Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
What Are You Going To Learn?: The Union of Two Sets
Загружено:
F X AGUS SISWANTOИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
What Are You Going To Learn?: The Union of Two Sets
Загружено:
F X AGUS SISWANTOАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
6.
What are you going to The Union of Two Sets
learn?
To state the concept
of the union of sets
To determine the Recall the sets you have learned before, namely:
union of two sets A = set of subjects tested in a elementary school (SD)
To draw the Venn that Ani had learned, or
diagram of the union
A = {PPKN, Bahasa Indonesia, Matematika}
of two sets
To solve story
and
problems on the B = set of subjects tested in a elementary school, or
union of two sets (SD) that Budi had learned
using a Venn
B = {Matematika, IPA}.
diagram.
If we unite all subjects that either Ani or Budi had
Key Terms: learned, then we get a new set, that is
À union the set of subjects that Ani or Budi had learned, or
{PPKN, Bahasa Indonesia, Matematika, IPA},
The set formed is called the union of set A and set B,
written as A ∪ B.
Using the Venn diagram, you can draw the union of two sets as
follows:
U B A
• PPKN
• Science • Mat.
• B. Indon.
The shaded area shows A ∪ B
Mathematics for Junior High School Year 7 / 2 5 5
How can we form the union of two sets mathematically?
Using the set-builder notation, you can state the union of two sets as
follows:
Union The union of two sets A and B is the set whose
elements are elements of A or elements of B, or
elements of both sets. The union of A and B is
denoted by
A ∪ B = { x | x ∈ A or x ∈ B }
Can you distinguish the intersection of two sets from the union
of two sets?
If A = { 1, 2, 3, 4 } and B = { 2, 3, 5, 7, 8 }, then
A ∪ B = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, }
Drawing a Venn diagram, we have:
U A B
1 2 5
8
4 3 7
The shaded area shows A ∪ B
Find an example of two other sets, and then determine the
union of the sets.
2 5 6 / Student’s Book - Sets
Determining the Union of Two Sets
There are some methods of determining the union of two sets.
a. If one set is a subset of the other set
If A = { a, b, c, d, e, f }, B = { a, c, d },
then A ∪ B = { a, b, c, d, e, f } = A.
The Venn diagram is as follows.
.
U
a
c
f b
B
d e
A
The shaded area shows A ∪ B
If A = the set of natural numbers not greater than 7,
B = the set of odd natural numbers not greater than 7,
then A = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 }
B = { 1, 3, 5, 7 }
A ∪ B = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 } = A.
Mathematics for Junior High School Year 7 / 2 5 7
The Venn diagram is as follows.
U
B
1 3 4
6 A
5 7 2
The shaded area shows A ∪ B
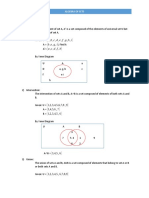
Based on the above examples, it can be concluded that:
Property 3 If B ⊂ A then A ∪ B = A
b. If the two sets are the same
If A = the set of natural numbers less than 7, and
B = { x ¦ 0 < x < 7, x is whole number },
then A = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }
B = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }
A ∪ B = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 } = A = B.
The Venn diagram is as follows:
U
1 3 4
5 6 2
A=B
The shaded area shows A ∪ B
2 5 8 / Student’s Book - Sets
Given A= the set of prime numbers between 1 and 10
B = { 2, 3, 5, 7 }
Find A∪B.
Solution:
Because A = { 2, 3, 5, 7 } and B = { 2, 3, 5, 7 }
then A ∪ B = { 2, 3, 5, 7 } = A = B.
The Venn diagram is as follows:
U A=B
3 2
5 7
The shaded area shows A ∪ B
What can we conclude from the above examples?
We can conclude that:
Property If A = B then A ∪ B = A = B
of Union
c. If the two sets are disjoint
If A = the set of odd natural numbers less than 10
B = the set of even whole number less than 10,
then A = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 }
B = { 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 }
A ∪ B = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}.
Mathematics for Junior High School Year 7 / 2 5 9
The Venn diagram is shown below.
