Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ca1 - Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
Загружено:
larissedeleonАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ca1 - Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
Загружено:
larissedeleonАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1. Discuss the significance of left main coronary artery stenosis.
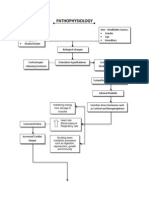
Left main coronary artery is the artery from the point of origin to the first major branch. There is also two branches arise from Left main coronary artery: the left anterior descending artery which courses down the anterior wall of the heart, and the circumflex artery , which circles around to the lateral left wall of the heart. In LMCA stenosis, what happens is that there is a narrowing of the blood vessel resulting to decreased blood supply to the heart and a decreased cardiac output of the heart. Whenever there is a decreased CO there would also be less blood circulating in the system. Which may cause decreased in urine output, weak and often irregular pulse, changes in cellular structure that may cause changes in the LOC. 2. Explain the rationale of Mr. Romulos urinary output values. Mr. Romulos urine output decreases because the bypass that serves as another route for the blood to flow and supplies blood to the heart and circulation was terminated. Meaning, there is still stenosis on mr.romulos heart. This happens because of a decrease perfusion on the kidney. And this could also be a compensatory mechanism of our body that reserves the available fluid. 3. Discuss 4 postoperative exercises that a patient should perform to prevent postoperative complications. a. Deep breathing exercise improves lung function and helps clear secretions as we exhale. b. Splinting and coughing c. Leg exercise prevents DVT by promoting circulation and compressing of the muscle that can pump the blood back to the circulation d. Range of motion exercise prevent muscle atrophy and improves circulation. 4. Discuss the mode of action of all the drugs mentioned in the situation. DRUG ACTION 1. Amlodipine besilate + Valsartan is a type of medicine called an valsartan (exforge) 1 tab angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Amlodipine is a HS. type of medicine called a calcium-channel blocker. These are both medicines used to lower high blood pressure. Valsartan works by preventing the action of a hormone in the body called angiotensin II. Angiotensin II normally acts on special receptors
2. Enalapril Maleate (hypace) 1 tab OD
in the body, with two main results. It causes the peripheral blood vessels to narrow, and it also stimulates the production of another hormone called aldosterone. Aldosterone causes salt and water to be retained by the kidneys, which increases the volume of fluid in the blood vessels. Valsartan blocks the receptors that angiotensin II acts on and so prevents its actions. The main result of this is that the peripheral blood vessels are allowed to widen, which means that there is more space and less resistance in these blood vessels. This helps lower blood pressure. Enalapril is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension ). Lowering high blood pressure helps prevent strokes, heart attacks, and kidney problems. It is also used to treat heart failure. Enalapril is an ACE inhibitor and works by relaxing blood vessels so that blood can flow more easily. Aspirin belongs to a group of medicines called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It works by blocking the action of a substance in the body called cyclo-oxygenase. Cyclo-oxygenase is involved in the production of various chemicals in the body. These are known as prostaglandins, prostacyclins and thromboxane. By blocking the action of cylo-oxygenase, aspirin prevents the production of these chemicals. Low doses of aspirin prevent the production of thromboxane by blood cells called platelets. Thromboxane is one of the chemicals that cause platelets to clump together and start off the clotting process. Stopping its production therefore reduces the likelihood of clots forming in the blood. Clots in the blood can cause a heart attack or stroke, and low dose aspirin is therefore used to prevent this in people who are at risk. Cordarone X tablets contain the active ingredient amiodarone, which is a type of medicine called an
3. Aspirin 80mg 1 tab OD
4. Amiodarone (cordarone) 1 tab OD
5. Dobutamine (Dobutrex)
6. Nitroglycerin
antiarrhythmic. Amiodarone is used to control abnormal heartbeats. The heart's pumping action is controlled by electrical signals that pass through the heart muscle. The electrical signals causes the two pairs of heart chambers (left and right atria and ventricles) to contract in a regular manner that produces the heartbeat. If the electrical activity in the heart is disturbed for any reason, irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) of various types can result. These can seriously undermine the pumping action of the heart and result in inefficient blood circulation around the body. Dobutamine is a sympathomimetic drug used in the treatment of heart failure and cardiogenic shock. Its primary mechanism is direct stimulation of 1 receptors of the sympathetic nervous system. The effects of this drug include positive inotropic effects with minimal changes in chronotropic activities or systemic vascular resistance. For these reasons, dobutamine is useful in managing congestive heart failure when an increase in heart rate is not desired. Nitroglycerin has a dose-dependent vasodilator effect in arteries and veins and is active in the systemic and pulmonary circulations. When the drug is given by continuous infusion, venous dilator effects are prominent at low dose rates. As low-dose infusions are titrated upward, the earliest response is a decrease in cardiac filling pressures (i.e., central venous pressure and wedge pressure) with little or no change in cardiac output. As the dose rate is increased further, the cardiac output begins to rise as a result of progressive arterial vasodilation. Further increases in the dose rate will eventually produce a drop in blood pressure
5. Explain the purpose of the swan-ganz catheter in Mr. Romulo. What are the potential complications associated with its use? The purpose of Swan-Ganz or PAC (pulmonary artery catheterization) is the insertion of a catheter into a pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery catheter allows direct, simultaneous measurement of pressures in the right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery, and the filling pressure ("wedge" pressure) of the left atrium. Some of the potential complications with its use are; arrhythmias, rupture of the pulmonary artery, thrombosis, infection, pneumothorax and bleeding.
