicator Species o Frogs and fish are good indicator species because pollution from all areas makes it into the water, and creates birth defects o Pfiesteria red algae, creates red tide (algae which produce toxin) From hog waste in North Carolina Lesions on fish fish were indicator species o Fish are also indicators of medications making it into the water, which are not removed in wastewater treatment plants Confused gender fish o Indicator species are canaries in the coal mine
Sharks Keystone species o Top predator APEX predator o Maintains healthy population: has the capacity to take deformed, diseased animals out of the gene pool, and therefore making the gene pool healthy Endang ered or threatened (as most apex predators are) because people fear the shark and very few look highly upon it many people kill them Biomass pyramid 2nd law of thermodynamics the transfer of energy from one level to another leads to a loss of some energy, many times due to heat 10% of energy from one trophic level is transferred to another Predation avoidance by prey Adaptation o Mimicry King and Coral snake
o Camouflage Crab o Shell Armadillo o Warning coloration Frog o Sharp spikes Puffer fish o Spray Skunk Competitive Exclusion Principle Two species with similar needs for the same limiting resources cannot coexist in the same place for very long OR No two species can occupy the same niche in the same community indefinitely Interspecific competition the most common interaction between species where species compete for shared resources like space and food Tree with birds o Temperature variation o Sunlight variation o Moisture variation o New growth is softer (at top) o Lots of micro-niches - Competition - Interference o Mesquite trees relatively equally dispersed o The resource they are attempting to outcompete for is water o They spread out and have wide roots o Secrete toxins and limit root growth in their area o Creosote? - Exploitation o Eating all the food before another specie can Symbiosis A living relationship between species and includes: 1. Parasitism: One species (parasite) feeds on part of another organism (host) by living on or in the host Tape worm Heart worm Leech 2. Commensalism: One species benefits and one species is neither helped or harmed Barnacles and whales- barnacles are crustaceans/ filter feeders
Spanish moss and oak tree- moss lays across the plant and gets habitat from the plant 3. Mutualism: Two species interact and both benefit Coral (polyp and zooanthellae) Mycorrhizal fungi (The fungus helps the roots grow. The fungi are heterotropic and recieve sugars from the plantsthe fungi can be killed by acid precipitation) Bird and alligator (bird cleans alligators teeth, alligator gets clean teeth and bird gets food) Acacia tree and ants (ants swarm anything on the tree and kill it, when the ants are removed, the tree dies)
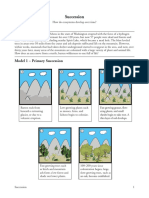
Succession - Change in an ecosystem over time - Primary succession is the gradual establishment of various biotic communities in lifeless areas where there is no soil in a terrestrial community or no bottom sediment in an aquatic community - Pioneer species are the first to inhabit an area *lichens and moss are the pioneer species of primary succession *lichens are a mutualistic relationship between fungi and algae *then weeds and grasses displace the lichens and mosses *then shrubs and small trees *then larger trees *because we live in temperate deciduous forest, succession is easy to see *intermediate specie in temperate deciduous forest? Pine trees (trees growing along interstate are pine trees) *hardwoods like dappled or shady areas, where as pine trees prefer direct sunlight *where do we find bare rock? They come from tops of mountains, left behind from glaciers, igneous rock from volcanoes - Secondary Succession *a series of communities with different species develop in places containing soil or bottom sediment *pioneer species for secondary succession would be grasses and weeds *what types of things lead to this type of succession? Fire, deforestation, mowing the lawn Volcanoes - Volcanoes can be the source of both types of succession (depends on type of volcano though) - Pyroclastic flow
