Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
VM PMI-126 2ND MIDTERM Exam
Загружено:
Evan YuИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
VM PMI-126 2ND MIDTERM Exam
Загружено:
Evan YuАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
VM PMI-126
2ND MIDTERM
Mark this exam with your answer and take it with you. You can use it to check the key we will post on CERE and establish your successes and failures. The scantrons will not be returned.
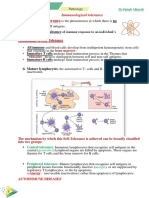
1. A macrophage binds a bacteria via a receptor ligand interaction, i.e. cell surface mannose receptors engage the bacterial membrane. Which of the following would probably occur? a. The macrophage would undergo apoptosis b. The macrophage would phagocytose the bacteria c. The macrophage would become activated due to receptor-mediated signal transduction d. All of the above e. b and c only Which of the following soluble mediators (cytokines) would you expect an activated macrophage to secrete (assume the macrophage was activated by binding bacteria to toll-like receptors)? a. IL-1 b. TNF- c. IL-6 d. All of the above e. None of the above IL-1, TNF- and IL-6 are all considered pro-inflammatory cytokines and can have systemic effects such as inducing a fever. a. True b. False The acute-phase response is characterized by the production of C-reactive protein and mannose-binding lectin by local lymph nodes. a. True b. False Which of the following attributes would you associate with C-reactive protein (CRP) and mannose binding lectin? a. Opsonization b. Activation of the complement cascade c. Increased levels in the blood during an acute inflammatory response d. All of the above e. None of the above Upon induction of a local inflammatory response due to a bacterial infection that has been initiated through a skin abrasion, neutrophils, monocytes and memory lymphocytes roll and stick to the walls of blood vessels underlying the insult. The leukocytes exit the blood via a process termed diapedesis that involves squeezing between vascular endothelial cells and migrating into the infected tissue. Questions 6-8 relate to this process. 6. Which of the following would you directly associate with the margination and sticking of the leukocytes to the vessel wall? a. Surface immunoglobulin (Sig) b. C3 convertase c. Adhesion proteins d. Granzymes e. All of the above Which of the following would you directly associate with attracting the leukocytes (attract by setting up a concentration gradient) through the tissue to the site of the bacterial insult? a. Adhesion proteins b. Chemokines c. Granzymes d. Fas ligands e. All of the above
2.
3.
4.
5.
7.
8.
In addition to the migration of leukocytes out of the vasculature and into the infected tissue, many soluble serum proteins including antibodies and components of the complement cascade will also enter the tissue. a. True b. False The complement cascade can be activated via which of the following pathways? a. Alternative pathway b. Lectin pathway c. Classical Pathway d. All of the above e. a and b only During an innate immune response to a bacterial insult the complement cascade is typically activated via the classical pathway. a. True b. False Which of the following would you expect to occur following a bacterial insult that has resulted in activation of the complement cascade? a. Opsonization of the bacteria b. Production of pro-inflammatory mediators c. Generation of a membrane attack complex d. All of the above e. a and b only The terminal sequence of events in the complement cascade is generation of C3a and C5a. Their hydrophobic nature permits penetration of the bacterial cell wall resulting in loss of osmotic integrity and lysis. a. True b. False Antibody can be considered a secretory form of the antigen-specific B cell receptor. a. True b. False How many antigen-binding sites would a B cell receptor (surface Ig) have? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 10 The B cell receptor is composed of two heavy chains and two light chains, all of which are held together by a combination of electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. a. True b. False The antigen-binding site of a B cell receptor is generated by a combination of 5 hypervariable regions on the light chain and 3 hypervariable regions on the heavy chain. a. True b. False The binding of antigen by the B cell receptor is very strong due to the generation of disulfide bonds between the antibody binding site and the antigenic epitope? a. True b. False
