Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
BI 121le - ch1 - ST
Загружено:
hughe2rjОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
BI 121le - ch1 - ST
Загружено:
hughe2rjАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
BI 121 INTRODUCTION to HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I.
Introductory terms: Science study of the natural world BIOLOGY study of life and living organisms Very broad field requiring division into several Subspecialties (botany, zoology, microbiology, etc) ANATOMY t e study of form and relations ip of parts of t e body Gross !n!tomy " study of macroscopic forms (visible to t e na!ed eye) M#crosco$#c !n!tomy " study of structures not visible "it out a microscope Cyto%o&y "study of cells H#sto%o&y "study of tissues (groups of closely related cells) De'e%o$ment!% An!tomy " study of structural c anges t roug out life span (m)ryo%o&y " study of developmental c anges before birt # branc of developmental anatomy PHYSIOLOGY t e study of function (subspecialties "it in t e field)$ Ce%% P*ys#o%o&y " study of molecular events in cells System#c P*ys#o%o&y " t e study of specific organ systems (i%e% &espiratory p ysiology) P!t*o%o&#c P*ys#o%o&y " study of disease process
An!tomy !nd P*ys#o%o&y !re #nterconnected )ec!use: structure d#ct!tes +unct#on, II. TH( LANGUAG( O- ANATOMY used #n order to descr#)e %oc!t#on o+ structures )e#n& e.!m#ned An!tom#c!% Pos#t#on " /!s#s o+ Re+erence0 !%1!ys re+er to )ody #n t*#s $os#t#on re&!rd%ess o+ #t !ctu!% $os#t#on. A. D#rect#on!% Terms ' 2re%!t#'e $os#t#on3 " Descr#)e t*e %oc!t#on o+ one )ody $!rt 1#t* res$ect to !not*er. (.!m$%e. " See $#cture #n t*e Te.t0 It #s ! re%!t#ons*#$ 2one #n re%!t#on to !not*er3 Sternum #s med#!% to t*e *e!rt. (nterior vs% )osterior *edial vs% +ateral Superior vs% Inferior Superficial vs% ,eep ,istal vs% )ro-imal (fingers are distal to t e elbo") I$s#%!ter!% 2on t*e s!me s#de3 's. Contr!%!ter!% 2o$$os#te s#de3 /. /ody P%!nes !nd Sect#ons (to observe internal parts) (.. S!&#tt!% " %en&t*1#se cut d#'#d#n& #nto r#&*t !nd %e+t $ort#ons Tr!ns'erse 2*or#4ont!%3 " su$er#or !nd #n+er#or $ort#ons
coron!% 2+ront!%3 !nter#or !nd $oster#or $ort#ons C. /ody Re&#ons (broad areas)$ .otes are in t e noteboo!
Body /uadrants$ .otes are in t e noteboo!%
D. Re&#on!% Terms (smaller areas) (.. Ot#c 5 0ar S!cr!% 5 )osterior region bet"een t e ips 1arpal ' "rist 2emoral ' 3 ig region ,igital 4 2inger or toe 3arsal ' (n!le
6NO7 ALL -#&.8.9: 2$$ 9; 9<3 (. /ody C!'#t#es " =s$!ces> protect organs, allo" for e-pansion "it out infringing upon ot er organs% 8. DORSAL 2$oster#or3: !3 Cr!n#!% C!'#ty M!de u$ )y s?u%% )ones See P#cture D#!&r!m #n t*e T(@T )3 S$#n!% C!'#ty M!de u$ )y 'erte)r!e 2Aerte)r!% C!n!%3 9. A(NTRAL 2!nter#or3: !3 T*or!c#c !)o'e t*e d#!$*r!&m: P%eur!% 293 +ungs reside ere Per#c!rd#!% 5eart resides ere (6it in t e *ediastinum) Med#!st#num Space bet"een pleural cavities contains$ eart, esop agus, trac ea, great vessels )3 A)dom#no$e%'#c )e%o1 t*e d#!$*r!&m: A)dom#n!%$ Stomac , liver, gallbladder, intestines, spleen
Pe%'#c$ 0nclosed by pelvic bones 7 muscle end of large intestine, urinary bladder, internal reproductive organs ACTIAITY: Or&!n Systems 28.90 P!&e B3 Or&!n System Inte&ument!ry An!tomy S?#n0 n!#%s 0 *!#r P*ys#o%o&y Protect#on o+ dee$er t#ssues0 e.cret#on o+ 1!stes0 t*ermore&u%!t#on
S?e%et!%
/ones0 c!rt#%!&es0 %#&!ments0 tendonsSu$$ort !nd $rotect#on0 m#ner!% stor!&e
Muscu%!r Musc%es Ner'ous /r!#n0 s$#n!% cord0 ner'es (ndocr#ne
Mot#on0 en'#ronment m!n#$u%!t#on0 *e!t &ener!t#on Res$onse to e.tern!% !nd #ntern!% st#mu%#
G%!nds t*!t secrete t*e *ormones. P#tu#t!ry0 T*yro#d0 P!ncre!s0 !dren!%0 He%$ contro% met!)o%#c !ct#'#t#es o+ )ody t*ymus &%!nds structures.
