Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Bio Exam Question New Official
Загружено:
nabilahИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bio Exam Question New Official
Загружено:
nabilahАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
What is the reaction that joins two amino acids called?
Condensation What is the name of the bond formed by this reaction? Peptide bond What is the process of breaking the bond by adding water, called? Hydrolysis Describe the sequence of events involved when amino acids join to make polypeptides: Primary structure the initial sequence of amino acids in a chain Secondary structure alpha helices (coils) or beta pleated sheets (parallel chains joined) emerge due to hydrogen bonds between the C=O and N-H of the amino acids. Tertiary structure The alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets are folded into a compact globular, 3D structure. Disulphide covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds as well as hydrophobic/philic interactions are all present. Quaternary structure A complex structure of more than one amino acid chain, clustered together. Explain how the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain determines the 3D shape of a functional protein: The sequence of amino acids determines the secondary and tertiary structures of a protein. It also determines the types of bonds between the amino acids and between the residual groups e.g. ionic/hydrogen/disulphide bonds. What is the importance of hydrogen bonds in protein folding? Hydrogen bonds are present in secondary (hydrogen bonds hold the alpha coil and beta parallel sheets together) They are also present in tertiary structures, and are involved in maintaining the 3D shape. Hydrogen bonds form links between adjacent AAs, which in turn alters the shape of the protein and therefore the correct enzyme it is meant to be. Hydrogen bonds form between the O and H groups of the AAs, due to the weak electrostatic bond. Hydrogen bonds are also formed between residual groups. What is the importance of water-repelling and water-attracting amino acid side groups in protein folding? Water-repelling side groups are known as hydrophobic the hydrophobic side chains are turned outwards to keep out of contact with water. Water-attracting side groups are known as hydrophilic the hydrophilic side chains are turned inwards to keep in contact with water. The hydrophobic and hydrophilic qualities to the molecules are important in maintaining the structure of the tertiary and secondary shape.
Amino acids join together into polypeptide chains by peptide bonds, which are formed through condensation reactions.
The linking bonds are formed between the (carboxylic) acid and amine groups of the amino acids, once water has been released rom the condensation reaction. Polypeptide chains can e folded into secondary structures such as alpha helices or beta pleated sheets. Secondary structures can be further folded into tertiary structures such as the globular protein. Polypeptides are then further combined to give the quaternary structure of the protein. The 3D shape is held firmly in place by ionic, hydrogen and covalent disulphide bonds. Disruption of these bonds, by pH extremes or increased temperature, can lead to a denaturing of the protein. Hydrogen and ionic bonds in particular are susceptible to denaturing because they are not heat stable. Protein Keratin Elastin Collagen Myoglobin Ligase Function Forms a waterproof hard layer on skins surface Enables joint capsules to stretch Forms strong fibers in muscle tendons Holds oxygen in muscles Joins molecules using ATP energy
During inspiration (breathing in), air reaches the alveoli through small tubes known as bronchioles. The alveolar wall is composed of a thin layer of epithelial cells, which increase the diffusion rate of oxygen from the alveolar air into the capillaries surrounding the alveoli.