U A B
1 0
4
3 5
7 6 2
9 8
The shaded area shows A ∪ B
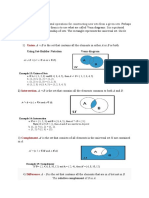
d. If the two sets are not disjoint and one set is not the subset
of the other set (the two sets have an intersection)
Given A = set of the square of the first six square natural
numbers
B = set of multiple of four of the first six
Find A ∪ B.
Solution:
Because A = { 1, 4, 9, 16, 25 } and B = { 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24 },
then A ∪ B = { 1, 4, 8, 9, 16, 20, 24, 25 }.
The Venn diagram is as follows:
U
8
1 4 12
25
A 20 B
9 16 24
The shaded area shows A ∪ B
2 6 0 / Student’s Book - Sets
Using the Venn diagram of the Union of Two Sets to
Solve Story Problems
Among 57 students, there are 40 students who like meatballs, 32
students who like soup, and 17 students who like both meatballs and
soup.
a. Draw the Venn diagram showing the data.
b. How many students like meatballs or soup?
c. How many students like neither meatballs nor soup?
Solution:
a. The Venn diagram is as follows.
(Numbers show the number of students)
B∪T
23 17 15
B T
2
Given:
B = set of students who like meatballs,
T = set of students who like soup,
B ∪ T = set of students who like meatballs or soup.
b. The number of students who like meatballs or soup is
(23 + 17+15) students or 55 students.
c. The number of students who neither like meatballs nor soup
is (57 - 55) = 2
Mathematics for Junior High School Year 7 / 2 6 1
Discuss the following example with your friends.
Among 100 students of an SMP, the following data are obtained:
32 students like poultry farm,
30 students like farming birds,
20 students like cats,
8 students like poultry farm and farming birds,
7 students like poultry farm and cats,
9 students like farming birds and cats, and
5 students like poultry farm, farming birds, and cats
Based on the data,
a. draw the Venn diagram showing the data.
b. determine the number of students who:
1) like poultry farm or farming birds.
2) like poultry farm only.
3) like only one kind of the three animals.
4) like farming birds, but do not like chicken.
5) like poultry farm, but do not like cats.
6) do not like any of the three kinds of animals.
Solution:
Given:
A = set of students who like poultry farm,
B = set of students who like farming birds,
K = set of students who like cats.
Then:
a. The Venn diagram showing the data is as follows.
(Numbers show the number of students)
2 6 2 / Student’s Book - Sets
U
22 3 18
B
A 5
2 4
b. The number of students who:
1) like poultry farm or farming birds is (22 + 2 + 5 + 3 +4 + l8) =
54
2) like poultry farm only is 22
3) like only one kind of three animals is (22 + 9 + 18) = 49
4) like farming bird, but not poultry farm is (18 + 4) = 22
5) like poultry farm, but do not like cats is (3 + 22) = 25
6) do not like any of the three animals is 37.
Mathematics for Junior High School Year 7 / 2 6 3
1. Given A = { 1, 2, 3, 5, 7 }
B = { 4, 5, 6, 7, 9 }
C = { 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 }.
Listing the elements, determine:
a. A ∪ B b. A ∪ C c. B ∪ C
d. Draw each union as a Venn diagram.
2. Given A = { x ¦ x ≤ 5, x natural number }
B = { x ¦ 3 < x < 8, x natural number }
C = { x ¦ 5 ≤ x ≤ 10, x natural number }.
Listing the elements, determine:
a. A ∪ B b. A ∪ C c. B ∪ C
3. Given A = set of squared natural numbers less than 30
B = set of multiple of 5 less than 30
C = set of multiple of 6 less than 35
Listing the elements, determine:
a. A ∪ B
b. A ∪ C
c. B ∪ C
d. Draw each union as a Venn diagram.
Critical Thinking :
4. Among 60 people, there are 20 people subscribing to
magazines, 35 people subscribing to newspapers, and 5
people subscribing to both.
a. Draw the Venn diagram showing the data, letting M =
The set of people subscribing to magazines, and K = The
set of people subscribing to newspapers.
b. How many people neither subscribe to magazines nor
newspapers?
c. How many people subscribe to magazines or newspapers?
d. How many people subscribe to newspapers only?
e. How many people subscribe to magazines only?
