Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lead (II) Azide
Загружено:
MB-RPИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lead (II) Azide
Загружено:
MB-RPАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lead(II) azide
Lead(II) azide
Lead(II) azide
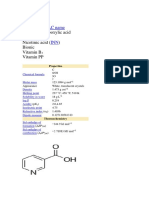
Identifiers CAS number PubChem UN number 13424-46-9 61600 0129 Properties Molecular formula Molar mass Appearance Density Melting point Solubility in water Pb(N3)2 291.24 g/mol white powder 4.71 g/cm , solid 350 C (explodes) 2.3 g/100 mL (18 C) [3] 9.0 g/100 mL (70 C) very soluble in acetic acid; insoluble in ammonia Explosive data Shock sensitivity Friction sensitivity Explosive velocity High High 5180 m/s Hazards Main hazards Autoignition temperature Harmful, Explosive 350C; 662F; 623K Related compounds Other cations Related compounds
(verify) [4]
3
[1]
[2]
Solubility
Potassium azide Hydrazoic acid
(what is: / ?) Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25C (77F), 100kPa)
Infobox references
Lead azide (Pb(N3)2) is an inorganic compound. More so than other azides, Pb(N 3) 2 is explosive. It is used in detonators to initiate secondary explosives. In a commercially usable form, it is a white to buff powder.
Lead(II) azide
Preparation and handling
Lead azide is prepared by metathesis between sodium azide and lead nitrate. Dextrin can be added to the solution to stabilize the precipitated product. The solid is not very hygroscopic, and water does not reduce its impact sensitivity. It is normally shipped in a dextrinated solution that lowers its sensitivity. When protected from humidity, it is completely stable in storage. An alternative method involves dissolving lead acetate in a sodium azide solution.[5]
Explosive characteristics
Lead azide is highly sensitive and usually handled and stored under water in insulated rubber containers. It will explode after a fall of around 150 mm (6 in) or in the presence of a static discharge of 7 millijoules. Its detonation velocity is around 5.18 km/s (17,500 ft/s). Ammonium acetate and sodium dichromate are used to destroy small quantities of lead azide. Lead azide reacts with copper, zinc, cadmium, or alloys containing these metals to form other azides. For example, copper azide is even more explosive and too sensitive to be used commercially. Lead azide was a component of the six .22 caliber Devastator rounds fired from a Rhm RG-14 revolver by John Hinckley, Jr. in his assassination attempt on U.S. President Ronald Reagan on March 30, 1981. The rounds consisted of lead azide centers with lacquer-sealed aluminum tips designed to explode upon impact.[6]
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] http:/ / www. commonchemistry. org/ ChemicalDetail. aspx?ref=13424-46-9 http:/ / pubchem. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov/ summary/ summary. cgi?cid=61600 Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8 http:/ / en. wikipedia. org/ w/ index. php?title=Special:ComparePages& rev1=440042195& page2=Lead%28II%29+ azide http:/ / www. lambdasyn. org/ synfiles/ bleiazid. htm The Exploding Bullets, by Pete Barley and Charles Babcock, Washington Post, 4 Apr, 1981. Retrieved 28 February, 2007.
External links
National Pollutant Inventory Lead and Lead Compounds Fact Sheet (http://www.npi.gov.au/database/substance-info/profiles/ 50.html)
Lead azide (modified beta)
Article Sources and Contributors
Article Sources and Contributors
Lead(II) azide Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?oldid=586373719 Contributors: A4, Aussie Alchemist, Beetstra, Bobblewik, Bryan Derksen, Centrx, Chachilongbow, Chem-awb, Chowells, Czar, Daniel Grohmann, DePiep, Dmuren, Emerson7, Epeefleche, Frank-Wilcox, GCarty, Gecg, GeeJo, Ghostofgauss, Gruzd, Hugo-cs, Ian Pitchford, JeremyA, Jewell.box, Kamil9243, Keenan Pepper, Knutux, Leyo, Ma bakken, Majorgeneralpanic, Mav, Mh26, MichaelCYoung, Msjayhawk, NReitzel, Nabokov, Physchim62, Pillcrow, PizzaofDoom, Pjacobi, Puppy8800, Rand21, Rickjpelleg, Rifleman 82, Rmrf1024, RyanJones, Saehrimnir, ScienceRulez, Shaunw, Shining.Star, Smokefoot, Stone, Tetracube, Thricecube, Uncle Milty, YOSF0113, 37 anonymous edits
