Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lesson Plan Activity Sheet
Загружено:
api-249173384Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lesson Plan Activity Sheet
Загружено:
api-249173384Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name________________ Date_________________
Structure and Function
1. Stores material within the cell 2. Closely stacked, flattened sacs (plants only) 3. The sites of protein synthesis 4. Transports materials within the cell 5. Jelly-like substance in the cell 6. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell 7. Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps energy from sunlight and gives plants their green color 8. Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria 9. Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum 10. Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products 11. Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists 12. Produces a usable form of energy for the cell 13. Packages proteins for transport out of the cell 14. Produces lipids 15. The membrane surrounding the cell Vacuole Chloroplasts (grana) Ribosome Vesicles Cytoplasm Nucleus
Chloroplasts
Lysosome/Peroxisome Ribosome Vesicles
Cell Wall
Mitochondrion
Golgi Apparatus Smooth ER Plasma Membrane
http://www.scsc.k12.in.us/SMS/Teachers/Martin/replacelevelsoforganization.htm
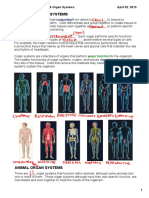
Levels of Organization
Cells: Level One Within a multicellular organism there is a __________________ _____ __________________. Division of labor means that the work of keeping the organism alive is divided among the different parts of the body. Each part has a ______________________ job to do. The arrangement of specialized parts within a living this is sometimes referred to as _________________ _____ _______________________. Cells of course, are the _______________ level of organization.
Tissues: Level Two In any multicellular organism, ____________ rarely work alone. Cells that are ___________________ in structure and function are usually joined together to form _________________. Tissues are the _________________ level of organization. Bone cells in your body form bone tissue. Blood cells in your body form blood tissue. Organs: Level Three Tissues are further organized into __________________, the ____________ level of organization in living things. Organs are groups of different tissues that work together. Your heart, for example, is made up of _________________ tissue, __________________ tissue, and ________________ tissue. You are probably familiar with the names of many of the body organs. The brain, ____________________, kidneys, and ________________ are some examples. Organ Systems: Level Four Like cells and tissues, organs seldom work _______________. They cooperate with one another and form specific _________________ __________________. Organ systems are the ________________ level of organization in living things. An organ system is a ________________ of organs working together to perform a specific function for the organism. An example would be your digestive system. It is made up of several organs such as your esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Organisms: Level Five __________ are an organism. Dogs, trees and buttercups are also organisms. Even a unicellular (one celled) bacterium is an organism. An organism is an entire ________________ ________________ that carries out all the basic life functions. The organism is the _____________ level of organization. ____________ tissues organs __________ _____________ _________________ -each level of organization interacts with every other level. The smooth functioning of a
complex ___________________ is the result of all its various parts __________________ together.
Вам также может понравиться
- Science F1 - Cell As A Unit of LifeДокумент8 страницScience F1 - Cell As A Unit of LifeamyryuzainiОценок пока нет
- Ds47-Cell Types Organelles Summative AssessmentДокумент6 страницDs47-Cell Types Organelles Summative Assessmentapi-110789702100% (1)
- Cell Parts Functions WorksheetДокумент2 страницыCell Parts Functions WorksheetIan CausseauxОценок пока нет
- Cells and Organelles New - Answer KEY - FinalДокумент9 страницCells and Organelles New - Answer KEY - FinalMelyza Ann Pronebo50% (2)
- Cell Structure and Function ReviewerДокумент4 страницыCell Structure and Function ReviewerLeandre Jasmine ReyesОценок пока нет
- Pengantar Biologi Sel Dan MolekulerДокумент47 страницPengantar Biologi Sel Dan MolekulerAndra AdityaОценок пока нет
- Exam t1 5th ScienceДокумент3 страницыExam t1 5th Sciencemaartiius11Оценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and Function HWДокумент2 страницыCell Structure and Function HWareej salimОценок пока нет
