Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Copyright 2004 Martian Auctions
Загружено:
humayunkk2002Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Copyright 2004 Martian Auctions
Загружено:
humayunkk2002Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
49
GARAGE
Copyright 2004 Martian Auctions 221
1. Build the foundation and floor
1.1 Carefully mark the location of the garage on your lot. Hire a surveyor to
precisely locate the site for the garage and define the excavation area.
1.2 Have a contractor excavate the designated site to the required depth. He will properly dispose
of the dirt excavated.
1.3 In order to build the foundation, we recommend you contract out this job. The foundation specialist will start with the footing, the
concrete walls and backfilling before making the foundation slab. Make sure that anchor bolts are encased, centered every 4 feet (1.2
m).
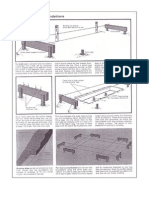
2. Build the walls
2.1 Outside walls
Start the outside walls building them flat on the ground, using lumber with less than 19% moisture content. Wall studs should be
centered every 16 in. (406 mm) and made of 2 x 4 in. (50 x 100 mm) timber. Strengthen the base of the walls with a 4 in. (100
mm) bottom plate in which you will drill holes every 4 ft. (1.2 m) for the anchor bolts.
2.1.1
Copyright 2004 Martian Auctions 222
Separate the top and bottom plate slightly more than a stud's
length apart with the bottom plate positioned nearest the wall's
final location. Center the studs every 16 in. (406 mm). Attach pre-nailed double 2 x 4 in. (50 x 100 mm) top plates above
the studs.
2.1.2 A secondary stud made of two planks solidly nailed together will delineate the sides of the
door or window opening and support the coping.
2.1.3 The lintel (window contour) load will be transmitted to the twin
studs on each side of the opening. To install a lintel, nail a 2 x 10
in. (50 x 254 mm) each wall face. Fill the empty space between
them with insulation material.
2.2 The garage door framing
Build the two short sections on either side of the large opening using
three 2 x 6 in. (50 x 152 mm) studs nailed together. The top part of
the frame (called lintel or header), is made up of three 2 x 10 in. (50 x
254 mm) nailed together then nailed to the trimmer studs of the two
side sections.
2.3 Sheathing and air barrier
Copyright 2004 Martian Auctions 223
2.3.1 The suggested sheathing material is 4 x 8 ft (1.2 x 2.4 m) tarred
fiberboard panels. Use a thin plastic air barrier.
2.3.2 First, apply the sheathing, positioning the panels on the wall (that is still flat on the ground)
and nail to frame with dog nails. Apply the air barrier and nail or staple into place. Lastly,
install fillers every 16 in. (406 mm).
2.4 Before lifting the wall into place, make sure the bottom plate is well
positioned. At this stage, make sure you have enough people to lift and hold
the wall in position while bracing. Nail braces from the top of the wall into
stakes driven into the ground outside the wall and nail the wall upright to hold
it temporarily.
3. Build the roof
3.1 With the walls up, you should close the roof as soon as possible to avoid rain or wind damage
to the inside of your garage. Roof trusses are a pre-built series of structural members
designed to carry the load of the roof to the outside walls. Trusses are built in special
factories to the individual specifications for your garage plans.
Copyright 2004 Martian Auctions 224
3.2 Trusses are designed to resist loads only when they are in a vertical position. That is why
they should not be lifted flat or laid over the top of the outside walls. Gently lift the trusses
mechanically or with a rope and pulley.
3.3 Beginning at one end, measure and mark every 24 in. (610 mm) the location of the roof trusses on the top plate. Nail the trusses
in place.
3.4 With the trusses installed, nail a temporary brace to each one. You can now start putting
up the edge boards. Apply roof sheathing. Plywood or particleboard roof sheathing is
most commonly used, being rigid, durable, non-slip and easy to apply.
3.5 Align panels perpendicular to the rafters and stagger the joints of each course. Panels
should meet in the center of a truss or rafter. Leave a small gap between the panels for
contraction of the material. According to the truss spacing, the horizontal edges of the
panels should be attached every 24 in. (610 mm). To prevent sagging, use sheathing
clips to attach the panels between the trusses.
4. Install doors and windows
Doors usually come with comprehensive installations, a pre-mung door is expensive and if not properly installed, will loose it,s
energy efficiency and will not operate properly in the long run. It is recoomended to have your door indtalled by a professionnal.
However, if you decide to do itself follow these instructions and get some help as they tend to be heavy.