Image Sources, Licenses and Contributors
Image:Lead(II)azide.svg Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Lead(II)azide.svg License: Creative Commons Attribution-Sharealike 3.0,2.5,2.0,1.0 Contributors: Mrgreen71 File:Yes check.svg Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Yes_check.svg License: Public Domain Contributors: Anomie File:X mark.svg Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:X_mark.svg License: Public Domain Contributors: User:Gmaxwell File:Lead azide (modified beta) 05.jpg Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Lead_azide_(modified_beta)_05.jpg License: Creative Commons Attribution-Sharealike 3.0 Contributors: User:Daniel Grohmann
License
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 //creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Вам также может понравиться
- 1Документ19 страниц1Rayadi Sinaga100% (1)
- Modern Heterogeneous Oxidation Catalysis: Design, Reactions and CharacterizationОт EverandModern Heterogeneous Oxidation Catalysis: Design, Reactions and CharacterizationNoritaka MizunoОценок пока нет
- Raymond Fellerman Biology 464 Aquatic Toxicology Professor Zed Mason 03 May, 2011Документ13 страницRaymond Fellerman Biology 464 Aquatic Toxicology Professor Zed Mason 03 May, 2011Amar BrkićОценок пока нет
- Sodium AluminateДокумент3 страницыSodium AluminatelumengentiunОценок пока нет
- Presentation 01Документ28 страницPresentation 01Rexona KhanomОценок пока нет
- Colegio de San Juan de Letran: Engineering DepartmentДокумент31 страницаColegio de San Juan de Letran: Engineering DepartmentRobin LayogОценок пока нет
- DL Metal HydridesДокумент20 страницDL Metal HydridesGoutam Gottumukkala100% (1)
- Chemistry 12 Data BookletДокумент12 страницChemistry 12 Data BookletEtoileCamelliaОценок пока нет
- Lithium Chloride: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchДокумент11 страницLithium Chloride: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchChaeyoung SonОценок пока нет
- Potassium Iodate - Wikipedia PDFДокумент17 страницPotassium Iodate - Wikipedia PDFAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Mercury(II) Fulminate: Highly Toxic Shock Sensitive ExplosiveДокумент4 страницыMercury(II) Fulminate: Highly Toxic Shock Sensitive ExplosiveFrancesco ManiscalcoОценок пока нет
- Rhodium Recovery and Recycling From Spent MaterialsДокумент9 страницRhodium Recovery and Recycling From Spent MaterialsLựuLiềuLìОценок пока нет
- Lithium Borohydride: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchДокумент14 страницLithium Borohydride: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchChaeyoung SonОценок пока нет
- Copper(II) bromide chemical compoundДокумент7 страницCopper(II) bromide chemical compoundEusebia MaedzwaОценок пока нет
- Properties of Potash AlumДокумент8 страницProperties of Potash AlumAminu TeslimОценок пока нет
- Applications of Sodium ElementДокумент6 страницApplications of Sodium ElementHassan RazaОценок пока нет
- 2020-11 Product Data Sheet LiOH TG CMP PDFДокумент5 страниц2020-11 Product Data Sheet LiOH TG CMP PDFSergey GlazzОценок пока нет
- Oxidizing Agent - WikipediaДокумент4 страницыOxidizing Agent - WikipediaMirza Bilal MughalОценок пока нет
- Sodium SilicateДокумент12 страницSodium Silicatemoses_cОценок пока нет
- What is lithium carbonate and how is it usedДокумент8 страницWhat is lithium carbonate and how is it usedNurAneesaОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Word DocumentДокумент42 страницыNew Microsoft Word DocumentSalamat AliОценок пока нет
- Sodium Dithionite - Wikipedia PDFДокумент23 страницыSodium Dithionite - Wikipedia PDFAbdullahОценок пока нет