- Sciebce Cell GrowthДокумент3 страницыSciebce Cell GrowthMr Ling Tuition CentreОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and Function HW AnswersДокумент2 страницыCell Structure and Function HW Answersareej salimОценок пока нет
- Science7 Q2 WeeK4 LAS1Документ2 страницыScience7 Q2 WeeK4 LAS1maeshengОценок пока нет
- ENGLISH IN MEDICINE 1 (Y đa khoa) -đã chuyển đổiДокумент16 страницENGLISH IN MEDICINE 1 (Y đa khoa) -đã chuyển đổiNguyễn Thị HiênОценок пока нет
- Grade 7 Biology Crosswords: June JaydipДокумент10 страницGrade 7 Biology Crosswords: June JaydipMelanie AbaldeОценок пока нет
- Science Chapter 2 Form 1Документ23 страницыScience Chapter 2 Form 1Kelvin0% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structure & FunctionДокумент9 страницChapter 3 - Cell Structure & Functionapi-517602393Оценок пока нет
- B U1L4 WorksheetДокумент3 страницыB U1L4 WorksheetLBM PLAYZОценок пока нет
- Cells: Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeДокумент8 страницCells: Cells: The Building Blocks of Lifems_m_tan100% (8)
- Cells and OrganellesДокумент8 страницCells and OrganellesWilliam RyandinataОценок пока нет
- Cell Structures Functions Study Guide KeyДокумент2 страницыCell Structures Functions Study Guide Keyapi-260817414Оценок пока нет
- Cells Objectives For Exam #1Документ6 страницCells Objectives For Exam #1Nelsi Antonius Kala100% (1)
- Cell-Modification LectureДокумент6 страницCell-Modification LectureFiona LeeОценок пока нет
- Dajana Lucaj - Cells & Their Organelles PDFДокумент8 страницDajana Lucaj - Cells & Their Organelles PDFdajanaОценок пока нет
- Grade 8 Unit B Notes 2010 FITBДокумент17 страницGrade 8 Unit B Notes 2010 FITBAchindra PaulОценок пока нет
- Cells and Organelles - 1Документ6 страницCells and Organelles - 1Izabayo philippeОценок пока нет
- Worksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedДокумент7 страницWorksheet: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private LimitedKaung Myat SanОценок пока нет
- Module 5 - Body TissuesДокумент10 страницModule 5 - Body Tissues10. Briol AlvinОценок пока нет
- L.5 Cell PartsДокумент2 страницыL.5 Cell PartsColtonОценок пока нет
- CH 2-4 Notes Fill in BlankДокумент3 страницыCH 2-4 Notes Fill in Blankapi-233611431Оценок пока нет
- Human Body TerminologyДокумент5 страницHuman Body TerminologyAna CucusciucОценок пока нет
- 6.4 Multicellular OrganismsДокумент4 страницы6.4 Multicellular Organismspriya sundaramОценок пока нет
- Final Shs 12 Genbio1 q1 Module 4Документ18 страницFinal Shs 12 Genbio1 q1 Module 4Demetri Dela TorreОценок пока нет
- SCIENCE 7 2nd Periodical TestДокумент2 страницыSCIENCE 7 2nd Periodical TestAngelica BacolodОценок пока нет
- Cells and Tissues: Biosci 107 Cellular Processes and DevelopmentДокумент8 страницCells and Tissues: Biosci 107 Cellular Processes and Developmentjyip947Оценок пока нет
- General Biology 1 Tissues and Cell Types Quarter 3, Module 2bДокумент17 страницGeneral Biology 1 Tissues and Cell Types Quarter 3, Module 2bSam KimОценок пока нет
- 5th Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets - Fifth Grade Week 4Документ2 страницы5th Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets - Fifth Grade Week 4Julius CesarОценок пока нет
- Organs and Organ Systems P1Документ8 страницOrgans and Organ Systems P1Arniel CatubigОценок пока нет
- 10th BioДокумент4 страницы10th BioBumbble BeeОценок пока нет
- Cells and Tissue Trial ExamДокумент24 страницыCells and Tissue Trial ExamReno Miranda EnticoОценок пока нет
- Activity 2. Plant Cell Vs Animal CellДокумент5 страницActivity 2. Plant Cell Vs Animal CellMary Joyce BonayonОценок пока нет
- Biology For Kids Fill in The BlankДокумент2 страницыBiology For Kids Fill in The Blankapi-297681510Оценок пока нет
- Name: - Grade & Section: - Date: - Topic: Introduction To Life Science Learning CompetenciesДокумент7 страницName: - Grade & Section: - Date: - Topic: Introduction To Life Science Learning Competenciesjanice alquizarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ10 страницChapter 2Deolita BadiangОценок пока нет
- The Virtual Cell WorksheetДокумент2 страницыThe Virtual Cell WorksheetRafael CunetaОценок пока нет
- 7.3 - Cell Structures & Organelles: State StandardДокумент20 страниц7.3 - Cell Structures & Organelles: State StandardCyndel TindoyОценок пока нет
- 2 Organ SystemsДокумент5 страниц2 Organ SystemsBeaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Vocabulary.2 - HomeworkДокумент2 страницыUnit 1 - Vocabulary.2 - Homeworkhuyphuong66.12Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy Lecture Preliminary ExamДокумент4 страницыAnatomy Lecture Preliminary ExamNadiel FerrerОценок пока нет
- Study Guide Body SystemsДокумент3 страницыStudy Guide Body SystemsMatthew BrennanОценок пока нет
- Science 7 Q2 Lesson 2 Biological OrderДокумент2 страницыScience 7 Q2 Lesson 2 Biological OrderArianne Jane Mae ManОценок пока нет