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
How many antigen binding sites would a secreted molecule of IgM have? a. 2 b. 4 c. 6 d. 8 e. 10 How many antigen binding sites would a secreted molecule of IgG have? a. 2 b. 4 c. 6 d. 8 e. 10 Which of the following classes of antibody is in the highest concentration in the blood? a. IgD b. IgG c. IgM d. IgE e. IgA Which of the following antibodies is secreted onto mucosal surfaces in great quantities? a. IgD b. IgG c. IgM d. IgE e. IgA Hybridomas (plasma cell fused with an immortal cell) are generated for the purpose of producing commercial quantities of polyclonal antibody with a single antigen-specificity. a. True b. False The ability of B cells to generate a near infinite variety of antigen-specific antibodies is a hallmark of the adaptive immune system. This variability requires that the B cell commit a large portion of the genome to their production due to the age-old one gene one protein concept. a. True b. False Which of the following genes are involved in the generation of a heavy chain of an antibody? a. J region gene b. V region gene c. D region gene d. All of the above e. Only a and b are correct Which of the following genes are involved in the generation of a light chain of an antibody? a. J region gene b. V region gene c. D region gene d. All of the above e. a and b only P nucleotides are added at the joining sites of D-J and V-D genes but do not contribute to the generation of receptor diversity because the reading frame must be maintained. a. True b. False
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
Which of the following assays would you best associate with blood typing (ABO and Rh blood groups)? a. Agar gel immunodiffusion b. Western blot c. Agglutination d. ELISA e. Neutralization Which of the following assays would you best associate with confirming that antibodies from a patients serum are specific for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)? a. Agar gel immunodiffusion b. Western blot c. Agglutination d. ELISA e. Neutralization T cell receptors typically bind conformational epitopes on complex antigens. a. True b. False T lymphocytes recognize antigen that is processed and presented on a cell membrane by proteins encoded within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Which of the following classes of MHC proteins typically present viral antigens synthesized in the cytoplasm of an infected cell? a. MHC class I b. MHC class II c. MHC class III d. All of the above e. None of the above Antigens phagocytosed (or pinocytosed) from the extracellular spaces by dendritic cells are typically processed by immunoproteosomes and presented on MHC class II proteins a. True b. False Which of the following cells typically expressed MHC I proteins? a. Macrophages b. Dendritic cells c. Epithelial cells d. All of the above e. Only a and b are correct Cytotoxic T cells (TC) express which of the following proteins on their cell membranes? a. TCRs b. CD4 c. CD8 d. a and b are both correct e. a and c are both correct Newly synthesized MHC class I proteins can be loaded with self-antigens and presented on the cell surface of most nucleated cells. a. True b. False Which of the following would be true for the MHC gene complex? a. Polygenic b. Polymorphic c. Multiple alleles d. All of the above e. None of the above
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