5. Install the asphalt shingles
The next step is to install the asphalt shingles.
Copyright 2004 Martian Auctions 225
6. Install the outside siding
It is now the very last step, the one that has to do with the outside siding.
The construction of a garage is a huge project. Once it is completed you'll be proud of it. You will find it
very useful and not only to put your car away in Winter.
Copyright 2004 Martian Auctions 226
Вам также может понравиться
- A Complete Guide To Building Your Own DeckДокумент16 страницA Complete Guide To Building Your Own DeckAdrian Berna100% (5)
- How To Build A Bomb Shelter-1Документ9 страницHow To Build A Bomb Shelter-1dmac27100% (1)
- Shed 10x16 PlansДокумент8 страницShed 10x16 PlansLory Dena Heath100% (1)
- Hydroponic Cheat SheetДокумент3 страницыHydroponic Cheat SheetNarcisMarin100% (12)
- Building A Garden Shed Step By Step Instructions and PlansОт EverandBuilding A Garden Shed Step By Step Instructions and PlansРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
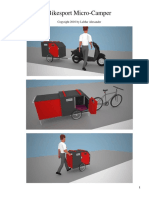
- Bikesport Micro-Camper PDFДокумент15 страницBikesport Micro-Camper PDFviocons72Оценок пока нет
- How To Build A DeckДокумент8 страницHow To Build A DeckDavid Somes100% (2)
- A Complete Guide To Building Your Own Deck PDFДокумент16 страницA Complete Guide To Building Your Own Deck PDFremowood100% (1)
- Build A Colonial-Style Storage Shed - Popular MechanicsДокумент9 страницBuild A Colonial-Style Storage Shed - Popular Mechanicsrockhard4wd9696Оценок пока нет
- Portable Box Stand: How To Build AДокумент5 страницPortable Box Stand: How To Build AJohn E FosterОценок пока нет
- 8x10 Lean To Shed 2022-09-04Документ29 страниц8x10 Lean To Shed 2022-09-04Steven 659Оценок пока нет
- Weatherproofing: The DIY Guide to Keeping Your Home Warm in the Winter, Cool in the Summer, and Dry All Year AroundОт EverandWeatherproofing: The DIY Guide to Keeping Your Home Warm in the Winter, Cool in the Summer, and Dry All Year AroundОценок пока нет
- Bricklaying ManualДокумент24 страницыBricklaying Manualdonaldduck23100% (2)
- Durock Cement Board Installation Guide en CB237 PDFДокумент11 страницDurock Cement Board Installation Guide en CB237 PDFRonald KahoraОценок пока нет
- How to Build a Simple Three Bedroom Shipping Container HouseОт EverandHow to Build a Simple Three Bedroom Shipping Container HouseРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Window Installation BTДокумент18 страницWindow Installation BTArnelyn Angel AbarquezОценок пока нет
- Cabins & Cottages, Revised & Expanded Edition: The Basics of Building a Getaway Retreat for Hunting, Camping, and Rustic LivingОт EverandCabins & Cottages, Revised & Expanded Edition: The Basics of Building a Getaway Retreat for Hunting, Camping, and Rustic LivingОценок пока нет
- Outdoor Storage Locker: Easy To BuildДокумент13 страницOutdoor Storage Locker: Easy To BuildjoseduardoОценок пока нет
- Hacksaw Wire Cutter Laser Level Hammer Measuring Tape Pencil Wall AngleДокумент24 страницыHacksaw Wire Cutter Laser Level Hammer Measuring Tape Pencil Wall AngleCentaur ArcherОценок пока нет
- Atlas Copco Air Compressor Parts Catalog PDFДокумент881 страницаAtlas Copco Air Compressor Parts Catalog PDFLicínio Dâmaso100% (4)
- Dropped/false CeilingДокумент78 страницDropped/false CeilingSamiul Kadri100% (1)
- Mirocabin Plans FinishedДокумент39 страницMirocabin Plans FinishedJeffrey WittyОценок пока нет
- 10 Chapter 16 Composite MaterialsДокумент27 страниц10 Chapter 16 Composite MaterialsZain FarhanОценок пока нет
- Aisi 4140 En8 En19Документ1 страницаAisi 4140 En8 En19Jose KurianОценок пока нет
- Low Cost HousingДокумент48 страницLow Cost HousingManish Solanki71% (7)
