Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
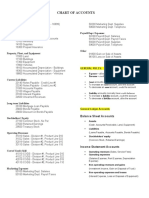
Chart of Accounts
Загружено:
acir_05Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chart of Accounts
Загружено:
acir_05Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
ArabBritishAcademyforHigherEducation.
Chart of Accounts
The chart of accounts is a listing of all the accounts in the general ledger, each account accompanied by a reference number. To set up a chart of accounts, one first needs to define the various accounts to be used by the business. Each account should have a number to identify it. For very small businesses, three digits may suffice for the account number, though more digits are highly desirable in order to allow for new accounts to be added as the business grows. With more digits, new accounts can be added while maintaining the logical order. Complex businesses may have thousands of accounts and require longer account reference numbers. It is worthwhile to put thought into assigning the account numbers in a logical way, and to follow any specific industry standards. An example of how the digits might be coded is shown in this list: Account Numbering 1000 - 1999: asset accounts 2000 - 2999: liability accounts 3000 - 3999: equity accounts 4000 - 4999: revenue accounts 5000 - 5999: cost of goods sold 6000 - 6999: expense accounts 7000 - 7999: other revenue (for example, interest income) 8000 - 8999: other expense (for example, income taxes) By separating each account by several numbers, many new accounts can be added between any two while maintaining the logical order. Defining Accounts Different types of businesses will have different accounts. For example, to report the cost of goods sold a manufacturing business will have accounts for its various manufacturing costs whereas a retailer will have accounts for the purchase of its stock merchandise. Many industry associations publish recommended charts of accounts for their respective industries in order to establish a consistent standard of comparison among firms in their industry. Accounting software packages often come with a selection of predefined account charts for various types of businesses. There is a trade-off between simplicity and the ability to make historical comparisons. Initially keeping the number of accounts to a minimum has the advantage of making the
1 www.abahe.co.uk
ArabBritishAcademyforHigherEducation.
accounting system simple. Starting with a small number of accounts, as certain accounts acquired significant balances they would be split into smaller, more specific accounts. However, following this strategy makes it more difficult to generate consistent historical comparisons. For example, if the accounting system is set up with a miscellaneous expense account that later is broken into more detailed accounts, it then would be difficult to compare those detailed expenses with past expenses of the same type. In this respect, there is an advantage in organizing the chart of accounts with a higher initial level of detail. Some accounts must be included due to tax reporting requirements. For example, in the U.S. the IRS requires that travel, entertainment, advertising, and several other expenses be tracked in individual accounts. One should check the appropriate tax regulations and generate a complete list of such required accounts. Other accounts should be set up according to vendor. If the business has more than one checking account, for example, the chart of accounts might include an account for each of them. Account Order Balance sheet accounts tend to follow a standard that lists the most liquid assets first. Revenue and expense accounts tend to follow the standard of first listing the items most closely related to the operations of the business. For example, sales would be listed before non-operating income. In some cases, part or all of the expense accounts simply are listed in alphabetical order. Sample Chart of Accounts The following is an example of some of the accounts that might be included in a chart of accounts. Sample Chart of Accounts Asset Accounts Current Assets
1000 1010 1020 1030 1040
Petty Cash Cash on Hand (e.g. in cash registers) Regular Checking Account Payroll Checking Account Savings Account
2 www.abahe.co.uk
ArabBritishAcademyforHigherEducation.
1050 1060 1070 1100 1140 1150 1200 1205 1210 1215 1220 1230 1400 1410 1420 1430 1470
Special Account Investments - Money Market Investments - Certificates of Deposit Accounts Receivable Other Receivables Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Raw Materials Inventory Supplies Inventory Work in Progress Inventory Finished Goods Inventory - Product #1 Finished Goods Inventory - Product #2 Finished Goods Inventory - Product #3 Prepaid Expenses Employee Advances Notes Receivable - Current Prepaid Interest Other Current Assets
Fixed Assets
1500 1510 1520 1530 1540 1550 1560 1690 1700 1710 1720 1730 1740 1750
Furniture and Fixtures Equipment Vehicles Other Depreciable Property Leasehold Improvements Buildings Building Improvements Land Accumulated Depreciation, Furniture and Fixtures Accumulated Depreciation, Equipment Accumulated Depreciation, Vehicles Accumulated Depreciation, Other Accumulated Depreciation, Leasehold Accumulated Depreciation, Buildings
3 www.abahe.co.uk
ArabBritishAcademyforHigherEducation.