Hematologic study Haemoglobin (Hgb)
Actual finding 10.3 % g/dl
Normal finding 13-18 g/dl
Implications Transports oxygen to the cell. Low Hgb may indicate frequent angina episodes or MI Glucose level increases in stressful situation. When mobilization of endogenous epinephrine results in conversion of liver glycogen to glucose. Decreased potassium level may cause many forms of dysrhythmias including life threatening ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation. Absorption of calcium, maintenance of potassium stores and metabolism of ATP. Plays a major role in CHO, CHON synthesis and muscular contraction.
Hematocrit (Hct) Glucose
33% 250 mg/dl
42-52% 60-100 mg/dl
Potassium
3.2 mmo/L
3.5-5 mmo/l
Magnesium
1.5
1.3-2.3
ABG COMPONENT pH PO2 PCO2 HCO3 SaO2
Actual finding 7.3 156 mmHg 48 mmHg 16mmol/L 96%
Nomal Value 7.35-7.45 80-100 35-45 22-26 95-100%
Implication
Вам также может понравиться
- Nutrition in PregnancyДокумент60 страницNutrition in PregnancylarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- Care of Patients With Neurological DisordersДокумент82 страницыCare of Patients With Neurological Disorderslarissedeleon100% (1)
- MNT in Diabetes and Related Disorders and StrategiesДокумент122 страницыMNT in Diabetes and Related Disorders and StrategieslarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- NCM 102 Power and PsycheДокумент13 страницNCM 102 Power and Psychelarissedeleon100% (1)
- Pathophysiology FinalДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology FinallarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- NCM 102 Post Partal Complications HemorrhageДокумент10 страницNCM 102 Post Partal Complications HemorrhagelarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- Pre Gestational ConditionsДокумент17 страницPre Gestational Conditionslarissedeleon100% (2)
- NCM 102 - Anesthesia and AnalgesiaДокумент3 страницыNCM 102 - Anesthesia and AnalgesialarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- Prolonged Labor Complications and Fetal MalpositionsДокумент9 страницProlonged Labor Complications and Fetal Malpositionslarissedeleon100% (1)
- NCM 102 - High Risk NewbornДокумент4 страницыNCM 102 - High Risk NewbornlarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- COMDISEASEДокумент39 страницCOMDISEASElarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- NCM 102 Puerperal InfectionДокумент8 страницNCM 102 Puerperal InfectionlarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- CA 2 LMR Handout 2s1314Документ8 страницCA 2 LMR Handout 2s1314larissedeleonОценок пока нет
- Myocardial InfarctionДокумент4 страницыMyocardial InfarctionlarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- CVD Infarct-HpniiДокумент3 страницыCVD Infarct-HpniilarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- PRC Cases FormДокумент4 страницыPRC Cases FormlarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisДокумент13 страницAcute TonsillopharyngitislarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- NursesДокумент2 страницыNursesDhingskie100% (5)
- Ketoacidosis, DysrhythmiasДокумент39 страницKetoacidosis, DysrhythmiaslarissedeleonОценок пока нет
- Cervical Cancer 2.0Документ9 страницCervical Cancer 2.0larissedeleonОценок пока нет
- Chapters15 20&24Документ64 страницыChapters15 20&24larissedeleonОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Auto GasketsДокумент24 страницыAuto GasketspilveniОценок пока нет
