Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 2 - May 2011
Загружено:
asjawolverineАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Cape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 2 - May 2011
Загружено:
asjawolverineАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2.
Section A consists of THREE structured questions, one from each Module . . Section B consists of THREE extended response questions, one from each Module. For Section A, write your answers in the spaces provided in this booklet. Section B, write your answers in the answer booklet provided. For
3.
Copyright 2009 Caribbean Examinations All rights reserved.
Council.
In 1803, John Dalton came up with a series of postulates concerning the atom which later became known as Dalton's atomic theory.
(ii)
Identify TWO of Dalton's postulates which were proven invalid by modem atomic theory.
(b)
A student was asked to investigate the relative reducing abilities of the elements zinc and copper. (i) List TWO chemicals and ONE piece of apparatus that the student may use to carry out the investigation.
(iv)
Write relevant half equations to illustrate the chemical changes that occur with EACH element.
(c)
One type of kidney stones is formed by the precipitation of calcium phosphate (Ca/P04)2)' which has a Ksp of 1.3 x 10-32 at 25C. A patient submitted a urine sample which contained concentrations of 1.2 x 10-4 mol dm-3 calcium ions and 1.1 x 10-8 mol dm-3 phosphate ions. (i) Write a balanced equation for the formation of calcium and phosphate ions from calcium phosphate.
(d)
Outline an experimental procedure for the determination constant of barium hydroxide Ba(OH)20
of the solubility
product
Elements
Mg
Ca
Sr
Ba
Second lonisation Energy (kJ mol-i)
1450
1150
1060
970
Use the information in Table 1 to account for the differences in reactivity of the elements shown.
(c)
Radium, Ra, is the last member of the Group II elements. Group II chemistry,
Using a knowledge
of
(ii)
write the balanced radium, Ra(N03)2.
equation for the thermal decomposition
of the nitrate of
State the steps that should be taken in the investigation of the differences in solubility of the sulphates of magnesium, calcium and barium.
State the FOUR basic assumptions
of the kinetic theory with reference to an idc:.l1 :1. I 4 ma.-!<sl
(b)
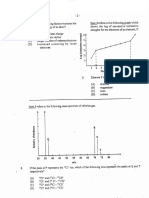
0.785 g of an organic compound, Z, was vapourized at 100C and 101.325 kPa. The vapour occupied a volume of 0.40 dm3. Calculate the relative molecular mass of Z (R = 8.314 J mol-1 K-I dm3 kPa). 3 marks]
(ii)
Construct a diagram of a well-labelled Born-Haber cycle showing the formation of magnesium oxide (MgO) from magnesium metal and oxygen gas. On your diagram, show clearly ALL the enthalpy changes and species involved in the process. [ 6 marks]
(b)
Define the equi Iibri um constant, Kc' and de cribc its significance to a system in dynamic equilibrium. In your response make reference to the importance of its magnitude. [ 3 marks] At a certain temperature, Kc = 4.66 X 10-3 for the reaction N204 (g) ~ 2N02(g), t..H8 = +58 kJ mol-I. (i) Calculate the equilibrium concentration of EACH gas, at the same temperature, if 0.800 moles ofN204 were injected into a closed container of volume 1 dm3 [ 6 marks] Using Le Chatelier's principle, describe the effect, on the equilibrium position, of decreasing the volume of the container. [ 1 mark] Describe the effect on the equilibrium constant, Kc' of increasing the temperature of the reaction. [ 1 mark]
(c)
(ii)
(iii)
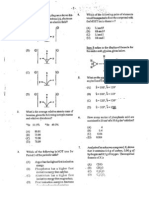
Copy and complete the information in Table 2 regarding elements in Group IV of the Periodic Table.
some physical properties
of
Element Electrical Conductivity Structure
C (Diamond)
Si Semi-conductor
Sn
Pb Conductor
Giant molecular
Giant metallic
(b)
Both melting and boiling points of Group IV elements decrease from carbon to lead while there is an increase in their densities.
(ii)
When exposed to the atmosphere, fumes are produced with CCI4.
