Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
The Human Body Is Made Up of A Head
Загружено:
yabaeveОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The Human Body Is Made Up of A Head
Загружено:
yabaeveАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The Human Body is made up of a head, neck, torso, two arms and two legs.
The average Height of and adult human is about 5 to 6 feet tall. The Human body is made to stand erect, walk on two feet, use the arms to carry and lift, and has opposable thumbs (able to grasp). The adult body is made up of: 100 Trillion cells 206 Bones 600 Muscles 22 Internal organs 3. There are many systems in the Human Body Circulatory System (heart, blood, vessels) Respiratory System (nose, trachea, lungs) Immune System (many types of protein, cells, organs, tissues) Skeletal System (Bones) Excretory System (lungs, large intestine, kidneys) Urinary System (bladder, kidneys) Muscular System (muscles) Endocrine System (glands) Digestive System (mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines) Nervous System (brain, spinal cord, nerves) Reproductive System (male and female reproductive organs) 4. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all organisms. All cells in the body share some common structures. They are: (1) Enclosed by a limiting boundary, a semipermeable structure called the cell membrane (2) Have a control center the nucleus; (3) And contain a fluid like medium, cytoplasm, between the membrane and the nucleus. The cytoplasm has specialized small functional units called organelles, which are suspended in the nutrient-filled medium. Materials move across the membrane by both passive (no energy is involved) and active (energy is expanded) processes. These are further differentiated by what materials are moved across the membrane. Upon disruption of the normal function of organelles, cellucal disorder results. If cells exhibit uncontrolled cell growth and division, cancer Is a result. 5. Food provides us with fuel to live, energy to work and play, and the raw materials to build new cells. All the different varieties of food we eat are broken down by our digestive system and transported to every part of our body by our circulatory system. Our Digestive system is a 9 meter long tube. The digestive process begins in the mouth, where the teeth and tongue break up the food after it has been softened with saliva. The food is then swallowed and travels down the esophagus to the stomach. While the food is in the stomach, it is mixed with the mild acid which breaks the food down into a paste similar to porridge. The food the passes, a little at a time, into the small intestine, which is rougly 6 meters long. Here the food is broken down even further until it is small enough to pass through the walls of the small intestine into the bloodstream. Food that cannot be digested passes into the large intestine, where the water and minerals are absorbed into the bloodstream. The solid waste, the feces, is then expelled from the body through the rectum and anus. 6. The Respiratory System is the system of the body that deals with breathing. When we breathe, the body takes in the oxygen that it needs and removes the carbon dioxide that it doesnt need. First the body breathes in the air which is sucked through the nose or mouth and down through the Trachea (windpipe). The trachea is a pipe shaped by rings cartilage. It divides into two tubes called bronchi. These carry air into each lung. Inside the lung, the tubes divide into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchiolies. At the end of each of these tubes are small air balloons called alveoli. Capillaries which are small blood vessels with thin walls, are wrapped around the alveolies. The walls are so thin and close to each other that the air easily seeps through. In this way, oxygen seeps through into the bloodstream, and carbon dioxide, in the bloodstream, seeps through into the alveoli, and is then removed from the body when we breathe out. The diaphragm is the muscle that controls the breathing process. As the diaphragm flattens, it causes the chest to expand and air is sucked into the lungs. When the diaphragm relaxes, the chest collapses and the air in the lungs is forced out.
7. The Human brain is a very complex, yet relatively small organ. Brain function is involved in all of our daily activities, including breathing, planning a trip, talking, maintaining temperature, doing homework, and walking about The brain is also the center for memory, emotions, intellect and behaviour. It is connected to the rest of the body through the spinal cord and the cranial nerves. The Nervous System is a complex network of interconnected neurons, which are information- processing cells. There are two divisions to the nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of nerves outside the CNS. The CNS can be considered a central processing unit. Neurons carry signals from the CNS through peripheral nerves to effectors (muscles and glands) to carry out responses. 8. To maintain the species, humans must reproduce. In males, special cells is called a sperm cell, whereas in females it is called an ovum. In males, the reproductive organs are the testes, and in females they are called ovaries. The sperm cells are produced by testes while ovaries produce eggs. The union of sperm with egg is called fertilization. The fertilized egg, called an embryo (zygote). It grows and forms a baby inside the body of a female. 