Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CH01
Загружено:
សារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CH01
Загружено:
សារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Management Information Systems
Learning Objectives (cont.)
MANAGING THE DIGITAL FIRM, 12TH EDITION, GLOBAL EDITION
Chapter 1
Define complementary assets and explain how they ensure that information systems provide genuine value to an organization. Describe the different academic disciplines used to study information systems and explain how each contributes to our understanding of them. Explain what is meant by a sociotechnical systems perspective.
INFORMATION SYSTEMS IN BUSINESS TODAY
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Learning Objectives
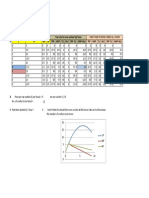
Efficiency in Wood Harvesting with Information Systems
Understanding the effects of information systems on business and their relationship to globalization.
Problem: How to keep in contact with the various parties of the wood production and procurement chain Solutions: Use information systems to enhance experience. Cutting plans, maps and working instructions delivered via a dedicated email system. Ponsse provides technology to make them the most wired in all of the timber machine industry. Demonstrates ITs role in providing new products and services. Illustrates the benefits of utilizing networks and mobile applications to enhance customer service, information.
Explain why information systems are so essential in business today.
Define an information system and describe its management, organization, and technology components.
Pearson Education 2012
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Management Information Systems
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
How information systems are transforming business
In the emerging, fully digital firm
Significant business relationships are digitally enabled and mediated Core business processes are accomplished through digital networks Key corporate assets are managed digitally
Increase in wireless technology use, Web sites Increased business use of Web 2.0 technologies Cloud computing, mobile digital platform allow more distributed work, decision-making, and collaboration
Globalization opportunities
Digital firms offer greater flexibility in organization and management
Time shifting, space shifting
7 Pearson Education 2012
Internet has drastically reduced costs of operating on global scale Presents both challenges and opportunities
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
Information Technology Capital Investment
Growing interdependence between ability to use information technology and ability to implement corporate strategies and achieve corporate goals Business firms invest heavily in information systems to achieve six strategic business objectives:
FIGURE 1-1
Information technology capital investment, defined as hardware, software, and communications equipment, grew from 32 percent to 52 percent of all invested capital between 1980 and 2009.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Pearson Education 2012 8
Operational excellence New products, services, and business models Customer and supplier intimacy Improved decision making Competitive advantage Survival
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Management Information Systems
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
Operational excellence:
Customer and supplier intimacy:
Serving customers well leads to customers returning, which raises revenues and profits Example: High-end hotels that use computers to track customer preferences and use to monitor and customize environment Intimacy with suppliers allows them to provide vital inputs, which lowers costs Example: J.C.Penneys information system which links sales records to contract manufacturer
11 Pearson Education 2012
Improvement of efficiency to attain higher profitability Information systems, technology an important tool in achieving greater efficiency and productivity Walmarts RetailLink system links suppliers to stores for superior replenishment system
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
Improved decision making
Without accurate information:
Managers must use forecasts, best guesses, luck Leads to:
Overproduction, underproduction of goods and services Misallocation of resources Poor response times
New products, services, and business models:
Business model: describes how company produces, delivers, and sells product or service to create wealth Information systems and technology a major enabling tool for new products, services, business models Examples: Apples iPod, iTunes, iPhone, iPad, Googles Android OS, and Netflix
Pearson Education 2012 12
Poor outcomes raise costs, lose customers
Example: Verizons Web-based digital dashboard to provide managers with real-time data on customer complaints, network performance, line outages, etc.
Pearson Education 2012
10
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Management Information Systems
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
Operational excellence:
Improvement of efficiency to attain higher profitability
Survival
New products, services, and business models:
Enabled by technology
Customer and supplier intimacy:
Serving customers raises revenues and profits Better communication with suppliers lowers costs
Information technologies as necessity of business May be: Industry-level changes, e.g. Citibanks introduction of ATMs Governmental regulations requiring recordkeeping
Examples: Toxic Substances Control Act, SarbanesOxley Act
15 Pearson Education 2012
Improved decision making
Pearson Education 2012
More accurate data leads to better decisions
13
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
The Role of Information Systems in Business Today
The Interdependence Between Organizations and Information Technology
Competitive advantage
Delivering better performance
Charging less for superior products
Responding to customers and suppliers in real time
Figure 1.2 In contemporary systems there is a growing interdependence between a firms information systems and its business capabilities. Changes in strategy, rules, and business processes increasingly require changes in hardware, software, databases, and telecommunications. Often, what the organization would like to do depends on what its systems will permit it to do.