Describe three ways in which alveoli are adapted for their functions: Large surface areas to volume ratio The alveoli are folded, providing a much greater surface area for gas exchange to occur. More oxygen can diffuse across the alveoli due to its increased surface area. The rate of oxygen diffusion is faster. Thin epithelial well because the alveolar wall is one-cell thick, there is a shorter distance for the oxygen to diffuse across to reach the capillaries. This ensures rapid diffusion between the alveoli and capillaries. Steep concentration gradient oxygen travels from a high-low concentration. This means that oxygen is continuously being diffused from the alveoli (higher concentration) to the capillaries/blood (lower concentration). Each alveolus is surrounded by blood capillaries, which ensure a good blood supply. This is important as the blood is constantly taking oxygen away and bringing in more carbon dioxide - which helps to maintain the maximum concentration gradient between the blood and the air in the alveoli. Each alveolus is ventilated, removing waste carbon dioxide and replenishing oxygen levels in the alveolar air. This also helps to maintain the maximum concentration
gradient between the blood and the air in the alveoli. Explain how the structure of the lungs is adapted for rapid gas exchange: Narrow branches blood is travelling at high pressure, which increases the rate of diffusion. Numerous branches/bronchioles allow more deoxygenated blood to gain oxygen, which in turn increases the rate of diffusion. Thin capillary walls reduce the distance for gas to travel and therefore ensure rapid gas exchange. Capillary network the capillaries are wrapped around the alveoli which reduces the distance for the oxygen to travel to the deoxygenated blood and therefore increases rate of diffusion. The purpose of inhalation is to take in oxygen from the surroundings. The purpose of exhalation is to remove waste products/gasses from the body e.g. carbon dioxide.
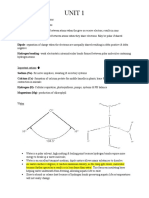
List four functions of the plasma membrane: o split the interior of all cells from the outside environment, serves a gateway between the fluid inside and outside the cell, works as a communicative device, recognizes a cell coming from a particular individual and retains the cell whole and intact. It gives a definite shape to the cell. 2. It provides protection to the internal contents of the cell. 3. It is selectively permeable. 4. It can take in solid and liquid materials by in folding. 5. In animal cells, it is involved in the formation of vesicles, cilia, flagella, microvilli, etc. List the parts and functions of the cell membrane: Phospholipid bilayer Integral protein Fatty acid tails Phosphate heads Peripheral proteins Cholesterol Glycoprotein Glycolipid
Explain how the properties of phospholipids results in the formation of a bilayer:
Вам также может понравиться
- Edexcel As Biology Unit 1 Exam Revision NotesДокумент19 страницEdexcel As Biology Unit 1 Exam Revision NotesFatma Zorlu100% (1)
- BS 3604-2 - 1991 Steel Pipes and Tubes For Pressure Purposes Ferritic Alloy Steel With Specified ElevatedДокумент24 страницыBS 3604-2 - 1991 Steel Pipes and Tubes For Pressure Purposes Ferritic Alloy Steel With Specified ElevatedtienlamОценок пока нет
- Interview Preparation (Mayer Brown Associate)Документ4 страницыInterview Preparation (Mayer Brown Associate)nabilahОценок пока нет
- Molecular BiologyДокумент21 страницаMolecular BiologyvaishnaviОценок пока нет
- CarbohydratesДокумент6 страницCarbohydratesJada HartОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Frequently Asked QuestionsДокумент13 страницUnit 1 - Frequently Asked QuestionsIx CuriousОценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент10 страницThermodynamicsJeric Nichol DaquizОценок пока нет