1760
Accumulated Depreciation, Building Improvements
Other Assets
1900 1910 1915 1920 1990
Deposits Organization Costs Accumulated Amortization, Organization Costs Notes Receivable, Non-current Other Non-current Assets
Liability Accounts Current Liabilities
2000 2300 2310 2320 2330 2335 2340 2350 2360 2370 2380 2390 2400 2410 2420 2440 2480
Accounts Payable Accrued Expenses Sales Tax Payable Wages Payable 401-K Deductions Payable Health Insurance Payable Federal Payroll Taxes Payable FUTA Tax Payable State Payroll Taxes Payable SUTA Payable Local Payroll Taxes Payable Income Taxes Payable Other Taxes Payable Employee Benefits Payable Current Portion of Long-term Debt Deposits from Customers Other Current Liabilities
Long-term Liabilities
4 www.abahe.co.uk
ArabBritishAcademyforHigherEducation.
2700 2702 2704 2706 2708 2710 2740
Notes Payable Land Payable Equipment Payable Vehicles Payable Bank Loans Payable Deferred Revenue Other Long-term Liabilities
Equity Accounts
3010 3020 3030
Stated Capital Capital Surplus Retained Earnings
Revenue Accounts
4000 4020 4040 4060 4080 4540 4550 4800 4900
Product #1 Sales Product #2 Sales Product #3 Sales Interest Income Other Income Finance Charge Income Shipping Charges Reimbursed Sales Returns and Allowances Sales Discounts
Cost of Goods Sold
5000 5010 5020 5050 5100
Product #1 Cost Product #2 Cost Product #3 Cost Raw Material Purchases Direct Labor Costs
5 www.abahe.co.uk
ArabBritishAcademyforHigherEducation.
5150 5200 5250 5300 5700 5730 5750 5800 5850 5900 5950
Indirect Labor Costs Heat and Power Commissions Miscellaneous Factory Costs Cost of Goods Sold, Salaries and Wages Cost of Goods Sold, Contract Labor Cost of Goods Sold, Freight Cost of Goods Sold, Other Inventory Adjustments Purchase Returns and Allowances Purchase Discounts
Expenses
6000 6010 6050 6100 6150 6200 6250 6300 6350 6400 6450 6500 6510 6520 6530 6550 6600 6650 6660 6670
Default Purchase Expense Advertising Expense Amortization Expense Auto Expenses Bad Debt Expense Bank Fees Cash Over and Short Charitable Contributions Expense Commissions and Fees Expense Depreciation Expense Dues and Subscriptions Expense Employee Benefit Expense, Health Insurance Employee Benefit Expense, Pension Plans Employee Benefit Expense, Profit Sharing Plan Employee Benefit Expense, Other Freight Expense Gifts Expense Income Tax Expense, Federal Income Tax Expense, State Income Tax Expense, Local
6 www.abahe.co.uk
ArabBritishAcademyforHigherEducation.
