Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fracture Intro
Загружено:
Shiela Marie CastroАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fracture Intro
Загружено:
Shiela Marie CastroАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
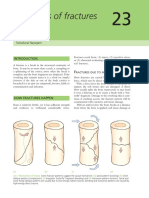
Introduction A fracture by definition is a break in the continuity of bone.
There are many causes of fractures but the most common cause if trauma, an impact or stress to the bone. There are also pathologic conditions that affect the density and strength of the bone structure thus resulting in what is known as a Pathologic Fracture. Generally fractures are classified according to the cause, extent and appearance of breakage. There are many types of fractures, but the main categories are displaced, non-displaced, open, and closed. Displaced and non-displaced fractures refer to the way the bone breaks. In a displaced fracture, the bone snaps into two or more parts and moves so that the two ends are not lined up straight. If the bone is in many pieces, it is called a comminuted fracture. In a nondisplaced fracture, the bone cracks either part or all of the way through, but does move and maintains its proper alignment. A closed fracture is when the bone breaks but there is no puncture or open wound in the skin. An open fracture is one in which the bone breaks through the skin; it may then recede back into the wound and not be visible through the skin. Other fracture types are: Greenstick fracture: an incomplete fracture in which the bone is bent. This type occurs most often in children. Transverse fracture is a fracture at a right angle to the bone's axis. Oblique fracture is a fracture in which the break has a curved or sloped pattern. Comminuted fracture is a fracture in which the bone fragments into several pieces. An impacted fracture is one whose ends are driven into each other. This is commonly seen in arm fractures in children and is sometimes known as a buckle fracture. Other types of fracture are pathologic fracture, caused by a disease that weakens the bones, and stress fracture, a hairline crack. Other types of fracture are pathologic fracture, caused by a disease that weakens the bones, and stress fracture. (KarriemNorwood, MD, 2012) The severity of a fracture depends upon its location and the damage done to the bone and tissue near it. Serious fractures can have dangerous complications if not treated promptly; possible complications include damage to blood vessels or nerves and infection of the bone (osteomyelitis) or surrounding tissue. Recuperation time varies depending on the age and health of the patient and the type of fracture. A minor fracture in a child may heal within a few weeks; a serious fracture in an older person may take months to heal. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons) Treatment depends on the extent of the fracture in the case of the client, an Open Reduction Internal Fixation pinning was proposed, in which pins and rods are inserted to align the broken bone fragments. Prognosis is generally good and management is generally directed towards pain management and rehabilitation.
Вам также может понравиться
- Dosage CalculationsДокумент39 страницDosage CalculationsShiela Marie Castro100% (2)
- Nursing ManagementДокумент84 страницыNursing ManagementShiela Marie CastroОценок пока нет
- Philippine Red Cross: Lapu-Lapu/Cordova Health ServicesДокумент33 страницыPhilippine Red Cross: Lapu-Lapu/Cordova Health ServicesShiela Marie Castro100% (1)
- Directing FunctionДокумент70 страницDirecting FunctionShiela Marie CastroОценок пока нет
- Anesthetic DrugsДокумент7 страницAnesthetic DrugsSpahneОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology AspirinДокумент14 страницPharmacology AspirinShiela Marie CastroОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- 2017 Guidelines ACP OsteoporosisДокумент27 страниц2017 Guidelines ACP OsteoporosisSolange Vargas LiclaОценок пока нет
- Jurnal 3Документ7 страницJurnal 3chloramphenicolОценок пока нет
- NCM 104 Musculo Anaphy, DxticsДокумент80 страницNCM 104 Musculo Anaphy, DxticsJordz PlaciОценок пока нет
- Bone, Joints and Muscle InjuriesДокумент35 страницBone, Joints and Muscle InjuriesCdrrmc DigosОценок пока нет
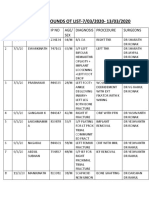
- Unit 2 Grandrounds Ot ListДокумент2 страницыUnit 2 Grandrounds Ot ListBhavvОценок пока нет
- NBCOPAДокумент22 страницыNBCOPAollaОценок пока нет
- Fractures of The Humerus in The Neonatal PeriodДокумент4 страницыFractures of The Humerus in The Neonatal PeriodSandroОценок пока нет
- Maxillofacial Trauma and Management - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Документ24 страницыMaxillofacial Trauma and Management - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Vinnie SinghОценок пока нет
- Beach Bunny Bimbos With BlastersДокумент66 страницBeach Bunny Bimbos With BlastersDonald Thomas50% (2)
- Dsem TRM 0815 0473 1 - LRДокумент28 страницDsem TRM 0815 0473 1 - LRFitri Cii CeriaОценок пока нет
- Fractures in ChildrenДокумент5 страницFractures in ChildrenAbigaille ChuaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент5 страницNursing Care PlanLaceth Joyce T. LASATОценок пока нет
- 1st Lecture (NCM106 ABC I) Care of Clients in Cellular Aberrations, ABC, Emergency and Disaster NursingДокумент14 страниц1st Lecture (NCM106 ABC I) Care of Clients in Cellular Aberrations, ABC, Emergency and Disaster NursingKamx Mohammed100% (1)
- Apley MSK Orthopedi-706-771Документ66 страницApley MSK Orthopedi-706-771Jimly AsshiddiqieОценок пока нет
- Bone Biomechanics - AgingДокумент59 страницBone Biomechanics - AgingpupuliciouzОценок пока нет
- Surgery Short QuestionsДокумент22 страницыSurgery Short QuestionsDevanshОценок пока нет
- Subtrochanteric Femur Fractures: Current Review of ManagementДокумент7 страницSubtrochanteric Femur Fractures: Current Review of ManagementErmiОценок пока нет
- Z Effect & Reverse Z Effect in PFNДокумент7 страницZ Effect & Reverse Z Effect in PFNNandan SurОценок пока нет
- Ankita KhandelwalДокумент26 страницAnkita Khandelwaldr. saОценок пока нет
- "Approwed" On The Meeting of The Department of Surgical Dentistry and Maxillofacial SurgeryДокумент10 страниц"Approwed" On The Meeting of The Department of Surgical Dentistry and Maxillofacial SurgeryMadeline WanhartОценок пока нет
- Ngueguim 2013Документ7 страницNgueguim 2013tri sutrianiОценок пока нет
- Mapeh9 1st Quarterly Assessment - FinalДокумент6 страницMapeh9 1st Quarterly Assessment - FinalmaikoОценок пока нет
- SoK Ortho MedExДокумент14 страницSoK Ortho MedExsharvindan subramaniamОценок пока нет
- Nikita (2021) IntroductionBurnedRemainsДокумент65 страницNikita (2021) IntroductionBurnedRemainsangela milena murcia sepulvedaОценок пока нет
- Back Pain and FracturesДокумент2 страницыBack Pain and FracturesAlex CostaОценок пока нет
- Elastic Bandage Applying PDFДокумент4 страницыElastic Bandage Applying PDFDaniIrawanОценок пока нет
- Orthopaedic PocketДокумент22 страницыOrthopaedic PocketAbdullah AzmyОценок пока нет
- Scary NCLEX Topics Student Workbook 2020Документ23 страницыScary NCLEX Topics Student Workbook 2020Kristen Nate100% (2)
- X-Ray Interpretation Skills: Dr. Hisham AlsanawiДокумент68 страницX-Ray Interpretation Skills: Dr. Hisham AlsanawiVika DamayОценок пока нет
- Health Promotion and MaintenanceДокумент3 страницыHealth Promotion and MaintenanceYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)Оценок пока нет