Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Beef Cattle Production
Загружено:
Anusia NadarajanИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Beef Cattle Production
Загружено:
Anusia NadarajanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Beef Cattle production Issues in Malaysia & world 1. Cattle integration with oil palm plantation 2.
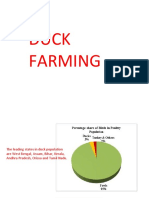
Mean for infant development and mother by world nutritionist 3. BSE/ Mad cow 4. Dioxine in milk and meat contamination cancer hazard, severe reproductive and developmental problem 5. FMD affecting hoofed mammal 6. Brucellosis zoonotic disease and carrier animals (infected cows transferring the disease) 7. Gelatin in almost 70% food products Current scenario 1. Beef cattle prod still belong to smallholder (free roaming in kampong/urban area)/ subsistence type of prod system 2. Most production in Kedah / Kelantan 3. Type cattle: KK Cattle 4. Total prod in Malaysia ~approx 800,000 5. Open pasture majuternak farm 6. Newly prod system integration with palm oil plantation 7. Small scale feedlot operations in Selangor, Johor, Pahang, Perak, Penang 8. Beef importation >rm3 billion/annum 9. Imported from India (70%), Aussie (20%), Others (10%) Breeds 2 type of domestic cattle 1. Bos indicus (KK Cattle, Brahman, Sahiwal, Nellore, Yellow Cattle China) 2. Bos Taurus (Hereford, Angus, Limousin, Simmental, Shorthorn, Charolis) Bos Indicus characteristic/features 1. Have dewlap-flabby skin under neck (gelambir) to increase surface area,repel insect, better heat dissipation 2. Have hump (bonggol), pendulous prepuce (in Brahman) 3. Well adapted to local climate 4. Hardiness, good resistance to tropical environment 5. Resistant breed 6. Immune to local disease 7. Low maintenance requirement usually small in size 8. High fertility 9. Slow growth/low ADG 10. Poor shape 11. Zebu cattle suitable for work cattle 12. Gone through Natural Selection good as adaptive traits in crossbreeding for beef cattle production in tropical environment
KK Cattle 1. Male: 330-350 kg 2. Female:180-250kg 3. Age at first calving: 26-50 kg 4. Conception rate: >90% 5. Calving rate: >85% 6. Mortality rate: < 5% 7. Birth weight: 15-16 kg 8. Waning wt.(6 mnth): 55-10 kg 9. ADG: 0.3-0.4 KG/DAY Bos Taurus 1. Beefy,round,body shape (square rear view) 2. Improved animal breeding & selection a. Selected for traits that: fast growth, high fertility, high calving rate. Good mothering ability, good conformation, high dressing %, high libido 3. Usually less adaptable to tropics a. Heat stress b. Parasites problem c. High maintenance requirement Wild Cattle types / Other Bovidae 1. Bos Gaurus (Gaur) a. Seladang b. Huge head c. Gestation period: 9 mnth d. Gross with cattle selembu (sterile offspring) 2. Bos javanicus/ Bos sondaicus (Banteng/tembadau) 3. Bos mutus yak 4. Bos bison 5. Bubalus bubalis / bos bubalis (buffalo) Mating methods 1. Natural mating a. Used of selected bulls b. Ratio male: female 1:20 (due to estrous cycle female 20 days) 2. Artificial insemination (A.I) a. Usually for research in beef cattle breeding / using exotic European type cattle for mating with zebu b. Eg: i. Hereford x KK cows ii. Charolis x KK iii. Limousin x KK c. Imported frozen semen used d. Teaser bulls used for estrous detection is more efficient in beef cattle mating program using A.I i. Kk teaser bull penile deviation at right abdomen
Mating system 1. Seasonal mating a. Bull + cow for 3 months , 1 or 2 times/year b. Arrange according to rainy season/pasture prod c. Advantages: i. planned calving periods ii. calves similar ages & uniform in sizes iii. management seasonal d. Disadvantages i. Calves crops ii. Busy/heavy duty iii. Some cows escape 2. Continuous mating system a. Continuously throughout years b. Advantage: All fertile cows pregnant, no escape / empty cow c. Disadvantage: disorganized management of calves
Management of beef calves Quality important for 1. Replacement 2. Beef production Required.. 1. Good planning 2. Management strategy (reproduction, breed selection, nutrition , disease control)