- Sodium Chloride - WikipediaДокумент53 страницыSodium Chloride - WikipediadaribeefaОценок пока нет
- Nitric Acid: Dictionary Sci-Tech Encycl. Dental Dictionary Britannica Concise Columbia Ency. Wikipedia CitationsДокумент13 страницNitric Acid: Dictionary Sci-Tech Encycl. Dental Dictionary Britannica Concise Columbia Ency. Wikipedia CitationsmusmanafzalОценок пока нет
- Maleic Anhydride - WikipediaДокумент31 страницаMaleic Anhydride - WikipediaObaidullah ObaidiОценок пока нет
- Etching and Recovery of Gold From Aluminum SubstraДокумент4 страницыEtching and Recovery of Gold From Aluminum Substraمحمود محمودОценок пока нет
- Denumiri FormuleДокумент11 страницDenumiri FormuleStan Maria100% (2)
- Specialty ChemicalsДокумент30 страницSpecialty ChemicalsucheОценок пока нет
- Material Safety Data Sheet.: 1. Identification of Product and CompanyДокумент7 страницMaterial Safety Data Sheet.: 1. Identification of Product and Companyjacc009Оценок пока нет
- Basma K 2Документ5 страницBasma K 2Anonymous j5JiMo55cОценок пока нет
- Chemical NameДокумент21 страницаChemical Nameochilliane_45Оценок пока нет
- 2 Calcium Aluminate Cements - Raw Materials, Diffferences, Hydration and PropertiesДокумент82 страницы2 Calcium Aluminate Cements - Raw Materials, Diffferences, Hydration and PropertiesAditya Bhorde100% (1)
- Recovery and Separation of Palladium From Spent CatalystДокумент5 страницRecovery and Separation of Palladium From Spent Catalystm_angel_monroyОценок пока нет
- ExperimentsДокумент22 страницыExperimentsAndile ManyoniОценок пока нет
- Major ContaminantsДокумент3 страницыMajor ContaminantsandreililioanceaОценок пока нет
- Corrosion Course Work 2Документ6 страницCorrosion Course Work 2Charles NtaОценок пока нет
- S Block NcertДокумент7 страницS Block NcertStock CheckОценок пока нет
- Better Safe Than Sorry!: Lead Battery Know-How and Accident PreventionДокумент0 страницBetter Safe Than Sorry!: Lead Battery Know-How and Accident PreventionchokribОценок пока нет
- Gold-Telluride Ore Processing OptionsДокумент9 страницGold-Telluride Ore Processing OptionsErick EscalanteОценок пока нет
- RhodiumДокумент5 страницRhodiumkiki_riana31Оценок пока нет
- Antimony PDFДокумент6 страницAntimony PDFRinaOktapianiОценок пока нет
- Handbook of Organopalladium Chemistry For Organic Synthesis Vol 1 - Negishi-0041 - 42Документ3 страницыHandbook of Organopalladium Chemistry For Organic Synthesis Vol 1 - Negishi-0041 - 42gombossandor0% (1)
- Contaminant/Pollutant Characterististics: 1. Physical CharacteristicsДокумент10 страницContaminant/Pollutant Characterististics: 1. Physical CharacteristicsNeni Puji AstutikОценок пока нет
- 10 1016@j Apcata 2019 02 012 PDFДокумент10 страниц10 1016@j Apcata 2019 02 012 PDFIntan FauziyahОценок пока нет
- Maleinanhydrid ENG WIKIДокумент7 страницMaleinanhydrid ENG WIKIKrushnang JoshiОценок пока нет
- Determination of Accelerated Iron Corrosion in Petroleum Product As Per ASTM D7548Документ9 страницDetermination of Accelerated Iron Corrosion in Petroleum Product As Per ASTM D7548Farwa NaeemОценок пока нет
- AluminumДокумент7 страницAluminumjagadish.kvОценок пока нет
- Wiki Sodium HydroxideДокумент15 страницWiki Sodium HydroxidesaiОценок пока нет
- Plating - Interpharm PDFДокумент4 страницыPlating - Interpharm PDFvasudev_nОценок пока нет
- Quia - Chemical Names and Formulas PDFДокумент8 страницQuia - Chemical Names and Formulas PDFkvinodan73Оценок пока нет
- PB Nelement Facts.Документ1 страницаPB Nelement Facts.Anubhav SwaroopОценок пока нет
- Applications of Redox ReactionsДокумент21 страницаApplications of Redox ReactionshamnaОценок пока нет
- 18) The Study of Possibilities of Selective Recovery of Palladium (II) From Chlorides Solutions by Ion Exchange Resin Lewatit TP-214Документ7 страниц18) The Study of Possibilities of Selective Recovery of Palladium (II) From Chlorides Solutions by Ion Exchange Resin Lewatit TP-214SrikanthОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentДокумент28 страницNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentskljoleОценок пока нет