SiCl4 produces white fumes while no such [ 3 marks]
(ii)
state the name and the formula of the substance responsible the white fumes.
for the presence of [ 2 marks]
Вам также может понравиться
- Cape Chemistry - Unit 1 Paper 1 2011Документ12 страницCape Chemistry - Unit 1 Paper 1 2011asjawolverine94% (34)
- CAPE Chemistry 2016 U1 P2Документ20 страницCAPE Chemistry 2016 U1 P2CJ100% (3)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 1 2012 Paper 1Документ9 страницCape Chemistry Unit 1 2012 Paper 1Shekila Isaacs62% (13)
- Cape Chemistry - Unit 1 Paper 2 - 14 May 2007Документ11 страницCape Chemistry - Unit 1 Paper 2 - 14 May 2007asjawolverine100% (7)
- CAPE Chemistry Unit 1 June 2012 P2Документ12 страницCAPE Chemistry Unit 1 June 2012 P2Sachin BahadoorsinghОценок пока нет
- CAPE June2011 Physics Unit2.ExДокумент12 страницCAPE June2011 Physics Unit2.ExRaymond Scott100% (1)
- Cape Biology Specimen Paper 1 2007Документ11 страницCape Biology Specimen Paper 1 2007Jamal Joseph100% (2)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 2 - May 2012Документ12 страницCape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 2 - May 2012asjawolverine89% (9)
- CAPE Chemstry 2012 U1 P2 - Cram SheetДокумент2 страницыCAPE Chemstry 2012 U1 P2 - Cram SheetDenison DwarkahОценок пока нет
- Cape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 1 - 2009Документ12 страницCape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 1 - 2009asjawolverine100% (10)
- CAPE Unit 1 Biology May/June 2016 P2Документ24 страницыCAPE Unit 1 Biology May/June 2016 P2Kelsey86% (7)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 1 2012 Paper 2Документ11 страницCape Chemistry Unit 1 2012 Paper 2s.vaish141991% (22)
- Cape Biology Paper 1 Mark SchemeДокумент12 страницCape Biology Paper 1 Mark SchemeYagna LallОценок пока нет
- Cape Biology 2018 PDFДокумент13 страницCape Biology 2018 PDFFelecia HutchinsОценок пока нет
- Cape Biology Unit 1 Mutiple Choice 2007Документ12 страницCape Biology Unit 1 Mutiple Choice 2007Robert Edwards80% (5)
- CAPE 2015 - Suggested AnswersДокумент16 страницCAPE 2015 - Suggested Answerssoumya12355% (11)
- CAPE Chemistry Unit 1 Papers 2007-2015Документ63 страницыCAPE Chemistry Unit 1 Papers 2007-2015alyss ramdath100% (1)
- 2022 Unit 1 P2 BiologyДокумент19 страниц2022 Unit 1 P2 BiologyMartyn PereiraОценок пока нет
- Cape Biology 2008 and Past Paper Answers (2007-2011)Документ14 страницCape Biology 2008 and Past Paper Answers (2007-2011)Jamal Joseph62% (34)
- Cape Biology Unit 1 Mutiple Choice 2009Документ11 страницCape Biology Unit 1 Mutiple Choice 2009Robert Edwards50% (2)
- Cape Biology 2013 U1 p1Документ11 страницCape Biology 2013 U1 p1Fayeed Ali RassulОценок пока нет
- CAPE Chemistry Unit 1Документ6 страницCAPE Chemistry Unit 1Audi SweetangelОценок пока нет
- CAPE Biology 2015 U2 P2 MSДокумент18 страницCAPE Biology 2015 U2 P2 MSYagna Lall100% (2)
- CAPE Physics Unit 2 Paper 2 2008Документ18 страницCAPE Physics Unit 2 Paper 2 2008migo1010% (1)
- CAPE Chemistry 2014 U1 P1Документ9 страницCAPE Chemistry 2014 U1 P1Chanell M.Оценок пока нет
- CAPE Chemistry Unit 2 2018Документ14 страницCAPE Chemistry Unit 2 2018Student HelpОценок пока нет
- CAPE Chemistry 2018 Unit 2 Paper 1Документ14 страницCAPE Chemistry 2018 Unit 2 Paper 1Jay Joseph100% (1)
- Cape Biology 2017 PDFДокумент11 страницCape Biology 2017 PDFFelecia HutchinsОценок пока нет
- Cape Biology 2018 U1 p2 MsДокумент16 страницCape Biology 2018 U1 p2 MsYagna Lall80% (15)
- Detecting Reducing SugarsДокумент12 страницDetecting Reducing SugarsSparta100% (3)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2012Документ13 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2012asjawolverine88% (8)