- Files For Everybody #05 Evocation SpellsДокумент7 страницFiles For Everybody #05 Evocation SpellsMark PorterОценок пока нет
- 5797 5537 308.8104.3.4-1 Serie 4E ENДокумент2 страницы5797 5537 308.8104.3.4-1 Serie 4E ENRajeevОценок пока нет
- Kellen Beckwith Coaching ResumeДокумент1 страницаKellen Beckwith Coaching Resumeapi-298433593Оценок пока нет
- 2022-23 UEFA Women's Champions League - WikipediaДокумент22 страницы2022-23 UEFA Women's Champions League - WikipediaLidetu HabtmichaelОценок пока нет
- Gas Turbine Parts and ComponentsДокумент16 страницGas Turbine Parts and ComponentsMorgen GumpОценок пока нет
- MessageДокумент2 страницыMessagePok LovОценок пока нет
- Treasure HuntДокумент4 страницыTreasure HuntJe RomeОценок пока нет
- Performance Evaluation Test 101Документ8 страницPerformance Evaluation Test 101moB0BОценок пока нет
- Ally From The EastДокумент6 страницAlly From The EastqmebtcuzoОценок пока нет
- Idc4 Inglese v2Документ8 страницIdc4 Inglese v2Matt MarkОценок пока нет
- 895 KW 1,200 HP: Gross HorsepowerДокумент16 страниц895 KW 1,200 HP: Gross HorsepowerYuzar StuffОценок пока нет
- Airthmatic Reasoning 2Документ4 страницыAirthmatic Reasoning 2Lass RoparОценок пока нет
- Hamstring Strains. Classification and ManagementДокумент3 страницыHamstring Strains. Classification and ManagementJesusNavarrete97Оценок пока нет
- 05 11 2021 CW Not EligibleДокумент56 страниц05 11 2021 CW Not Eligiblemaanik bhardwajОценок пока нет
- Conditionals Workshop - Review For The Exam: 1. Choose The Right FormДокумент4 страницыConditionals Workshop - Review For The Exam: 1. Choose The Right FormDAYANNA MERCADOОценок пока нет
- Soft palate and tongue exercises strengthen musclesДокумент5 страницSoft palate and tongue exercises strengthen musclesTomeziy StrivesОценок пока нет
- Pinan Sono Ichi v7Документ4 страницыPinan Sono Ichi v7Bzchut HaBaba SaliОценок пока нет
- Jan 2020 - Jnanagangothri E-MagazineДокумент78 страницJan 2020 - Jnanagangothri E-MagazineShivu KiranОценок пока нет
- Fallschirmjäger Stug Assault Gun Company German 67: Pick List: Card ListДокумент1 страницаFallschirmjäger Stug Assault Gun Company German 67: Pick List: Card ListAlexander ShereshovetsОценок пока нет
- RE505 Service PartsДокумент2 страницыRE505 Service PartsJose Felipe EstradaОценок пока нет
- Anima Creature SheetДокумент1 страницаAnima Creature Sheetshogunboy100% (1)
- Modern Chess Strategy PDFДокумент162 страницыModern Chess Strategy PDFSoham Saha100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration MDL361Документ46 страницCellular Respiration MDL361Krystal CraigОценок пока нет
- 250 SEF-R and 300 SEF-R Workshop ManualДокумент75 страниц250 SEF-R and 300 SEF-R Workshop Manualbouvret100% (1)
- Physio Ex 9.0 Ejercio 6Документ5 страницPhysio Ex 9.0 Ejercio 6Anthony Huaman AlayoОценок пока нет
- K9K - Dci 75, Dci 90, Dci 110 1.5 Turbo DieselДокумент4 страницыK9K - Dci 75, Dci 90, Dci 110 1.5 Turbo DieselGcmarshall8267% (6)
- VI 8 Body MovementsДокумент16 страницVI 8 Body MovementsManisha VarmaОценок пока нет
- Is golf an Olympic sport? Why it took so long to become oneДокумент3 страницыIs golf an Olympic sport? Why it took so long to become oneMumtahina OishyОценок пока нет
- DCT Dual Clutch TransmissionДокумент16 страницDCT Dual Clutch TransmissionSudharshan SrinathОценок пока нет