The polymorphic residues of MHC class I proteins are concentrated in the following: a. Alpha chain b. Beta chain c. 2-microgolobulin d. All of the above e. None of the above Because of the polymorphic nature of genes encoding MHC class II proteins, allelic exclusion insures that only one allele on a single chromosome will be expressed in a single cell. a. True b. False An inbred species such as the elephant seal and African cheetah are considered to be at increased risk of infectious disease due to excessive polymorphism in the MHC gene complex? a. True b. False T cell receptors have a much lower affinity for antigen (peptide-MHC complex) as compared to B cell receptors. a. True b. False Which of the following are involved in the processing and presentation of endogenous (synthesized within the cell) antigen to TC cells? a. Immunoproteosome b. MHC class I proteins c. TAP proteins d. Chaperone proteins e. All of the above The loading and presentation of foreign exogenous antigen by MHC class II proteins is a competitive process as the majority of newly synthesized MHC II proteins are loaded with self-peptides in the endoplasmic reticulum before they are exported to the membrane via the endosomal compartment. a. True b. False The ability of IgG to cross the human placenta and gain access to the developing fetus is a characteristic inherent in the following: a. Complementarity determining regions of the heavy and light chains b. The hinge region of the light chain c. The Fc part of the antibody d. The Fab part of the antibody e. The VDJ regions of the heavy chain Upon binding and ingesting bacteria that have entered the skin via a puncture wound, dendritic cells become activated, undergo a maturation process and migrate from the insulted tissue into the blood vasculature where they are transported to secondary lymphoid structures. Upon entering the lymphoid tissue the dendritic cells adhere to high endothelial venules, exit the blood, and present the nowprocessed antigen to nave T lymphocytes. a. True b. False Which of the following professional antigen-presenting cells will typically play the most important role in presenting antigen to nave TH lymphocytes in a primary immune response (first exposure to a pathogen)? a. B lymphocytes b. Neutrophils c. Dendritic cells d. Macrophages
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
Вам также может понравиться
- Immunology Short Quiz With AnswersДокумент6 страницImmunology Short Quiz With AnswersPeter SewehaОценок пока нет
- Kuis Imun UTSДокумент8 страницKuis Imun UTSichiОценок пока нет
- ImmunologyДокумент34 страницыImmunologydenekeОценок пока нет
- The Immune System, Fourth Edition Chapter 7: The Development of T LymphocytesДокумент13 страницThe Immune System, Fourth Edition Chapter 7: The Development of T Lymphocyteslina lopez100% (1)
- Immunology Practice QuestionsДокумент52 страницыImmunology Practice QuestionsBigBoostingОценок пока нет
- MLS Immunology Exam QuestionsДокумент13 страницMLS Immunology Exam QuestionsDjdjjd SiisusОценок пока нет
- KUBYДокумент5 страницKUBYCristina CisnerosОценок пока нет
- Practice Final Exam 19Документ8 страницPractice Final Exam 19Bira maroОценок пока нет
- 2005719194923738Документ10 страниц2005719194923738DenizDerenОценок пока нет
- PCB 42SS immunology lecture guideДокумент2 страницыPCB 42SS immunology lecture guideEduardo CarderoОценок пока нет
- ImmunologyДокумент69 страницImmunologyburhaninho100% (5)
- Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) : Rispah Torrorey Immunology Department June 2017Документ35 страницMajor Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) : Rispah Torrorey Immunology Department June 2017Jacob MasikaОценок пока нет
- BIOL 5200 Final Review GuideДокумент18 страницBIOL 5200 Final Review GuideClaudia Ann RutlandОценок пока нет
- Test 3 Study Guide INNATE DEFENSES A&P2Документ13 страницTest 3 Study Guide INNATE DEFENSES A&P2Sarah C. SnooksОценок пока нет
- Imuno QuizДокумент5 страницImuno Quizᖴᗩᗫᓾ ᘜᓏᒪᕲᘍᘉОценок пока нет
- Clinical Immunology and Allergic Disease: Asthma Acquired Cat Acute Asthma Cell AllergenДокумент8 страницClinical Immunology and Allergic Disease: Asthma Acquired Cat Acute Asthma Cell AllergenSarfaraz ansariОценок пока нет
- Bacteriostatic Agents: Drugs Which Bind To The 50s Ribosomal UnitДокумент3 страницыBacteriostatic Agents: Drugs Which Bind To The 50s Ribosomal UnitJoshua TrinidadОценок пока нет
- 2 SeminarДокумент39 страниц2 SeminarIka Gultom100% (1)
- Immunology Mid-ExamДокумент11 страницImmunology Mid-ExamNgMinhHaiОценок пока нет