C!rd#o'!scu%!r He!rt0 !rter#es0 'e#ns Lym$*!t#c Lym$*!t#c 'esse%s0 %ym$* nodes0 t*ymus0 s$%een
Mo'e )%ood t*rou&* t*e )odyCs 'esse%s !nd tr!ns$ort su)st!nces t*rou&*out t*e )ody. Return t#ssue +%u#d to t*e )%ood0 c!rry !)sor)ed +ood mo%ecu%es0 !nd de+end !&!#nst #n+ect#on.
Res$#r!tory
Int!?e !nd out$ut o+ !#r0 e.c*!n&e &!ses Lun&s0 N!s!% c!'#ty0 Tr!c*e!0 %!ryn.0 )et1een !#r !nd )%ood. $*!ryn.0 )ronc*# Mout*0 ton&ue0 sm!%% !nd %!r&e #ntest#nes0 stom!c*0 U$t!?e o+ +ood0 )re!?do1n !nd !)sor$t#on o+ +ood. (%#m#n!te un!)sor)ed m!ter#!%. Remo'!% o+ 1!ste +rom )%ood0 m!#nt!#n 1!ter !nd e%ectro%yte )!%!nce0 tr!ns$ort o+ ur#ne.
D#&est#'e
Ur#n!ry 6#dneys0 /%!dder0 ureters
Re$roduct#'e Pen#s0 scrotum0 testes M!#nt!#n !nd Produce s$erm ce%%s0 tr!ns+er s$erm #nto +em!%e re$roduct#'e or&!n.
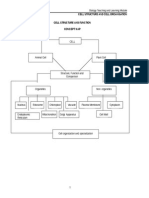
III. L(A(LS O- /IOLOGICAL ORGANIDATION De+: structur!% d#'#s#on !ccord#n& to t*e %e'e% o+ com$%e.#ty 8. Su)!tom#c P!rt#c%es " e%ectrons0 $rotons0 !nd neutrons 9. Atom " smallest unit of matter 0-ample$ 5ydrogen Atoms com)#ne to +orm Mo%ecu%es ;. Mo%ecu%es " 2 or more atoms 8oined by c emical bonds% 0-$ 6ater, 9-ygen Mo%ecu%es com)#ne to +orm Or&!ne%%es
<. Or&!ne%%es " intracellular structures t at perform specific functions% 0-$ *itoc ondria, &ibosome Or&!ne%%es +orm :. Ce%%s " smallest living unit% 0-$ Brain 1ell, .erve 1ell L#?e ce%%s Eo#n to +orm T#ssues Ce%%s
F. T#ssues " +i!e cells "it common functions% 0-$ *uscle 3issue T#ssues com)#ne to +orm Or&!ns
G. Or&!n " 2 or more tissues t at perform comple- functions% 0-$ 5eart Or&!ns Eo#n to&et*er to +orm !n Or&!n System
B. Or&!n System " group of organs "or!ing toget er to perform a vital body function% 0-$ ,igestive, cardiovascular Or&!ns systems com)#ne to +orm Or&!n#sm
H. Or&!n#sm " organ systems 8oined toget er to maintain life 7 ealt # sum total of all structural levels% 0-$ 5uman being IA. CHARACT(RISTICS o+ LI-( (every living structure e- ibits t ese)$ M!#nt!#n /ound!r#es
De+#n#t#on: :eeping internal environment distinct from e-ternal environment% Or&!n systems #n'o%'ed: Integumentary System A)sor$t#on
De+#n#t#on: (ctive or passive upta!e of substances (gases, fluids, solutes) by cells% Or&!n systems #n'o%'ed: ,igestive System# &espiratory System Met!)o%#sm
De+#n#t#on: (ll bioc emical reactions in t e body t at use or release energy at any given moment%
Or&!n systems #n'o%'ed: ,igestive 7 &espiratory Systems to ma!e nutrients and 92 available# 1ardiovascular System to transport t em, and t e 0ndocrine System to regulate metabolism% C#rcu%!t#on
