Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Icarr
Загружено:
Meena Sukumar0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
22 просмотров2 страницыColor each label in a different color and, where appropriate, color the structure indicated. The pharynx is a musculomembranous chamber common to the digestive and repiratory tracts. The rodlike lyssa consists of adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and some cartilage.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
icarr
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документColor each label in a different color and, where appropriate, color the structure indicated. The pharynx is a musculomembranous chamber common to the digestive and repiratory tracts. The rodlike lyssa consists of adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and some cartilage.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
22 просмотров2 страницыIcarr
Загружено:
Meena SukumarColor each label in a different color and, where appropriate, color the structure indicated. The pharynx is a musculomembranous chamber common to the digestive and repiratory tracts. The rodlike lyssa consists of adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and some cartilage.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Dog Antatomy a Coloring Atlas
Oral Cavity, Tongue, Pharynx and Esophagus
PLATE 51
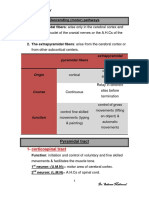
Figure 1 Right lateral view of a sagittal section of a dogs head. Figure 2. Dorsal view of the tongue and dissected laryngopharynx, trachea and esophagus. Figure 3. A puppys tongue. Color each label in a different color and, where appropriate, color the structure indicated. The pharynx is a musculomembranous chamber common to the digestive and repiratory tracts. Its three parts are: 1) Oropharynx ventral to the soft palate, 2) nasopharynx dorsal to the soft palate, extending caudad from the choanae (exits from the nasal fossa on each side), 3) laryngopharynx - dorsal to the layrnx and leading into the esophagus. During swallowing, muscles raise the tongue, pressing food and water against the hard palate. The soft palate is elevated. The root of the tongue moves caudad and dorsad in a boltlike manner, pushing the epiglottis partially over the laryngeal entrance. The rima glottidis (space between the vocal folds) in the larynx is narrowed. Pressure by pharyngeal muscles forces food or water into the esophagus where automatic contractions carry food through to the stomach. Color the dashed line indicating the movement of food or water. During breathing, the free edge of the soft palate is usually (but not always) under the epiglottis , and the larygeal entrance is open(See Plate 67). Within the apex of the tongue, the rodlike lyssa consists of adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and some cartilage. In olden times, the lyssa was thought to be the cause of rabies, and it is was sometimes removed to cure the disease. What a place for ones hands! Lyssa is also a synonym for rabies. Vallate, foliate and fungiform papillae contain taste buds, a complex of gustatory (taste) cells, supporting cells and nerve endings. Conical, filiform and marginal papillae do not contain taste buds. Marginal papillae on a neonatal (newborn) puppys tongue assist in suckling. As the diet changes from milk to solid food, marginal papillae regress until they no longer exist.
Digestive System
Plate 51 - Oral Cavity, Tongue, Pharynx and Esophagus
Figure 1 Nasopharynx
Oropharynx Choana Hard palate Nasal cavity Air
Food and water Oral cavity Lyssa Tongue
Laryngopharynx Esophagus Larynx Trachea Figure 2 Laryngopharynx Thyroid gland Soft palate Epiglottis
Genioglossal m. Geniohyoid m. Mylohyoid m.