Mating and breeding management 1. Joining bull + cows 2. Pregnancy diagnosis 3. Separating of pregnant cows to nearest paddocks 4. Calving Feeding pregnant cows 1. provide excess to high quality grass 3. give concentrate feed high energy diets Calving period cows sign 4. Isolating herself from herd & nervous 5. Stop eating 6. Swollen udder 7. Tails base ligament relax 8. Swollen vagina & appear reddish
9. Right sign : water bag come out from vagina. 3 hrs later..give birth. If no parturition after 3 hrs?? Need assistance After calving 1. Cow lick the calf 2. Clear nostrils from slime & placenta 3. Put tincture iodine at navel 4. Weight the calf birth weight 5. Make sure newly born calves have colostrums from the dam <36 hrs 6. Stored colustrum can be used 7. Let calf with the cow-preweaning period 8. Beef calves wean at age of 6-7 months Weaning 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. At age of 6-7 mnths (200 days) Send cows to far paddocks to recover again for next calving Treatment required deworming, weighing, tag ID Selected for replacement calves / to become feeder calves for falttening Use adjusted 200 days weaning weight for selection
Production system beef cattle 1. Open pasture 2. Integrated with palm oil plantation 3. Intensive system feedlot system for flattening
Beef production system 1. Open pasture a. Improved pastures/local grasses b. Extensive/range prod system c. Suitable pasture: - guinea grass + legumes, Setaria grass + legumes, Briachiara decumbens d. Stocking rate / carrying capacity depends on production of dry matter of pastures **method determining carrying capacity SR = GGR X ME content / MEVI Normal animal offer ad libitum feeds 2. Integrated with primary crops (LICRO system)
Вам также может понравиться
- Feeds & Feeding AssignmentДокумент12 страницFeeds & Feeding AssignmentRoseannae ParkОценок пока нет
- Rearing Young Ruminants On Milk Replacer and Starter FeedsДокумент95 страницRearing Young Ruminants On Milk Replacer and Starter FeedsZiaul HassanОценок пока нет
- Types of FeedsДокумент21 страницаTypes of FeedsMay Ann GuintoОценок пока нет
- Livestock Feeding PracticesДокумент12 страницLivestock Feeding Practicesbaskar100% (1)
- Beef Cattle Management-1'12Документ104 страницыBeef Cattle Management-1'12Anna AlthafunnisaОценок пока нет
- Soybean Meal An Excellent Protein Source For Poultry FeedsДокумент16 страницSoybean Meal An Excellent Protein Source For Poultry FeedsJohn HonestОценок пока нет
- Overview of The Beef Cattle IndustryДокумент34 страницыOverview of The Beef Cattle IndustryKyla Fanuñal100% (2)
- Ans311 Notes - Sept. 2020Документ141 страницаAns311 Notes - Sept. 2020Joy.B mwanzaОценок пока нет
- Goats & Sheep: What You Need To KnowДокумент74 страницыGoats & Sheep: What You Need To KnowAdrian BAGAYANОценок пока нет
- Grazing Animal Nutrition PDFДокумент46 страницGrazing Animal Nutrition PDFPaulo Junior100% (1)
- KMDP - MSF Mod CH Handbook Annex 4 Boqs Cow HouseДокумент9 страницKMDP - MSF Mod CH Handbook Annex 4 Boqs Cow HousephineasОценок пока нет
- AdvancedTrainingTechniquesforOxenTechGuide PDFДокумент23 страницыAdvancedTrainingTechniquesforOxenTechGuide PDFh1970hu100% (1)
- Animal NutritionДокумент28 страницAnimal NutritionIonela HoteaОценок пока нет
- Dairy Goats - With Information on the Breeds, Breeding and Management of Dairy GoatsОт EverandDairy Goats - With Information on the Breeds, Breeding and Management of Dairy GoatsОценок пока нет
- Feeding and Management of Dairy GoatsДокумент13 страницFeeding and Management of Dairy GoatsariaОценок пока нет
- AnSc 22 Laboratory Exercise No. 1Документ5 страницAnSc 22 Laboratory Exercise No. 1Kheng LeeОценок пока нет
- Sheep Production - With Information on the Breeding, Care and Management of SheepОт EverandSheep Production - With Information on the Breeding, Care and Management of SheepОценок пока нет
- Duck 2019Документ52 страницыDuck 2019Adrian BAGAYANОценок пока нет
- Animal Selection and Evaluation - Carcass Evaluation PP PresentationДокумент82 страницыAnimal Selection and Evaluation - Carcass Evaluation PP PresentationCk_psihОценок пока нет