De+#n#t#on: 3ransportation of substances t roug out t e internal environment% Or&!n systems #n'o%'ed: 1ardiovascular System# +ymp atic System (lipids) Gro1t*
De+#n#t#on: )rocess by " ic a structure enlarges% Or&!n systems #n'o%'ed: &eproductive System# 0ndocrine System Res$#r!t#on
De+#n#t#on: 0-c ange of gases bet"een blood and lungs, tissues and blood# cellular respiration, " ic releases energy from nutrients% Or&!n systems #n'o%'ed: &espiratory System (.cret#on
De+#n#t#on: 0limination of metabolic "astes (materials t at are not absorbed)% Or&!n systems #n'o%'ed: ;rinary System# ,igestive System# &espiratory System# Integumentary System +ymp atic System Mo'ement
De+#n#t#on: c ange in position# motion Or&!n systems #n'o%'ed: S!eletal System# *uscular System# .ervous System Res$ons#'eness
De+#n#t#on: (ctions resulting from a stimulus% Or&!n systems #n'o%'ed: .ervous System# 0ndocrine System Re$roduct#on
De+#n#t#on: 1ells reproduce and give rise to ne" cells# offspring formation% Or&!n systems #n'o%'ed: &eproductive System# 0ndocrine System A. -!ctors reIu#red +or MAINT(NANC( o+ LI-(: L#+e de$ends on +#'e 2:3 en'#ronment!% +!ctors: 83 7!ter *ost abundant substance in body Important in metabolism, transportation, regulation of body temperature% 2emales < =2> 52 ? *ales < @A> 52 ?
93 -ood !s source o+:
Building materials for ne" structures necessary nutrients for e-isting structures 0nergy of c emical bonds ;3 O.y&en 98J o+ !#r *olecule used to release energy from food and drive metabolism% <3 He!t 2orm of energy )roduct of metabolism 1ontrols rate of metabolic reactions SooooB Incre!sed *e!t 5 +!ster re!ct#on r!tes 2#m$ort!nt #n #mmun#ty3 :3 Pressure 2!$$%#c!t#on o+ +orce to somet*#n&3: (pplication of force on an ob8ect Atmospheric " e.erted )y !#r important for breat ing Hydrostatic " e.erted )y +%u#ds !eeps blood flo"ing Homeost!s#s " #m$ort!nt c*!r!cter#st#c necess!ry +or m!#nten!nce o+ %#+e: *aintenance of a stable yet not rigid internal environment Self4regulating control mec anisms ,ynamic (not rigid) equilibrium
7*!t re&u%!tes tem$er!ture #n your *ouseK Com$onents In'o%'ed #n Homeost!t#c Re&u%!t#on: Rece$tor " Somet*#n& t*!t senses ! c*!n&e or st#mu%us Contro% Center " 7*ere #n+orm!t#on #s rece#'ed !nd $rocessed o Loc!t#on o+ t*e #n+orm!t#on !)out des#red '!%ue 2=set $o#nt>3
(++ector " Ce%%Lor&!n t*!t res$onds to mess!&es +rom t*e contro% center !nd e#t*er o$$oses or en*!nces t*e st#mu%us S(( DIAGRAM IN TH( T(@T.
