Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
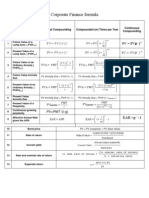
Corporate Finance Formula Sheet
Загружено:
ogsunnyАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
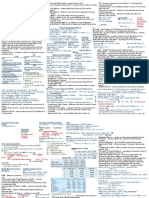
Corporate Finance Formula Sheet
Загружено:
ogsunnyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
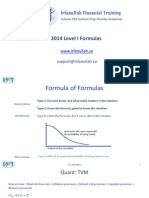
FORMULA SHEET FOR THE FINAL
=1+(D/E)
Earnings Per Share (EPS) = Net Income / Total shares Dividends per Share (DPS) = Total Dividends / Total shares Net Income = Cash Dividends + Addition to retained earnings
Dividend Payout Ratio = Cash Dividends / Net Income Net Working Capital (NWC) = Current Assets (CA) - Current Liabilities (CL)
1/4
CFFA = OCF - NET CAPITAL SPENDING - CHANGE IN NWC Net Capital Sp. = Ending net fixed assets - Beginning net fixed assets + Depreciation Change in NWC = Ending NWC - Beginning NWC CF to creditors = Interest Paid - Net new borrowing CF to stockholders = Dividends paid - Net new equity raised CFFA = CF to creditors + CF to stockholders OCF FORMULAS 1) OCF = EBIT+DEPRECIATION-TAXES 2) OCF = (SALES-COSTS)x(1-T) + DxT 3) OCF = NET INCOME + DEPRECIATION Depreciation tax shield = Depreciation x T Straight-line depreciation "D" = (Initial cost ending book value) / number of years Book value of an asset = initial cost accumulated depreciation After-tax salvage = salvage T(salvage book value) NPV = PV of future cash flows - cost PI = PV of future cash flows / cost AAR = Average Net Income / Average Book Value
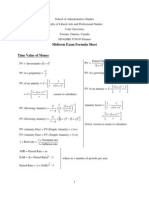
FV = PV (1+r)t PV = FV/(1+r)t r = (FV / PV)1/t 1 t = Ln(FV / PV) / Ln(1 + r) Annuity Future Value
Annuity Present Value
1 1 (1 + r ) t PV = C r
Annual Percentage Rate 1 APR = m (1 + EAR) m - 1 Effective Annual Rate m APR EAR = 1 + 1 m
(1 + r )t 1 FV = C r
PV for a perpetuity = C / r
2/4
1 1 (1 + r) t Bond Value = C r
F + t (1 + r)
Fisher Effect: (1 + R) = (1 + r)(1 + h), where, R = nominal rate, r = real rate, h = expected inflation rate
P0 is the PV of all expected future dividends:
Constant Dividend Case:
P0 =
D1 D2 D3 + + + ... (1 + R)1 (1 + R) 2 (1 + R) 3
P0 =
D R
Dividend Growth Model:
Using DGM to find R:
P0 =
D 0 (1 + g) D = 1 R -g R -g
D 0 (1 + g) D1 = R -g R -g rearrange and solve for R P0 = R= D 0 (1 + g) D +g= 1 +g P0 P0 D1 P0
Dividend yield =
Capital gains yield = g
3/4
Historical variance = sum of squared deviations from the mean / (number of observations 1) Historical Standard deviation = square root of the historical variance Expected Return: Expected Variance: Expected Standard deviation:
E ( R) = pi Ri
i =1
2 = pi ( Ri E ( R )) 2
i =1
= 2
(pi is the probability of state i occurring) Return of a portfolio in state i :
R portfolio,i = w j R j ,i
j
For example, let's say we have 2 assets: A and B and 2 states: boom and recession. Then the portfolio return in each state is calculated as:
where wj is the portfolio weight for asset j Rj,i is the return of asset j in state i
Rportfolio,boom = wAxRA,boom + wBxRB,boom Rportfolio,recession = wAxRA,recession + wBxRB,recession
Value of an unlevered firm (assuming perpetual cash flows) : Without Taxes V L = VU WACC = R A = (E/V)RE + (D/V)RD RE = RA + (RA RD)(D/E) Capital Asset Pricing Model (SML) Cost /Req. Return of Equity RE: Dividend growth model CAPM E(RA) = Rf + A(E(RM) Rf)
VU = EBIT(1-T) / RU With taxes VL = VU + DTC WACC = R A = (E/V)RE + (D/V)(RD)(1-TC) RE = RU + (RU RD)(D/E)(1-TC)
