Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Homework Assignment #3 ECO 3101, Fall 2011 Instructions: Answer Each of The Following Questions On Separate Paper. Be Sure To Show Your Work and
Загружено:
Pierre RodriguezОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Homework Assignment #3 ECO 3101, Fall 2011 Instructions: Answer Each of The Following Questions On Separate Paper. Be Sure To Show Your Work and
Загружено:
Pierre RodriguezАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Homework Assignment #3 ECO 3101, Fall 2011 Instructions: Answer each of the following questions on separate paper.
Be sure to show your work and justify your answers wherever appropriate. Due: Friday, December 2nd at the beginning of class
1. Consider a firm that manufactures widgets from labor, capital, and raw materials. The firms production function is q = 5KL. Each unit of capital costs $10,000 per month and each unit of labor costs $5000 per month. In addition to the capital and labor costs involved, $2000 of raw materials are required for each widget that gets produced. In the short run, the firms capital is fixed at 5 units. a. What is the short run total cost function for this firm (total cost as a function of q)? b. What is the short run marginal cost function for this firm (marginal cost as a function of q)? The short run average total cost function (ATC as a function of q)? c. In the long run, what capital/labor ratio should the firm pick if it wants to minimize total production costs at any level of output? d. What is the firms long run total cost function? The long run marginal cost function? The long run average total cost function?
2. In the context of a firms output decision, what is the difference between the short run and the long run? What determines the shape of a firms average total cost curve in the short run? What determines the shape of a firms average total cost curve in the long run? Explain.
3. Consider a firm that produces output from labor and capital according to the per-day production function: q = K2L. Suppose that the firms manager has been given a production target of 8000 units per day, and the firm can purchase capital and labor at per-day prices of $40/unit of capital and $20/unit of labor respectively. a. Suppose the firm employs 80 units of labor each day. What quantity of capital would it need to employ to meet the daily production target? What would be its total cost each day in that case? b. Calculate the marginal product per dollar spent on labor at the input bundle used in (a), and repeat the calculation for capital. Based on your calculations, should the firm move toward a more laborintensive production process or a less labor-intensive production process if it wants to cut costs? Explain. c. What input bundle should the firm employ if it wants to meet its production target at the lowest possible cost? What would be the total cost per day in that case?
4. Under what conditions is a firm considered to be perfectly competitive? What will its total revenue curve look like in that case? What will its marginal revenue curve look like? Explain.
5. Consider a perfectly competitive firm with the following cost curves:
a. b. c. d.
TC = 200 + 2q2 MC = 4q AVC = 2q
If output can be sold at P = $100 per unit, what is the profit-maximizing output level? How much profit will the firm earn when P = $100? What is the firms shutdown price? What is the firms break-even price? Assume that TC is the same in the short run and long run.
6. Describe the difference between a firms accounting profit and their economic profit. Would a firm be satisfied earning an economic profit of 0? Explain.
7. Consider a perfectly competitive industry with 200 identical firms. Each firm has short run production function: q = 10L1/2. Each firm pays $4000 per unit for labor and has short run fixed costs of $1000. a. What is the short run total cost function (TC, expressed as a function of q) for each firm in the industry? b. What is the short run supply function for each firm in the industry (q as a function of P)? c. What is the short run market supply function for the industry (QS as a function of P) d. If the market demand curve is given by Qd = 5400 2P, what will be the short run equilibrium price and quantity? e. How much profit will each firm earn in the short run?