Ty$es o+ *omeost!t#c Contro% Mec*!n#sms: 8. Ne&!t#'e +eed)!c? " =O$$oses>: )revents sudden, severe c anges in t e body 1orrects t e set point
1auses opposite of bodily disruption to occur, i%e% t e CnegativeD Most common ty$e of feedbac! loop 0-amples$ body temperature, blood pressure 7 glucose regulation
MMOST *omeost!t#c re&u%!t#on #s ne&!t#'e (opposes stimulus) 9. Pos#t#'e -eed)!c? Mec*!n#sms " =(n*!nces> 1ontrol center tells t e effector to en*!nce t e effects of t e stimulus# not as common DIAGRAM IN TEXT
Вам также может понравиться
- Causes of Learning Disabilities: Maigue, Czarina Norean M. Iii - 9 Bs PsychologyДокумент18 страницCauses of Learning Disabilities: Maigue, Czarina Norean M. Iii - 9 Bs Psychologyinah.maigueОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 (Teacher)Документ19 страницChapter 2 (Teacher)ajakazОценок пока нет
- Unit 3Документ1 страницаUnit 3Ana Isabel TadeoОценок пока нет
- Animal Tissues and Organs: Chapter OutlineДокумент5 страницAnimal Tissues and Organs: Chapter OutlineAmirah SyahirahОценок пока нет
- Dalam Artikel Ini Ada 2 Soal Yang Harus Dijawab Untuk Nilai Quiz Mata Kuliah EkolingkДокумент31 страницаDalam Artikel Ini Ada 2 Soal Yang Harus Dijawab Untuk Nilai Quiz Mata Kuliah EkolingkDiah Ayu WulandariОценок пока нет
- Haptic Perception of Multi-Joint Hypertonia During Simulated Patient-Therapist Physical Tele-InteractionДокумент5 страницHaptic Perception of Multi-Joint Hypertonia During Simulated Patient-Therapist Physical Tele-InteractionDavide PiovesanОценок пока нет
- Paper 1 Mid Year SC f4Документ22 страницыPaper 1 Mid Year SC f4Jeremiah SmithОценок пока нет
- Study Sheet - Gross Anatomy Lower - ExtremityДокумент12 страницStudy Sheet - Gross Anatomy Lower - ExtremityMuhammad BilalОценок пока нет
- Urr Issues Intest MicrobiolДокумент1 страницаUrr Issues Intest MicrobiolAna-Maria SiminescuОценок пока нет
- CV of Jaime LagunezДокумент5 страницCV of Jaime Lagunezfcpcdls-1Оценок пока нет
- Body System ReviewДокумент7 страницBody System Reviewapi-241282073Оценок пока нет
- 11 DoftoeДокумент8 страниц11 Doftoeapi-237532227Оценок пока нет
- PDF Unit Plan For Sem 1 DLДокумент17 страницPDF Unit Plan For Sem 1 DLDiksha chaudharyОценок пока нет
- APP Ch.3 OutlineДокумент5 страницAPP Ch.3 OutlineAlliePalmerОценок пока нет
- Local Anesthesia / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyДокумент57 страницLocal Anesthesia / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyОценок пока нет
- K. J. Rawson - Maritime System Design MethodologyДокумент13 страницK. J. Rawson - Maritime System Design Methodologynf_azevedoОценок пока нет
- AEL NotesДокумент34 страницыAEL NotesAnie Guiling-Hadji GaffarОценок пока нет
- Vitamin As 7Документ10 страницVitamin As 7PattyAchinОценок пока нет
- Referat Engleza: NUME STUDENT: Oleniuc (Vilcu) LucyДокумент12 страницReferat Engleza: NUME STUDENT: Oleniuc (Vilcu) LucyGeorgianaMardaleОценок пока нет
- GC Roadshow BioSTPM PrintДокумент12 страницGC Roadshow BioSTPM PrintazharsarahОценок пока нет
- hw410 Ashley Lindemann Final ProjectДокумент13 страницhw410 Ashley Lindemann Final Projectapi-256577647Оценок пока нет
- Teacher's Copy Chapter2Документ12 страницTeacher's Copy Chapter2Yen BuYenОценок пока нет
- Embryology BY DRДокумент58 страницEmbryology BY DRshibhiОценок пока нет
- Psychiatric Nursing DsecseanielДокумент46 страницPsychiatric Nursing DsecseanielDan HernandezОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 - Approaches To Systems-BuildingДокумент17 страницChapter 4 - Approaches To Systems-BuildingKing BradleyОценок пока нет
- Health Promotion: NANDA Domain DefinitionsДокумент13 страницHealth Promotion: NANDA Domain DefinitionsDesy NurprasetiyoОценок пока нет
- Body Fat and Eating Disorders PaperДокумент6 страницBody Fat and Eating Disorders PaperNatasha ArringtonОценок пока нет