- Bio Unit 1 and Unit 2 Revision Posters - ComprehensiveДокумент70 страницBio Unit 1 and Unit 2 Revision Posters - Comprehensiveapi-247243068Оценок пока нет
- Aircraft Materials BrochureДокумент6 страницAircraft Materials BrochureAdnan ColoОценок пока нет
- Biology Unit 1 Repeat Questions PDFДокумент12 страницBiology Unit 1 Repeat Questions PDFFarah100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Biological Molecules: SummaryДокумент9 страницChapter 2: Biological Molecules: SummaryMerimaОценок пока нет
- CH 0 Cleaning Cross Refference Table DREW AMEROIDДокумент36 страницCH 0 Cleaning Cross Refference Table DREW AMEROIDPavel ViktorОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes IB Free ResponseДокумент26 страницBiology Notes IB Free ResponseLarry LohОценок пока нет
- Design of Formwork For Column R0 - 3.7 MTRДокумент5 страницDesign of Formwork For Column R0 - 3.7 MTRrahul1433Оценок пока нет
- BMAT Biology Revision NotesДокумент9 страницBMAT Biology Revision Notesmissymar123100% (5)
- Four Steps To Effective Pigment Dispersions Jadel Baptista DCC LanscoДокумент5 страницFour Steps To Effective Pigment Dispersions Jadel Baptista DCC LanscoEyad AlsheiikhОценок пока нет
- 2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesДокумент6 страниц2.4 - Membranes: 2.4.1 - Draw and Label A Diagram To Show The Structure of MembranesDuong TongОценок пока нет
- Mao's China Notes Edexcel AS Level NotesДокумент33 страницыMao's China Notes Edexcel AS Level NotesnabilahОценок пока нет
- Palm Oil RefiningДокумент10 страницPalm Oil Refiningharrison_sОценок пока нет
- Computational MHDДокумент106 страницComputational MHDgdegrezОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Biology - Topic 7Документ15 страницUnit 5 Biology - Topic 7ladzville1014860100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 1 STPM Sem1Документ12 страницBiology Chapter 1 STPM Sem1Jia Hui100% (4)
- CFBC BoilerДокумент7 страницCFBC Boilerkaruna346Оценок пока нет
- SilaneCouplingAgents eДокумент24 страницыSilaneCouplingAgents eElisabeth Kurnia Bloom100% (1)
- API - RP - 571 - Edited - 42 - Questions - PDF - Filename UTF-8''API RP 571 Edited - 42 QuestionsДокумент5 страницAPI - RP - 571 - Edited - 42 - Questions - PDF - Filename UTF-8''API RP 571 Edited - 42 Questionsأحمد صبحى100% (1)
- A Level Biology NotesДокумент6 страницA Level Biology NotesMira AluedeОценок пока нет
- Biology Unit 1 FAQsДокумент8 страницBiology Unit 1 FAQskhinhtetОценок пока нет
- IAL Edexcel Biology AS Unit 1 RevisionДокумент42 страницыIAL Edexcel Biology AS Unit 1 Revisionschoolnada19Оценок пока нет
- ProteinДокумент2 страницыProteinSHA ASHОценок пока нет
- Topic 8 Transport in Mammals Notes-MinДокумент11 страницTopic 8 Transport in Mammals Notes-MinShean LimОценок пока нет
- Bio Notes 1Документ14 страницBio Notes 1Thomas PhillipsОценок пока нет
- BloodДокумент13 страницBloodDr. Ashu NagpalОценок пока нет
- As 2 Biological MoleculesДокумент29 страницAs 2 Biological MoleculesisaacОценок пока нет
- Membranes, Proteins, DNA and Gene ExpressionДокумент15 страницMembranes, Proteins, DNA and Gene ExpressionAshley ArnoldОценок пока нет
- Biology Qns v2Документ37 страницBiology Qns v2randomvidsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesДокумент20 страницChapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological Moleculesjosue868Оценок пока нет
- Topic 3 Digestion and The Circulatory SystemДокумент15 страницTopic 3 Digestion and The Circulatory SystemAddan AddanОценок пока нет
- Biology Test 1 Review Chapters 3-6 Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Carbohydrates, Lipids + Review of Basic Biological ChemistryДокумент7 страницBiology Test 1 Review Chapters 3-6 Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Carbohydrates, Lipids + Review of Basic Biological ChemistryChad SinghОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes Unit 1Документ40 страницBiology Notes Unit 1MirzaAteeqAhmedBaigОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Документ7 страницBIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Student Alejandro Zhou WeiОценок пока нет