Disturbances - Drought - Flood - Fire - Volcanic eruption - Hurricane - Tornado - Change in stream course - Disease *Katrina brought saltwater which killed a lot of trees in several areas of land Mature Community is preferred by some to Climax Community because ecological succession is NOT necessarily an orderly sequence in which each stage leads to the next more stable stage Rather each species struggles for enough light, nutrients, food and space to survive and reproduce However, general patterns of succession in temperate deciduous forests are known Communities that experience fairly frequently moderate disturbances have the greatest species diversityaccording (we left off on this slide)
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Key Questions: Chapter 4.3: SuccessionДокумент2 страницыKey Questions: Chapter 4.3: SuccessionChizara IdikaОценок пока нет
- Community Ecology ReadingДокумент3 страницыCommunity Ecology Readingapi-189616674Оценок пока нет
- Successional Changes in CommunitiesДокумент4 страницыSuccessional Changes in CommunitiesSofia Christel JavierОценок пока нет
- GE15 Reviewer For 2nd ExamДокумент5 страницGE15 Reviewer For 2nd ExamCohen KnoxОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3Документ20 страницLesson 3Jomarie PauleОценок пока нет
- SpatialandTemporalE4 27 03Документ12 страницSpatialandTemporalE4 27 03Israel Glean EsmileОценок пока нет
- Kinds of Ecosystem and CommunitiesДокумент18 страницKinds of Ecosystem and CommunitiesBelmas CarbonellОценок пока нет
- Succession 2Документ18 страницSuccession 2waranya kasemchittОценок пока нет
- How Do Species and Communities EvolveДокумент5 страницHow Do Species and Communities EvolveAdrian P. TabanaoОценок пока нет
- Post Fire Succession in Tegal Panjang Grassland, Mount Papandayan, West Java, IndonesiaДокумент12 страницPost Fire Succession in Tegal Panjang Grassland, Mount Papandayan, West Java, IndonesiaRika AdriantiОценок пока нет
- Succession and StabilityДокумент6 страницSuccession and StabilityMichael Smith100% (1)
- Yarranton & Morrison 1974 NucleationДокумент13 страницYarranton & Morrison 1974 NucleationStephanie Niño BeltranОценок пока нет
- SUCCESSIONДокумент40 страницSUCCESSIONRialyn Kate BinagОценок пока нет
- Ecological Succession WorksheetДокумент2 страницыEcological Succession WorksheetwingsОценок пока нет
- Ecological Succession WorksheetДокумент2 страницыEcological Succession WorksheetSketchoholic RahulОценок пока нет
- Restoration Ecology - 2022 - Rapson - Tertiary Succession A New Concept To Help Vegetation RestorationДокумент7 страницRestoration Ecology - 2022 - Rapson - Tertiary Succession A New Concept To Help Vegetation Restorationstella.mdlrОценок пока нет
- C.2 - Communities & Ecosystems PowerPointДокумент63 страницыC.2 - Communities & Ecosystems PowerPointCaroline AlmeidaОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 Ecosystems: Stability and ChangeДокумент8 страницUnit 4 Ecosystems: Stability and ChangeKennade BarberОценок пока нет
- Ecological Succession ActivityДокумент3 страницыEcological Succession Activityapi-236697820100% (1)
- Amity Institute of Environmental Sciences Ug-Evs: EcosystemДокумент50 страницAmity Institute of Environmental Sciences Ug-Evs: EcosystemMichael ScottОценок пока нет
- Biomes Zonation and SuccessionДокумент43 страницыBiomes Zonation and Successionjulia wolfmanОценок пока нет
- PEOPLE and The Earth's Ecosystem - Third v. ZabalaДокумент30 страницPEOPLE and The Earth's Ecosystem - Third v. ZabalaRhiena Joy Bosque100% (1)
- 27 Succession-S Manuel TzulДокумент6 страниц27 Succession-S Manuel Tzulapi-323831182Оценок пока нет
- 4 3wrkbkanswrky PDFДокумент10 страниц4 3wrkbkanswrky PDF3.6B viewsОценок пока нет
- Ecological SuccessionДокумент67 страницEcological SuccessionSaket KumarОценок пока нет
- Succession in Americas Forests PDFДокумент7 страницSuccession in Americas Forests PDFLisa SchnellingerОценок пока нет
- Unit-2 Ecosystem - Che110Документ53 страницыUnit-2 Ecosystem - Che110Arihant Dev SharmaОценок пока нет
- Ecological Succession by Isaiah Erin MoniqueДокумент20 страницEcological Succession by Isaiah Erin Moniqueisaiah roland100% (1)
- Interactions Within EcosystemsДокумент20 страницInteractions Within EcosystemsMELISSA MORENOОценок пока нет
- Ecological SuccessionДокумент13 страницEcological SuccessionMk Verma0% (1)