- RE: Proposed Plan For Change: NKPC P.O. Box 86231, Tucson, AZ 85754Документ14 страницRE: Proposed Plan For Change: NKPC P.O. Box 86231, Tucson, AZ 85754NKPimaCounty100% (1)
- Hesi Study GuidДокумент44 страницыHesi Study GuidStefanie Henry80% (5)
- The Endocrine SystemДокумент16 страницThe Endocrine Systemanon_63895130Оценок пока нет
- Biology Syllabus 2014Документ6 страницBiology Syllabus 2014api-256430958Оценок пока нет
- OPP 101 Fall 2010 Syllabus1Документ3 страницыOPP 101 Fall 2010 Syllabus1ferry7765Оценок пока нет
- What Is LifeДокумент15 страницWhat Is Lifeapi-254851257Оценок пока нет
- Qi Gong Exercises: Gain Mental and Spiritual Balance: The Mind UnleashedДокумент4 страницыQi Gong Exercises: Gain Mental and Spiritual Balance: The Mind UnleashedMarcos X AlmeidaОценок пока нет
- Overview: Divided Into Central Nervous System (Brain and Spinal Cord) and PeripheralДокумент21 страницаOverview: Divided Into Central Nervous System (Brain and Spinal Cord) and PeripheraldanieljohnarboledaОценок пока нет
- Syllabus1301 1Документ14 страницSyllabus1301 1Iwana RademaekersОценок пока нет
- Common CD - Part 4 Sexually Transmitted (Revised)Документ43 страницыCommon CD - Part 4 Sexually Transmitted (Revised)Rye AnchОценок пока нет
- Citadel Fine Pharmaceuticals v. Ramaniyam Real Estates (P) LTD (2011) 9 SCC 147Документ47 страницCitadel Fine Pharmaceuticals v. Ramaniyam Real Estates (P) LTD (2011) 9 SCC 147Ashish Davessar100% (1)
- Proiect Engleza: Universitatea Ovidius Facultatea de Matematica Si Informatica ConstantaДокумент16 страницProiect Engleza: Universitatea Ovidius Facultatea de Matematica Si Informatica ConstantaCobra NeagraОценок пока нет
- Management Control System in Public Administration: Beyond Rational MythsДокумент16 страницManagement Control System in Public Administration: Beyond Rational MythsArief JauhariОценок пока нет
- Amity Business SchoolДокумент3 страницыAmity Business Schoolanujhanda29Оценок пока нет
- Nota RingkasДокумент9 страницNota RingkasNorafiza HashimОценок пока нет
- Comparative AssigДокумент7 страницComparative AssigBhannu RamananОценок пока нет
- 7 Habits of Highly Effective Teens Semester ReadingДокумент6 страниц7 Habits of Highly Effective Teens Semester Readingxal22950Оценок пока нет
- Sensory Organs and Their FunctionsДокумент35 страницSensory Organs and Their FunctionsThevagi GovindasamyОценок пока нет
- Internship Report and Project Main - Apurv PranavДокумент136 страницInternship Report and Project Main - Apurv PranavApurv Sinha100% (3)
- Experiment 9: Preparation and Analysis of A Coordination CompoundДокумент4 страницыExperiment 9: Preparation and Analysis of A Coordination CompoundDaizLee AhmadОценок пока нет
- Nursing Bullets - MCHN ReviewerДокумент18 страницNursing Bullets - MCHN ReviewerAileen AblanОценок пока нет
- Esclerosis MultipleДокумент18 страницEsclerosis MultipleHéctor HernándezОценок пока нет
- BM - National Enterprise EmergencyДокумент23 страницыBM - National Enterprise EmergencycefmarchiОценок пока нет
- Dowry SystemДокумент59 страницDowry SystemSubhash BajajОценок пока нет
- The Transhumanist Faq 1.5Документ51 страницаThe Transhumanist Faq 1.5RatitoОценок пока нет
- Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Pahang Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2010Документ28 страницJabatan Pelajaran Negeri Pahang Science Curriculum Specifications Yearly Lesson Plan For Form Four 2010magisperanОценок пока нет
- Billy Meier & The Plejarische KontaktberichteДокумент54 страницыBilly Meier & The Plejarische KontaktberichteMyffi100% (1)
- Pediatric NursingДокумент33 страницыPediatric Nursingiamdarn100% (1)
- Nevada State College Teacher Preparation Program Lesson Plan FormatДокумент3 страницыNevada State College Teacher Preparation Program Lesson Plan FormatbriantrenholmОценок пока нет
- MSC Genetics Ref BooksДокумент21 страницаMSC Genetics Ref Bookssk912220% (1)