- Build A Basement Root CellarДокумент3 страницыBuild A Basement Root Cellarjonjeys100% (1)
- Iso 5149-1 - 2014-04Документ52 страницыIso 5149-1 - 2014-04Raj KumarОценок пока нет
- Fresco Painting - Modern Methods and Techniques for Painting in Fresco and SeccoОт EverandFresco Painting - Modern Methods and Techniques for Painting in Fresco and SeccoОценок пока нет
- Walls FloorsДокумент8 страницWalls Floorsapi-310517163Оценок пока нет
- Build A CarportДокумент6 страницBuild A CarportMilko MilkovОценок пока нет
- Skylight InstallationДокумент9 страницSkylight InstallationJ Paul VarelaОценок пока нет
- Acoustic & Lighting SystemsДокумент18 страницAcoustic & Lighting Systemscyssa2202Оценок пока нет
- STEICO Floor Deck Fixing en IДокумент4 страницыSTEICO Floor Deck Fixing en IClaudiu BaditaОценок пока нет
- Method Statement Partition WorksДокумент3 страницыMethod Statement Partition WorksDipin NediyaparambathОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ7 страницAssignment 1Raj SalviОценок пока нет
- Avalon Log Homes: Construction ManualДокумент34 страницыAvalon Log Homes: Construction ManualyolcharnnguenОценок пока нет
- Thin Brick Installation GuideДокумент12 страницThin Brick Installation GuideGlavanRafaelОценок пока нет
- 8 X 12 Garden Shed 0Документ22 страницы8 X 12 Garden Shed 0Jeremy SmathersОценок пока нет
- Rooftiles Unicoppo Installation GuideДокумент6 страницRooftiles Unicoppo Installation GuideJessica SandersОценок пока нет
- Guidelines For Construction of Masonry With Siporex BlocksДокумент12 страницGuidelines For Construction of Masonry With Siporex Blockspremadhikari007Оценок пока нет
- Instalación de VentanasДокумент4 страницыInstalación de VentanasLeonardo Moreno Pérez.Оценок пока нет
- H2 TimberWindowsДокумент8 страницH2 TimberWindowsdjDangerBurgersОценок пока нет
- Cavity Wall Insulation Is An Effective Way To Save EnergyДокумент3 страницыCavity Wall Insulation Is An Effective Way To Save EnergyAbishaTeslinОценок пока нет
- Wickes Laying PatioДокумент8 страницWickes Laying PatiofiachduhОценок пока нет
- Horizontal Wall CladdingДокумент3 страницыHorizontal Wall Claddingrobld56Оценок пока нет
- Install Cork Underlayment 3 6 MMДокумент4 страницыInstall Cork Underlayment 3 6 MMjustintoneyОценок пока нет
- Cedar Renditions Install CAДокумент32 страницыCedar Renditions Install CAcherbats1Оценок пока нет
- Flat RoofДокумент2 страницыFlat RoofHarry ThienОценок пока нет
- Wood Trellis ArborДокумент32 страницыWood Trellis Arborصبا باسلОценок пока нет
- The Wind: Protecting Your Home From Hurricane Wind DamageДокумент8 страницThe Wind: Protecting Your Home From Hurricane Wind DamageLuís BarrosoОценок пока нет
- Concrete Pad Found NewДокумент5 страницConcrete Pad Found NewImran CaderОценок пока нет
- Foundation Systems 1, Spread Foundations: - The Foundation's Primary Purpose IsДокумент13 страницFoundation Systems 1, Spread Foundations: - The Foundation's Primary Purpose IsJimmy Villca SainzОценок пока нет
- How To Calculate Bricks in A WallДокумент2 страницыHow To Calculate Bricks in A WallShaker Ullah ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- How To Build A Child's Playhouse: 1. Determine Lay OutДокумент9 страницHow To Build A Child's Playhouse: 1. Determine Lay OutMar PopОценок пока нет
- Installation Guide: Ventilated SystemДокумент2 страницыInstallation Guide: Ventilated SystemNuno MarquesОценок пока нет
- Technical Document: How To Use Wood-Based Panels As Wall FinishДокумент18 страницTechnical Document: How To Use Wood-Based Panels As Wall FinishLAGAN MARWAHОценок пока нет
- Technical SpecificationsДокумент3 страницыTechnical SpecificationsJohnОценок пока нет