- 120 Manufacture and Uses Includes Sulfur Dioxide Questions Topic Booklet 1 CIE IGCSE ChemistryДокумент7 страниц120 Manufacture and Uses Includes Sulfur Dioxide Questions Topic Booklet 1 CIE IGCSE ChemistryLmao you funnyОценок пока нет
- Guide to Handling Sodium Hypochlorite SafelyДокумент28 страницGuide to Handling Sodium Hypochlorite SafelyamrezzatОценок пока нет
- CN DISPONIBLE D6888 - 4082mthdДокумент13 страницCN DISPONIBLE D6888 - 4082mthdwcenttiОценок пока нет
- Develop Non-Amine Engine CoolantДокумент8 страницDevelop Non-Amine Engine CoolantOscar Rivera100% (1)
- Chem 12 DatabookletДокумент10 страницChem 12 Databookletapi-246864303Оценок пока нет
- Bredberg - On The Wall Boundary Condition For Turbulence ModelsДокумент26 страницBredberg - On The Wall Boundary Condition For Turbulence ModelsMB-RPОценок пока нет
- AFFDL-TR-67-140 - Design Criteria For The Prediction and Prevention of Panel Flutter - Volume I - Criteria PresentationДокумент64 страницыAFFDL-TR-67-140 - Design Criteria For The Prediction and Prevention of Panel Flutter - Volume I - Criteria PresentationMB-RPОценок пока нет
- Faa STD 002fДокумент72 страницыFaa STD 002fMB-RPОценок пока нет
- Dassault Systems Catia v5 SketcherДокумент176 страницDassault Systems Catia v5 Sketchercatio000Оценок пока нет
- DTU - CFD Computations of Wind Turbine Blade Loads During Standstill Operation KNOW BLADE, Task 3.1 ReportДокумент28 страницDTU - CFD Computations of Wind Turbine Blade Loads During Standstill Operation KNOW BLADE, Task 3.1 ReportMB-RPОценок пока нет
- NACA TN3237 - Hovering Performance of A Helicopter Rotor - Perfiles (Naca 8-H-12)Документ15 страницNACA TN3237 - Hovering Performance of A Helicopter Rotor - Perfiles (Naca 8-H-12)MB-RPОценок пока нет
- Dean WilsonДокумент7 страницDean WilsonMB-RP100% (1)
- Openfoamfinal PDFДокумент34 страницыOpenfoamfinal PDFumair35Оценок пока нет
- Aircraft manuals set repair maintenanceДокумент151 страницаAircraft manuals set repair maintenanceMB-RPОценок пока нет
- A Generalized Vortex Lattice Method For Subsonic and Supersonic Flow Applications - Nasa Contractor Report PDFДокумент382 страницыA Generalized Vortex Lattice Method For Subsonic and Supersonic Flow Applications - Nasa Contractor Report PDFMB-RP100% (1)
- Model 95 Operator's Manual - Safety, Use, MaintenanceДокумент29 страницModel 95 Operator's Manual - Safety, Use, MaintenanceMB-RPОценок пока нет
- Ballistic CoefficientДокумент6 страницBallistic CoefficientMB-RPОценок пока нет
- NeratorsДокумент6 страницNeratorsimtiyazОценок пока нет
- Barrett M82A1 ManualДокумент35 страницBarrett M82A1 ManualGasMaskBobОценок пока нет
- Gun Recoil FormulaДокумент5 страницGun Recoil Formulablowmeasshole1911Оценок пока нет
- Perfil Kline FoglemanДокумент27 страницPerfil Kline FoglemanMB-RPОценок пока нет
- Steped AirfoilsДокумент4 страницыSteped AirfoilsMB-RPОценок пока нет
- Unsafe Firearm-Ammunition CombinationsДокумент14 страницUnsafe Firearm-Ammunition CombinationsMB-RP100% (1)
- CheyTac M200 Intervention Sniper Rifle SolidWorks ModelДокумент3 страницыCheyTac M200 Intervention Sniper Rifle SolidWorks ModelMB-RPОценок пока нет
- SAAMI Sets Firearms and Ammo StandardsДокумент9 страницSAAMI Sets Firearms and Ammo StandardsMB-RPОценок пока нет
- CD4511 BCD To 7-Segment DecoderДокумент9 страницCD4511 BCD To 7-Segment DecoderBon Ndu OsonwanneОценок пока нет
- Nitrocelulosa SintesisДокумент4 страницыNitrocelulosa SintesisMB-RPОценок пока нет
- Aviacion - Aviones XДокумент65 страницAviacion - Aviones XsincobrarenfechaОценок пока нет
- Malaysia's Trade Potential in Colourful AfricaДокумент18 страницMalaysia's Trade Potential in Colourful AfricaThe MaverickОценок пока нет
