Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Class 10 Cbse Science Sample Paper Term 1 Model 2
Загружено:
Sunaina RawatАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Class 10 Cbse Science Sample Paper Term 1 Model 2
Загружено:
Sunaina RawatАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Sample Question Paper
SCIENCE
Class X
Term I
Time: 3 hrs. MM: 90
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS:
i) The question paper comprises of two sections, A and B, You are to attempt both the
sections.
ii) All questions are compulsory.
iii) There is no overall choice. However internal choice has been provided in all the five
questions of five marks category. Only one option in such questions is to be
attempted.
iv) All questions of section A and all questions of section B are to be attempted
separately.
v) Questions numbers 1 to 3 in section A are one mark questions. These are to be
answered in one word or one sentence.
vi) Question numbers 4 to 7 are two marks, to be answered in about 30 words each.
vii) Question numbers 8 to 19 are three mark questions, to be answered in about 50
words each.
viii) Questions numbers 20 to 24 are five mark questions, to be answered in about 70
words each.
ix) Question numbers 25 to 42 in section B are multiple choice questions based on
practical skills. Each question is a one ark question. You are to choose one most
appropriate response out of the four provided to you.
SECTION - A
1. Give an example of a metal which is a liquid at room temperature.
2. Identify the compound which is oxidized in the following reaction:
H
2
S + Br
2
2HBr + S
3. Why do we use copper and aluminium wire for transmission of electric current?
4. Write observation with reaction for the following: Granulated zinc reacts with dil.sulphuric
acid.
5. Draw circuit symbols of the following components:
(i) Variable resistance or rheostat
(ii) Plug key or switch (closed)
6. What happens in a displacement reaction? Justify your answer giving one example.
7. What is a n alloy> give the composition and one use each of the following:
(i) Brass
(ii) Solder
8. A thick wire and a thin wire made from the same material and of same length are
connected one by one to the same source. In which case a larger current will flow in the
circuit? Justify your answer.
9. Define nerve impulse which structure in a neuron helps to conduct a nerve impulse.
10. (a) Identify the substance oxidized, substance reduced, oxidizing agent and reducing agent
in the following reaction: ZnO + C Zn + CO
(b) Packets of potato chips are flushed with nitrogen gas, why?
11. What do you understand by short circuiting? Why is it not advisable to handle domestic
electrical circuit with wet hands?
12. (a) Why should we use iodized salt in our diet>
(b) If iodine is insufficient in ones diet, what might be the deficiency disease?
13. A whit coloured powder is used by the doctors for supporting fractured bones.
(a) Write the chemical name of the powder.
(b) Write its formula.
(c) Write chemical equation, when this white powder is mixed with water.
14. (a) An electric bulb is rated as 50W, 220V. Calculate the energy consumed by the bulb in 20
minutes. Express your answer in commercial units of electricity.
(b) Distinguish between Overloading and Short Circuiting in a domestic circuit.
(c) Why is it essential to earth electrical appliances having metallic body?
15. (a) What is reflex arc?
(b) How do muscle cells move?
16. Name the hormone that
(i) Is produced by thyroid gland
(ii) Prepares the body for action
(iii) Controls the amount of sugar in blood
(iv) Brings about the changes in boys at puberty
(v) Brings about the changes the girls at puberty
17. A student performs an experiment with 4 cells and a resistance wire and an ammeter in
series and observes that when the number of cells in the circuit is decreased, the value of
current through the wire also decreases. Name the law that is involved in the experiment
and write its mathematical form. V-I graph for two resistors R1, R2 and their series
combination are shown in the figure below. Which graph represents the series combination
of the other two? Give reason.
18. List the disadvantages of using biomass as fuel in the conventional manner. Give two
examples of technological input to improve efficiency of these fuels.
19. How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
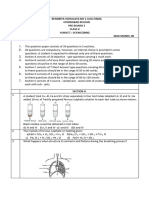
20. (a) Draw the structure of a nephron and label on it the following parts:
(i) Glomerulus
(ii) Bowmans capsule
(iii) Renal artery
(iv) Collecting duct
(b) What happens to glucose, amino acids, salts and water that enter the nephron along
with filtrate?
21. (i) Write the electron dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
(ii) Show the formation of magnesium oxide by transfer of electrons and name the ions
present in it.