- AP Bio Unit 7 Study Guide Chapter 43Документ7 страницAP Bio Unit 7 Study Guide Chapter 43Huma KhanОценок пока нет
- ImmunologyДокумент5 страницImmunologyKymi TanОценок пока нет
- Immunology Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент34 страницыImmunology Multiple Choice QuestionsMohsen HaleemОценок пока нет
- Antigen Presenting CellДокумент26 страницAntigen Presenting CellSurja DasОценок пока нет
- The Immune Response Defends Against InfectionДокумент55 страницThe Immune Response Defends Against InfectionKoushali BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Janeways Immunobiology 9th EditionДокумент19 страницJaneways Immunobiology 9th EditionDevin MckayОценок пока нет
- Immunology MCQ BY: Dr. AlgassimДокумент4 страницыImmunology MCQ BY: Dr. AlgassimmohamedОценок пока нет
- Microbiology 2Документ53 страницыMicrobiology 2pikachuОценок пока нет
- Immuno SeroДокумент80 страницImmuno SeroDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalОценок пока нет
- FRCPath Part 1 Immunology Exam QuestionsДокумент15 страницFRCPath Part 1 Immunology Exam QuestionsRehab KhaledОценок пока нет
- Hemoglobin Determination: Cyanmethemoglobin MethodДокумент31 страницаHemoglobin Determination: Cyanmethemoglobin Methodبراءة أحمد السلاماتОценок пока нет
- Exam 2Документ6 страницExam 24157Оценок пока нет
- Para & MycoДокумент14 страницPara & MycoALI HASSANОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Notes Chapers 1-2Документ3 страницыMicrobiology Notes Chapers 1-2dinkinpdОценок пока нет
- CiullahemaДокумент60 страницCiullahemaMariel AbatayoОценок пока нет
- Nelson's Pediatrics Self-Assessments QuizДокумент3 страницыNelson's Pediatrics Self-Assessments Quizmma24100% (1)
- Molbio HandoutДокумент29 страницMolbio HandoutHazel FlorentinoОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms of Immunologic Tolerance and AutoimmunityДокумент65 страницMechanisms of Immunologic Tolerance and AutoimmunityPrincewill Seiyefa100% (1)
- Test Bank Exam 3Документ81 страницаTest Bank Exam 3Sajjad AhmadОценок пока нет
- Immuno Sero CompleteДокумент33 страницыImmuno Sero CompleteAngela ReyesОценок пока нет
- Immunodeficiency: Faculty of Applied Science Department of Medical Lab. Ml3A, ML3C, ML3DДокумент35 страницImmunodeficiency: Faculty of Applied Science Department of Medical Lab. Ml3A, ML3C, ML3Dالدنيا ساعة فاجعلها طاعةОценок пока нет
- Clinical Instrumentation, MLT 2760, BCC, EXAM 01Документ5 страницClinical Instrumentation, MLT 2760, BCC, EXAM 01alphacetaОценок пока нет
- @PIDs Curs 200903Документ43 страницы@PIDs Curs 200903Mohammad_Islam87Оценок пока нет
- Score Report - Immunology & Serology at Free Online Quiz SchoolДокумент29 страницScore Report - Immunology & Serology at Free Online Quiz SchoolThomas GiangОценок пока нет
- Bacteriology Lab Midterm ExamДокумент9 страницBacteriology Lab Midterm ExamLloydan EstacioОценок пока нет
- 1 Edited My Class Note 1 On Blood BankДокумент42 страницы1 Edited My Class Note 1 On Blood Bankmatewos100% (1)
- B Cell ActivationДокумент62 страницыB Cell ActivationAYSHAMOHD88Оценок пока нет
- Immunopathology Lec 4Документ11 страницImmunopathology Lec 4zaharОценок пока нет
- Harrisons: Introduction To Infectious DiseasesДокумент3 страницыHarrisons: Introduction To Infectious Diseasesapi-3704562Оценок пока нет
- Autoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersДокумент46 страницAutoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersJennifer EvansОценок пока нет
- A) Immunization B) Vaccination C) Attenuation D) None of TheseДокумент4 страницыA) Immunization B) Vaccination C) Attenuation D) None of TheseYadav rupeshОценок пока нет
- ImmunologyДокумент1 страницаImmunologySenthilkumar PalanisamyОценок пока нет
- Intro To Molecular DiagnosticsДокумент39 страницIntro To Molecular Diagnosticsmaxwell amponsahОценок пока нет
- Immune MonitoringДокумент6 страницImmune MonitoringcandiddreamsОценок пока нет
- Microbiology (Chapter - Immunology) Solved MCQs (Set-1)Документ5 страницMicrobiology (Chapter - Immunology) Solved MCQs (Set-1)خلطة علومОценок пока нет
- 04 AntigenДокумент30 страниц04 AntigenVivin Syamsul ArifinОценок пока нет
- Mycobacterium Lecture NotesДокумент10 страницMycobacterium Lecture NotesHansmeet KourОценок пока нет