- Installation InstructionsДокумент3 страницыInstallation Instructionsdangtuan27Оценок пока нет
- PanellingДокумент27 страницPanellingShubham nigamОценок пока нет
- Building A Geodesic DomeДокумент7 страницBuilding A Geodesic DomeCarlosBertossiFerrariОценок пока нет
- Squash Court Finish PDFДокумент5 страницSquash Court Finish PDFFrancis T. TolibasОценок пока нет
- Project 02 SpecificationДокумент16 страницProject 02 SpecificationDUMLAO, ANGELIE M.Оценок пока нет
- Copyright 2004 Martian AuctionsДокумент9 страницCopyright 2004 Martian Auctionshumayunkk2002Оценок пока нет
- Bird House2Документ3 страницыBird House2khunchaiyai100% (1)
- Bedside TableДокумент3 страницыBedside Table- yAy3e -Оценок пока нет
- Size Conversion ChartsДокумент3 страницыSize Conversion ChartsYounes BarakaОценок пока нет
- Luminate PDS BF 10609 USLДокумент2 страницыLuminate PDS BF 10609 USLArash AbbasiОценок пока нет
- A Comparison of PH Eur and DSP RequirementsДокумент4 страницыA Comparison of PH Eur and DSP RequirementsAyoub TofixОценок пока нет
- Aimer Bathroom CatalogДокумент12 страницAimer Bathroom CatalogmdnajmieОценок пока нет
- Rmi Verif RC Columns 3 2Документ76 страницRmi Verif RC Columns 3 2Fernando MartinezОценок пока нет
- Style 3020 - Chemares Tank Lid Packing: Accord International, IncДокумент1 страницаStyle 3020 - Chemares Tank Lid Packing: Accord International, Incdanny_sosa_3Оценок пока нет
- Sugar Industry: Presented by Aparna Prasenan Enroll. No.-12519001Документ41 страницаSugar Industry: Presented by Aparna Prasenan Enroll. No.-12519001Jasdeep SinghОценок пока нет
- WACS Villaba, LeyteДокумент11 страницWACS Villaba, Leyteroderick biazonОценок пока нет
- Royal Continental, Niger Project - Pi - 3751Документ9 страницRoyal Continental, Niger Project - Pi - 3751ashishvaidОценок пока нет
- Anchor Cage DocumentsДокумент13 страницAnchor Cage DocumentsDan BitcaОценок пока нет
- Controlled Polymers For Pigment DispersantsДокумент9 страницControlled Polymers For Pigment Dispersantstrường phạmОценок пока нет
- Full Book MCQs (Chemistry)Документ12 страницFull Book MCQs (Chemistry)raosbhsp35Оценок пока нет
- Solid Waste ManagementДокумент19 страницSolid Waste Managementayush maheshwariОценок пока нет
- Effect of Backstay On 3B+G+20 Storey RC BuildingДокумент5 страницEffect of Backstay On 3B+G+20 Storey RC Buildingdharashah28Оценок пока нет
- Water Purification Using Solar Still: A Technical Seminar OnДокумент18 страницWater Purification Using Solar Still: A Technical Seminar Onashna latheefОценок пока нет
- Experimental Study of Cement-Asphalt Emulsion Composite: PII S0008-8846 (98) 00038-6Документ7 страницExperimental Study of Cement-Asphalt Emulsion Composite: PII S0008-8846 (98) 00038-6margarethsmОценок пока нет
- Formation Constants of Complex IonsДокумент1 страницаFormation Constants of Complex IonsIuliaHortОценок пока нет
- Encyclopedia of Polymers and CompositesДокумент713 страницEncyclopedia of Polymers and CompositesvladoferdОценок пока нет
- M-08 Hull Piping DiagramДокумент51 страницаM-08 Hull Piping DiagramĐức Nguyễn ĐìnhОценок пока нет
- Asconium: Technical NoticeДокумент14 страницAsconium: Technical NoticenanoОценок пока нет
- Basf Masterseal Roof 3000 TdsДокумент2 страницыBasf Masterseal Roof 3000 TdsmidaОценок пока нет
- Cost-Eff Ective Shoulder Milling Cutter For: High ProductivityДокумент16 страницCost-Eff Ective Shoulder Milling Cutter For: High ProductivityVinicius Sabrina PedroОценок пока нет
- Four Probe MethodДокумент5 страницFour Probe MethodSarthakJainОценок пока нет
- SimXpert R3.2 Crash Workspace GuideДокумент344 страницыSimXpert R3.2 Crash Workspace Guidepaulkastle100% (1)
- Analytical ChemistryДокумент5 страницAnalytical ChemistryChristian FloresОценок пока нет