Left palatine tonsil (in tonsillar fossa) Foliate papillae Vallate papillae Apex of tongue
Median groove
Esophagus Trachea Laryngeal entrance Epiglottis Base of tongue Conical papillae Filiform papillae Fungiform papillae
Figure 3
Marginal papillae
Вам также может понравиться
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Tympanoplasty Indications, Types, ProcedureДокумент55 страницTympanoplasty Indications, Types, ProcedurePrasanna DattaОценок пока нет
- Paint Draw Paint, With Ross Bowns - Drawing Basics - Drawing The Head, A Step by Step of The Constructive MethodДокумент13 страницPaint Draw Paint, With Ross Bowns - Drawing Basics - Drawing The Head, A Step by Step of The Constructive MethodSoc Rua Nguyen100% (1)
- BonesДокумент25 страницBonesJohnvee Magana100% (2)
- Functional Areas of Cerebral CortexДокумент3 страницыFunctional Areas of Cerebral CortexMatet MonjeОценок пока нет
- Growth and Development OF Nasomaxillary ComplexДокумент41 страницаGrowth and Development OF Nasomaxillary ComplexaannuusshhaaОценок пока нет
- Flaps and Grafts in Dermatologic Surgery by Thomas E. Rohrer, Jonathan L. Cook, Andrew J. Kaufman - PDF - WДокумент50 страницFlaps and Grafts in Dermatologic Surgery by Thomas E. Rohrer, Jonathan L. Cook, Andrew J. Kaufman - PDF - WNicolas Tapia RivasОценок пока нет
- 1Документ146 страниц1ijereps100% (2)
- Human Nervous SystemДокумент28 страницHuman Nervous SystemMuhammad HaqОценок пока нет
- Bacillus ReviewДокумент10 страницBacillus ReviewMeena SukumarОценок пока нет
- Bacillus ReviewДокумент10 страницBacillus ReviewMeena SukumarОценок пока нет
- Mill Creek Veterinary ServicesДокумент1 страницаMill Creek Veterinary ServicesMeena SukumarОценок пока нет
- Malayalam CalenderДокумент8 страницMalayalam CalenderMeena SukumarОценок пока нет
- Coffee Lovers Recipes - Have Fun!: 1. Alexander EspressoДокумент1 страницаCoffee Lovers Recipes - Have Fun!: 1. Alexander Espressomeeras600Оценок пока нет
- Wedeen2012-Grid Structure of Brain PathwaysДокумент9 страницWedeen2012-Grid Structure of Brain Pathwaysiulia andreeaОценок пока нет
- Ear MedicationДокумент15 страницEar MedicationPascalina Monts'onyaneОценок пока нет
- For Print - Adult PAДокумент3 страницыFor Print - Adult PAJU DYОценок пока нет
- 11-DeSCENDING Motor PathwaysДокумент15 страниц11-DeSCENDING Motor PathwaysMai OssamaОценок пока нет
- Oston Oston: System Options Professional ReferencesДокумент5 страницOston Oston: System Options Professional Referencesjfcule1Оценок пока нет
- Pituitary Gland Anatomy: Embryologic DevelopmentДокумент9 страницPituitary Gland Anatomy: Embryologic DevelopmentRafaelPetitОценок пока нет
- Reflux Symptom IndexДокумент3 страницыReflux Symptom IndexMuhammad Rizal ArdianaОценок пока нет
- Neuroanatomy Text and Atlas 4 e Inkling Chapter Enhanced Ebook Neuroanatomy Text Atlas Martin 4th Edition Ebook PDFДокумент62 страницыNeuroanatomy Text and Atlas 4 e Inkling Chapter Enhanced Ebook Neuroanatomy Text Atlas Martin 4th Edition Ebook PDFgerald.mims287100% (39)
- Ent, Head and Neck SurgeryДокумент1 страницаEnt, Head and Neck Surgeryjoynal abedeenОценок пока нет
- Anatomy, Head and Neck, Temporomandibular Joint - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfДокумент8 страницAnatomy, Head and Neck, Temporomandibular Joint - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDrishti ShahОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Temporomandibular JointДокумент36 страницAnatomy of Temporomandibular JointMELYANA_WANTIОценок пока нет
- Cranial Nerves TableДокумент1 страницаCranial Nerves TablePIOZRОценок пока нет
- Dev of Hard & Soft PalateДокумент94 страницыDev of Hard & Soft PalatepriyaОценок пока нет
- CNS TumorsДокумент32 страницыCNS TumorsjaveriaОценок пока нет
- Semi-Open Rhinoplasty: Getting Together The Best of Both, Open and Closed RhinoplastyДокумент4 страницыSemi-Open Rhinoplasty: Getting Together The Best of Both, Open and Closed RhinoplastyJorge MarcosОценок пока нет
- PigДокумент34 страницыPigVanessa CarinoОценок пока нет
- Muscles of The Head and NeckДокумент49 страницMuscles of The Head and NeckMarili Camille CoquiaОценок пока нет
- Lec6 2010 08 16Документ7 страницLec6 2010 08 16ocean1234Оценок пока нет
- Meninges PPT NPДокумент21 страницаMeninges PPT NPEmshellr RomeОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Practice QuestionsДокумент5 страницAnatomy Practice Questionsfrank davidОценок пока нет
- Salivary GlandsДокумент18 страницSalivary GlandsSumeet N RautОценок пока нет
- 1 - Cranial Nerve 5, 6,7Документ44 страницы1 - Cranial Nerve 5, 6,7ewijayapalaОценок пока нет