- How To Make Broilers Grow Faster and BiggerДокумент3 страницыHow To Make Broilers Grow Faster and Biggerchris mubiruОценок пока нет
- Review Animal Breeding - 10Документ52 страницыReview Animal Breeding - 10Mc Wilson DecenaОценок пока нет
- Annex 3 - Dairy Cattle ManagementДокумент62 страницыAnnex 3 - Dairy Cattle Managementnjuguna63100% (2)
- ANS 312 - Applied Animal Nutrition Feedstuffs and Ration Formulation - OSU Extended Campus - Oregon State UniversityДокумент4 страницыANS 312 - Applied Animal Nutrition Feedstuffs and Ration Formulation - OSU Extended Campus - Oregon State UniversityRAHULОценок пока нет
- Breeding and Rearing of Cattle - Milk and Beef ProductionОт EverandBreeding and Rearing of Cattle - Milk and Beef ProductionРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Dairy Farmer or EntrepreneurДокумент204 страницыDairy Farmer or EntrepreneurSenthura PandianОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Bos Taurus Bos Indicus Breed Crosses With Straigttbred Bos Indicus Breeds of Cattle For Maternal and Individual TraitsДокумент7 страницComparison of Bos Taurus Bos Indicus Breed Crosses With Straigttbred Bos Indicus Breeds of Cattle For Maternal and Individual TraitsManuel Vegas0% (1)
- Goat Farming PDFДокумент35 страницGoat Farming PDFShiva KarthikОценок пока нет
- Veterinary Medicine and Animal Keeping in Ancient IndiaДокумент11 страницVeterinary Medicine and Animal Keeping in Ancient IndiaSwanand Raikar0% (1)
- Quail Farming Mastery: Expert Insights and Solutions to Common ChallengesОт EverandQuail Farming Mastery: Expert Insights and Solutions to Common ChallengesОценок пока нет
- Ag Sci G10 StudyguideДокумент206 страницAg Sci G10 StudyguideEsther MwapechisalaОценок пока нет
- Goat Milk Marketing Feasibility Study Report - Only For ReferenceДокумент40 страницGoat Milk Marketing Feasibility Study Report - Only For ReferenceSurajSinghalОценок пока нет
- Animal NutritionДокумент53 страницыAnimal Nutritionsaren raajОценок пока нет
- Ann 121Документ311 страницAnn 121dahiphalehОценок пока нет
- On-Farm Biosecurity, Dr. DoДокумент32 страницыOn-Farm Biosecurity, Dr. DodawnОценок пока нет
- Breeding Management of Sheep and GoatДокумент8 страницBreeding Management of Sheep and Goaturssulthan4416Оценок пока нет
- Final Animal Feeds and Nutrition 2nd Year VetДокумент263 страницыFinal Animal Feeds and Nutrition 2nd Year Vetfamiabadir13Оценок пока нет
- Various Methods of SlaughterДокумент33 страницыVarious Methods of SlaughterAnand JeughaleОценок пока нет
- Dairy Paper IIДокумент137 страницDairy Paper IIvishalsuman4uОценок пока нет
- AG SCI 205 - Advance Methods in Animal Breedind SyllabusДокумент4 страницыAG SCI 205 - Advance Methods in Animal Breedind SyllabusKRIZZAPEARL VERОценок пока нет
- Horse Digestive SystemДокумент5 страницHorse Digestive SystemChai YawatОценок пока нет
- Pseudo RuminantДокумент61 страницаPseudo RuminantMurl CasteloОценок пока нет
- Agric-114-Chapter 3: Handling Animals Before SlaughteringДокумент8 страницAgric-114-Chapter 3: Handling Animals Before SlaughteringAgrikultura 2600Оценок пока нет
- ANSC3101 Animal NutritionДокумент3 страницыANSC3101 Animal NutritionAbery AuОценок пока нет
- Goats and Their Nutrition PDFДокумент4 страницыGoats and Their Nutrition PDFdebmallya403750% (2)
- Classification of Farm Animals Based On Mode of Reproduction and Stomach TypeДокумент14 страницClassification of Farm Animals Based On Mode of Reproduction and Stomach TypeChidiogo IlohОценок пока нет
- Selecting Meat GoatsДокумент11 страницSelecting Meat GoatsqfarmsОценок пока нет
- Animal Science Rview 2012Документ57 страницAnimal Science Rview 2012Ophalene Althea OdoyaОценок пока нет
- Swine NutritionsДокумент50 страницSwine NutritionsAfiQah Bt Abd RahimОценок пока нет
- Uestions Nswers: Ruminations UminationsДокумент23 страницыUestions Nswers: Ruminations Uminationsleyla meclulОценок пока нет
- Balancing RationsДокумент10 страницBalancing RationsalmorsОценок пока нет
- RDR-Calf Nutrition PDFДокумент16 страницRDR-Calf Nutrition PDFidfan 01Оценок пока нет
- TMR and Its Use in Dairy and FatteningДокумент19 страницTMR and Its Use in Dairy and FatteningAyubОценок пока нет