- Summary Notes - Topic 2 Membranes, Proteins, DNA and Gene Expression - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelДокумент15 страницSummary Notes - Topic 2 Membranes, Proteins, DNA and Gene Expression - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-LevelJad ElhajjОценок пока нет
- ESSAYДокумент4 страницыESSAYgayatribala306Оценок пока нет
- 11S HSB Notes The Circulatory SystemДокумент4 страницы11S HSB Notes The Circulatory SystemTenika RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Bio ChemДокумент6 страницBio ChemabasheinОценок пока нет
- AP Biology Study GuideДокумент69 страницAP Biology Study GuideEllie GriffinОценок пока нет
- Condensation and HydrolysisДокумент2 страницыCondensation and HydrolysisLeeWeiОценок пока нет
- Edexcel A Level Biology Unit 1 TransportДокумент5 страницEdexcel A Level Biology Unit 1 TransportNavoditteОценок пока нет
- Mass Transport Animals AqaДокумент15 страницMass Transport Animals AqaM MОценок пока нет
- 1.4 Lungs & DiseasesДокумент10 страниц1.4 Lungs & DiseasesRayonesh RayanaОценок пока нет
- AS Biology - Revision Notes Unit 1 - Core PrinciplesДокумент5 страницAS Biology - Revision Notes Unit 1 - Core PrinciplesŞặЇf ДћӎєđОценок пока нет
- Module 10: ProteinsДокумент2 страницыModule 10: ProteinsMariam EskandariОценок пока нет
- Biological Moleculer: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiДокумент24 страницыBiological Moleculer: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiYasmine HadiastrianiОценок пока нет
- L - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkДокумент7 страницL - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkNotImmortalОценок пока нет
- ProteinsДокумент9 страницProteinsJada HartОценок пока нет
- Gas Exchange and BloodДокумент5 страницGas Exchange and Bloodsemirah anthonyОценок пока нет
- Mathematics and Science Faculty Makassar State University 2013-2014Документ6 страницMathematics and Science Faculty Makassar State University 2013-2014Embunku Dan PagimuОценок пока нет
- Flow of ReportingsДокумент3 страницыFlow of ReportingsrenieljrebuengaОценок пока нет
- Proteins Include A Diversity of Structures, Resulting in A Wide Range of FunctionsДокумент12 страницProteins Include A Diversity of Structures, Resulting in A Wide Range of FunctionsDanielle GuerraОценок пока нет
- RespirationДокумент25 страницRespirationfacultyfisheriesОценок пока нет
- Protein Synthesis تصنيع البروتينДокумент12 страницProtein Synthesis تصنيع البروتينBra himОценок пока нет
- Cap 2Документ19 страницCap 2Francesca PrevitaliОценок пока нет
- Topic3 ImprovementsДокумент8 страницTopic3 Improvementsmahmood.mОценок пока нет
- Gas Exchange in HumansДокумент23 страницыGas Exchange in HumansVОценок пока нет
- Biology As/A Level Classwork: Submitted By: Kannita Sipaseuth (Jane)Документ5 страницBiology As/A Level Classwork: Submitted By: Kannita Sipaseuth (Jane)Kannita SIPASEUTHОценок пока нет
- 3 1Документ7 страниц3 1Zainab FahadОценок пока нет
- Respiration NotesДокумент7 страницRespiration NotesTamisha JacobsОценок пока нет
- Metabolism Life Life Sciences Botany Medicine Cells: Kim Janxent P. Berlon Grade 9 STE-Platinum (CMT)Документ4 страницыMetabolism Life Life Sciences Botany Medicine Cells: Kim Janxent P. Berlon Grade 9 STE-Platinum (CMT)Ronnel Mendoza VasquezОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsОт EverandAnatomy and Physiology For Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsОценок пока нет
- What's in A MedicinesДокумент9 страницWhat's in A MedicinesnabilahОценок пока нет
