Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
6 6 Reproduction
Загружено:
api-235355872Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
6 6 Reproduction
Загружено:
api-235355872Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
HUMAN HEALTH & PHYSIOLOGY
Topic 6.6 Reproduction
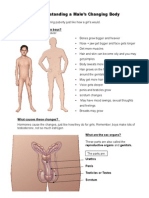
6.6.1a Male Reproductive System
6.6.1b Female Reproductive System
6.6.2 Hormones in the Menstrual Cycle
Hypothalamus produces a hormone (when estrogen and progesterone levels are low), gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH). (Negative feedback system) This activates the pituitary gland causing it to produce two hormones FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) and LH (Luteinizing Hormone) to be released into the blood and active on the ovaries. FSH & LH effect the ovaries by:
Increases production & secretion of estrogen in the ovaries, which targets the endometrium of the uterus (increasing the blood vessels). Another effect is creation of Graafian follicles from follicle cells and oocytes. Once the Graafian follicle releases its oocyte and inner lining of the follicle into the Fallopian tube, the outer ring of the follicle cells remain in the ovary and secrete another hormone, progesterone. These remaining cells begin to form a corpus luteum which remains active for 10-12 days after ovulation producing progesterone. Progesterone is responsible for maintaining the thickened, highly vascular endometrium. (as long as it is present endometrium wont break down and embryo can implant, then when levels drop capillaries & small blood vessels rupture and menstruation begins)
6.6.2 Hormones in the Menstrual Cycle
Negative Feedback Loop
Signaled by high levels of estrogen and progesterone Hypothalamus does not produce GnRH when estrogen & progesterone levels are high FSH and LH at high levels is not conducive to the production of Graafian follicle Corpus luteum begins to break down, leads to a decline in progesterone & estrogen.
Not Pregnant
Endometrium can not be maintained Capillaries & blood vessels rupture menstration begins Drop in hormones signals hypothalmus to secret GnRH
Negative Feedback Loop
Hormone Levels & Menstrual Cycle
6.6.4 Three Roles of Testosterone
Determines the development of male genitalia during embryonic development; Ensures development of secondary sex characteristics during puberty; Maintains the sex drive of males throughout their lifetime.
6.6.5 In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Woman is usually injected with FSH for about 10 days in preparation to ensure the development of many Graafian follicles. Several eggs (secondary oocytes) are harvested surgically Sperm cells are collected Harvested eggs are mixed with sperm cells in separate culture dishes and observed microscopically to find fertilized and healthy embryos. Usually two or three healthy embryos are introduces into the womans uterus for implantation.
Process is very expensive and introduction of one could mean high risk of failure.
Unused cultures can be frozen and used for another implantation if necessary.
6.6.6 Ethical Issues associated with IVF
For:
Against:
It enables those unable to have children to have a family Enbryos that are not visibly healthy can be eliminated from implantation Genetic screening is possible before implanting to eliminate change of passing on some genetic disorders. IVF technology will advance and lead to further benefits in reproductive technology.
Embryos produced but not used are frozen or destroyed. Legal issues concerning frozen embryos when couples split up. Genetic screening of embryos could lead to society choosing desirable characteristics. Some reproductive problems of an individual are genetically passed on and IVF bypasses natures way of decreasing the genetic frequency of that reproductive problem. Multiple births and problems associated with multiple births are more likely with IVF than with natural conception.
DBQ
Identify hormones I and II.
I:_____________ Progestero
ne Estrogen II:_____________
DBQ
Outline the roles of FSH in the menstrual cycle.
FSH
stimulates follicle development; FSH stimulates estrogen secretion (by the follicle/ovary)
DBQ
FSH is secreted by the pituitary gland. During pregnancy, FSH is inhibited. Suggest how FSH secretion could be inhibited during pregnancy.