- Types of Feed StuffДокумент1 страницаTypes of Feed StuffOyedotun TundeОценок пока нет
- Breeds of LivestockДокумент24 страницыBreeds of LivestockAdiol Bangit AowingОценок пока нет
- Syllabus LPM - PGДокумент13 страницSyllabus LPM - PGRAHULОценок пока нет
- Hormonal Regulation of Farm Animal GrowthДокумент232 страницыHormonal Regulation of Farm Animal GrowthMihai MolnarОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 9 RevisedДокумент25 страницCHAPTER 9 RevisedAlliah MendozaОценок пока нет
- Castrating PigletsДокумент2 страницыCastrating PigletsVeterinary Online InstituteОценок пока нет
- Beef Cattle Management Practices (Unit Plan)Документ12 страницBeef Cattle Management Practices (Unit Plan)api-285777799Оценок пока нет
- Goat Production ManualДокумент32 страницыGoat Production ManualctamilОценок пока нет
- 2-Lecture 1-Ransum Ruminansia-Balancing Rations - 8Документ80 страниц2-Lecture 1-Ransum Ruminansia-Balancing Rations - 8Aksa KasimОценок пока нет
- Basic Horse NutrictionДокумент4 страницыBasic Horse NutrictionpatriciabrdОценок пока нет
- A Framework For Traceability and Transparency in The Dairy Supply Chain NetworksДокумент10 страницA Framework For Traceability and Transparency in The Dairy Supply Chain NetworksDragana IlijevskaОценок пока нет
- Dairy Feedpad Guidlines - by DPIДокумент108 страницDairy Feedpad Guidlines - by DPIFaisal NaveedОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Agriculture Form I - IVДокумент129 страницLesson Plan Agriculture Form I - IVGodfrey Muchai67% (3)
- B - 21PGP095 - Jayraj Agrawal - BMCДокумент2 страницыB - 21PGP095 - Jayraj Agrawal - BMCJAYRAJ AGRAWALОценок пока нет
- 3D1 Feedlot LayoutsДокумент7 страниц3D1 Feedlot LayoutsSofik SampurnoОценок пока нет
- Synopsis Dr. B.R. Ambedkar University, Agra Doctor of PhilosophyДокумент19 страницSynopsis Dr. B.R. Ambedkar University, Agra Doctor of PhilosophyMordhwaj Singh TomarОценок пока нет
- Neo 72Документ16 страницNeo 72marrog0802Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 AnSc, SeidДокумент15 страницChapter 3 AnSc, SeidseidОценок пока нет
- Pulsation Systems: Setting The Standard For Durable and Consistent PulsationДокумент8 страницPulsation Systems: Setting The Standard For Durable and Consistent PulsationbanerjeeamlanОценок пока нет
- CB 9660 enДокумент52 страницыCB 9660 enYebikat DriversОценок пока нет
- Feasibility StudyДокумент3 страницыFeasibility StudyLorenzo Cenal RaguntonОценок пока нет
- 40257-Article Text-143957-1-10-20190417Документ17 страниц40257-Article Text-143957-1-10-20190417Rica ParillaОценок пока нет
- Animal Husbandry (NABARD Projects)Документ125 страницAnimal Husbandry (NABARD Projects)AkanchhaОценок пока нет
- DHRUVA Natural Resource Regeneration Approach DHRUVA Experience PDFДокумент11 страницDHRUVA Natural Resource Regeneration Approach DHRUVA Experience PDFChittesh SachdevaОценок пока нет
- The Economics of Automatic Calf FeedersДокумент4 страницыThe Economics of Automatic Calf Feedersanthonius70Оценок пока нет
- Red Bull Steeple Assignment Alisha JasaniДокумент4 страницыRed Bull Steeple Assignment Alisha JasaniAlisha JasaniОценок пока нет
- Feasibility of On-Farm Milk Processing Packaging and Marketing PDFДокумент174 страницыFeasibility of On-Farm Milk Processing Packaging and Marketing PDFAmit Kumar Singh0% (1)
- NCAPДокумент62 страницыNCAPMuwonge StephanoОценок пока нет
- Livestock - The Backyard Dairy BookДокумент90 страницLivestock - The Backyard Dairy BookbigulinОценок пока нет
- Bag Leather From Lower Grade Cow HideДокумент76 страницBag Leather From Lower Grade Cow HidePriyankaОценок пока нет
- Clifton Farm Business PlanДокумент11 страницClifton Farm Business PlanUBUNTU SHOPОценок пока нет
- Adem Yusuf DairyteДокумент12 страницAdem Yusuf DairyteAdem YusufОценок пока нет
- Economic Contribution of RangelandДокумент19 страницEconomic Contribution of RangelandkutoyaОценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting DMIДокумент17 страницFactors Affecting DMIgokullptОценок пока нет
- Proposals For Development of Non-Profitable Livestock Farms of The NLDBДокумент9 страницProposals For Development of Non-Profitable Livestock Farms of The NLDBMark WuОценок пока нет