M&M Proposition I M&M Proposition II
P0 = RE =
D1 RE g D1 +g P0
RE = R f + E ( E ( RM ) R f )
Cost/Req. Return Debt: R D = YTM on debt Cost/Req. Return Preferred: R P = D / P0 Weighted Average Cost of Capital a.k.a. WACC = W ExRE + W DxRD(1-TC) + W PxRP V=E+D+P; W E=E/V; W D=D/V; W P=D/V
Page 4
Вам также может понравиться
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionОт EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (8)
- CheatSheet (Finance)Документ1 страницаCheatSheet (Finance)Guan Yu Lim100% (3)
- Kelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6Документ2 страницыKelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6Kelly Koh100% (4)
- Corporate Finance - FormulasДокумент3 страницыCorporate Finance - FormulasAbhijit Pandit100% (1)
- CFA Formula Cheat SheetДокумент9 страницCFA Formula Cheat SheetChingWa ChanОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance Formula SheetДокумент5 страницCorporate Finance Formula SheetChan Jun LiangОценок пока нет
- Finance Cheat SheetДокумент4 страницыFinance Cheat SheetRudolf Jansen van RensburgОценок пока нет
- Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceДокумент6 страницFormulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceNaeemОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance Math SheetДокумент19 страницCorporate Finance Math Sheetmweaveruga100% (3)
- CorpFinance Cheat Sheet v2.2Документ2 страницыCorpFinance Cheat Sheet v2.2subtle69100% (4)
- Corporate Finance FormulasДокумент3 страницыCorporate Finance FormulasMustafa Yavuzcan83% (12)
- Cheat Sheet Corporate - FinanceДокумент2 страницыCheat Sheet Corporate - FinanceAnna BudaevaОценок пока нет
- Cheat Sheet Final - FMVДокумент3 страницыCheat Sheet Final - FMVhanifakih100% (2)
- Corporate Finance CheatsheetДокумент4 страницыCorporate Finance CheatsheetLynetteОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance - Beny W2011Документ38 страницCorporate Finance - Beny W2011cparka12Оценок пока нет
- Time Value of Money FormulasДокумент1 страницаTime Value of Money FormulasAmit Shankar Choudhary100% (1)
- Fnce 100 Final Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыFnce 100 Final Cheat SheetToby Arriaga100% (2)
- CH 10Документ18 страницCH 10prashantgargindia_93Оценок пока нет
- Corporate FinanceДокумент19 страницCorporate FinanceBilal Shahid100% (4)
- CFA Level 1 Corporate Finance - Our Cheat Sheet - 300hoursДокумент14 страницCFA Level 1 Corporate Finance - Our Cheat Sheet - 300hoursMichОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance LSEДокумент66 страницCorporate Finance LSESharon Manzini100% (2)
- FIN6215-Cheat Sheet BigДокумент3 страницыFIN6215-Cheat Sheet BigJojo Kittiya100% (1)
- Investment Banking - How To Become An Investment BankerДокумент193 страницыInvestment Banking - How To Become An Investment BankerMichael Herlache MBA100% (4)
- Fundamentals of Corporate Finance Test BДокумент188 страницFundamentals of Corporate Finance Test Bengel044100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, SlideДокумент250 страницFundamentals of Corporate Finance, SlideYIN SOKHENG100% (4)
- NYSF Walmart TemplateДокумент50 страницNYSF Walmart TemplateTung Ngo100% (2)
- The Statement of Cash Flow - Cheat SheetДокумент3 страницыThe Statement of Cash Flow - Cheat SheetSayorn Monanusa Chin100% (1)