Examples: Apple, Walmart, UPS
14
Pearson Education 2012
16
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Management Information Systems
Perspectives on Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Perspectives on Information Systems
Information system:
Set of interrelated components Collect, process, store, and distribute information Support decision making, coordination, and control
Three activities of information systems produce information organizations need
Information vs. data
Data are streams of raw facts Information is data shaped into meaningful form
1. Input: Captures raw data from organization or external environment 2. Processing: Converts raw data into meaningful form 3. Output: Transfers processed information to people or activities that use it
17
Pearson Education 2012
19
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Perspectives on Information Systems
Perspectives on Information Systems
Data and Information
Feedback:
Output returned to appropriate members of organization to help evaluate or correct input stage
Computer/Computer program vs. information system
Computers and software are technical foundation and tools, similar to the material and tools used to build a house
Figure 1.3
Raw data from a supermarket checkout counter can be processed and organized to produce meaningful information, such as the total unit sales of dish detergent or the total sales revenue from dish detergent for a specific store or sales territory.
18
Pearson Education 2012
20
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Management Information Systems
Perspectives on Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Perspectives on Information Systems
Functions of an Information System
An information system contains information about an organization and its surrounding environment. Three basic activitiesinput, processing, and output produce the information organizations need. Feedback is output returned to appropriate people or activities in the organization to evaluate and refine the input. Environmental actors, such as customers, suppliers, competitors, stockholders, and regulatory agencies, interact with the organization and its information systems.
Organizational dimension of information systems
Hierarchy of authority, responsibility Senior management Middle management Operational management Knowledge workers Data workers Production or service workers
Pearson Education 2012 23 Pearson Education 2012
Figure 1.4
21
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Perspectives on Information Systems
Levels in a Firm
Perspectives on Information Systems
Information Systems Are More Than Computers
Business organizations are hierarchies consisting of three principal levels: senior management, middle management, and operational management. Information systems serve each of these levels. Scientists and knowledge workers often work with middle management. Figure 1.6
Using information systems effectively requires an understanding of the organization, management, and information technology shaping the systems. An information system creates value for the firm as an organizational and management solution to challenges posed by the environment.
Figure 1.5
22
Pearson Education 2012
24
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Management Information Systems
Perspectives on Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Perspectives on Information Systems
Organizational dimension of information systems (cont.)
Technology dimension of information systems
Computer hardware and software Data management technology Networking and telecommunications technology Networks, the Internet, intranets and extranets, World Wide Web IT infrastructure: provides platform that system is built on
Separation of business functions
Sales and marketing Human resources Finance and accounting Manufacturing and production
Unique business processes Unique business culture Organizational politics
Pearson Education 2012 27
25
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Perspectives on Information Systems
Perspectives on Information Systems
Management dimension of information systems
Dimensions of UPS tracking system
Organizational: Procedures for tracking packages and managing inventory and provide information Management: Monitor service levels and costs Technology: Handheld computers, bar-code scanners, networks, desktop computers, etc.
Managers set organizational strategy for responding to business challenges In addition, managers must act creatively: Creation of new products and services Occasionally re-creating the organization
26
Pearson Education 2012
28
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Management Information Systems
Perspectives on Information Systems
The Business Information Value Chain
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Perspectives on Information Systems
Business perspective on information systems:
Information system is instrument for creating value Investments in information technology will result in superior returns: Productivity increases Revenue increases Superior long-term strategic positioning
Figure 1-7
From a business perspective, information systems are part of a series of value-adding activities for acquiring, transforming, and distributing information that managers can use to improve decision making, enhance organizational performance, and, ultimately, increase firm profitability.
29
Pearson Education 2012
31
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Perspectives on Information Systems
Perspectives on Information Systems
Variation in Returns On Information Technology Investment
Although, on average, investments in information technology produce returns far above those returned by other investments, there is considerable variation across firms. Figure 1.8
Business information value chain
Raw data acquired and transformed through stages that add value to that information Value of information system determined in part by extent to which it leads to better decisions, greater efficiency, and higher profits
Business perspective:
Calls attention to organizational and managerial nature of information systems
Pearson Education 2012 32 Pearson Education 2012
30
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Management Information Systems
Perspectives on Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Perspectives on Information Systems
Investing in information technology does not guarantee good returns
Organizational assets, e.g.