2 6 4 / Student’s Book - Sets
5. Among 50 students, there are 20 students who like playing tennis,
33 students who like playing basketball, and 8 students who like
playing both tennis and basketball.
a. Draw the Venn diagram showing the data.
b. How many students like playing tennis or basketball?
c. How many students do not like playing both?
d. How many students like playing tennis only?
e. How many students like playing basketball only?
6. Among 50 people shopping in a market, there are 25 people
buying apples, 23 people buying bananas, and 8 people buying
both kinds of fruit
a. Draw the Venn diagram showing the data.
b. How many people buy apples or bananas?
c. How many people buy apples only?
d. How many people buy one kind of fruit only?
e. How many people do not buy either apple or banana?
7. Given:
S = set of students who like soup,
B = set of students who like meatballs,
G =set of students who like gado-gado.
the Venn diagram showing the relationship between the sets is as
follows, (number is showing the number of students),
15 5 13
B
S 12
18 17
9
11
Mathematics for Junior High School Year 7 / 2 6 5
Determine the number of students who:
a. like soup or meatballs.
b. like meatballs or gado-gado.
c. like meatballs only.
d. like gado-gado only.
e. like soup, but do not like gado-gado.
f. like soup, but do not like meatballs.
g. like meatballs, but do not like soup.
2 6 6 / Student’s Book - Sets
Вам также может понравиться
- Activity No. 3 Union and Intersection of SetsДокумент1 страницаActivity No. 3 Union and Intersection of Setsjessymai alontagaОценок пока нет
- Algebra of Sets EXAMДокумент3 страницыAlgebra of Sets EXAMtijeje8401Оценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Concept of The Intersection of Two SetsДокумент14 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Concept of The Intersection of Two SetsF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Intersection and UnioinДокумент26 страницIntersection and UnioinRico PalmaОценок пока нет
- Unit 2: Background Notes: Part 1: 1. MathematicsДокумент7 страницUnit 2: Background Notes: Part 1: 1. MathematicsRaja JoseОценок пока нет
- For Sections 1.1-1.4, See The Previous Set of SlidesДокумент66 страницFor Sections 1.1-1.4, See The Previous Set of SlidesGabriel A. ContrerasОценок пока нет
- Ppt-Venn Diagram and Set Operations - Part 1Документ28 страницPpt-Venn Diagram and Set Operations - Part 1Jonjon Marcos100% (2)
- Slide DicretemathДокумент37 страницSlide DicretemathduygiodalonroiОценок пока нет
- MathlpДокумент21 страницаMathlpKathy FernandezОценок пока нет
- Pairs of SetДокумент23 страницыPairs of SetElla mei OralloОценок пока нет
- Set - PPT G7Документ58 страницSet - PPT G7AllanEvangelistaОценок пока нет
- Mat 115: Discrete Mathematics I: Set Theory Lecture NotesДокумент31 страницаMat 115: Discrete Mathematics I: Set Theory Lecture NotesFrank WanderiОценок пока нет
- Union of SetДокумент3 страницыUnion of SetRC AnimationОценок пока нет
- Discrete Mathematics Sets Relations FunctionsДокумент15 страницDiscrete Mathematics Sets Relations FunctionsMuhd FarisОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2Документ13 страницLesson 2Udeshika WanninayakeОценок пока нет
- CH 6Документ47 страницCH 6Hooriah RAUFОценок пока нет
- Set Theory Exercise 3Документ3 страницыSet Theory Exercise 3Noreen PatayanОценок пока нет
- 2 Sets and Operations Final 2023 - 2024Документ31 страница2 Sets and Operations Final 2023 - 2024caeli.2028Оценок пока нет
- Soal Himpunan CambridgeДокумент10 страницSoal Himpunan CambridgeFirsty VirianiОценок пока нет
- 2 SET OPERATIONS - LectureДокумент3 страницы2 SET OPERATIONS - Lecturestar fireОценок пока нет
- Week 2 Math 7 ModuleДокумент27 страницWeek 2 Math 7 Moduleronnie yago79% (19)
- Operastion On Sets and Venn DiagramДокумент19 страницOperastion On Sets and Venn DiagramsamiОценок пока нет
- Sets & Relation TheoryДокумент8 страницSets & Relation TheorySushila TanwarОценок пока нет