- Should The Developed World Should Be Responsible For The Health Problems in The Developing World?Документ5 страницShould The Developed World Should Be Responsible For The Health Problems in The Developing World?nabilah100% (1)
- Stomach ComplaintДокумент5 страницStomach ComplaintnabilahОценок пока нет
- India Notes Final Completed ForeverДокумент106 страницIndia Notes Final Completed ForevernabilahОценок пока нет
- India Notes Final Completed ForeverДокумент106 страницIndia Notes Final Completed ForevernabilahОценок пока нет
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic: SimilaritiesДокумент8 страницProkaryotic Eukaryotic: SimilaritiesnabilahОценок пока нет
- Chem Atmosphere Notes StrtedДокумент3 страницыChem Atmosphere Notes StrtednabilahОценок пока нет
- Es SpecДокумент6 страницEs SpecnabilahОценок пока нет
- Stalin Caused The Purges Because He Sat at The Top of A Totalitarian SystemДокумент7 страницStalin Caused The Purges Because He Sat at The Top of A Totalitarian SystemnabilahОценок пока нет
- India and The Nationalist Challenge TIMELINE OFFICIAL COMPLETEDДокумент3 страницыIndia and The Nationalist Challenge TIMELINE OFFICIAL COMPLETEDnabilahОценок пока нет
- Early Nazi Foreign PolicyДокумент20 страницEarly Nazi Foreign PolicynabilahОценок пока нет
- Poem 1400Документ16 страницPoem 1400nabilahОценок пока нет
- SEO News CompactДокумент17 страницSEO News CompactnabilahОценок пока нет
- Fatal Beta Blockers: MDMA EcstasyДокумент2 страницыFatal Beta Blockers: MDMA EcstasynabilahОценок пока нет
- The LibraryДокумент13 страницThe LibrarynabilahОценок пока нет
- CH 8 Handouts (All) PDFДокумент34 страницыCH 8 Handouts (All) PDFSandipan SahaОценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Science and Light Emitting DiodesДокумент218 страницSemiconductor Science and Light Emitting DiodesBalaji Raja RajanОценок пока нет
- Factors Influencing ToxicityДокумент7 страницFactors Influencing ToxicityderrickОценок пока нет
- New Atlanta Specifications For HdpeДокумент14 страницNew Atlanta Specifications For HdpeMarvin MartinezОценок пока нет
- Spek Dan Gambar Lelang 2Документ3 страницыSpek Dan Gambar Lelang 2Fajar Pandu WijayaОценок пока нет
- Void Swelling StraalsundДокумент7 страницVoid Swelling StraalsundAzif Ali MoothantevileyilОценок пока нет
- SOPs AcidfyingRiceДокумент2 страницыSOPs AcidfyingRiceTrinh NgoОценок пока нет
- Is 248-1987 Ra 2021Документ14 страницIs 248-1987 Ra 2021Aadarsh Kumar ShitalОценок пока нет
- Module 1 - WMDT BTAM SEA - 2022Документ87 страницModule 1 - WMDT BTAM SEA - 2022Light ManОценок пока нет
- Heating and Cooling CurveДокумент4 страницыHeating and Cooling CurveADogThat GoesBarkОценок пока нет
- EmileorConcerningEducation 10106815Документ165 страницEmileorConcerningEducation 10106815Túlio Coelho SampaioОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual 02Документ158 страницLab Manual 02Stephen VivekОценок пока нет
- Production of X-RAYS Using X-RAY Tube: Journal of Physics: Conference SeriesДокумент13 страницProduction of X-RAYS Using X-RAY Tube: Journal of Physics: Conference SeriesATWIJUKIRE DICKENSОценок пока нет
- Fuel Cells Article in ISOFT by Inderraj GulatiДокумент6 страницFuel Cells Article in ISOFT by Inderraj GulatiInderraj_Gulati100% (1)
- Entropy PDFДокумент19 страницEntropy PDFcarlogarroОценок пока нет
- NiSlip 520AДокумент8 страницNiSlip 520ASTI InspiredОценок пока нет
- F748669CT Process TechnologyДокумент6 страницF748669CT Process Technologyতুহিন ভট্টাচার্য্যОценок пока нет
- 2003, PRASAD-Phytoremediation of Metal-Polluted Ecosystems HypeДокумент15 страниц2003, PRASAD-Phytoremediation of Metal-Polluted Ecosystems HypeMayra FonsecaОценок пока нет
- Gasha International School Homework PolicyДокумент12 страницGasha International School Homework PolicyOmar KhidhirОценок пока нет