Appropriate business model Efficient business processes
Complementary assets include:
Considerable variation in the returns firms receive from systems investments
Managerial assets, e.g.
Factors:
Social assets, e.g.
Adopting the right business model Investing in complementary assets (organizational and management capital)
Pearson Education 2012 35
Incentives for management innovation Teamwork and collaborative work environments The Internet and telecommunications infrastructure Technology standards
Pearson Education 2012
33
Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Perspectives on Information Systems
Contemporary Approaches to Information Systems
Contemporary Approaches to Information Systems
The study of information systems deals with issues and insights contributed from technical and behavioral disciplines. Figure 1.9
Complementary assets:
Assets required to derive value from a primary investment Firms supporting technology investments with investment in complementary assets receive superior returns E.g.: invest in technology and the people to make it work properly
Pearson Education 2012
34
36
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Management Information Systems
Contemporary Approaches to Information Systems
A Sociotechnical Perspective on Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Contemporary Approaches to Information Systems
Technical approach
Emphasizes mathematically based models Computer science, management science, operations research
Behavioral approach
Behavioral issues (strategic business integration, implementation, etc.) Psychology, economics, sociology
Figure 1-10 In a sociotechnical perspective, the performance of a system is optimized when both the technology and the organization mutually adjust to one another until a satisfactory fit is obtained.
37
Pearson Education 2012
39
Pearson Education 2012
Management Information Systems
CHAPTER 1: INFORMATION IN BUSINESS SYSTEMS TODAY
Contemporary Approaches to Information Systems
Management Information Systems
Combines computer science, management science, operations research and practical orientation with behavioral issues
Four main actors
Suppliers of hardware and software Business firms Managers and employees Firms environment (legal, social, cultural context)
Pearson Education 2012
38
Вам также может понравиться
- Freight Credit Application Packet April 2014Документ12 страницFreight Credit Application Packet April 2014សារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Gkánaykdæanbn Dar: Cati Sasna RbhmhaksrtДокумент2 страницыGkánaykdæanbn Dar: Cati Sasna Rbhmhaksrtសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Final Final ATT Quiz Assis + HW Mid-Term: 10 Nath PuthearaДокумент1 страницаFinal Final ATT Quiz Assis + HW Mid-Term: 10 Nath Puthearaសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Nhoung Neng PDFДокумент3 страницыNhoung Neng PDFសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Gkánaykdæanbn Dar: Cati Sasna RbhmhaksrtДокумент2 страницыGkánaykdæanbn Dar: Cati Sasna Rbhmhaksrtសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Name: - Date: - Quiz On The Intr Oduction To AccountingДокумент3 страницыName: - Date: - Quiz On The Intr Oduction To Accountingសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- INS-Group Assignment: Meada Rabrong Prevoir Micro InsuranceДокумент2 страницыINS-Group Assignment: Meada Rabrong Prevoir Micro Insuranceសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- รักต้องฆ่าДокумент177 страницรักต้องฆ่าសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- ล่าสุสานอะเล็กซานเดอร์Документ480 страницล่าสุสานอะเล็กซานเดอร์សារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Business BasicДокумент4 страницыBusiness Basicសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Quiz IДокумент2 страницыQuiz Iសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Combining Sentences I (L18) PDFДокумент3 страницыCombining Sentences I (L18) PDFសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- 7.steps in The Decision ProcessДокумент7 страниц7.steps in The Decision Processសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍100% (3)
- Descriptive Paragraph: TopicДокумент2 страницыDescriptive Paragraph: Topicសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- The Reality of Decision MakingДокумент8 страницThe Reality of Decision Makingសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍100% (4)