- Selected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIОт EverandSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- The Pyridine Nucleotide CoenzymesОт EverandThe Pyridine Nucleotide CoenzymesJohannes EverseОценок пока нет
- Cell Cycle and Cell Growth Control-2011 TextДокумент68 страницCell Cycle and Cell Growth Control-2011 TextShang-JuiTsaiОценок пока нет
- Irreversible Cell Injury and Cell DeathДокумент38 страницIrreversible Cell Injury and Cell DeathPradeep100% (2)
- Kwatra 2017Документ12 страницKwatra 2017Daniel OctavianusОценок пока нет
- r7412311 Metabolic EngineeringДокумент4 страницыr7412311 Metabolic EngineeringsivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry 7th Edition (2013) Chapter23 PDFДокумент44 страницыBiochemistry 7th Edition (2013) Chapter23 PDFAryan KumarОценок пока нет
- Molecular Mechanism of Aloe Barbadensis MillerДокумент8 страницMolecular Mechanism of Aloe Barbadensis MillerSusyana IrianiОценок пока нет
- 2 PassivetransportДокумент8 страниц2 PassivetransportFayeОценок пока нет
- Purf Brief 1Документ61 страницаPurf Brief 1Prabhavathy KannappanОценок пока нет
- Linkers and AdaptersДокумент11 страницLinkers and AdaptersYogesh Pawar0% (1)
- 5 - 481316 - HematologyДокумент1 страница5 - 481316 - HematologyChristopher MolinaОценок пока нет
- GB 2003 4 3 207Документ7 страницGB 2003 4 3 207Giulia AndreeaОценок пока нет
- 1.3 Components of The Cell II (Subcellular Organelles)Документ20 страниц1.3 Components of The Cell II (Subcellular Organelles)Alexa Julienne RazОценок пока нет
- BLOODДокумент5 страницBLOODSora TensaiОценок пока нет
- Hhis Lec Prelims FinalsДокумент101 страницаHhis Lec Prelims FinalsJOANNA MARIE SIGUAОценок пока нет
- Drug Delivery Systems - Advanced Technologies Potentially Applicable in Personalised TreatmentДокумент432 страницыDrug Delivery Systems - Advanced Technologies Potentially Applicable in Personalised TreatmentlirisОценок пока нет
- Role of lac repressor and cAMP in regulation of lac operonДокумент1 страницаRole of lac repressor and cAMP in regulation of lac operonQum ArОценок пока нет
- CSIR Unit 2 - Full NotesДокумент74 страницыCSIR Unit 2 - Full NotesSubhrajyoti BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Metabolism Exam 2 - GIFT - Spring 2016Документ9 страницMetabolism Exam 2 - GIFT - Spring 2016shafa_nathani100% (2)
- Difference Between Acetyl CoA and Acyl CoA - Compare The Difference Between Similar TermsДокумент7 страницDifference Between Acetyl CoA and Acyl CoA - Compare The Difference Between Similar Termsteam TSOTAREОценок пока нет
- Metalloproteinases and Their Tissue Inhibitors in Alzheimer's Disease and Other Neurodegenerative DisordersДокумент25 страницMetalloproteinases and Their Tissue Inhibitors in Alzheimer's Disease and Other Neurodegenerative DisordersyusufОценок пока нет
- PrecipitationДокумент5 страницPrecipitationSukanthan RОценок пока нет
- ALWAYS REMEMBER GOD KNOWS YOUR THOUGHTSДокумент35 страницALWAYS REMEMBER GOD KNOWS YOUR THOUGHTSDOUGLAS KIPRUTOОценок пока нет
- Cellular and Molecular Immunology 9th Edition Abbas Test BankДокумент4 страницыCellular and Molecular Immunology 9th Edition Abbas Test Bankdrkevinlee03071984jki100% (28)
- Cellular Respiration 9-12Документ56 страницCellular Respiration 9-12David BayaniОценок пока нет
- Benchmarking of ATAC Sequencing Data From BGI's Low-Cost DNBSEQ-G400 Instrument 2022Документ15 страницBenchmarking of ATAC Sequencing Data From BGI's Low-Cost DNBSEQ-G400 Instrument 2022Vera Brok-VolchanskayaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12Документ62 страницыChapter 12Anupa GhoseОценок пока нет
- Class Eleventh 50 Marks Question PaperДокумент5 страницClass Eleventh 50 Marks Question PaperA-01 SNEHAL AHERОценок пока нет
- IB Biology Assessment Statements - DrawДокумент33 страницыIB Biology Assessment Statements - DrawSchuyler Huff100% (1)
- Connective Tissue: Dr. Jan Tambayong, PHK Histologi FK-UPHДокумент51 страницаConnective Tissue: Dr. Jan Tambayong, PHK Histologi FK-UPHJoshua ObrienОценок пока нет
- Chapter 39: Plant Responses To Internal and External SignalsДокумент9 страницChapter 39: Plant Responses To Internal and External SignalsdarthОценок пока нет