- Bonds Exam Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыBonds Exam Cheat SheetSergi Iglesias CostaОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance - Berk - 4CE - SolutionsДокумент4 страницыCorporate Finance - Berk - 4CE - SolutionsZhichang ZhangОценок пока нет
- Quick Reference To Managerial AccountingДокумент2 страницыQuick Reference To Managerial AccountingAmilius San Gregorio100% (1)
- Corporate FinanceДокумент4 страницыCorporate FinanceMogul Dodger Kevin100% (1)
- Corporate FinanceДокумент398 страницCorporate FinanceLongeni Hendjala100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet For Financial AccountingДокумент1 страницаCheat Sheet For Financial Accountingmikewu101Оценок пока нет
- Corporate FinanceДокумент96 страницCorporate FinanceRohit Kumar80% (5)
- Finance Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыFinance Cheat SheetMarc MОценок пока нет
- BF2201 Cheat Sheet FinalsДокумент2 страницыBF2201 Cheat Sheet Finalssiewhong93100% (1)
- Corporate FinanceДокумент410 страницCorporate Financedavidrill100% (2)
- Test Questions and Solutions True-FalseДокумент99 страницTest Questions and Solutions True-Falsekabirakhan2007100% (1)
- Cheat SheetДокумент3 страницыCheat SheetjakeОценок пока нет
- HBS Case Study - FinanceДокумент8 страницHBS Case Study - Financerahul84803100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet - EXAM Version - BARBARAДокумент2 страницыCheat Sheet - EXAM Version - BARBARAJosé António Cardoso RodriguesОценок пока нет
- IB ManualДокумент466 страницIB ManualSunpreet Singh100% (3)
- Management Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыManagement Cheat Sheetnightmonkey215100% (2)
- Financial Analyst CFA Study Notes: Derivatives Level 1Документ33 страницыFinancial Analyst CFA Study Notes: Derivatives Level 1Andy Solnik100% (7)
- Case 2 Corporate FinanceДокумент5 страницCase 2 Corporate FinancePaula GarciaОценок пока нет
- FIN 401 - Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыFIN 401 - Cheat SheetStephanie NaamaniОценок пока нет
- FRL 300 Formula Sheet Common FinalДокумент3 страницыFRL 300 Formula Sheet Common FinalAnonymous WimU99ilUОценок пока нет
- CFA Level I Formula SheetДокумент27 страницCFA Level I Formula SheetAnonymous P1xUTHstHT100% (4)
- Formula SheetДокумент3 страницыFormula SheetAshley ShaddockОценок пока нет
- Exam Formula SheetДокумент2 страницыExam Formula SheetYeji KimОценок пока нет
- Fin All Formula - Docx 1Документ9 страницFin All Formula - Docx 1Marcus HollowayОценок пока нет
- Finance NoteДокумент19 страницFinance NoteHui YiОценок пока нет
- List of Corporate Finance FormulasДокумент9 страницList of Corporate Finance FormulasYoungRedОценок пока нет
- Important FormulasДокумент5 страницImportant FormulasKhalil AkramОценок пока нет
- Financial Management Formula SheetДокумент2 страницыFinancial Management Formula SheetSantosh Kumar100% (2)
- Formula Sheet-2nd QuizДокумент6 страницFormula Sheet-2nd QuizEge MelihОценок пока нет
- Midterm Exam Formula Sheet: R C G R CДокумент2 страницыMidterm Exam Formula Sheet: R C G R Cleafsfan85Оценок пока нет
- Form 20B: (Refer Section 159 of The Companies Act, 1956)Документ6 страницForm 20B: (Refer Section 159 of The Companies Act, 1956)Surendra DevadigaОценок пока нет
- Income Generating ProjectДокумент5 страницIncome Generating ProjectZwei Gonzaga FernandezОценок пока нет
- Operational Objectives DefinitionДокумент1 страницаOperational Objectives DefinitionZven BlackОценок пока нет
- PFRS 13 - Fair Value MeasurementДокумент7 страницPFRS 13 - Fair Value MeasurementMary Yvonne AresОценок пока нет