- BIRADS Lexicon and Its Histopathological Corroboration in The Diagnosis of Breast LesionsДокумент7 страницBIRADS Lexicon and Its Histopathological Corroboration in The Diagnosis of Breast LesionsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Directory of Frequently Called Numbers: Maj. Sheikh RahmanДокумент1 страницаDirectory of Frequently Called Numbers: Maj. Sheikh RahmanEdward Ebb BonnoОценок пока нет
- Solids Level Measurement Application Guide en 78224 PDFДокумент144 страницыSolids Level Measurement Application Guide en 78224 PDFwalcalОценок пока нет
- Siemens MV Gas Insulated Switch GearДокумент14 страницSiemens MV Gas Insulated Switch GearSajesh Thykoodan T VОценок пока нет
- Auditor General Insurance Regulation Dec 2011Документ23 страницыAuditor General Insurance Regulation Dec 2011Omar Ha-RedeyeОценок пока нет
- Dimensional Data: For Valves and ActuatorsДокумент52 страницыDimensional Data: For Valves and ActuatorsPaulОценок пока нет
- Module A Specimen Questions January2020 PDFДокумент5 страницModule A Specimen Questions January2020 PDFShashi Bhusan SinghОценок пока нет
- Jounce Therapeutics Company Events and Start DatesДокумент48 страницJounce Therapeutics Company Events and Start DatesEquity NestОценок пока нет
- Tugas B InggrisДокумент9 страницTugas B InggrisDellyna AlmaОценок пока нет
- Treatment of Fruit Juice Concentrate Wastewater by Electrocoagulation - Optimization of COD Removal (#400881) - 455944Документ5 страницTreatment of Fruit Juice Concentrate Wastewater by Electrocoagulation - Optimization of COD Removal (#400881) - 455944Victoria LeahОценок пока нет
- EcR - 1 Leading and Lagging IndicatorsДокумент10 страницEcR - 1 Leading and Lagging IndicatorsMiloš ĐukićОценок пока нет
- Analisis Dampak Reklamasi Teluk Banten Terhadap Kondisi Lingkungan Dan Sosial EkonomiДокумент10 страницAnalisis Dampak Reklamasi Teluk Banten Terhadap Kondisi Lingkungan Dan Sosial EkonomiSYIFA ABIYU SAGITA 08211840000099Оценок пока нет
- A&P 2 - Digestive System Flashcards - QuizletДокумент1 страницаA&P 2 - Digestive System Flashcards - QuizletMunachande KanondoОценок пока нет
- Rapid Cycling in Bipolar DisorderДокумент1 страницаRapid Cycling in Bipolar Disorderdo leeОценок пока нет
- OC - PlumberДокумент6 страницOC - Plumbertakuva03Оценок пока нет
- Classification of Nanomaterials, The Four Main Types of Intentionally Produced NanomaterialsДокумент5 страницClassification of Nanomaterials, The Four Main Types of Intentionally Produced NanomaterialssivaenotesОценок пока нет
- DR - Hawary Revision TableДокумент3 страницыDR - Hawary Revision TableAseel ALshareefОценок пока нет
- 3-Step Mindset Reset: Overcome Self-Doubt with Mel Robbins' TrainingДокумент11 страниц3-Step Mindset Reset: Overcome Self-Doubt with Mel Robbins' TrainingBožana RadošОценок пока нет
- Insects, Stings and BitesДокумент5 страницInsects, Stings and BitesHans Alfonso ThioritzОценок пока нет
- The National Building Code of The PhilippinesДокумент390 страницThe National Building Code of The PhilippinesJohn Joseph EstebanОценок пока нет
- 2-D Motion Based Real Time Wireless Interaction System For Disabled PatientsДокумент5 страниц2-D Motion Based Real Time Wireless Interaction System For Disabled PatientsSantalum AlbumОценок пока нет
- Very Easy Toeic Units 7 - 12 (Q1)Документ39 страницVery Easy Toeic Units 7 - 12 (Q1)Minh KhaiОценок пока нет
- Health 6 Q 4 WK 6 Module 6 Version 4Документ16 страницHealth 6 Q 4 WK 6 Module 6 Version 4Kassandra BayogosОценок пока нет
- Impact of Energy Consumption On The EnvironmentДокумент9 страницImpact of Energy Consumption On The Environmentadawiyah sofiОценок пока нет
- Akshaya Trust NgoДокумент24 страницыAkshaya Trust NgodushyantОценок пока нет
- Simple Syrup I.PДокумент38 страницSimple Syrup I.PHimanshi SharmaОценок пока нет
- WSAWLD002Документ29 страницWSAWLD002Nc BeanОценок пока нет
- Aging and Elderly IQДокумент2 страницыAging and Elderly IQ317537891Оценок пока нет
- Formularium ApotekДокумент12 страницFormularium ApotekNurul Evi kurniatiОценок пока нет