Вам также может понравиться
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageОт EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Micro Tutorial 8 - 2017Документ2 страницыMicro Tutorial 8 - 2017AndyОценок пока нет
- F23 Assignment 2mestaДокумент8 страницF23 Assignment 2mestashreyaxspamsОценок пока нет
- 621904314547 (2)Документ6 страниц621904314547 (2)Furkan NazırОценок пока нет
- Homework 2 - MGMT 335Документ3 страницыHomework 2 - MGMT 335julettagabrielyanОценок пока нет
- Pcu Topic Number 4 ActivityДокумент1 страницаPcu Topic Number 4 ActivityAilyn S. BulataoОценок пока нет
- ME - Problem Set 5Документ4 страницыME - Problem Set 5AbhiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ19 страницChapter 6Zayed Mohammad Johny100% (1)
- C - 6 T C P: Hapter HE Ost of RoductionДокумент19 страницC - 6 T C P: Hapter HE Ost of RoductionAtiqueSouravОценок пока нет
- Assignment 5Документ2 страницыAssignment 5Pratik RajОценок пока нет
- Answer CH 7 Costs of ProductionДокумент11 страницAnswer CH 7 Costs of ProductionAurik IshОценок пока нет
- Sup Questions 4Документ17 страницSup Questions 4Anonymous bTh744z7E6Оценок пока нет
- Exam 2 - Answer Key PDFДокумент6 страницExam 2 - Answer Key PDFMarjser Planta SagarinoОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 6 - SchemeДокумент5 страницTutorial 6 - SchemeTeo ShengОценок пока нет
- ME Cost Problem SetДокумент3 страницыME Cost Problem SetPrithiraj MahantaОценок пока нет
- Micro Tutorial 8 - 2018Документ2 страницыMicro Tutorial 8 - 2018LuisLoОценок пока нет
- ME Cost Prob Set RevisedДокумент3 страницыME Cost Prob Set RevisedPrithiraj MahantaОценок пока нет
- B Micro HA 3 Problem SetДокумент13 страницB Micro HA 3 Problem SetAzar0% (1)
- Assignment 6Документ2 страницыAssignment 6Pratik RajОценок пока нет
- Microeconomics II Teaching MaterialsДокумент16 страницMicroeconomics II Teaching MaterialsWendafrash AregaОценок пока нет
- Eco101a Tutorial Problem Set 06 Summer Term 2018 (16079)Документ4 страницыEco101a Tutorial Problem Set 06 Summer Term 2018 (16079)Mukul Chandra0% (1)
- 100-F2014 Assignment 6 Perfect Competition, Monopoly and Consumer Choice TheoryДокумент6 страниц100-F2014 Assignment 6 Perfect Competition, Monopoly and Consumer Choice TheoryKristina Phillpotts-BrownОценок пока нет
- Problem SetДокумент10 страницProblem SetDaksh AnejaОценок пока нет
- Homework 1Документ8 страницHomework 1sierrasoОценок пока нет
- Optimization Tutorial QuestionsДокумент5 страницOptimization Tutorial QuestionsManuel BoahenОценок пока нет
- MICRO Ass. 4Документ3 страницыMICRO Ass. 4Sidramushtaq IoBMОценок пока нет
- Microeconomics Problem Set 5Документ7 страницMicroeconomics Problem Set 5Thăng Nguyễn BáОценок пока нет
- Exam 21082011Документ8 страницExam 21082011Rabah ElmasriОценок пока нет
- TUTORIALMBA 605 Managerial Economics Market StructureДокумент9 страницTUTORIALMBA 605 Managerial Economics Market StructureGARUIS MELIОценок пока нет
- HW3 QuestionsДокумент5 страницHW3 QuestionsJason LeungОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomic ExerciseДокумент1 страницаMacroeconomic ExercisedanzeluОценок пока нет
- Tutorial - Chapter 4 - Cost of Production - QuestionsДокумент4 страницыTutorial - Chapter 4 - Cost of Production - QuestionsNandiie100% (1)
- F5 - Mock B - QuestionsДокумент15 страницF5 - Mock B - QuestionsUmar AwanОценок пока нет
- Econ 100A s12 Midterm 2 Practice ExamДокумент14 страницEcon 100A s12 Midterm 2 Practice ExamJennifer WangОценок пока нет
- ProductionДокумент6 страницProductionjoshcastv27Оценок пока нет
- ECO101 PS8 QuestionsДокумент3 страницыECO101 PS8 Questionschuyue jinОценок пока нет
- PQs 5 AДокумент4 страницыPQs 5 Aalex-bookОценок пока нет
- HW 7 Solutions 2 PDFДокумент5 страницHW 7 Solutions 2 PDFUmerSaeedОценок пока нет
- Lesson Number: 9 Topic: Costs of Production: Course Code and Title: BACR2 Basic MicroeconomicsДокумент10 страницLesson Number: 9 Topic: Costs of Production: Course Code and Title: BACR2 Basic MicroeconomicsVirgie OrtizОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ4 страницыChapter 1sadsadsa100% (1)
- Chapter 7 1Документ9 страницChapter 7 1Andika SaputraОценок пока нет
- Breakeven and EOQ Exercises (With Answers)Документ6 страницBreakeven and EOQ Exercises (With Answers)Charlene ChorОценок пока нет
- Exam 2 BankДокумент27 страницExam 2 BankRishabh SinhaОценок пока нет
- Midterm Examination Iii Intermediate MicroeconomicsДокумент5 страницMidterm Examination Iii Intermediate MicroeconomicsOng Wei LingОценок пока нет
- Assignment 4Документ1 страницаAssignment 4Pratik RajОценок пока нет
- Ghadsway's Eco301 Question BNKДокумент18 страницGhadsway's Eco301 Question BNKwww.desmondopoku615Оценок пока нет
- Individual AssignmentДокумент7 страницIndividual Assignmentbekele amenaОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 1Документ1 страницаProblem Set 1peanut yayОценок пока нет
- Homework AssignmentДокумент11 страницHomework AssignmentHenny DeWillisОценок пока нет
- Rift Valley University Bole Campus, Post Graduate Program - MBA Assignment For Managerial Economics To Be Submitted Together With Final Exam Answer Sheets (Home Take-Time Limited Exam) QuestionsДокумент2 страницыRift Valley University Bole Campus, Post Graduate Program - MBA Assignment For Managerial Economics To Be Submitted Together With Final Exam Answer Sheets (Home Take-Time Limited Exam) QuestionsMohammed AdemОценок пока нет
- ChapC15 PDFДокумент12 страницChapC15 PDFRafik RafikОценок пока нет
- ECO701 Economics and The Business Environment Coursework 1 May 21 SemesterДокумент4 страницыECO701 Economics and The Business Environment Coursework 1 May 21 SemesterAbhinav P KrishnaОценок пока нет
- CF Qs C4 (B11)Документ6 страницCF Qs C4 (B11)shah gОценок пока нет
- Midterm Examination Iii Intermediate MicroeconomicsДокумент5 страницMidterm Examination Iii Intermediate MicroeconomicsAhmed LakhaniОценок пока нет
- EconomicsДокумент37 страницEconomicsegy1971Оценок пока нет
- Exercise 1 - Cost Concepts-1Документ7 страницExercise 1 - Cost Concepts-1Vincent PanisalesОценок пока нет
- Quiz Week 2 NewДокумент4 страницыQuiz Week 2 NewMuhammad M BhattiОценок пока нет
- Problem Set Perfect Competition March 2024Документ2 страницыProblem Set Perfect Competition March 2024asmitamittal1998Оценок пока нет
- Exam #2 Practice ProblemsДокумент3 страницыExam #2 Practice Problemsbalaji0907Оценок пока нет
- Thesis StatementsДокумент4 страницыThesis StatementsPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- The Shawl QuizДокумент2 страницыThe Shawl QuizPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Essay StructureДокумент3 страницыEssay StructurePierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Marine Geography: Module 6. Deep SeaДокумент20 страницMarine Geography: Module 6. Deep SeaPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- The Sociological Imagination - The Promise CH 1 - 5Документ5 страницThe Sociological Imagination - The Promise CH 1 - 5Rodrigo SalgueroОценок пока нет
- Chapter Six: Measuring and Evaluating The Performance of Banks and Their Principal CompetitorsДокумент28 страницChapter Six: Measuring and Evaluating The Performance of Banks and Their Principal Competitorscynthiaaa sОценок пока нет