9. The Skeleton is the name given to the collection of bones that holds the rest of our body up. Our Skeleton is very important for us. It does three major jobs. (1) It protects our vital organs such as the brain, the heart, and the lungs. (2) It gives us the shape that we have. Without our skeleton, we would just be a blob of blood and tissue on the floor. (3) It allows us to move. Because our muscles our attached to our bones, when our muscles move, they move the bones, and we move. When you were born, your skeleton had around 350 bones. By the time you became an adult, you will only have around 206 bones. This is because, as you grow, some of the bones join together to form one bone. Our bones dont simply work on their own. The bones join together to form joints. The end of each bone is covered by a tough, smooth shiny substance called cartilage. The cartilage- coated bone- ends are kept apart by a thin film of slippery fluid that works like oil in a car. All of this is so your bones wont scratch and bump against each other when you move. Our bones are held together by strong stretchy bands called ligaments. 10. The blood is the transport system by which oxygen and nutrients reach the bodys cells, and waste materials are carried away. The heart, a muscular organ, positioned behind the ribcage and between the lungs, is the pump that keeps this transport system moving. (1) Blood that is rich in oxygen appears red. (2) Blood that is poor in oxygen appears blue. Blood leaves the left side of the heart and travels through arteries, which gradually divide into capillaries. In the capillaries, food and oxygen are released to the body cells, and carbon dioxide and other waste products are returned to the bloodstream. The blood then travels in veins back to the right side of the heart, where it is pumped directly to the lungs. In the lungs, carbon dioxide is changed for oxygen, and this renewed blood flows back to the left side of the heart, and the whole process begin again. 11. We depend upon on our muscles for every moment we make, for sitting or standing still. Muscle tissue permits us to walk, run, speak and write words on a piece of paper. The body has three types of muscles, skeletal, smooth, or cardiac, which contract or shorten to accomplish these functions. Skeletal (voluntary) muscle is attached to bones, and extend across the joints of the skeleton to facilitate movement of the body. Smooth (involuntary) muscle is located in the walls of internal organs where its contraction pushes food along the digestive tract, eliminates urine from the bladder, and is in the walls
of blood vessels to help control blood pressure. Cardiac muscle occurs only in the heart, where its contraction pushes blood through the blood vessels of the cardiovascular system. 12. Q1 What is the name given to a blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the body? Ans An artery Q2 How many bones are there in the human body? Ans 206 bones Q3 Which is the longest bone in the adult human body? Ans Thigh Bone Q4 How many muscles are there in the human body? Ans There are 650 Q5 How many teeth in an adult human mouth? Ans There are 32 Q6 How often do humans dream each night, on average? Ans Apparently its 5 times a night! Q7 Which helps in clotting of blood? Ans Vitamin K Q8 How many bones are there in an adult human being? Ans 206 Q9 The largest part of the human brain is the Ans Cerebrum 13. Q10 The main constituent of hemoglobin is Ans Iron Q11 The main function of the kidney is Ans To remove waste product from the body Q12 The function of hemoglobin is Ans Prevention of Anemia Q13 Which is the largest gland in the human body? Ans Liver Q14 A person which of the following blood groups is called a universal donor? Ans O Q15 How many bones are there in a newly born infant? Ans 300 Q16 Which vitamins promote healthy functioning of eyes in human beings? Ans Vitamin A Q17 The average heartbeat per minute in a normal human is Ans 70 Q18 Medulla oblongata is a part of human Ans Brain Q19 Food is normally digested in the Ans Stomach Q20 Rickets is a Ans Bones
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- HttpsДокумент4 страницыHttpsyabaeveОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Four Priorities For ActionДокумент2 страницыThe Four Priorities For ActionyabaeveОценок пока нет
- Philippine Map Indicating All Provinces Including Metro Manila, The National Capital Region (NCR) of The PhilippinesДокумент1 страницаPhilippine Map Indicating All Provinces Including Metro Manila, The National Capital Region (NCR) of The PhilippinesyabaeveОценок пока нет
- Club Election ScriptДокумент2 страницыClub Election ScriptyabaeveОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Your Scenarios Here Are Examples of The Three Types of Fluid Volume DeficitДокумент2 страницыYour Scenarios Here Are Examples of The Three Types of Fluid Volume DeficityabaeveОценок пока нет
- IDRN 1300 Spear v5 20120110Документ6 страницIDRN 1300 Spear v5 20120110yabaeveОценок пока нет
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction HandoutsДокумент4 страницыDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction HandoutsyabaeveОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Biology Finals 1bДокумент1 страницаBiology Finals 1byabaeveОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
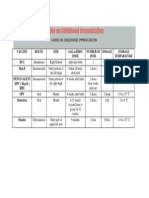
- Guide On Childhood Immunization 2014Документ1 страницаGuide On Childhood Immunization 2014yabaeveОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- General ScienceДокумент147 страницGeneral ScienceyabaeveОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Earthquake and Fire DrillДокумент51 страницаEarthquake and Fire Drillyabaeve100% (1)