- Animal Tissues SummativeДокумент1 страницаAnimal Tissues SummativeLouie Jane EleccionОценок пока нет
- SCIENCE 7 Q2 Week 4Документ2 страницыSCIENCE 7 Q2 Week 4Edsel BelbarОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Test Ls 7Документ2 страницыUnit 1 Test Ls 7MonalisaОценок пока нет
- Cell Theory and Types of CellsДокумент6 страницCell Theory and Types of CellsLance Afraim MortelОценок пока нет
- Revision Module 1Документ1 страницаRevision Module 1Raquel ColladoОценок пока нет
- Question Chapter 2Документ3 страницыQuestion Chapter 2Kenneth JamesОценок пока нет
- Diet and Digestion & Photosynthesis and RespirationДокумент12 страницDiet and Digestion & Photosynthesis and RespirationIrina KorolevaОценок пока нет
- General Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresДокумент18 страницGeneral Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresHannah CastroОценок пока нет
- Taller Grado Quinto - Semana 6 Al 10 de MayoДокумент3 страницыTaller Grado Quinto - Semana 6 Al 10 de MayoMelinaОценок пока нет
- Human Body WorksheetsДокумент20 страницHuman Body Worksheetsnona wayne dela peñaОценок пока нет
- Anaphy Lab ManualДокумент9 страницAnaphy Lab ManualKen KanekiОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksОт EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Learning Activity Sheet in Biology 1: Quarter 1 Week 1Документ10 страницLearning Activity Sheet in Biology 1: Quarter 1 Week 1Ryan NegadОценок пока нет
- Cell Parts and FunctionsДокумент2 страницыCell Parts and FunctionsMian Nakahara0% (1)
- General Science 4Документ44 страницыGeneral Science 4dayakar100% (1)
- AGB 121: Principles of Animal Genetics and Population Genetics (2+1)Документ299 страницAGB 121: Principles of Animal Genetics and Population Genetics (2+1)Deep PatelОценок пока нет
- CELLSДокумент21 страницаCELLSPhia LhiceraОценок пока нет
- Earth and Life Science ReviewerДокумент11 страницEarth and Life Science ReviewerVicente MarkОценок пока нет
- Hsslive Xi Botany Notes by Sunil KumarДокумент27 страницHsslive Xi Botany Notes by Sunil Kumarmurshida murshida cОценок пока нет
- Biology Eukaryote Prokaryote CellДокумент8 страницBiology Eukaryote Prokaryote CellmIZZshaNaОценок пока нет
- B2 2+Organelles+and+Compartmentalization+SL+Документ24 страницыB2 2+Organelles+and+Compartmentalization+SL+Jiwoo ParkОценок пока нет
- Epithiliam Tissue OutlineДокумент11 страницEpithiliam Tissue OutlineAleks BlackОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure QuestionsДокумент16 страницCell Structure QuestionsDila OzdolОценок пока нет
- Cell MembraneДокумент100 страницCell MembranephyMedza AppОценок пока нет
- Sports Adaptology: V. N. SeluyanovДокумент9 страницSports Adaptology: V. N. Seluyanovdan_partelly4103Оценок пока нет
- M. Sc. Botany Syllabus As Per Credit System: A. Examination Pattern: 1. Total Marks of Examination/courseДокумент40 страницM. Sc. Botany Syllabus As Per Credit System: A. Examination Pattern: 1. Total Marks of Examination/courseshubham9ahire-1Оценок пока нет
- Cell Structure and Function: DR - Satish Gupta PДокумент42 страницыCell Structure and Function: DR - Satish Gupta Pgarimashah2012Оценок пока нет
- Cell: The Unit of Life: Jon Paul M. Reyes, RMT, MBA, MSMLS Program Chair Medical Technology DepartmentДокумент133 страницыCell: The Unit of Life: Jon Paul M. Reyes, RMT, MBA, MSMLS Program Chair Medical Technology DepartmentRich Darlene Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- The Cellular Level of Organization - AnaphyДокумент12 страницThe Cellular Level of Organization - AnaphyJean Rose SalahayОценок пока нет
- GenBio NotesДокумент14 страницGenBio NotesGavrielle DelacruzОценок пока нет
- Cell Organelles WorksheetДокумент9 страницCell Organelles Worksheetapi-238421605Оценок пока нет
- The Cell 1: Group 2Документ37 страницThe Cell 1: Group 2Vỹ KhangОценок пока нет
- Genesis - Biology (PHASE - 1) : (Crash Course - Jstse)Документ65 страницGenesis - Biology (PHASE - 1) : (Crash Course - Jstse)Vinod AgrawalОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGYFINALanswers (1stedition)Документ61 страницаBIOLOGYFINALanswers (1stedition)Abhinav VermaОценок пока нет
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureДокумент7 страницStudent Exploration: Cell StructureTNT x TOXICОценок пока нет
- Cambridge Science Worksheet 8Документ13 страницCambridge Science Worksheet 8ozmanОценок пока нет
- GenBio (1st Long Exam Reviewer)Документ20 страницGenBio (1st Long Exam Reviewer)Ethan Erika BionaОценок пока нет
- Mod 6 - Micro To paraДокумент18 страницMod 6 - Micro To paraDonzzkie DonОценок пока нет
- Cell Processes Hand Out '21Документ3 страницыCell Processes Hand Out '21Amazing GreenОценок пока нет
- Cell Parts Practice QuizДокумент3 страницыCell Parts Practice QuizAnonymous yFS1ZfmBpОценок пока нет