High
levels of progesterone/estrog en inhibit FSH production (during pregnancy)
Вам также может понравиться
- 3 1 and 3 2Документ28 страниц3 1 and 3 2api-235355872Оценок пока нет
- 6 5 Nerves Hormones and HomeostasisДокумент19 страниц6 5 Nerves Hormones and Homeostasisapi-235355872Оценок пока нет
- 6 4 Gas ExchangeДокумент14 страниц6 4 Gas Exchangeapi-235355872Оценок пока нет
- 6 2 The Transport SystemДокумент18 страниц6 2 The Transport Systemapi-235355872Оценок пока нет
- Option G 1 PowerpointДокумент17 страницOption G 1 Powerpointapi-235355872Оценок пока нет
- STD DeviationДокумент17 страницSTD Deviationapi-235355872Оценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- 3 DAY HCG Stimulation TestДокумент2 страницы3 DAY HCG Stimulation TestMj CОценок пока нет
- Testicular Growth and Development in PubertyДокумент10 страницTesticular Growth and Development in PubertyRaul DoctoОценок пока нет
- IntersexДокумент46 страницIntersexGeeta DoppaОценок пока нет
- MENSTRUALДокумент18 страницMENSTRUALAnonymous o3ZKP646E7100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Hyspopadias and Epispadias PDFДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Hyspopadias and Epispadias PDFCharlaine Gripal SudlaОценок пока нет
- Rosenfield2015 PDFДокумент27 страницRosenfield2015 PDFdanilacezaraalinaОценок пока нет
- What Is The Follicular Phase?: Good To KnowДокумент3 страницыWhat Is The Follicular Phase?: Good To KnowNancy SinghОценок пока нет
- AnavarДокумент10 страницAnavarRadu GrigorescuОценок пока нет
- Sistem ReproducatorДокумент7 страницSistem ReproducatorTabarcea EduardОценок пока нет
- Anabolic SteroidsДокумент45 страницAnabolic Steroidsgirgray75% (4)
- PubertyДокумент18 страницPubertyNuhaYahyaОценок пока нет
- Nilai Normal TorchДокумент3 страницыNilai Normal Torchirma RDОценок пока нет
- AmenorrheaДокумент11 страницAmenorrheaDr.med SurduckiОценок пока нет
- Absence of A Menstrual PeriodДокумент2 страницыAbsence of A Menstrual PeriodDragan PetrovicОценок пока нет
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Response To StimulationДокумент14 страницPolycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Response To StimulationMeizaОценок пока нет
- Reproductive HormonesДокумент26 страницReproductive HormonesInji IdupalagiОценок пока нет
- Kontrasepsi Hormonal Up To DateДокумент79 страницKontrasepsi Hormonal Up To DatearmedianОценок пока нет
- Menstrual CycleДокумент58 страницMenstrual CycleJoanBangitОценок пока нет
- 3 - Puberty Male Notes - TeacherДокумент3 страницы3 - Puberty Male Notes - Teacherapi-241585431100% (1)
- Anabolic SteroidsДокумент11 страницAnabolic SteroidsRichard Limas83% (6)
- Biology Project IndexДокумент3 страницыBiology Project Indexmansi60% (5)
- The Gonadal Hormones & InhibitorsДокумент41 страницаThe Gonadal Hormones & InhibitorsSaddamix AL OmariОценок пока нет
- CDGP Versus HypogonadismДокумент25 страницCDGP Versus HypogonadismmpintobОценок пока нет
- Pro CyclesДокумент7 страницPro Cyclestselentisharris15867% (3)
- Male Versus Female Reproductive SystemsДокумент6 страницMale Versus Female Reproductive SystemsAssignmentLab.comОценок пока нет
- Viva Level Endocrine MCQ 1Документ1 страницаViva Level Endocrine MCQ 1imnnayakОценок пока нет
- Androgens and Anabolic SteroidsДокумент37 страницAndrogens and Anabolic SteroidsRezy Arina PutriОценок пока нет
- Gamefowl - Priming For BreedingДокумент1 страницаGamefowl - Priming For BreedingLester Acosta75% (8)
- Testosterone Cypionate ProtocolДокумент2 страницыTestosterone Cypionate ProtocolWidfdsafdsaОценок пока нет
- 3-What Is Endometrial Hyperplasia?Документ4 страницы3-What Is Endometrial Hyperplasia?shahzeb memonОценок пока нет