- China Is A Socialist Country. The Government Owns and Controls Almost All Natural ResourcesДокумент6 страницChina Is A Socialist Country. The Government Owns and Controls Almost All Natural ResourcesyabaeveОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Step To Follow Intrapartal CareДокумент3 страницыStep To Follow Intrapartal CareyabaeveОценок пока нет
- From Continental Drift To Plate TectonicsДокумент6 страницFrom Continental Drift To Plate TectonicsyabaeveОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Environmental Science SyllabusДокумент4 страницыEnvironmental Science Syllabusyabaeve100% (5)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Geological Science Final Examination: 1. Stages of Thunder Storm 10-12 (Plate Boundaries)Документ1 страницаGeological Science Final Examination: 1. Stages of Thunder Storm 10-12 (Plate Boundaries)yabaeveОценок пока нет
- Integumentary SystemДокумент4 страницыIntegumentary SystemyabaeveОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Delivery Room Rating SheetДокумент2 страницыDelivery Room Rating Sheetyabaeve100% (2)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Eve Application LetterДокумент1 страницаEve Application LetteryabaeveОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- 10 Herbal PlantsДокумент12 страниц10 Herbal PlantsyabaeveОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Tracheostomy 2Документ41 страницаTracheostomy 2Khor Kee GuanОценок пока нет
- Practice of Nature CureДокумент340 страницPractice of Nature CureKartik VashishtaОценок пока нет
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Case StudyДокумент26 страницCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Case StudyMenggay SanDiego57% (7)
- TracheostomyДокумент40 страницTracheostomysuciОценок пока нет
- Thyroid & Parathyroid GlandsДокумент21 страницаThyroid & Parathyroid GlandsAzizan HannyОценок пока нет
- Idoc - Pub - Critical Care Nursing Assessment FormДокумент3 страницыIdoc - Pub - Critical Care Nursing Assessment FormNamra AnsariОценок пока нет
- Module 4 Respiratory SystemДокумент8 страницModule 4 Respiratory SystemJake Donely C. PaduaОценок пока нет
- Jazzle George E. Oteyza NCMB 312 Rle BSN 3Y1-3A Lab Module Course TaskДокумент3 страницыJazzle George E. Oteyza NCMB 312 Rle BSN 3Y1-3A Lab Module Course TaskwokorowОценок пока нет
- DR Amsalu Bekele Ass - Professor of Medicine Head of Chest Unit Department of Internal Medicine Addis Ababa University, School of Medicine Addis Ababa, EthiopiaДокумент81 страницаDR Amsalu Bekele Ass - Professor of Medicine Head of Chest Unit Department of Internal Medicine Addis Ababa University, School of Medicine Addis Ababa, EthiopiaBethelhem BirhanuОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Chapter 23 ExcretionДокумент3 страницыChapter 23 Excretionmmido1425Оценок пока нет
- 04.06.2018 - 6 - V. Kushakovsky - Pediatric AnaesthesiaДокумент46 страниц04.06.2018 - 6 - V. Kushakovsky - Pediatric AnaesthesiaPhilippe KinnaerОценок пока нет
- Histology of Respiratory SystemДокумент6 страницHistology of Respiratory SystemEzyan Syamin100% (2)
- AirwayДокумент1 страницаAirwaykushishaОценок пока нет
- JBS Haldane On Being The Right SizeДокумент8 страницJBS Haldane On Being The Right Sizeboygenius21_39464798100% (2)
- Laryngeal Amyloidosis: ReviewДокумент8 страницLaryngeal Amyloidosis: ReviewLuis De jesus SolanoОценок пока нет
- 1st GNM VivaДокумент144 страницы1st GNM VivaPatel MitanshiОценок пока нет
- Respiratory and Excretory System ReviewДокумент27 страницRespiratory and Excretory System ReviewJoyce Catherine Buquing UysecoОценок пока нет
- Management of Elective LaryngectomyДокумент6 страницManagement of Elective LaryngectomyKj BrionesОценок пока нет
- Surgical Correction Subglottic Stenosis of The Larynx: AnnoldДокумент6 страницSurgical Correction Subglottic Stenosis of The Larynx: Annoldcanndy202Оценок пока нет
- Respiratory System (Chart)Документ4 страницыRespiratory System (Chart)Rommel Urbano YabisОценок пока нет
- Physiotherapy of Avian RespiratoryДокумент3 страницыPhysiotherapy of Avian RespiratoryMichael MekhaОценок пока нет
- Surgery CaseДокумент43 страницыSurgery CaseAvni GuptaОценок пока нет
- Systemi Respirator 14-21 RSДокумент44 страницыSystemi Respirator 14-21 RSRejhan SadikuОценок пока нет
- ?1 - Chest X-Ray Interpretation - A Structured Approach - Radiology - OSCEДокумент14 страниц?1 - Chest X-Ray Interpretation - A Structured Approach - Radiology - OSCEVerónicaОценок пока нет
- The Technique: of ThyroidectomyДокумент5 страницThe Technique: of Thyroidectomyعمر كمالОценок пока нет
- Kuliah Radiologi Thorax Trachea Jantung VasculatureДокумент56 страницKuliah Radiologi Thorax Trachea Jantung VasculatureZahra Jamilah SabrinaОценок пока нет
- Secondary Science Units 1 3 SP (Year 8 Learner Book)Документ127 страницSecondary Science Units 1 3 SP (Year 8 Learner Book)Zoom 10100% (9)
- BreathingДокумент46 страницBreathingRamnaresh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Sijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia EditДокумент75 страницSijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia EditDiana Ana0% (2)
- SuctioningДокумент23 страницыSuctioningrnrmmanphd100% (2)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseОт EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (52)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldОт EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (597)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsОт EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)