6700 6710 6750 6800 6850 6900 6950 7000 7050 7100 7200 7250 7300 7350 7400 7450 7460 7550 7600 7620 7650 7700 7750 7800 8900 9000
Insurance Expense, Product Liability Insurance Expense, Vehicle Interest Expense Laundry and Dry Cleaning Expense Legal and Professional Expense Licenses Expense Loss on NSF Checks Maintenance Expense Meals and Entertainment Expense Office Expense Payroll Tax Expense Penalties and Fines Expense Other Taxes Postage Expense Rent or Lease Expense Repair and Maintenance Expense, Office Repair and Maintenance Expense, Vehicle Supplies Expense, Office Telephone Expense Training Expense Travel Expense Salaries Expense, Officers Wages Expense Utilities Expense Other Expense Gain/Loss on Sale of Assets
7 www.abahe.co.uk
Вам также может понравиться
- Computerised Accounting Practice Set Using Xero Online Accounting: Australian EditionОт EverandComputerised Accounting Practice Set Using Xero Online Accounting: Australian EditionОценок пока нет
- Controlling Payroll Cost - Critical Disciplines for Club ProfitabilityОт EverandControlling Payroll Cost - Critical Disciplines for Club ProfitabilityОценок пока нет
- Abm1 PPTДокумент161 страницаAbm1 PPTPavi Antoni Villaceran100% (1)
- Accounting Fundamental: BY: Bayani D. Edlagan Ma. Cecilia S. MercadoДокумент270 страницAccounting Fundamental: BY: Bayani D. Edlagan Ma. Cecilia S. MercadoSai Kumar Ponna100% (2)
- Contra AccountsДокумент6 страницContra AccountsRaviSankarОценок пока нет
- CH 7, 8Документ4 страницыCH 7, 8Irfan UllahОценок пока нет
- Adjusting EntriesДокумент9 страницAdjusting EntriesCharmaine Montimor OrdonioОценок пока нет
- Financial Accounting Chapter 3Документ5 страницFinancial Accounting Chapter 3NiraniyaОценок пока нет
- ACCT 101 Module 1 - The World of AccountingДокумент53 страницыACCT 101 Module 1 - The World of AccountingApril Naida100% (1)
- Basic Accounting EquationДокумент17 страницBasic Accounting EquationArienaya100% (1)
- 7 Different Types of Journal in Accounting With ExamplesДокумент8 страниц7 Different Types of Journal in Accounting With ExamplesHaroon YousafОценок пока нет
- Statement of Cash Flows - Lecture NotesДокумент6 страницStatement of Cash Flows - Lecture NotesSteven Sanderson100% (8)
- Accounts ReceivableДокумент3 страницыAccounts ReceivableVishal DahiwalОценок пока нет
- Accounting For Merchandising OperationsДокумент63 страницыAccounting For Merchandising OperationsWijdan saleemОценок пока нет
- Subsidiary BooksДокумент7 страницSubsidiary BooksADEYANJU AKEEMОценок пока нет
- Excel Skills - Basic Accounting Template: InstructionsДокумент39 страницExcel Skills - Basic Accounting Template: InstructionsStorage BankОценок пока нет
- Period Cost Is Related To Level of Production and SaleДокумент6 страницPeriod Cost Is Related To Level of Production and SaleMd. Saiful AlamОценок пока нет
- Statement of Comprehensive IncomeДокумент30 страницStatement of Comprehensive IncomeSheilaMarieAnnMagcalas100% (4)
- Charts of AccountsДокумент7 страницCharts of Accountszindabhaag100% (1)
- Step 1 - Transactions And/or EventsДокумент5 страницStep 1 - Transactions And/or EventsJEFFREY GALANZA0% (1)
- Outline of A Business PlanДокумент5 страницOutline of A Business PlanFarisha RazОценок пока нет
- 2 Financial AnalysisДокумент22 страницы2 Financial AnalysisAB11A4-Condor, Joana MieОценок пока нет
- Basic Accounting ConceptДокумент19 страницBasic Accounting ConcepttundsandyОценок пока нет
- Basic Accounting-Made EasyДокумент20 страницBasic Accounting-Made EasyRoy Kenneth Lingat100% (1)
- The Petty Cash FundДокумент10 страницThe Petty Cash FundLilian TaiОценок пока нет
- Accounting For Branches and Combined FSДокумент112 страницAccounting For Branches and Combined FSEcka Tubay100% (1)
- Statement of Cash FlowsДокумент18 страницStatement of Cash FlowsJPYADAV27Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 1Документ9 страницLesson 1Bervette HansОценок пока нет
- Basic BookkeepingДокумент80 страницBasic BookkeepingCharity CotejoОценок пока нет
- Week Introduction To AccountingДокумент24 страницыWeek Introduction To AccountingPurl'z GreenОценок пока нет
- Journalizing, Posting and BalancingДокумент21 страницаJournalizing, Posting and Balancinganuradha100% (1)
- Module 8 Special and Combination Journals, and Voucher SystemДокумент64 страницыModule 8 Special and Combination Journals, and Voucher SystemMCM EnterpriseОценок пока нет
- Principles of Accounting ExercisesДокумент3 страницыPrinciples of Accounting ExercisesAB D'oriaОценок пока нет
- Statement of Cash FlowsДокумент30 страницStatement of Cash FlowsNocturnal Bee100% (1)
- Lesson 8 Elements of FsДокумент53 страницыLesson 8 Elements of FsSoothing BlendОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Statement of Cash FlowsДокумент33 страницыChapter 4 Statement of Cash FlowsSucreОценок пока нет
- Module 9 - Merchandising Accounting CycleДокумент62 страницыModule 9 - Merchandising Accounting CycleRandolph Collado100% (1)
- Philippine School of Business Administration: Cpa ReviewДокумент13 страницPhilippine School of Business Administration: Cpa ReviewLoi GachoОценок пока нет
- Reversing EntriesДокумент9 страницReversing EntriesHumair Ahmed100% (1)
- Adjusting Entries - Theory #4Документ27 страницAdjusting Entries - Theory #4Rae Antonette Solana100% (1)
- My Presentation About PayRoll SystemДокумент3 страницыMy Presentation About PayRoll SystemAzeem Asim MughalОценок пока нет
- Basic Accounting Crash CourseДокумент5 страницBasic Accounting Crash CourseCyra JimenezОценок пока нет
- Module 1C - ACCCOB2 - Conceptual Framework For Financial Reporting - FHVДокумент56 страницModule 1C - ACCCOB2 - Conceptual Framework For Financial Reporting - FHVCale Robert RascoОценок пока нет
- Basic Accounting SlidesДокумент61 страницаBasic Accounting SlidesSathyaОценок пока нет
- 3cash and AccrualДокумент9 страниц3cash and AccrualABDUL RAUF100% (2)
- Taxation - Allowable Business DeductionsДокумент51 страницаTaxation - Allowable Business DeductionsHannah OrosОценок пока нет
- Journal EntryДокумент14 страницJournal EntryPACO AliporeОценок пока нет
- 1 SOP Petty Cash ManagementДокумент27 страниц1 SOP Petty Cash ManagementMuhammad Julianto FardanОценок пока нет
- Accounting Perpetual & Periodic ComparisonДокумент1 страницаAccounting Perpetual & Periodic ComparisonAbbey LiОценок пока нет
- Account Closure Form - v2Документ1 страницаAccount Closure Form - v2OTHER Work100% (1)
- Chart of AccountsДокумент11 страницChart of AccountsTrisha Panaligan100% (1)
- Accounts Payable Interview QuestionsДокумент11 страницAccounts Payable Interview QuestionsBandita RoutОценок пока нет
- Merchandising Business Pt. 2Документ18 страницMerchandising Business Pt. 2Angelo ReyesОценок пока нет
- Accounting ExercisesДокумент5 страницAccounting Exercisesjj100% (1)
- Introduction To AccountingДокумент27 страницIntroduction To Accountingdhanyasugukumar100% (2)
- Fundamentals OF Accounting: Accounting by Meigs, Williams, Haka, BettnerДокумент64 страницыFundamentals OF Accounting: Accounting by Meigs, Williams, Haka, BettnerAliya SaeedОценок пока нет
- Statement of Financial PositionДокумент28 страницStatement of Financial Positionsammie helsonОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Accounting CH 1-Chapter 7Документ81 страницаFundamentals of Accounting CH 1-Chapter 7Nati PUFFxKIDОценок пока нет
- Bomay Dieng ReportsДокумент22 страницыBomay Dieng ReportsR SreenuОценок пока нет
- Indian Audit in An IndependentДокумент10 страницIndian Audit in An IndependentHeraldWilsonОценок пока нет
- Income Tax Questions and AnswersДокумент9 страницIncome Tax Questions and AnswersHeraldWilsonОценок пока нет
- Skincare IntakeДокумент4 страницыSkincare IntakeHeraldWilsonОценок пока нет
- Advanced Series - Ashtanga Yoga PDFДокумент2 страницыAdvanced Series - Ashtanga Yoga PDFDavid Goodwin67% (3)
- Yoga Routine PDFДокумент13 страницYoga Routine PDFYasharОценок пока нет
- Programs BrochureДокумент6 страницPrograms BrochureHeraldWilsonОценок пока нет
- Programs BrochureДокумент6 страницPrograms BrochureHeraldWilsonОценок пока нет