- CAPE Answer SheetДокумент2 страницыCAPE Answer Sheetabby jackson100% (1)
- Cape Chemistry U2 P1 2008 - TrinidadДокумент10 страницCape Chemistry U2 P1 2008 - TrinidadC.Оценок пока нет
- CAPE Physics 2012 U1 P2 Mark SchemeДокумент7 страницCAPE Physics 2012 U1 P2 Mark SchemeTiffany PanchumОценок пока нет
- CAPE Chemistry Unit 2 Paper 1 2007-2017Документ108 страницCAPE Chemistry Unit 2 Paper 1 2007-2017CAPE_PP77% (30)
- Chemistry Unit 1 P2 2017 PDFДокумент18 страницChemistry Unit 1 P2 2017 PDFNalini Gangaram40% (5)
- CAPE Chemistry 2016 U1 P1Документ11 страницCAPE Chemistry 2016 U1 P1Ismadth2918388100% (5)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 2 p1 Answer SheetДокумент2 страницыCape Chemistry Unit 2 p1 Answer Sheetvalrie bryanОценок пока нет
- Physics Unit 2 CAPE Past Paper P1 and P2 2000-2004Документ80 страницPhysics Unit 2 CAPE Past Paper P1 and P2 2000-2004Jerome JAckson100% (2)
- Physics Past Paper Cape 2007-2011Документ58 страницPhysics Past Paper Cape 2007-2011Romon Deane90% (10)
- CAPE Physics 2017 U1 P2 Mark SchemeДокумент15 страницCAPE Physics 2017 U1 P2 Mark SchemeTiffany PanchumОценок пока нет
- Cape Physics Unit 1 Paper 1 AnswersДокумент2 страницыCape Physics Unit 1 Paper 1 AnswersGill46% (13)
- Bio Unit 1 MC answers (2007-2015Документ1 страницаBio Unit 1 MC answers (2007-2015mama1222250% (2)
- Physics Unit 1 Paper 2 May June 2015Документ22 страницыPhysics Unit 1 Paper 2 May June 2015John SmithОценок пока нет
- Cape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 1 - 2008 (Trinidad Only)Документ9 страницCape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 1 - 2008 (Trinidad Only)asjawolverine83% (6)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2003Документ12 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2003asjawolverine100% (1)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2013Документ15 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2013asjawolverine100% (9)
- Chemistry Unit2 Paper2 May 2010Документ9 страницChemistry Unit2 Paper2 May 2010dela2100% (1)
- Biology P2 2012 CSECДокумент17 страницBiology P2 2012 CSECshannee_lei75% (8)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 1Документ22 страницыCape Chemistry Unit 1Audi Sweetangel100% (1)
- Cape Communication Studies: Practical Exercises for Paper 02 EssaysОт EverandCape Communication Studies: Practical Exercises for Paper 02 EssaysОценок пока нет
- Communication Studies: Preparing Students for CapeОт EverandCommunication Studies: Preparing Students for CapeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Inorganic Chemistry Practice QuestionsДокумент7 страницInorganic Chemistry Practice QuestionskitoniumОценок пока нет
- Cat - Take AwayДокумент5 страницCat - Take Awayvictor ngetichОценок пока нет
- 2013 YJC H2 Chem Prelim P2Документ15 страниц2013 YJC H2 Chem Prelim P2Chow Kim WanОценок пока нет
- pt-1 Xii ChemДокумент2 страницыpt-1 Xii ChemPrempal KumarОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 1 - Exam N AnswersДокумент32 страницыChemistry 1 - Exam N AnswersMakame AliОценок пока нет
- CHEM-1Документ5 страницCHEM-1kakajumaОценок пока нет
- Chem f2 Mod08042022001Документ9 страницChem f2 Mod08042022001Nickyz AОценок пока нет
- 11 CHEMISTRY - CopyДокумент8 страниц11 CHEMISTRY - CopydhanushbodybuilderОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Form 3 Exam Term 2 2013Документ10 страницChemistry Form 3 Exam Term 2 2013asjawolverine100% (1)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2005Документ11 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2005asjawolverine100% (1)
- Mobile Handheld Electronic Devices Guidelines PDFДокумент10 страницMobile Handheld Electronic Devices Guidelines PDFMCTCOLTDОценок пока нет