- Playing PuzzleДокумент5 страницPlaying Puzzleសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Separation of Power Under Cambodian ConstitutionДокумент5 страницSeparation of Power Under Cambodian Constitutionសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Listening Test - AnswerДокумент3 страницыListening Test - Answerសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Creating Customer Value Satisfaction and LoyaltyДокумент41 страницаChapter 5 Creating Customer Value Satisfaction and Loyaltyសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍61% (28)
- Estimation of Production - Exercise 6Документ1 страницаEstimation of Production - Exercise 6សារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Estimation of Production - Exercise 2Документ2 страницыEstimation of Production - Exercise 2សារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- Passive With Past SimpleДокумент2 страницыPassive With Past SimpleJennyfer DsОценок пока нет
- Exam For Managerial AccountingДокумент8 страницExam For Managerial Accountingសារុន កែវវរលក្ខណ៍Оценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Kiruna Iron Drilling SuccessДокумент12 страницKiruna Iron Drilling SuccessHannans Reward LtdОценок пока нет
- Training ProjectДокумент93 страницыTraining ProjectSimu Matharu100% (1)
- CV - Muhammed Hasnain Kabir NayeemДокумент3 страницыCV - Muhammed Hasnain Kabir NayeemMuhammed NayeemОценок пока нет
- List of Tools, Equipment and Materials For Assessment CenterДокумент7 страницList of Tools, Equipment and Materials For Assessment CenterVillamor NiezОценок пока нет
- Unit I Management Information Systems (MIS) : Other NamesДокумент6 страницUnit I Management Information Systems (MIS) : Other Namesfelix777sОценок пока нет
- Steel SolutionsДокумент4 страницыSteel Solutionsgodzillafood100% (1)
- Dear Mahendra, Dear AllДокумент25 страницDear Mahendra, Dear AllMahendra SinghОценок пока нет
- Cardinal Pump - Unifin PresentationДокумент226 страницCardinal Pump - Unifin PresentationManibalanОценок пока нет
- Trimble R4 GPSДокумент2 страницыTrimble R4 GPSgustalcОценок пока нет
- MEG ProfileДокумент1 страницаMEG ProfileelainejournalistОценок пока нет
- NIKKI Precision Locknut Catalog 2019Документ32 страницыNIKKI Precision Locknut Catalog 2019George babuОценок пока нет
- Pds Fire Door SlowДокумент55 страницPds Fire Door SlowRachel IngramОценок пока нет
- Masdar City: The World'S Greenest City?: InshareДокумент7 страницMasdar City: The World'S Greenest City?: InshareMohd HazaziОценок пока нет
- Cost Metrics For Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: September 2005Документ7 страницCost Metrics For Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: September 2005Elias Jose Akle VillarealОценок пока нет
- Republic of Indonesia Ministry of Transportation: Moored Balloons, Kites, Unmanned Rockets and Unmanned Free BalloonsДокумент12 страницRepublic of Indonesia Ministry of Transportation: Moored Balloons, Kites, Unmanned Rockets and Unmanned Free BalloonsastriwiditakОценок пока нет
- Tyler Scott - Professional PortfolioДокумент7 страницTyler Scott - Professional Portfolioapi-266320901Оценок пока нет
- DBT416 Airbnb FinalreportДокумент29 страницDBT416 Airbnb FinalreportButsakan NuankaewОценок пока нет
- Plagiarism Scan Report: Plagiarism Unique Plagiarized Sentences Unique SentencesДокумент2 страницыPlagiarism Scan Report: Plagiarism Unique Plagiarized Sentences Unique Sentencesshreya100% (1)
- QuizДокумент3 страницыQuizCARL JAMESОценок пока нет
- Gear Box NoiseДокумент3 страницыGear Box NoiseKumar SanthanamОценок пока нет
- Project ManagementДокумент371 страницаProject Managementdheerendra prajapatiОценок пока нет
- Design of Off Shor Structures IIT Professor Presentation PDFДокумент20 страницDesign of Off Shor Structures IIT Professor Presentation PDFPremalatha JeyaramОценок пока нет
- Introsoft Company Profile-2014Документ11 страницIntrosoft Company Profile-2014arshad.vickyОценок пока нет
- Business IntelligenceДокумент10 страницBusiness IntelligenceHGFERNANОценок пока нет
- Electrical: Section - V Technical SpecificationsДокумент6 страницElectrical: Section - V Technical SpecificationsvijaysatawОценок пока нет
- 5500 Get StartedДокумент46 страниц5500 Get StartedRangga K NegaraОценок пока нет
- MYOB AE Practice Manager ViztopiaДокумент14 страницMYOB AE Practice Manager Viztopiarjmv busisolutionsОценок пока нет
- Hyderabad TicketДокумент1 страницаHyderabad TicketRudra RoyОценок пока нет
- Investor Presentation (Company Update)Документ46 страницInvestor Presentation (Company Update)Shyam SunderОценок пока нет