- CCNHS - Grade 7 Intro To SetsДокумент109 страницCCNHS - Grade 7 Intro To SetsIQup AchieversОценок пока нет
- Venn Diagram and Operation SetsДокумент17 страницVenn Diagram and Operation SetsValencia DevinaОценок пока нет
- 5 6249032366044479593 PDFДокумент22 страницы5 6249032366044479593 PDFs91Оценок пока нет
- Chapter2 SC Part 2 PDFДокумент10 страницChapter2 SC Part 2 PDFShunui SonodaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Notes-SetsДокумент9 страницLecture 1 Notes-SetsWebby ZimbaОценок пока нет
- Gemmw Module 2Документ14 страницGemmw Module 2Randolph Peralta100% (1)
- HW 12 SEPT Union Intersection PracticeДокумент1 страницаHW 12 SEPT Union Intersection PracticeFILOGULLIОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Sets, Relations FunctionsДокумент20 страницChapter 2 Sets, Relations Functionsbusiness dealОценок пока нет
- 1: Sets: IT2106-Mathematics For Computing IДокумент36 страниц1: Sets: IT2106-Mathematics For Computing ITHE MOODОценок пока нет
- Week6Lecture6 153577Документ29 страницWeek6Lecture6 153577dimanpunmagar160Оценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Sets and RelationsДокумент14 страницUnit 2 Sets and RelationsDanielaОценок пока нет
- Activity No. 4 Complement of A SetДокумент1 страницаActivity No. 4 Complement of A Setjessymai alontagaОценок пока нет
- Dll2324 Math7 q1w3d1 San Miguel Leah Mae oДокумент4 страницыDll2324 Math7 q1w3d1 San Miguel Leah Mae oMiss LeahОценок пока нет
- Maths Art Integrated Project: Venn Diagram and Representation of SetsДокумент23 страницыMaths Art Integrated Project: Venn Diagram and Representation of SetsMaca Rena100% (1)
- MODULE 2 Language of Mathematics - Copy1Документ11 страницMODULE 2 Language of Mathematics - Copy1Har VyОценок пока нет
- Use Venn Diagram To Represent The Union and Intersection of SetsДокумент5 страницUse Venn Diagram To Represent The Union and Intersection of SetsARNEL PAGHACIANОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7-Operation On SetsДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan in Mathematics 7-Operation On SetsMelissa Navarro GuiangОценок пока нет
- School Grade Level Quarter Learning Area Section and Time DateДокумент3 страницыSchool Grade Level Quarter Learning Area Section and Time DatePeterson Dela Cruz EnriquezОценок пока нет
- Operations On Sets: Learning Enhancement TeamДокумент6 страницOperations On Sets: Learning Enhancement TeamZephanie Aesh VicozēoОценок пока нет
- Math ReviewerДокумент6 страницMath ReviewerPutungan AnsherinaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 89FundamentalsofMathematicsiДокумент12 страницWorksheet 89FundamentalsofMathematicsiPiyush BawejaОценок пока нет
- With Question/Answer AnimationsДокумент34 страницыWith Question/Answer AnimationsGamesome GoshawkОценок пока нет
- O'level Mathematics Notes1Документ320 страницO'level Mathematics Notes1David ochoraОценок пока нет
- Sets and SubsetsДокумент11 страницSets and Subsetsyaoi yuriОценок пока нет
- Mathematics For Computing - I: Sets (07 HRS.)Документ39 страницMathematics For Computing - I: Sets (07 HRS.)hashir34Оценок пока нет
- Chap 2 - SetsДокумент13 страницChap 2 - SetsaminzurazakОценок пока нет
- The Relationship in Sets Using Venn Diagram Are Discussed BelowДокумент9 страницThe Relationship in Sets Using Venn Diagram Are Discussed BelowAysha FidaОценок пока нет
- There Are Several Fundamental Operations For Constructing New Sets From A Given SetsДокумент2 страницыThere Are Several Fundamental Operations For Constructing New Sets From A Given SetsAresta, Novie MaeОценок пока нет
- Local Media7035845918342573677Документ28 страницLocal Media7035845918342573677Oracion, Bernette Meiji B.Оценок пока нет
- Topic 3: Venn DiagramsДокумент8 страницTopic 3: Venn Diagramsissei dragneelОценок пока нет
- MBA-502 Business Mathematics Course Instructor: Dr. A.S.A.Noor Set TheoryДокумент20 страницMBA-502 Business Mathematics Course Instructor: Dr. A.S.A.Noor Set Theoryজুবায়ের আমিনОценок пока нет