- Revised National School Code of ConductДокумент83 страницыRevised National School Code of ConductAnnisa Arthur-CastroОценок пока нет
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2003Документ12 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2003asjawolverine100% (1)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2010Документ12 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2010asjawolverine100% (15)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2014Документ12 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2014asjawolverine89% (19)
- Thesis and Dissertation Template APA FormatДокумент20 страницThesis and Dissertation Template APA FormatasjawolverineОценок пока нет
- Dissertation Template 2Документ23 страницыDissertation Template 2asjawolverineОценок пока нет
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2009Документ9 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2009asjawolverine100% (3)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2012Документ13 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2012asjawolverine88% (8)
- Biology Unit 2 P 2 2002Документ12 страницBiology Unit 2 P 2 2002asjawolverine100% (1)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2013Документ15 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2013asjawolverine100% (9)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2011Документ14 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2011asjawolverine100% (12)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2008Документ9 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2008asjawolverine100% (4)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2007Документ12 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2007asjawolverine100% (2)
- CAPE Chemistry U1 P1 2007 SpecimenДокумент9 страницCAPE Chemistry U1 P1 2007 Specimenasjawolverine100% (3)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2006Документ10 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2006asjawolverine100% (1)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 1 2012 Paper 2Документ11 страницCape Chemistry Unit 1 2012 Paper 2s.vaish141991% (22)
- CAPE Chemistry Unit2 Module3 Industry and The Environment 2013Документ24 страницыCAPE Chemistry Unit2 Module3 Industry and The Environment 2013dela250% (2)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 2Документ133 страницыCape Chemistry Unit 2asjawolverine85% (39)
- Biology Unit 1 p2 2002Документ8 страницBiology Unit 1 p2 2002asjawolverineОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Unit2 Paper2 May 2010Документ9 страницChemistry Unit2 Paper2 May 2010dela2100% (1)
- CAPE Unit 1 Chemistry Equilibrium Constant Based On StoichiometryДокумент12 страницCAPE Unit 1 Chemistry Equilibrium Constant Based On StoichiometryasjawolverineОценок пока нет
- Caper Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 2 - 15 MAY 2006Документ14 страницCaper Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 2 - 15 MAY 2006asjawolverine100% (1)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 1 - 2010Документ9 страницCape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 1 - 2010asjawolverine100% (9)
- CAPE Past Paper P1 and P2 2008-2010Документ23 страницыCAPE Past Paper P1 and P2 2008-2010Jerome JAckson67% (6)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 2 - May 2012Документ12 страницCape Chemistry Unit 1 Paper 2 - May 2012asjawolverine89% (9)
- Cape Chem Unit 01 Paper 01 SpecimenДокумент16 страницCape Chem Unit 01 Paper 01 Specimenasjawolverine0% (1)
- Skksiesc 110Документ14 страницSkksiesc 110Rhydum KejriwalОценок пока нет
