Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Generic Name: Brand Name:: Classifications
Загружено:
billyktoubattsОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Generic Name: Brand Name:: Classifications
Загружено:
billyktoubattsАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
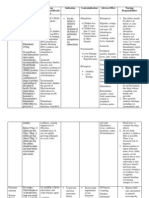
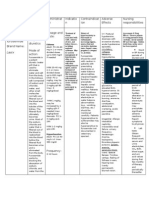
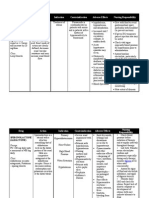
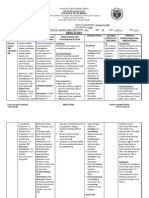
GENERIC NAME: FUROSEMIDE Brand name: Apo-Furosemide (CAN), Furosemide Special (CAN), Lasix Classifications: Loop diuretic
DOSE & ROUTES: IM: IV: 20-40 mg, may repeat in 12 hr and increase by 20 mg every 1-2 hr until response is obtained; PO: 20-80 mg/day as a single dose initially, may repeat in 6-8 hr ADULTS Edema: Initially, 2080 mg/day PO as a single dose. If needed, a second dose may be given in 68 hr. If response is unsatisfactory, dose may be increased in 20- to 40-mg increments at 6- to 8-hr intervals. Up to 600 mg/day may be given. Intermittent dosage schedule (24 consecutive days/wk) is preferred for maintenance, or 2040 mg IM or IV (slow IV injection over 12 min). May increase dose in increments of 20 mg in 2 hr. High-dose therapy should be given as infusion at rate not exceeding 4 mg/min. Acute pulmonary edema: 40 mg IV over 12 min. May be increased to 80 mg IV given over 12 min if response is unsatisfactory after 1 hr. Hypertension: 40 mg bid PO. If needed, additional antihypertensive agents may be added. PEDIATRIC PATIENTS Avoid use in premature infants: stimulates prostaglandin E2 synthesis and may increase incidence of patent ductus arteriosus and complicate respiratory distress syndrome. Edema: Initially, 2 mg/kg/day PO. If needed, increase by 12 mg/kg in 68 hr. Do not exceed 6 mg/kg. Adjust maintenance dose to lowest effective level. Pulmonary edema: 1 mg/kg IV or IM. May increase by 1 mg/kg in 2 hr until the desired effect is seen. Do not exceed 6 mg/kg. PATIENTS WITH RENAL IMPAIRMENT
Up to 4 g/day has been tolerated. IV bolus injection should not exceed 1 g/day given over 30 min. Parenteral: IM:10 mg/mL Oral : Tablets-20,40,80 mg; oral solution 10mg/mL, 40mg/5 mL
Therapeutic Action: Furosemide inhibits reabsorption of Na and chloride mainly in the medullary portion of the ascending Loop of Henle. Excretion of potassium and ammonia is also increased while uric acid excretion is reduced. It increases plasma-renin levels and secondary hyperaldosteronism may result. Furosemide reduces BP in hypertensives as well as in normotensives. It also reduces pulmonary oedema before diuresis has set in. Indications: Ad Oral, IV: Edema associated with CHF, cirrhosis, renal disease IV: Acute pulmonary edema Oral: Hypertension
Adverse effects: Fluid and electrolyte imbalance. Rashes, photosensitivity, nausea, diarrhoea, blurred vision, dizziness, headache, hypotension. Bone marrow depression (rare), hepatic dysfunction. Hyperglycaemia, glycosuria, ototoxicity. Potentially Fatal: Rarely, sudden death and cardiac arrest. Hypokalaemia and magnesium depletion can cause cardiac arrhythmias.
Nursing Responsibilities: Observe 15 rights in drug administration. Assess closely for signs of vascular thrombosis and embolism, particularly in the elderly Assess for other contraindications.
During After
With rapid diaresis, observe for dehydration and circulatory collapse; monitor BP and pulse In CHF or chronic renal failure, oral and parenteral doses of 2 2.5g/day are well tolerated Give direct IV doses slowly over 1-2 minutes. Monitor electrolytes; observe for signs and symptoms of hypokalemia Educate patient about side effects. Immediately report any muscle weakness/ cramps, dizziness, numbness or tingling Drug may cause BP drop. Change positions from lying to standing slowly Do proper documentation
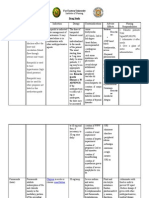
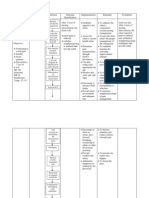
Assessment:
History: Allergy to furosemide, sulfonamides, tartrazine; electrolyte depletion anuria, severe renal failure; hepatic coma; SLE; gout; diabetes mellitus; lactation, pregnancy Physical: Skin color, lesions, edema; orientation, reflexes, hearing; pulses, baseline ECG, BP, orthostatic BP, perfusion; R, pattern, adventitious sounds; liver evaluation, bowel sounds; urinary output patterns; CBC, serum electrolytes (including calcium), blood sugar, LFTs, renal function tests, uric acid, urinalysis, weight
Intervention: BLACK BOX WARNING: Profound diuresis with water and electrolyte depletion can occur; careful medical supervision is required. Administer with food or milk to prevent GI upset. Reduce dosage if given with other antihypertensives; readjust dosage gradually as BP responds. Give early in the day so that increased urination will not disturb sleep. Avoid IV use if oral use is at all possible. WARNING: Do not mix parenteral solution with highly acidic solutions with pH below 3.5. Do not expose to light, may discolor tablets or solution; do not use discolored drug or solutions. Discard diluted solution after 24 hr. Refrigerate oral solution. Measure and record weight to monitor fluid changes. Arrange to monitor serum electrolytes, hydration, liver and renal function.