OR
With the help of a suitable example, explain how ionic compounds are formed. State any
three general properties of ionic compounds.
22. (a) Name the metal which is low in activity series and exists as liquid at room temperature.
(b) Write the name and formula of its ore.
(c) How is the metal extracted from its ore?
(d) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
23. (a) Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
(b) Why does an aqueous solution of acid conduct electricity?
(c) Why plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture proof container?
(d) What is efflorescence?
(e) Why is baking soda used as an antacid?
24. (a) How is separation of right side and left side of the heart useful in mammals and birds?
(b) Some finger like projections are present in the inner wall of small intestine. Write their
name? Why are they important?
OR
(a) What are the constituents of gastric juice? Write any one function of each.
(b) What is the use of residual volume of air in lungs?
(c) How are carbohydrates stored in the body of plants and animals?
SECTION B
25. Two solutions A and B were found to have pH value of 6 and 8 respectively. The inference
which can be drawn is:
(a) The strength of solution B is higher than that of A.
(b) A is an acid while B is base.
(c) Both are acidic solutions.
(d) Both are basic solutions.
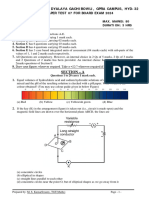
26. A student draws the circuit diagram as shown. The parts labelled X, Y and Z respectively are:
(a) Ammeter, resistor, voltmeter
(b) Ammeter, voltmeter, resistor
(c) Voltmeter, resistor, ammeter
(d) Voltmeter, ammeter, resistor
27. On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to granulated zinc placed in a test tube, a student would
observe that:
(a) The surface of the metal turns shining.
(b) The reaction mixture turns milky.
(c) The reaction mixture gives odour of chlorine.
(d) A colourless and odourless gas evolves with bubbles.
28. On adding a few drops of universal indicator to three unknown colourless solutions [P], [Q]
and [R] taken separately in three test tubes shown in the following diagrams, a student
observed the changes in colour as green in [P], red in [Q] and violet in [R]. The decreasing
order of pH of the solution taken is:
(a) P > Q > R
(b) R > P > Q
(c) Q > P > R
(d) R > Q > P
29. The current through a resistor connected in a electric circuit and the potential difference
across its ends are shown in the diagrams.
(a) 25
(b) 10
(c) 20
(d) 15
30. In which of the following diagram of the stomatal apparatus, which parts are correctly
labelled?
(a) (i) and (v)
(b) (ii) and (v)
(c) (iv) and (ii)
(d) (v) and (iv)
31. The resistors R1 and R2 are connected in:
(a) Parallel in both circuits.
(b) Series in both circuits.
(c) Parallel in circuit I and in series in circuit II.
(d) Series in circuit I and in parallel in circuit II.
32. To make the plant free of starch, it is kept:
(a) In darkness for 72 hrs.
(b) In a room, but with lights on at night only.
(c) Under the shade of a tree.
(d) Covered with coloured polythene in a shady place.
33. Sodium carbonate is not used as:
(a) Sodium chloride
(b) Calcium chloride
(c) Carbon tetrachloride
(d) Magnesium chloride
34. The end products of aerobic respiration are
(a) CO
2
energy and hydrogen
(b) CO
2
and water
(c) CO
2
, H
2
O and ATP
(d) ADP and CO
2
35. To determine that light is essential for photosynthesis, following are the steps, but not in
sequence:
(i) Pluck the leaf and do the starch test.
(ii) Keep the selected plant in sunlight.
(iii) Destarch the plant for 48 72 hours.
(iv) Cover the leaf with black paper strip.
36. When we observe the slide of epidermal leaf peel we find that the inner walls of guard cells
in contact with the stomatal pore are:
(a) Very thick
(b) Moderately thick
(c) Moderately thin
(d) Thin
37. A student adds dil.HCl to a test tube containing zinc granules and noted the following
observations:
(i) The zinc surface became dull and black.
(ii) A gas evolved which burnt with a pop sound.
(iii) The solution remained colourless.
The observations found correct are
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) iii and i
(d) i, ii and iii
38. A black strip of paper was clipped on to a destarched leaf in a potted plant to cover a part of
the leaf. The plant was then exposed to sunlight for four hours, the paper strip was
removed and the leaf tested for starch. When iodine solution was added:
(a) The entire leaf turned blue black.