- Science Notes For Class 10 Chapter 12 Physcis Electricity PDFДокумент3 страницыScience Notes For Class 10 Chapter 12 Physcis Electricity PDFMANOBHAV SACHANОценок пока нет
- M.Sc. Prev (Physics) PDFДокумент6 страницM.Sc. Prev (Physics) PDFAmit ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Three Dimensional HLB: Dr. Z PresentsДокумент21 страницаThree Dimensional HLB: Dr. Z PresentshbordasmОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1 (Aqu167)Документ12 страницExperiment 1 (Aqu167)Iqmal HafidzОценок пока нет
- Dubai Municipality Lists Approved B2B BiocidesДокумент14 страницDubai Municipality Lists Approved B2B BiocidesAhmed FathyОценок пока нет
- Energy and Chemical Change: Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 7EДокумент47 страницEnergy and Chemical Change: Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 7EpopoojiОценок пока нет
- Physical Mechanism of Sono-Fenton ProcesДокумент11 страницPhysical Mechanism of Sono-Fenton ProcesDebanjan DuttaОценок пока нет
- INPhO2018 Solution 20180213 PDFДокумент18 страницINPhO2018 Solution 20180213 PDFRishit SriwastavaОценок пока нет
- Bubble Column ReactorsДокумент34 страницыBubble Column ReactorsGhaya Bani Rushaid100% (2)
- F3-ANCQ-2018 (Year 8)Документ9 страницF3-ANCQ-2018 (Year 8)2G (01) Cho Joshua Chi HoОценок пока нет
- Standard Proctor Compaction Test ResultsДокумент12 страницStandard Proctor Compaction Test Resultsaidil adhaОценок пока нет
- ZAPANTA Chapter 3Документ3 страницыZAPANTA Chapter 3PlazaZapantaОценок пока нет
- Engineering Chemistry Module 1: An IntroductionДокумент35 страницEngineering Chemistry Module 1: An IntroductionAudrey MendozaОценок пока нет
- Course 8 9Документ27 страницCourse 8 9Bogdan Cel MicОценок пока нет
- Porosity and Wear Resistance of Flame Sprayed TungstenДокумент7 страницPorosity and Wear Resistance of Flame Sprayed Tungstenlacoste11111Оценок пока нет
- Synthetic Biology and Metabolic EngineeringДокумент8 страницSynthetic Biology and Metabolic EngineeringLALUKISОценок пока нет
- Mcmaster MECH ENG 3O04 - Fluid Mechanics Notes by Dr. Mohamed S. HamedДокумент394 страницыMcmaster MECH ENG 3O04 - Fluid Mechanics Notes by Dr. Mohamed S. Hamedcttiger7135100% (15)
- LEH01 01 Que 20120611Документ16 страницLEH01 01 Que 20120611Jane LeaОценок пока нет
- Review Related LiteratureДокумент5 страницReview Related LiteratureImman Ray Loriezo AguilarОценок пока нет
- Blower Selection and Purge Time ChartsДокумент2 страницыBlower Selection and Purge Time Chartsajengps11Оценок пока нет
- Expt 6Документ9 страницExpt 6Gracelle AnneОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 - Radiation Heat Transfer PDFДокумент52 страницыChapter 4 - Radiation Heat Transfer PDFSuraya Johari0% (1)
- I. Read The Statements or Questions Carefully and Then Shade The Letter of The Correct Answer From The Choices Given Before Each NumberДокумент4 страницыI. Read The Statements or Questions Carefully and Then Shade The Letter of The Correct Answer From The Choices Given Before Each NumberJoel BagalanonОценок пока нет
- PVC Catalogue CNДокумент2 страницыPVC Catalogue CNKiên PhùngОценок пока нет
- Metals and Non Metals Class 8 CBSE Science AssignmentДокумент1 страницаMetals and Non Metals Class 8 CBSE Science Assignmentgurdeepsarora873833% (3)
- RSC Li/chemical-ScienceДокумент24 страницыRSC Li/chemical-SciencePunita BathlaОценок пока нет
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryДокумент26 страницSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryAnuj SharmaОценок пока нет
- Polymers & Functional Materials: Search HereДокумент4 страницыPolymers & Functional Materials: Search HereR DuppallyОценок пока нет
- Mixtures and AllegationДокумент3 страницыMixtures and AllegationRahul JoshiОценок пока нет