- Production Planning and ControlДокумент10 страницProduction Planning and ControlRAlexanderSОценок пока нет
- Team 2 CIA 2Документ12 страницTeam 2 CIA 2Bhoomika BОценок пока нет
- (PPT) QuinnsModel PDFДокумент8 страниц(PPT) QuinnsModel PDFSomchai ChuananonОценок пока нет
- Ge 1Документ3 страницыGe 1Ali KhanОценок пока нет
- Improving Audit Efficiency: Fifteen Tools For Success: Drummond Kahn Director of Audit Services City of Portland, OregonДокумент34 страницыImproving Audit Efficiency: Fifteen Tools For Success: Drummond Kahn Director of Audit Services City of Portland, OregonadeelrahmaniОценок пока нет
- Service Operations Management FOR Imt-Ghaziabad: By: Jaideep SenguptaДокумент41 страницаService Operations Management FOR Imt-Ghaziabad: By: Jaideep SenguptaPrakharОценок пока нет
- Isilon Product FamilyДокумент7 страницIsilon Product FamilyrejnanОценок пока нет
- Bhanu Advani - Prospectus PDFДокумент19 страницBhanu Advani - Prospectus PDFBhanu AdvaniОценок пока нет
- Cyber Incident Response and Planning: A Flexible Approach: FeatureДокумент6 страницCyber Incident Response and Planning: A Flexible Approach: FeatureSenait MebrahtuОценок пока нет
- Eir August2020Документ1 963 страницыEir August2020vahnitejaОценок пока нет
- Huawei Certification Training Flyer-En-SecurityДокумент4 страницыHuawei Certification Training Flyer-En-SecurityPaulo CorreiaОценок пока нет
- Mendoza v. Officers of MWEUДокумент4 страницыMendoza v. Officers of MWEUEva TrinidadОценок пока нет
- Azgard Nine Limited-Internship ReportДокумент102 страницыAzgard Nine Limited-Internship ReportM.Faisal100% (1)
- Trans Sys Chap12Документ30 страницTrans Sys Chap12Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.Оценок пока нет
- Peerless Wire Goods CollectionДокумент2 страницыPeerless Wire Goods Collectionapi-666678197Оценок пока нет
- Audit: Firm Profile and Capacity StatementДокумент25 страницAudit: Firm Profile and Capacity StatementGODFREY JATHOОценок пока нет
- Merger, Acquisition, TakeoverДокумент25 страницMerger, Acquisition, Takeoverpintu_brownyОценок пока нет
- CFA Scholarship 2015 Dec NotificationДокумент1 страницаCFA Scholarship 2015 Dec NotificationZihad Al AminОценок пока нет
- Ethical Tourism PDFДокумент2 страницыEthical Tourism PDFLakeОценок пока нет
- Lec 1 Introduction To Industrial Management - MM112Документ24 страницыLec 1 Introduction To Industrial Management - MM112Asad KhokharОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Marketing in The Internet Age Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент14 страницChapter 3 Marketing in The Internet Age Multiple Choice QuestionsJRMSU Finance OfficeОценок пока нет
- Quantitative Finance Financial Economics Bank Risk Management Applied MicroeconomicsДокумент7 страницQuantitative Finance Financial Economics Bank Risk Management Applied MicroeconomicsRituparna DasОценок пока нет
- OpuДокумент12 страницOpuWho KnowsОценок пока нет
- Royal EnfieldДокумент2 страницыRoyal EnfieldGopinath GovindarajОценок пока нет
- EFFECT OF SUSTAINABLE PROCUREMENT PRACTICES ON OPERATIONAL PERFORMANCE - CASE STUDY GHANA GRID COMPANY LIMITED (GRIDCo)Документ69 страницEFFECT OF SUSTAINABLE PROCUREMENT PRACTICES ON OPERATIONAL PERFORMANCE - CASE STUDY GHANA GRID COMPANY LIMITED (GRIDCo)Korkor Nartey100% (1)
- Sales Quotation: Salesman Sign: Customer SignДокумент1 страницаSales Quotation: Salesman Sign: Customer SignjacobОценок пока нет