Arrange for potassium-rich diet or supplemental potassium as needed.
Health teaching: Record intermittent therapy on a calendar or dated envelopes. When possible, take the drug early so increased urination will not disturb sleep. Take with food or meals to prevent GI upset. Weigh yourself on a regular basis, at the same time and in the same clothing, and record the weight on your calendar. Blood glucose levels may become temporarily elevated in patients with diabetes after starting this drug. You may experience these side effects: Increased volume and frequency of urination; dizziness, feeling faint on arising, drowsiness (avoid rapid position changes; hazardous activities, like driving; and consumption of alcohol); sensitivity to sunlight (use sunglasses, wear protective clothing, or use a sunscreen); increased thirst (suck on sugarless lozenges; use frequent mouth care); loss of body potassium (a potassium-rich diet or potassium supplement will be needed).
Report loss or gain of more than 3 pounds in 1 day, swelling in your ankles or fingers, unusual bleeding or bruising, dizziness, trembling, numbness, fatigue, muscle weakness or cramps.
Вам также может понравиться
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcОт EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcОценок пока нет
- FurosemideДокумент4 страницыFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drugs For EmergencyДокумент25 страницDrugs For EmergencyJunathan L. DelgadoОценок пока нет
- Availability: Verapamil HydrochlorideДокумент21 страницаAvailability: Verapamil Hydrochloridesteffy sojanОценок пока нет
- Generic Name LasixДокумент4 страницыGeneric Name LasixSabita PaudelОценок пока нет
- The 10 Most Common Emergency DrugsДокумент28 страницThe 10 Most Common Emergency DrugsKrishna BalsarzaОценок пока нет
- ER Drug StudyДокумент13 страницER Drug StudyJaessa FelicianoОценок пока нет
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Документ13 страницEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoОценок пока нет
- Enalapril MaleateДокумент4 страницыEnalapril Maleateapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyДокумент39 страницEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyJenny Rose GriñoОценок пока нет
- Propranolol HydrochlorideДокумент8 страницPropranolol HydrochlorideKrima PatelОценок пока нет
- Dosage / Frequency Classification Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilititesДокумент4 страницыDosage / Frequency Classification Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilititesEmm Estipona HaoОценок пока нет
- Furosemide Drug ProfileДокумент34 страницыFurosemide Drug ProfileNur Ilmi SofiahОценок пока нет
- Lascuna-Drug StudyДокумент8 страницLascuna-Drug StudyAiza Pearl LascuñaОценок пока нет
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideДокумент3 страницыLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study Case PresentationДокумент5 страницDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaОценок пока нет
- FUROSEMIDEДокумент2 страницыFUROSEMIDEa_lavina02Оценок пока нет
- Icu Drug StudyДокумент7 страницIcu Drug StudyHazel Palomares100% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент9 страницDrug StudyEzshkha OngueОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент17 страницDrug StudyJoan RabeОценок пока нет
- Mata Drug Study FurosemideДокумент14 страницMata Drug Study FurosemideNicole Keesha MataОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент5 страницDrug StudyVic MagtotoОценок пока нет
- DRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateДокумент4 страницыDRUG STUDY Magnesium SulfateTempoОценок пока нет
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityДокумент5 страницDrug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoana Marie GuanОценок пока нет
- Drugs StudyДокумент35 страницDrugs StudyMark CapillanesОценок пока нет
- Propranolol Hydro ChlorideДокумент4 страницыPropranolol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsДокумент34 страницыDrug Study On Emergency DrugsMei-mei ZhuangОценок пока нет
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyДокумент33 страницыEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyNicole GarciaОценок пока нет
- DiazepamДокумент5 страницDiazepamapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsДокумент14 страницDrug Study On Emergency Drugsjcarysuitos100% (4)
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyДокумент8 страницEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyShaine WolfeОценок пока нет
- Drus Study AaaaaaДокумент6 страницDrus Study AaaaaamarkharoldОценок пока нет
- Parenteral NutritionДокумент5 страницParenteral NutritionReanne PaulineОценок пока нет
- RamiprilДокумент3 страницыRamiprilapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL ClassificationsДокумент5 страницTherapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL ClassificationsAbby MontealegreОценок пока нет
- FamotidineДокумент3 страницыFamotidineapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- Labs Drug Study 1Документ17 страницLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoОценок пока нет
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsДокумент14 страницDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRene John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- w15 - Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыw15 - Drug StudyGeneva LatorreОценок пока нет
- Lisinopril PDFДокумент3 страницыLisinopril PDFHannaОценок пока нет
- 33-36 Medications PDFДокумент15 страниц33-36 Medications PDFJeraldine GumpalОценок пока нет
- Methadone Hydro ChlorideДокумент4 страницыMethadone Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Furosemide - Drug InformationДокумент12 страницFurosemide - Drug InformationMuhammad Isnaini ZuhriОценок пока нет