- M1 L3 - Discussion On Integrating Quotes (D-03)Документ1 страницаM1 L3 - Discussion On Integrating Quotes (D-03)Pierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Econ2123 Quiz3 SolutionДокумент4 страницыEcon2123 Quiz3 SolutionPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Childs - 2019 - Greening The Blue Corporate Strategies For Legitimising Deep Sea MiningДокумент12 страницChilds - 2019 - Greening The Blue Corporate Strategies For Legitimising Deep Sea MiningPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Dover - 2011 - On Deep-Sea MiningДокумент3 страницыDover - 2011 - On Deep-Sea MiningPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Moscow AerostarДокумент11 страницMoscow AerostarPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- RIO Article 10528Документ48 страницRIO Article 10528Pierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Management: Chapter Eight: Managing Human Resources in OrganizationsДокумент46 страницFundamentals of Management: Chapter Eight: Managing Human Resources in OrganizationsPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Iucn - 2018 - Issues Brief Deep-Sea MiningДокумент2 страницыIucn - 2018 - Issues Brief Deep-Sea MiningBenjamin MendezОценок пока нет
- w338 Mixed Gas Laws WorksheetДокумент6 страницw338 Mixed Gas Laws WorksheetPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Practice Problem TrigДокумент9 страницPractice Problem TrigPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- SAT Math Strategies (Updated)Документ2 страницыSAT Math Strategies (Updated)Pierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- QMB SolutionsДокумент180 страницQMB SolutionsPierre Rodriguez0% (1)
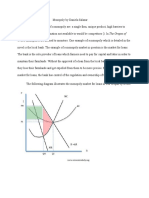
- Monopoly by Daniela SalazarДокумент2 страницыMonopoly by Daniela SalazarPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Corrections 2012 Chapter TwentyДокумент2 страницыCorrections 2012 Chapter TwentyPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- SPSS Assignment 1Документ3 страницыSPSS Assignment 1Pierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Thought in ReligionДокумент7 страницThought in ReligionPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Experimental Paper Part Two - Example W CommentsДокумент6 страницExperimental Paper Part Two - Example W CommentsPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- SPSS Assignment 1Документ3 страницыSPSS Assignment 1Pierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Environmental Chemistry Chm401Документ2 страницыEnvironmental Chemistry Chm401Pierre Rodriguez100% (1)
- Physics I Practice Problems Set 2 1Документ17 страницPhysics I Practice Problems Set 2 1killerspikeОценок пока нет
- CHM 401 Practice Exam II Spring 2011Документ6 страницCHM 401 Practice Exam II Spring 2011Pierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- World Religion Chapter Question Winter 2014Документ19 страницWorld Religion Chapter Question Winter 2014Pierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Balance Sheets, Income Statements and Net Cash FlowДокумент10 страницBalance Sheets, Income Statements and Net Cash FlowPierre RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Pex 09 05Документ4 страницыPex 09 05Pierre Rodriguez100% (7)
- The Dust Bunnies COL FKBДокумент36 страницThe Dust Bunnies COL FKBPradeep ManralОценок пока нет
- 762id - Development of Cluster-7 Marginal Field Paper To PetrotechДокумент2 страницы762id - Development of Cluster-7 Marginal Field Paper To PetrotechSATRIOОценок пока нет