- PCK 1-3 and Practical 1-6Документ20 страницPCK 1-3 and Practical 1-6Ronny WeiОценок пока нет
- Lidocaina Bajas DosisДокумент11 страницLidocaina Bajas DosisneuralterapianetОценок пока нет
- Cam4 6 1861Документ10 страницCam4 6 1861Ćatke TkećaОценок пока нет
- 1.1.4 Blood EvidenceДокумент3 страницы1.1.4 Blood EvidenceIlliana EddyОценок пока нет
- Surving Sepsis Campaign ResultДокумент8 страницSurving Sepsis Campaign Resultmaria arenas de itaОценок пока нет
- 5 After The Last Breath (Written in 1904 On The Death of Hardy's Mother, Jemima Hardy, 1813-1904) .PDДокумент3 страницы5 After The Last Breath (Written in 1904 On The Death of Hardy's Mother, Jemima Hardy, 1813-1904) .PDsylviaordoОценок пока нет
- Acetaminophen PoisoningДокумент19 страницAcetaminophen PoisoningMARIA TELLEZОценок пока нет
- Lefort Osteotomy PPT (Ing) - 1Документ22 страницыLefort Osteotomy PPT (Ing) - 1Chandra Budi100% (1)
- Anaphy (Lab) ReviewerДокумент3 страницыAnaphy (Lab) ReviewerAgatha Cristie AndradaОценок пока нет
- Check List of Claim DocumentsДокумент2 страницыCheck List of Claim Documentsmohammed hussainОценок пока нет
- Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2nd Ed. - W. Frontera, Et. Al., (Saunders, 2008) WW PDFДокумент847 страницEssentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2nd Ed. - W. Frontera, Et. Al., (Saunders, 2008) WW PDFRecuperare100% (9)
- Gurkeerat Singh - Textbook of Orthodontics, 2nd EditionДокумент5 страницGurkeerat Singh - Textbook of Orthodontics, 2nd EditionndranОценок пока нет
- Anger Management Best Practice HandbookДокумент122 страницыAnger Management Best Practice HandbookRomanic Mihaela100% (6)
- How To Rid The Body of CandidaДокумент2 страницыHow To Rid The Body of Candidaradio53fingerОценок пока нет
- Anaesthetic Management of Obstetric: HaemorrhageДокумент52 страницыAnaesthetic Management of Obstetric: Haemorrhagerevathidadam55555Оценок пока нет
- Fibula Wei 2018Документ11 страницFibula Wei 2018Rares CraciunОценок пока нет
- Electronic Surgical Logbook For Orthopedic Residents AcceptanceДокумент7 страницElectronic Surgical Logbook For Orthopedic Residents AcceptanceKhalil ur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Guidance To Understanding Implications of IRMERДокумент52 страницыGuidance To Understanding Implications of IRMERrochimОценок пока нет
- Mu 75 PDFДокумент4 страницыMu 75 PDFJerichoОценок пока нет
- Handouts 1Документ12 страницHandouts 1banana_rockОценок пока нет
- 766ue 2019-01Документ101 страница766ue 2019-01Angelita Kstro D SilvaОценок пока нет
- The Case of Mouthwash MarketДокумент6 страницThe Case of Mouthwash MarketAce ReytaОценок пока нет
- Soap NotesДокумент4 страницыSoap NotesLatora Gardner Boswell100% (3)
- Treatment and Prognosis of IgA Nephropathy - UpToDate PDFДокумент52 страницыTreatment and Prognosis of IgA Nephropathy - UpToDate PDFDerian Yamil Bustamante AngelОценок пока нет
- Microdosing Mushrooms: Fruiting Bodies Introduction ToДокумент12 страницMicrodosing Mushrooms: Fruiting Bodies Introduction ToPaulo Das Nuvens100% (2)
- Green Power DistributionДокумент30 страницGreen Power DistributionRazvan MarcuОценок пока нет
- GoniometryДокумент22 страницыGoniometryDuppala Sateesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Anaesthetic Management of A Case With Severe Mitral Stenosis Posted For Emergency Caesarean SectionДокумент2 страницыAnaesthetic Management of A Case With Severe Mitral Stenosis Posted For Emergency Caesarean SectionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Capstone OutlineДокумент3 страницыCapstone Outlineapi-395468231Оценок пока нет
- S11 XylitolДокумент4 страницыS11 XylitolJholanda Ninggar BahtriaОценок пока нет
- Treat CMD Gnat NMD Chan 2003Документ32 страницыTreat CMD Gnat NMD Chan 2003Constantin IonutОценок пока нет
- Burns Secret TestДокумент2 страницыBurns Secret TestChin ChanОценок пока нет