- Week 2Документ5 страницWeek 2Dr. Neelam AryaОценок пока нет
- XI-Worksheet 1 (SETS)Документ3 страницыXI-Worksheet 1 (SETS)Harshit PatilОценок пока нет
- MATHS GRADE 11 - Sets and Venn DiagramДокумент9 страницMATHS GRADE 11 - Sets and Venn DiagramLeslie ArmstrongОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Set 1Документ49 страницChapter 2 Set 1Nehsan TamilОценок пока нет
- WS2 Sets and Set NotationДокумент4 страницыWS2 Sets and Set NotationAngel ZetinaОценок пока нет
- Wahai PuterikuДокумент5 страницWahai PuterikuDwi Nugraha Abu MuhammadОценок пока нет
- References FinalДокумент5 страницReferences FinalF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Id Rights Advocated by Instinct and Established by AlshariaДокумент61 страницаId Rights Advocated by Instinct and Established by AlshariaF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Alamat Jurnal InternasionalДокумент1 страницаAlamat Jurnal InternasionalF X AGUS SISWANTO100% (1)
- 100 Unit 1: Section OneДокумент9 страниц100 Unit 1: Section Oneainnur istafadaОценок пока нет
- Hal Masing Masing BabДокумент9 страницHal Masing Masing BabF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Kalender Puasa Sunnah Tahun 1900-2078 Rev 01Документ1 страницаKalender Puasa Sunnah Tahun 1900-2078 Rev 01Kabir BediОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Parallelograms. Those Parallelograms Have Equal Forms and SizesДокумент6 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Parallelograms. Those Parallelograms Have Equal Forms and SizesF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Raport 7J Ganjil2009Документ2 страницыRaport 7J Ganjil2009fxagussisОценок пока нет
- Cover KuningДокумент1 страницаCover KuningF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Cover KuningДокумент1 страницаCover KuningF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Drawing Right Triangles, Isosceles Triangles and Equilateral TrianglesДокумент8 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Drawing Right Triangles, Isosceles Triangles and Equilateral TrianglesF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Cover BiruДокумент1 страницаCover BiruF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: TrapezoidДокумент6 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: TrapezoidF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: of TrianglesДокумент20 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: of TrianglesF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Mini LabДокумент6 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Mini LabF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?Документ6 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?F X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Buksis 8Документ8 страницBuksis 8F X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Definition of Complement of SetsДокумент10 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Definition of Complement of SetsF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Mini - LabДокумент8 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Mini - LabF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: À To Comprehend Inverse ProportionДокумент6 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: À To Comprehend Inverse ProportionF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Buksis-4.5 Revisi AkhirДокумент18 страницBuksis-4.5 Revisi AkhirF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Drawing AnglesДокумент8 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Drawing AnglesF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Position of Two Lines: What Are You Going To Learn?Документ18 страницPosition of Two Lines: What Are You Going To Learn?F X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Ali Has 9 Books, While Lia Has 6 BooksДокумент5 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Ali Has 9 Books, While Lia Has 6 BooksF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Scaled DrawingsДокумент10 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Scaled DrawingsF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?Документ4 страницыWhat Are You Going To Learn?F X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- What Are You Going To Learn?: Universal Set Universal SetДокумент14 страницWhat Are You Going To Learn?: Universal Set Universal SetF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Buksis-4.4 Revisi AkhirДокумент12 страницBuksis-4.4 Revisi AkhirF X AGUS SISWANTOОценок пока нет