- 120 Câu Tìm Từ Đồng Nghĩa-Trái Nghĩa-Dap AnДокумент9 страниц120 Câu Tìm Từ Đồng Nghĩa-Trái Nghĩa-Dap AnAlex TranОценок пока нет
- Elerick Ron Cynthia 1983 SouthAfricaДокумент4 страницыElerick Ron Cynthia 1983 SouthAfricathe missions networkОценок пока нет
- Amsterdam Pipe Museum - Snuff WorldwideДокумент1 страницаAmsterdam Pipe Museum - Snuff Worldwideevon1Оценок пока нет
- D15 Hybrid P1 QPДокумент6 страницD15 Hybrid P1 QPShaameswary AnnadoraiОценок пока нет
- Merchant Shipping MINIMUM SAFE MANNING Regulations 2016Документ14 страницMerchant Shipping MINIMUM SAFE MANNING Regulations 2016Arthur SchoutОценок пока нет
- B2B Marketing: Chapter-8Документ23 страницыB2B Marketing: Chapter-8Saurabh JainОценок пока нет
- Practical Applications of Electrical ConductorsДокумент12 страницPractical Applications of Electrical ConductorsHans De Keulenaer100% (5)
- Wall Panel SystemsДокумент57 страницWall Panel SystemsChrisel DyОценок пока нет
- Bankers ChoiceДокумент18 страницBankers ChoiceArchana ThirunagariОценок пока нет
- Enemies Beyond Character Creation SupplementДокумент8 страницEnemies Beyond Character Creation SupplementCain BlachartОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Sic Mosfet and Si IgbtДокумент10 страницComparison of Sic Mosfet and Si IgbtYassir ButtОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - Amino acids and Proteins: Trần Thị Minh ĐứcДокумент59 страницChapter 5 - Amino acids and Proteins: Trần Thị Minh ĐứcNguyễn SunОценок пока нет
- Resolution: Owner/Operator, DocketedДокумент4 страницыResolution: Owner/Operator, DocketedDonna Grace Guyo100% (1)
- Estill Voice Training and Voice Quality Control in Contemporary Commercial Singing: An Exploratory StudyДокумент8 страницEstill Voice Training and Voice Quality Control in Contemporary Commercial Singing: An Exploratory StudyVisal SasidharanОценок пока нет
- Acronyms and AbbreviationsДокумент875 страницAcronyms and AbbreviationsLacky KrishnanОценок пока нет
- Useful Methods in CatiaДокумент30 страницUseful Methods in CatiaNastase Corina100% (2)
- 8. Nguyễn Tất Thành- Kon TumДокумент17 страниц8. Nguyễn Tất Thành- Kon TumK60 TRẦN MINH QUANGОценок пока нет
- So Tim Penilik N10 16 Desember 2022 Finish-1Документ163 страницыSo Tim Penilik N10 16 Desember 2022 Finish-1Muhammad EkiОценок пока нет
- Geography NotesДокумент2 страницыGeography NotesMinethegroundОценок пока нет
- Tanque: Equipment Data SheetДокумент1 страницаTanque: Equipment Data SheetAlonso DIAZОценок пока нет
- Computer in Community Pharmacy by Adnan Sarwar ChaudharyДокумент10 страницComputer in Community Pharmacy by Adnan Sarwar ChaudharyDr-Adnan Sarwar Chaudhary100% (1)
- Catalogue Laboratory Products - Heraeus KulzerДокумент288 страницCatalogue Laboratory Products - Heraeus KulzerDentaDentОценок пока нет
- Bai Tap Av 12 Thi Diem Unit TwoДокумент7 страницBai Tap Av 12 Thi Diem Unit TwonguyenngocquynhchiОценок пока нет
- Case Study Analysis - WeWorkДокумент8 страницCase Study Analysis - WeWorkHervé Kubwimana50% (2)
- New - BMP3005 - ABF - Assessment Brief - FДокумент5 страницNew - BMP3005 - ABF - Assessment Brief - Fmilka traykovОценок пока нет
- Reservoir Bag Physics J PhilipДокумент44 страницыReservoir Bag Physics J PhilipJashim JumliОценок пока нет
- Lightolier Lytecaster Downlights Catalog 1984Документ68 страницLightolier Lytecaster Downlights Catalog 1984Alan MastersОценок пока нет
- Introduction To History AnswerДокумент3 страницыIntroduction To History AnswerLawrence De La RosaОценок пока нет