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oДокумент5 страницFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- TheophyllineДокумент6 страницTheophyllineapi-3797941100% (1)
- Brand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilДокумент3 страницыBrand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilPoinsithia OrlandaОценок пока нет
- Metformin: Dosing & UsesДокумент8 страницMetformin: Dosing & UsesMaria Alejandra Siachoque JaraОценок пока нет
- Furosemide Mims EngДокумент17 страницFurosemide Mims EngNur Ilmi SofiahОценок пока нет
- Less 2 Hrs After Meal: Goals For Blood Glucose Levels During Pregnany: 95 MG/DL or Less Before Meals and 120 MG/DL orДокумент6 страницLess 2 Hrs After Meal: Goals For Blood Glucose Levels During Pregnany: 95 MG/DL or Less Before Meals and 120 MG/DL orspain michaelisОценок пока нет
- High Alert MedicationsДокумент17 страницHigh Alert MedicationsJoanna Marie Datahan EstomoОценок пока нет
- Bumetanide (Drug Study)Документ2 страницыBumetanide (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse68880% (1)
- CVS PART 1 DiureticsДокумент31 страницаCVS PART 1 Diureticshishamasmaa5Оценок пока нет
- Metformin Hydrochloride PDFДокумент4 страницыMetformin Hydrochloride PDFHannaОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Документ13 страницCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaОценок пока нет
- gddrg0009 - 24652-Furosemide (Frusemide) - Intravenous v7 Final New Appendix, Continuous OnlyДокумент7 страницgddrg0009 - 24652-Furosemide (Frusemide) - Intravenous v7 Final New Appendix, Continuous Onlyأركان هيلث Arkan healthОценок пока нет
- V. Phenothiazines (ALIPHATIC)Документ3 страницыV. Phenothiazines (ALIPHATIC)Christine Pialan SalimbagatОценок пока нет
- Aripiprazole AbilifyДокумент2 страницыAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesОт EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Scope and LimitationДокумент1 страницаScope and Limitationbillyktoubatts100% (1)
- NCP Schizoprenia 4Документ3 страницыNCP Schizoprenia 4billyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- School of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeДокумент2 страницыSchool of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegebillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Bibliography Pre FInalДокумент5 страницBibliography Pre FInalbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Otitis Media NCPДокумент2 страницыOtitis Media NCProneln100% (9)
- DS BiperidenДокумент3 страницыDS BiperidenbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- NCP SchizopreniaДокумент4 страницыNCP SchizopreniabillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Course in The Ward Date, Doctor'S Order AnalysisДокумент8 страницCourse in The Ward Date, Doctor'S Order AnalysisbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Table of ContentsДокумент6 страницTable of ContentsbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Pscyhe Drawing InterpretationДокумент2 страницыPscyhe Drawing InterpretationbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- THESIS Significance of The StudyДокумент1 страницаTHESIS Significance of The Studybillyktoubatts70% (10)
- RpinsideorДокумент8 страницRpinsideorbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Scope and LimitationДокумент1 страницаScope and Limitationbillyktoubatts100% (1)
- Nursing Research ReviewerДокумент2 страницыNursing Research ReviewerbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- DS BiperidenДокумент3 страницыDS BiperidenbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент1 страницаChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasebillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Geria ReviewerДокумент2 страницыGeria ReviewerbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Psych Case Study GenogramДокумент1 страницаPsych Case Study GenogrambillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementati ON Rationale EvaluationДокумент4 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementati ON Rationale EvaluationbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- NCP Schizoprenia 4Документ3 страницыNCP Schizoprenia 4billyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- DS BiperidenДокумент3 страницыDS BiperidenbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- DS HaloperidolДокумент3 страницыDS HaloperidolbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- DS HaloperidolДокумент3 страницыDS HaloperidolbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Assignment Neurologic Assessment (Reflex)Документ4 страницыAssignment Neurologic Assessment (Reflex)billyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- GORDON Sample 65 Yrs OldДокумент2 страницыGORDON Sample 65 Yrs OldbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Signs and Symptoms Causes Risk Factors Lab Tets and DX TreatmentДокумент1 страницаSigns and Symptoms Causes Risk Factors Lab Tets and DX TreatmentbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- GORDON Sample 65 Yrs OldДокумент2 страницыGORDON Sample 65 Yrs OldbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Ii Anatomy+and+physiologyДокумент2 страницыIi Anatomy+and+physiologybillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- A Community Diagnosis of Barangay Addition Hills, Block 38 of Welfare Ville, Mandaluyong CityДокумент1 страницаA Community Diagnosis of Barangay Addition Hills, Block 38 of Welfare Ville, Mandaluyong CitybillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Case Study GoiterДокумент12 страницCase Study GoiterbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет