Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
02 - Boys Calorimeter LPG
Загружено:
Renu SekaranОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
02 - Boys Calorimeter LPG
Загружено:
Renu SekaranАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
BKG3741 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Sem 11-2012/2013
Faculty of Chemical & Natural Resources Engineering
BKG3721
Fuel & Combustion Lab
Experiment 2
BOYS CALORIMETER-LPG
Name
Matric No.
Group
Program
Section
Date
Sem. 11 - Session 2012/2013
1.0 Objective
BKG3741 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Sem 11-2012/2013
1.
To investigate the calorific value of LPG.
2.
To use and understand techniques for accurate calorimetric
analysis
2.0 Introduction
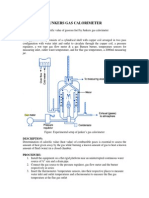
Boys Calorimeter
The Boys Non-recording Gas Calorimeter was designed by the late Sir
Charles Boys F.R.S. as simple but accurate equipment for ascertaining
the calorific values of a large range of gaseous fuels. The gas is fed to
the two burners mounted in the base of the calorimeter where it is
burnt in air. The exhaust gases from the burners are fed through the
calorimeter over the water filled calorimeter coils and leave the
apparatus through a vent in the top of the unit. A thermometer for
measuring the exhaust gas temperature is suspended in this vent. An
outlet drain is provided for any condensate, which is formed from the
exhaust gas. Coolant water is fed through the coils of the calorimeter
from the constant head overflow funnel fixed above the unit. The
water outlet from the calorimeter is fed into a changeover funnel,
which is used for diverting the outlet water from waste into a
measuring vessel or vice-versa. This enables the flow rate of water
through the calorimeter to be determined. The temperature of both
the inlet and outlet water is monitored by mercury in glass
thermometers. When the calorimeter is not in use during short
periods during the testing, the coils of the unit are kept immersed in a
tank containing an alkaline solution. This serves to neutralize any
acidic products deposited on the coils by the combustion of the gas.
Hyde Gas Meter
The gas for the calorimeter is fed via a Hyde type gas meter, which
consists of a specially designed measuring drum housed in a gas-tight
casing and sealed with water. On entry to the-meter the gas is
introduced into a space above the water in the outer casing and the
gas must pass through the measuring drum, causing it to rotate, to
get to the outlet connection of the meter. The measuring drum is
coupled to the pointer on the front of the meter.
3.0
DESCRIPTION
BKG3741 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Sem 11-2012/2013
The Boys Gas Calorimeter Set can be used to determine the calorific
value of a selection of gaseous fuels. The Cussons Type P5615 Boys
Gas Calorimeter set consists of the following items.
1.
A Boys non-recording gas calorimeter.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
A constant head overhead funnel with water connecting tubes,
2 thermometers engraved on stem 0-50 C for temperate
climates or 0-75 C for tropical climates, for inlet and outlet
water temperatures.
2 adjustable reading lenses, chromium plated, with spring clips
for attaching to stems of thermometers in item 3.
2 thermometers engraved on stem 0-35 C for temperate
climates or 0-50 C for tropical climates, for effluent gas and
room temperatures.
3 litre collecting vessel and 1000 ml graduated glass vessel, for
measuring outflow from calorimeter.
Graduated glass vessel, capacity 50 ml, for collecting
condensed products.
General purpose burner set comprising
Town gas and coke oven gas burner, - 14.9 - 22.35 MJ / m3
(400 - 600 BTU / ft 3.) Ref. No. 3 burner
Burner to BS3804; 22.3 - 33.5 MJ / m3 (600 - 900 BTU / ft 3.)
Ref. 5034/100
Natural gas and methane burner, 33.5 - 44.7 MJ / m3 (900 1200 BTU / ft 3.) Ref, 7443/60
Butane, propane, acetylene, ethylene & propylene burner, 44.7
- 130.4 MJ / m3 (1200 -3500 BTU / ft 3.) Ref. 7445/35
Gas control valve (quadrant cock).
A "Hyde" pattern meter of 2.0 liters per revolution capacity. The
dial is divided into 100 divisions and is enclosed by a glass
front. The casing and measuring drum are of tinned copper and
all brass fittings are lacquered. A spirit level, point setting key
and height gauge are provided for setting up the meter
together with fittings for a 0 - 35 C thermometer for
measuring the inlet temperature of the gas.
Cylindrical metal vessel to contain alkaline solution into which
the coils portion of the calorimeter is placed when not in use.
Three accessories are available for use with the calorimeter set.
These are a type P5617 reducing valve, a P5616 set of additional
burners and an automatic gas cut-off device. The reducing valve type
P5617 is intended to reduce the pressure of the incoming gas from
valves up to 30 cm H2O to 5 cm HA If gases at pressures higher than
30 cm H20 are to be used, then a primary stage of pressure reduction
should be used. The P5617 may not be required when testing high CV
bottled gases such as Butane and Propane mixtures if a suitable
pressure reducing valve and control valve are provided on the bottle.
The P5616 set of additional burners contains 3 extra burners to
extend the range of the calorimeter. The burners are suitable for
BKG3741 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Sem 11-2012/2013
Blast furnace gas and low calorific value gas 3.7 MJ / m 3 (150 - 300
BTU / ft3.) " Ref, No. 7 burner.
Propane only 93.1 MJ / m3 (2500 BTU / ft3.) - Ref. 5428/25 or
7458/25.
Butane-air 23.3 - 24.2 MJ / m3 (625 - 650 BTU / ft3.) - Ref.
5034/100.
The Automatic Gas Cut-off device is used for shutting off the gas
supply in the event of the water supply failing.
4.0
Experimental Procedures
1.
Check all the equipment is in good condition and is installed in
the right sequence
2.
Ignite the fire sources, followed by flowing the gas
3.
Put the burner into the calorimeter
4.
Flow the water into the boys calorimeter
5.
Keep the water flow constantly until the changes of temperature
constant.
6.
Note the inlet and outlet temperature for every cycle of the
hydro meter. Meanwhile, collect the water by the container.
Note it for 4 cycles.
7.
Remove the container and weight it
8.
Turn off the gas and the water source.
5.0
Results
BKG3741 Fuel and Combustion Lab
5.1
Sem 11-2012/2013
Calculating for Calorific Value
Table 5.1: Experimental Data
Set 1
Ti1
To1
Set2
Ti2
Set3
To2
Ti3
To3
Average
Temperature, (oC)
Ti
To
1st
Quadrant
2nd
Quadrant
3rd
Quadrant
4th
Quadrant
Mass of
collected
water
Mass of empty beaker, (g)
: ______________________________
Mass of (beaker + water), (g)
: _____________________________
Ambient Temperature,(oC)
: ______________________________
Barometric Pressure, (mmHg)
: ______________________________
Average Inlet Temperature, Ti ,(oC)
:_____________________
Average Oulet Temperature, To ,(oC)
:_____________________
Average Difference of Temperature, T , ( C)
o
:_____________________
6.0 ANALYSIS
6.1 Calculating for Calorific Value , CV (MJ/m3):
Formulae;
BKG3741 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Sem 11-2012/2013
1
4
CV = T W 4.187 GVF
10
3
metersize
,
(
m
)
revs
Where:
W
GVF
Meter Size
Revs
= collected water, (ml)
= gas volume factor (Appendix 1, Table 1)
= 20dm3,capacity of one revolution of the meter in m3
= number of revolutions of the meter (Appendix 1, Table 2)
Calculation examples:-
6.2
Calculating for gas volume correction at other pressures and
temperatures.
Formulae;
V
n a
Vo =
1 + 0.00367 t 760 ao
Where:
V0 = Gas volume at 0C and 760mmHg pressure
V = Gas volume at ambient temperature and pressure
n = Barometric pressure in mmHg
a0 = Vapor pressure in mmHg at temperature t
a = Vapor pressure in mmHg at temperature 0C
t = Ambient temperature
Calculation examples:-
BKG3741 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Sem 11-2012/2013
a)
From the result, described briefly process occurred in the calorimeter?
b)
Why is it important to determine the calorific value of gaseous fuels?
BKG3741 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Sem 11-2012/2013
BKG3741 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Appendix
Sem 11-2012/2013
BKG3741 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Sem 11-2012/2013
Table 1: Gas Volume Factors relative to 0"C and 760 mmHg. Note A formula for calculating the gas volume at
other temperatures and Pressures is given in the text.
mm 10C 11C 12C 13C 14C 15C 16C 17C 18C 19C 20C 21C 22C 23C 24C 25C 26C mmH
Hg 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.15 1.13 1.14 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.16 1.17 730
g
730
732 1.09 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.13 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.15 1.16 1.16 732
734 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.13 1.13 1.14 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.16 734
736 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.13 1.15 1.14 1.15 1.15 1.16 736
738 1.08 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.15 1.14 1.14 1.15 1.16 738
740 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.13 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.15 740
742 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.13 1.14 1.14 1.15 742
744 1.07 1.07 1.07 1.06 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.13 1.13 1.14 1.15 744
746 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.13 1.14 1.14 746
748 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.13 1.13 1.14 748
750 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.13 1.14 750
752 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.13 1.13 752
754 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.13 754
756 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.12 1.13 756
758 1.05 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 1.13 758
760 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.12 760
762 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.11 1.12 762
764 1.04 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 1.12 764
766 1.03 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.11 766
768 1.03 1.04 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 768
770 1.05 1.03 1.04 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.10 1.11 770
772 1.03 1.03 1.03 1.04 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 1.10 772
774 1.02 1.03 1.03 1.03 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 774
776 1.02 1.02 1.03 1.03 1.03 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.08 1.09 1.09 1.10 776
778 1.02 1.02 1.03 1.03 1.03 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.03 1.06 1.09 1.09 778
780 1.02 1.02 1.02 1.03 1.03 1.03 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.06 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.09 780
BKG3751 Fuel and Combustion Lab
mmH
730
732
734
736
738
740
742
744
746
748
750
752
754
756
758
760
762
764
766
768
770
772
774
776
778
780
27C
1.18
1.17
1.17
1.17
1.16
1.16
1.16
1.15
1.15
1.15
1.14
1.14
1.14
1.13
1.13
1.13
1.13
1.12
1.12
1.12
1.11
1.11
1.11
1.10
1.10
1.10
28C
1.18
1.18
1.18
1.17
1.17
1.17
1.16
1.16
1.16
1.15
1.15
1.15
1.14
1.14
1.14
1.14
1.13
1.13
1.12
1.12
1.12
1.12
1.11
1.11
1.11
1.10
29C
1.19
1.19
1.18
1.18
1.18
1.17
1.17
1.17
1.16
1.16
1.16
1.15
1.15
1.15
1.14
1.14
1.14
1.13
1.13
1.13
1.13
1.12
1.12
1.12
1.11
1.11
30C
1.20
1.19
1.19
1.19
1.18
1.18
1.1B
1.17
1.17
1.17
1.16
1.16
1.16
1.15
1.15
1.15
1.14
1.14
1.14
1.13
1.13
1.13
1.13
1.12
1.12
1.12
31C
1.20
502.
1.20
1.19
1.19
1.19
1.18
1.18
1.18
1.17
1.17
1.17
1.16
1.16
1.16
1.15
1.15
1.15
1.14
1.14
1.14
1.14
1.13
1.13
1.13
1.12
32C
1.21
1.21
1.20
1.20
1.20
1.19
1.19
1.19
1.18
1.18
1.18
1.17
1.17
1.17
1.16
1.16
1.16
1.15
1.15
1.15
1.15
1.14
1.14
1.14
1.13
1.15
33C
1.22
1.22
1.21
1.21
1.20
1.20
1.20
1.20
1.19
1.19
1.16
1.18
1.18
1.18
1.17
1.17
1.17
1.16
1.16
1.16
1.15
1.15
1.15
1.14
1.14
1.14
Sem II-2007/2008
34C
1.23
1.22
1.22
1.22
1.21
1.21
1.21
1.20
1.20
1.20
1.19
1.19
1.19
1.18
1.18
1.18
1.17
1.17
1.17
1.16
1.16
1.16
1.15
1.15
1.15
1.14
35C
1.23
1.23
1.23
1.22
1.22
1.22
1.21
1.21
1.21
1.20
1.20
1.20
1.19
1.19
1.19
1.13
1.13
1.13
1.17
1.17
1.17
1.16
1.16
1.16
1.15
1.15
36C
1.24
1.24
1.24
1.23
1.23
1.23
1.22
1.22
1.22
1.21
1.21
1.20
1.20
1.20
1.19
1.19
1.19
1.18
1.18
1.18
1.17
1.17
1.17
1.16
1.16
1.16
37C
1.25
1.25
1.24
1.24
1.24
1.23
1.23
1.23
1.22
1.22
1.22
1.21
1.21
1.21
1.20
1.20
1.20
1.19
1.19
1.19
1.18
1.18
1.13
1.17
1.17
1.16
38C
1.26
1.26
1.25
1.25
1.25
1.24
1.24
1.24
1.23
1.23
1.22
1.22
1.22
1.21
1.21
1.21
1.20
1.20
1.20
1.19
1
1.19
1.1B
1.18
1.18
1.17
39C
1.27
1.27
1.26
1.26
1.26
1.25
1.25
1.24
1.24
1.24
1.23
1.23
1.23
1.22
1.22
1.22
1.21
1.21
1.21
1.20
1.20
1.20
1.19
1.19
1.18
1.18
11
40C
1.26
1.26
1.27
1.27
1.26
1.26
1.26
1.25
1.25
1.25
1.24
1.24
1.23
1.23
1.23
1.22
1.22
1.22
1.21
1.21
1.21
1.20
1.20
1.20
1.19
1.19
mmH
730
732
734
736
738
740
742
744
746
748
750
752
754
756
758
760
762
764
766
768
770
772
774
776
778
780
BKG3751 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Sem II-2007/2008
Table 2: Meter Gas Rates & Water Collection Rates
Approximate
Calorific Value
Time for 1
rev of Meter
Pointer
Number of
rev of Meter
Pointer in
test
Water
Collected
during
Pointer in
test
Factor to be
used in
calculation 1/
(0.2m3xrevs)
18-19 MJ per m3
(500
B.
Th.
Us /cu ft)
52s-54s
2160-2260g
37-38 MJ per m3
(1000 B. Th. Us
/cu ft)
1min44s1min49s
864-904g
2.5
75-76 MJ per m3
(2000 B. Th. Us
/cu ft)
3min34s3min-38s
432-452g
12
BKG3751 Fuel and Combustion Lab
Sem II-2007/2008
Example:Outlet Temperature, C
Inlet Temperature, C
16.2
16.2
16.2
16.2
36.4
36.5
36.6
36.5
Average Inlet Temperature = 16.2C.
Average Outlet Temperature = 36.5C
Gives Average difference of temperature = 20.3 C
Number of revs
Meter Capacity
Water collected
Barometer
Meter temp.
G.V. Factor
5
0.2m3
2100 ml.
754 mm,
17.8C
1,089
Calorific Value =20.3*2100*4.187*1.089*(1 / (0.2 *5))*10 -4
=19.438MJ/m3
To convert MJ / m3 into BTU/ ft3. multiply MJ / m3
by 26.8413 Therefore in example A calorific value
in BTU/ ft3
19.438 x 26.8413 = 521.7 BTU/ ft3
13
Вам также может понравиться
- Lab 1 Boys CalorimeterДокумент11 страницLab 1 Boys CalorimeterHafizszul Feyzul100% (1)
- Calorific ValueДокумент14 страницCalorific Valuenfar100% (1)
- s2158812 Boys CalorimeterДокумент15 страницs2158812 Boys CalorimeterOmar A-gОценок пока нет
- Gas1 ManДокумент11 страницGas1 ManLahiru DilshanОценок пока нет
- Junkers Gas CalorimeterДокумент2 страницыJunkers Gas Calorimeterghambira83% (6)
- Operating Instruction Manual Of: Junker's Gas CalorimeterДокумент5 страницOperating Instruction Manual Of: Junker's Gas CalorimeterService MMIОценок пока нет
- V. Ganapathy. Simplify Heat Recovery Steam Generator Evaluation PDFДокумент7 страницV. Ganapathy. Simplify Heat Recovery Steam Generator Evaluation PDFgonzalezpcjОценок пока нет
- Boiler EfficiencyДокумент28 страницBoiler Efficiencybzkizo_sbbОценок пока нет
- To 2Документ32 страницыTo 2Miguel MatallanaОценок пока нет
- Boiler Fuel Savings by Heat Recovery and Reduced Standby Losses B. GrabsДокумент7 страницBoiler Fuel Savings by Heat Recovery and Reduced Standby Losses B. GrabsPhilip ShihОценок пока нет
- UOP 603 Trace CO and CO2 in Hydrogen and Light Gases Hydrocarbon by GCДокумент6 страницUOP 603 Trace CO and CO2 in Hydrogen and Light Gases Hydrocarbon by GCMorteza SepehranОценок пока нет
- 4.1 BoilerДокумент28 страниц4.1 Boilerrashm006ranjanОценок пока нет
- M.E. Lab 2 Act. 2Документ3 страницыM.E. Lab 2 Act. 2Patricia GalorioОценок пока нет
- By Adapted Plant Physical Compared: An To Can MeansДокумент15 страницBy Adapted Plant Physical Compared: An To Can MeansrajuОценок пока нет
- ASTM D5865 07A 53 3286 Poder Calorifico PDFДокумент14 страницASTM D5865 07A 53 3286 Poder Calorifico PDFCarol Perez TОценок пока нет
- 03po Ar 3 6 PDFДокумент4 страницы03po Ar 3 6 PDFMarcelo Varejão CasarinОценок пока нет
- The Invention: Zadgaonkars' ProcessДокумент3 страницыThe Invention: Zadgaonkars' ProcessHimanshu SukhadwalaОценок пока нет
- Sunway Practical Lab Bicarbonate Decomposition 2012Документ11 страницSunway Practical Lab Bicarbonate Decomposition 2012venkieeОценок пока нет
- Lab 1 CalorimeterДокумент3 страницыLab 1 CalorimeterAndrian NasirОценок пока нет
- Junker Gas CalorimeterДокумент1 страницаJunker Gas Calorimeterakashshinde648Оценок пока нет
- Bomb CalorimetryДокумент17 страницBomb Calorimetryglendale aguillonОценок пока нет
- Trace Hydrocarbons in Hydrogen or LPG by Gas ChromatographyДокумент12 страницTrace Hydrocarbons in Hydrogen or LPG by Gas ChromatographyDavinОценок пока нет
- Santosh Kumar: Producl Engineer / BPP FBДокумент17 страницSantosh Kumar: Producl Engineer / BPP FBjp mishraОценок пока нет
- NG Lab Report As at 2012Документ27 страницNG Lab Report As at 2012Amir O. Osho50% (2)
- BombCalorimeterManual1 PDFДокумент20 страницBombCalorimeterManual1 PDFAgnes YogaОценок пока нет
- Engineering Bulletin No 1: Boiler and Furnace TestingОт EverandEngineering Bulletin No 1: Boiler and Furnace TestingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Determination of Low Water Contents in PlasticsДокумент5 страницDetermination of Low Water Contents in Plasticsyouni_2005Оценок пока нет
- LP-Gas Service Mans ManualДокумент52 страницыLP-Gas Service Mans Manualprocha1100% (1)
- Experiment No 5 FinalДокумент27 страницExperiment No 5 FinalJule Renz PaguiaОценок пока нет
- Aph FireДокумент25 страницAph Firesekhar_ntpcОценок пока нет
- Astm D5865Документ14 страницAstm D5865Jaime Maciel71% (7)
- Astm D 5865-04Документ12 страницAstm D 5865-04Luis Alberto Curtidor GuataquiОценок пока нет
- Energy Performance Assessment of BoilersДокумент15 страницEnergy Performance Assessment of BoilersVishwarajОценок пока нет
- Mec554 Thermalfluid Lab: Experiment's TitleДокумент20 страницMec554 Thermalfluid Lab: Experiment's TitleMuhammad Khairul Afnan RoslanОценок пока нет
- Mohamed Ibrahim Darwish 15101468 12th ReportДокумент45 страницMohamed Ibrahim Darwish 15101468 12th ReportMohamed DarwishОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Manual Engineering Thermodynamics (ME-203)Документ30 страницLaboratory Manual Engineering Thermodynamics (ME-203)Ahmed AlrubeayОценок пока нет
- Testing Process For Bio Medical Waste IncineratorДокумент97 страницTesting Process For Bio Medical Waste IncineratorJeetendra KulkarniОценок пока нет
- Capacity Regulator CpceДокумент8 страницCapacity Regulator CpceNovan AndriantoОценок пока нет
- L-545 Servicemans ManualДокумент56 страницL-545 Servicemans ManualingenerproОценок пока нет
- Energy Performance Assessment of BoilersДокумент5 страницEnergy Performance Assessment of BoilersUsama SufyanОценок пока нет
- IEICOS Boys Gas Calorimeter Catalog 2011Документ1 страницаIEICOS Boys Gas Calorimeter Catalog 2011Shaho Abdulqader MohamedaliОценок пока нет
- Document 1Документ13 страницDocument 1Muhammad SaifuddinОценок пока нет
- M.E LAB 3 Experiment 5 Steam Generator Without Super Heating SurfaceДокумент14 страницM.E LAB 3 Experiment 5 Steam Generator Without Super Heating SurfaceDrw Arcy0% (1)
- 2 ERG 401 2015 Energy Performance Analysis of BOILERДокумент57 страниц2 ERG 401 2015 Energy Performance Analysis of BOILERnaveenОценок пока нет
- 08 Chapter 3Документ22 страницы08 Chapter 3BALAJI CHOUHANОценок пока нет
- Thermax BoilerДокумент10 страницThermax Boileramitrawal0100% (1)
- ASME - PTC4.1 .Boiler Efficiency TestДокумент29 страницASME - PTC4.1 .Boiler Efficiency TestBC Harish92% (13)
- Energy Efficiency Assessment BookДокумент170 страницEnergy Efficiency Assessment BookNoel Dunn100% (4)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersОт EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersОценок пока нет