(b) The covered part of the leaf became blue black.
(c) The uncovered part of the leaf became blue black.
(d) The colour of iodine solution remained unchanged.
39. While preparing a temporary stained mount of a leaf epidermal peel, the extra stain is
removed by:
(a) Washing with water
(b) Washing with calcium chloride
(c) Soaking with filter paper
(d) Absorbing with cotton wool
40. Before setting up an experiment to show that seeds release CO2 during respiration, the
seeds should be:
(a) Dried completely
(b) Boiled to make them soft.
(c) Soaked in vinegar.
(d) Kept moist till they germinate.
41. Which one of the following compounds is not ionic compound?
(a) Sodium chloride
(b) Calcium chloride
(c) Carbon tetrachloride
(d) Magnesium chloride
42. A student focused the leaf epidermal peel under a low power microscope, but he could not
see all the parts. He should:
(a) Use the coarse adjustment knob again to focus the slide
(b) Use the fine adjustment knob to increase magnification
(c) Focus under high power using coarse adjustment knob
(d) Focus under high power using fine adjustment knob
Вам также может понравиться
- Class X Summative I exam guideДокумент7 страницClass X Summative I exam guidesaikiranОценок пока нет
- 10 Sa1 Science Sample Paper1Документ11 страниц10 Sa1 Science Sample Paper1amanОценок пока нет
- Chennai Sahodaya Science Set 3 - QP 2022-23 - FOR EXAMДокумент7 страницChennai Sahodaya Science Set 3 - QP 2022-23 - FOR EXAMsethu ks100% (5)
- Class X Science 4Документ8 страницClass X Science 4api-246793885Оценок пока нет
- SC2 QP 570012 PDFДокумент16 страницSC2 QP 570012 PDFRAHULОценок пока нет
- SC2 QP 570014 PDFДокумент16 страницSC2 QP 570014 PDFRAHULОценок пока нет
- X Science QP - Docx - 2 1Документ9 страницX Science QP - Docx - 2 1aryanmathur0607Оценок пока нет
- Science Sample Paper-1-Class 10 - (SA-I)Документ8 страницScience Sample Paper-1-Class 10 - (SA-I)Firdosh KhanОценок пока нет
- CBSE 10th Science Sample Paper 5Документ7 страницCBSE 10th Science Sample Paper 5Aditya AcharyaОценок пока нет
- C.B.S.E. 2012 Sample Papers For X Science (5 Sets)Документ79 страницC.B.S.E. 2012 Sample Papers For X Science (5 Sets)Vinod Kumar0% (1)
- Summative Assessment - I (2011) Science Class XДокумент17 страницSummative Assessment - I (2011) Science Class XRAHULОценок пока нет
- Science CombinedДокумент315 страницScience CombinedRajkumar MathurОценок пока нет
- X ScienceДокумент5 страницX ScienceMickey xzОценок пока нет
- JSC Science SQP-5 2023-24Документ5 страницJSC Science SQP-5 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- CBSE 10th Science Sample Paper 1Документ5 страницCBSE 10th Science Sample Paper 1Aditya AcharyaОценок пока нет
- CBSE Sample Paper-01 (solved) Class X Science TheoryДокумент113 страницCBSE Sample Paper-01 (solved) Class X Science Theoryselva.uae8207Оценок пока нет
- CBSE Sample Paper-03 Science (Theory) Class – XДокумент6 страницCBSE Sample Paper-03 Science (Theory) Class – XAditya AcharyaОценок пока нет
- JSC Science SQP-1 2023-24Документ6 страницJSC Science SQP-1 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Class 10 SAI Science Paper 2014Документ13 страницClass 10 SAI Science Paper 2014poojaОценок пока нет
- 01 Subjective Test-02 X Science 25122022 QPДокумент6 страниц01 Subjective Test-02 X Science 25122022 QPViswa DharshanОценок пока нет
- JSC Science SQP-3 2023-24Документ5 страницJSC Science SQP-3 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Class 10 ScienceДокумент5 страницClass 10 ScienceDivyanshОценок пока нет
- PREVIOUSYEARPOSTMIDTERMTEST-QP-SET2_1be7f5e358554d7fb2cb72c25bbd74b9_88973Документ6 страницPREVIOUSYEARPOSTMIDTERMTEST-QP-SET2_1be7f5e358554d7fb2cb72c25bbd74b9_88973Hemant SinhmarОценок пока нет
- Chennai Sahodaya Science Set 1 QP 2022-23 - FOR PRACTICE ONLYДокумент7 страницChennai Sahodaya Science Set 1 QP 2022-23 - FOR PRACTICE ONLYvro hamza100% (14)
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2023Документ8 страницScience Class X Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2023SubhaОценок пока нет
- CBSE Sample Paper-02 (Solved) Summative Assessment - I Class - XДокумент7 страницCBSE Sample Paper-02 (Solved) Summative Assessment - I Class - XShivam0% (2)
- Science X QP Set BДокумент7 страницScience X QP Set BYogesh KhannaОценок пока нет
- Class X CBSE Science Question PaperДокумент10 страницClass X CBSE Science Question PaperVinayak Singh OberoiОценок пока нет
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024 1Документ8 страницScience Class X Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024 1rmgokul78Оценок пока нет
- MID-TERM EXAM 2018-19: Class-X Time 3 Hrs Subject-Science Full Marks-80Документ2 страницыMID-TERM EXAM 2018-19: Class-X Time 3 Hrs Subject-Science Full Marks-80rituОценок пока нет
- 10th CBSE Holiday HW DoneДокумент35 страниц10th CBSE Holiday HW Donepomkumar193Оценок пока нет
- Preboard 3 ScienceДокумент7 страницPreboard 3 Sciencenick tyagiОценок пока нет
- Chemistry F 3Документ5 страницChemistry F 3Yusuph kiswagerОценок пока нет
- CBSE 10th Pre Board Exam Model Question Paper 13 - ScienceДокумент11 страницCBSE 10th Pre Board Exam Model Question Paper 13 - Sciencermgokul78Оценок пока нет
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 06 For Board Exam 2023 1 PDFДокумент7 страницScience Class X Sample Paper Test 06 For Board Exam 2023 1 PDFSahasra YeruvaОценок пока нет
- JSC Science SQP-4 2023-24Документ5 страницJSC Science SQP-4 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- 2011 SA 1 ScienceДокумент17 страниц2011 SA 1 ScienceAkhilGovindОценок пока нет
- Science Class XДокумент6 страницScience Class Xbsqvw8pzvrОценок пока нет
- CBSE Science Class 10 Sample Paper 4Документ11 страницCBSE Science Class 10 Sample Paper 4manojboa100% (1)
- Section-A: Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 80 General InstructionДокумент3 страницыSection-A: Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 80 General InstructionHarshit ChoukseyОценок пока нет
- CBSE Sample Paper Solved for Class 10 Science with Detailed SolutionsДокумент5 страницCBSE Sample Paper Solved for Class 10 Science with Detailed SolutionsShivamОценок пока нет
- Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 90Документ3 страницыTime Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 90संघर्ष - सहयोग EducationОценок пока нет
- Top 10 Sample Papers Class 10 Science With Solution - CompressedДокумент151 страницаTop 10 Sample Papers Class 10 Science With Solution - CompressedDarshini P.SОценок пока нет
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Документ7 страницScience Class X Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Aayushi Mishra100% (1)
- SAMPLE PAPER 7 (2017-18) SCIENCE CLASS XДокумент4 страницыSAMPLE PAPER 7 (2017-18) SCIENCE CLASS XADITI RANJANОценок пока нет
- PB 3 Class XДокумент8 страницPB 3 Class Xmukeshyadav1111979Оценок пока нет
- ICSE X SP 05 (Questions)Документ9 страницICSE X SP 05 (Questions)aadithlamjonlОценок пока нет
- Summative Assessment - IiДокумент5 страницSummative Assessment - IiKaran DixitОценок пока нет
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 10 For Board Exam 2024Документ8 страницScience Class X Sample Paper Test 10 For Board Exam 2024Saravana StoreОценок пока нет
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 07 For Board Exam 2024Документ8 страницScience Class X Sample Paper Test 07 For Board Exam 2024i2iacademyinfoОценок пока нет
- Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2019 PDFДокумент4 страницыClass X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2019 PDFApex InstituteОценок пока нет
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 12 For Board Exam 2024Документ7 страницScience Class X Sample Paper Test 12 For Board Exam 2024ag17ayushgОценок пока нет
- Sample Question Paper-3 - Science Time: 3Hrs Max - Marks: 80 InstructionsДокумент8 страницSample Question Paper-3 - Science Time: 3Hrs Max - Marks: 80 Instructionskan PadmasreeОценок пока нет
- Sample Paper AIS MVДокумент10 страницSample Paper AIS MVNATASHA AGGARWALОценок пока нет
- Science PaperДокумент10 страницScience PaperchiragОценок пока нет
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current: I. DefineДокумент15 страницChemical Effects of Electric Current: I. Definemohan krishna poondotaОценок пока нет
- Vidya Bal Bhawan SR - Sec School Half Yearly Examination (2020-21) Class X Subject-Science (086) Level-BДокумент6 страницVidya Bal Bhawan SR - Sec School Half Yearly Examination (2020-21) Class X Subject-Science (086) Level-BLakshОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper SA1 2010Документ9 страницCBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper SA1 2010honey1002Оценок пока нет
- 10TH Cbse Science Co-1Документ11 страниц10TH Cbse Science Co-1manojboaОценок пока нет
- Class 7 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 2Документ2 страницыClass 7 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 2Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 7 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 1Документ3 страницыClass 7 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 1Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 7 ICSE English Sample PaperДокумент2 страницыClass 7 ICSE English Sample PaperSunaina Rawat100% (1)
- Class 6 ICSE Maths SyllabusДокумент1 страницаClass 6 ICSE Maths SyllabusSunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Документ3 страницыClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE History Civics SyllabusДокумент1 страницаClass 6 ICSE History Civics SyllabusSunaina Rawat0% (1)
- Class 6 ICSE History & Civics Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Документ2 страницыClass 6 ICSE History & Civics Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Sunaina Rawat100% (7)
- Class 6 ICSE Geography SyllabusДокумент1 страницаClass 6 ICSE Geography SyllabusSunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE History & Civics Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Документ2 страницыClass 6 ICSE History & Civics Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Sunaina Rawat100% (3)
- Class 6 ICSE Geography Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Документ2 страницыClass 6 ICSE Geography Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Sunaina Rawat100% (1)
- Class 6 ICSE Geography Term 2 Model 1Документ2 страницыClass 6 ICSE Geography Term 2 Model 1Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 3Документ3 страницыClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 3Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 1Документ3 страницыClass 6 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 1Sunaina Rawat67% (3)
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 2Документ3 страницыClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 2Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Документ3 страницыClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 4 ICSE EVS Sample Paper Set 1Документ2 страницыClass 4 ICSE EVS Sample Paper Set 1Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 3Документ2 страницыClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 3Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 1Документ3 страницыClass 6 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 1 Model 1Sunaina Rawat100% (2)
- Class 6 ICSE Biology Sample Paper Set IДокумент2 страницыClass 6 ICSE Biology Sample Paper Set ISunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 2Документ2 страницыClass 6 ICSE English Sample Paper Term 2Sunaina Rawat0% (1)
- Class 6 ICSE English Sample PaperДокумент3 страницыClass 6 ICSE English Sample PaperSunaina Rawat43% (7)
- Class 6 ICSE English SyllabusДокумент1 страницаClass 6 ICSE English SyllabusSunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE Chemistry Sample Paper Set IIДокумент3 страницыClass 6 ICSE Chemistry Sample Paper Set IISunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 5 ICSE EVS Sample Paper Set 2Документ2 страницыClass 5 ICSE EVS Sample Paper Set 2Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 6 ICSE Chemistry Sample Paper Set 1Документ3 страницыClass 6 ICSE Chemistry Sample Paper Set 1Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 5 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Документ2 страницыClass 5 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 2Sunaina Rawat100% (1)
- Class 6 ICSE Biology Sample Paper Set IIДокумент2 страницыClass 6 ICSE Biology Sample Paper Set IISunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Class 5 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Документ2 страницыClass 5 ICSE Maths Sample Paper Term 2 Model 1Sunaina Rawat100% (5)
- Class 5 ICSE Maths SyllabusДокумент1 страницаClass 5 ICSE Maths SyllabusSunaina Rawat57% (7)
- Class 5 ICSE Maths Sample Papers Term 1 Model 2Документ2 страницыClass 5 ICSE Maths Sample Papers Term 1 Model 2Sunaina Rawat64% (28)
- (1983) Stratum CorneumДокумент275 страниц(1983) Stratum CorneumfauzОценок пока нет
- Chem 160.1 Post LabДокумент7 страницChem 160.1 Post LabMarlyn AmanteОценок пока нет
- DissertationДокумент7 страницDissertationChandra SekharОценок пока нет
- Booklet - Consious Water v09Документ35 страницBooklet - Consious Water v09martinscodellerОценок пока нет
- Protocolo de Extracción de ADN Bacteriano - AusubelДокумент5 страницProtocolo de Extracción de ADN Bacteriano - AusubelLesly CastilloОценок пока нет
- Worksheet Week 5 and 6Документ16 страницWorksheet Week 5 and 6EuniceОценок пока нет
- FleaДокумент23 страницыFleaAAREEZ IMRAANОценок пока нет
- Experiment 5 - General and Specific Tests For CarbohydratesДокумент18 страницExperiment 5 - General and Specific Tests For CarbohydratesArthur Lorenz Paraguison100% (1)
- How Microbes Influence Mineral Growth and Dissolution: Chemical GeologyДокумент5 страницHow Microbes Influence Mineral Growth and Dissolution: Chemical GeologyMeghna SharmaОценок пока нет
- 09 Chapter 5Документ48 страниц09 Chapter 5Swagath NОценок пока нет
- Ch. 25 Body Defence MechanismsДокумент34 страницыCh. 25 Body Defence Mechanisms吴昊Оценок пока нет
- Muscular SystemДокумент5 страницMuscular SystemBОценок пока нет
- Erwin-Sheppard Autopsy Report - Redacted by Medical ExaminerДокумент17 страницErwin-Sheppard Autopsy Report - Redacted by Medical ExaminerCheryl Sullenger100% (1)
- Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology - 1908 - HerringДокумент39 страницQuarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology - 1908 - HerringdikhsyaguragainОценок пока нет
- ANPH 111 (Anatomy and Physiology) : Bachelor of Science in NursingДокумент11 страницANPH 111 (Anatomy and Physiology) : Bachelor of Science in NursingMary Grace MapulaОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 2Документ5 страницLab Report 2Jessica TysonОценок пока нет
- Articles About LinguisticsДокумент14 страницArticles About LinguisticslinhhkОценок пока нет
- Assessment of The Target-Capture PCR Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Quantitative Assay and Comparison With Commercial HBV DNA Quantitative AssaysДокумент6 страницAssessment of The Target-Capture PCR Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Quantitative Assay and Comparison With Commercial HBV DNA Quantitative AssaysdwimarufОценок пока нет
- Polymerase Chain ReactionДокумент16 страницPolymerase Chain ReactionAbdulati Abu RewillaОценок пока нет
- POST OP BrunnerДокумент7 страницPOST OP Brunnerjamie carpioОценок пока нет
- Report ViewerДокумент2 страницыReport Viewersufyan rasoolОценок пока нет
- Plants and EnvironmentДокумент284 страницыPlants and EnvironmentYen LeОценок пока нет
- Nervous CoordinationДокумент36 страницNervous CoordinationOlamide AyindeОценок пока нет
- 2019PSNLLB43642-648Syahdietal 1 PDFДокумент15 страниц2019PSNLLB43642-648Syahdietal 1 PDFAlina Vitali TabarceaОценок пока нет
- Skeletal Injury in The ChildДокумент1 216 страницSkeletal Injury in The ChildRizki KokoОценок пока нет
- MSU Campus Map and Building GuideДокумент3 страницыMSU Campus Map and Building GuidemindarsonОценок пока нет
- Dwnload Full Medical Terminology For Health Professions 7th Edition Ehrlich Test Bank PDFДокумент36 страницDwnload Full Medical Terminology For Health Professions 7th Edition Ehrlich Test Bank PDFmarchingpalmerbabg100% (9)
- Mothership Character SheetДокумент2 страницыMothership Character SheetAlexander Dalton0% (1)