- Anklet - Google SearchДокумент1 страницаAnklet - Google SearchManu KhannaОценок пока нет
- M/B Schematic Version Change List: Release Date PCB P/N Note Pcba P/N PCB DescriptionДокумент36 страницM/B Schematic Version Change List: Release Date PCB P/N Note Pcba P/N PCB DescriptionAdriano Neoaver Tavares100% (2)
- Link Belt Rec Parts LastДокумент15 страницLink Belt Rec Parts LastBishoo ShenoudaОценок пока нет
- Torque Converter Lock-Up FunctionДокумент2 страницыTorque Converter Lock-Up Functioncorie132100% (1)
- AMC Mining Brochure (A4 LR)Документ2 страницыAMC Mining Brochure (A4 LR)Bandung WestОценок пока нет
- DefinitionДокумент6 страницDefinitionRatul HasanОценок пока нет
- Product Management GemsДокумент14 страницProduct Management GemsVijendra GopaОценок пока нет
- David Sm15 Inppt 06Документ57 страницDavid Sm15 Inppt 06Halima SyedОценок пока нет
- DOLE Vacancies As of 01 - 10 - 13Документ17 страницDOLE Vacancies As of 01 - 10 - 13sumaychengОценок пока нет
- Aaa0030imb02 FДокумент30 страницAaa0030imb02 FJvr Omar EspinozaОценок пока нет
- L-2 Steel SectionsДокумент23 страницыL-2 Steel SectionsRukhsar JoueОценок пока нет
- Webdynpro ResumeДокумент4 страницыWebdynpro ResumeAmarnath ReddyОценок пока нет
- 20779A ENU CompanionДокумент86 страниц20779A ENU Companionmiamikk204Оценок пока нет
- Astm D2940 D2940M 09Документ1 страницаAstm D2940 D2940M 09INDIRA DEL CARMEN BERMEJO FERN�NDEZОценок пока нет
- Assignment Mid Nescafe 111173001Документ5 страницAssignment Mid Nescafe 111173001afnan huqОценок пока нет
- UnderstandingcpucoresДокумент5 страницUnderstandingcpucoresAbdul NabiОценок пока нет
- 9MFY18 MylanДокумент94 страницы9MFY18 MylanRahul GautamОценок пока нет
- The Effectiveness of Blended Learning Model During Covid-19 Pandemic On Automotive Engineering Major Program Students of SMK Negeri 10 SamarindaДокумент7 страницThe Effectiveness of Blended Learning Model During Covid-19 Pandemic On Automotive Engineering Major Program Students of SMK Negeri 10 SamarindaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- ScriptДокумент7 страницScriptAllen Delacruz100% (1)
- BS351: Financial Reporting: Learning ObjectivesДокумент3 страницыBS351: Financial Reporting: Learning ObjectivesMajeed Ullah KhanОценок пока нет
- E-Booklet Tacompact Board 2021Документ6 страницE-Booklet Tacompact Board 2021embenОценок пока нет
- Installing Oracle Fail SafeДокумент14 страницInstalling Oracle Fail SafeSantiago ArgibayОценок пока нет
- Comparison of The Gasification Performance in The Downdraftfixed-Bedgasifier Fed by Different Feedstocks Rice Husk, Sawdust, and Their MixtureДокумент8 страницComparison of The Gasification Performance in The Downdraftfixed-Bedgasifier Fed by Different Feedstocks Rice Husk, Sawdust, and Their MixturechaniefОценок пока нет
- Times Leader 02-06-2012Документ36 страницTimes Leader 02-06-2012The Times LeaderОценок пока нет
- CPCДокумент6 страницCPCpranjalОценок пока нет
- Katalog Bonnier BooksДокумент45 страницKatalog Bonnier BooksghitahirataОценок пока нет
- VMC Ballscrew 32mm Horizontal Plane ReplacementДокумент11 страницVMC Ballscrew 32mm Horizontal Plane ReplacementMarlon GeronimoОценок пока нет
- AP Physics Name: AP Thermal PracticeДокумент2 страницыAP Physics Name: AP Thermal PracticeMuddamsetty ArunkalyanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To AccountingДокумент36 страницIntroduction To AccountingRajnikant PatelОценок пока нет
- AДокумент2 страницыAẄâQâŗÂlïОценок пока нет