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SОт EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SОценок пока нет
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsОт EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsОценок пока нет
- Heat Exchanger Design Guide: A Practical Guide for Planning, Selecting and Designing of Shell and Tube ExchangersОт EverandHeat Exchanger Design Guide: A Practical Guide for Planning, Selecting and Designing of Shell and Tube ExchangersРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (13)
- Advanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionОт EverandAdvanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionОценок пока нет
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitОт EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitОценок пока нет
- Respiration Calorimeters for Studying the Respiratory Exchange and Energy Transformations of ManОт EverandRespiration Calorimeters for Studying the Respiratory Exchange and Energy Transformations of ManОценок пока нет
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewОт EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewОценок пока нет
- Heating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsОт EverandHeating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsОценок пока нет
- Cell As A Unit of LifeДокумент40 страницCell As A Unit of LifeRenu SekaranОценок пока нет
- For Section A, Write Your Answer in The Answer Sheet Provided in Page 12Документ12 страницFor Section A, Write Your Answer in The Answer Sheet Provided in Page 12Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1Документ22 страницыChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1siti zalikhaОценок пока нет
- Wesley Methodist School Klang MONTHLY TEST 1 (2019) Chemistry Form 4 Total: 50 MarksДокумент8 страницWesley Methodist School Klang MONTHLY TEST 1 (2019) Chemistry Form 4 Total: 50 MarksRenu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Rate of ReactionДокумент27 страницRate of ReactionziziОценок пока нет
- Science Form 1Документ15 страницScience Form 1Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- 06 Chapter 1 Rate of ReactionДокумент35 страниц06 Chapter 1 Rate of ReactionRenu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan (Subject: SCIENCE)Документ3 страницыLesson Plan (Subject: SCIENCE)Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Format 27-1 (Opal)Документ4 страницыLesson Plan Format 27-1 (Opal)Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Format 28-3 TopazДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan Format 28-3 TopazRenu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Format 24-2 (Opal)Документ3 страницыLesson Plan Format 24-2 (Opal)Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Format 27-1Документ4 страницыLesson Plan Format 27-1Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Format 24-2Документ3 страницыLesson Plan Format 24-2Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Format 31-3Документ3 страницыLesson Plan Format 31-3Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- E E:sl: Et Isl If:: I Ii:i I Il", 3:p:r I Et:sfДокумент1 страницаE E:sl: Et Isl If:: I Ii:i I Il", 3:p:r I Et:sfRenu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Format 28-3Документ3 страницыLesson Plan Format 28-3Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Intensive 4 Page 2Документ1 страницаIntensive 4 Page 2Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Form 2 - Page 2Документ1 страницаForm 2 - Page 2Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Form 2 - Page 1Документ1 страницаForm 2 - Page 1Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan (Subject: SCIENCE)Документ2 страницыLesson Plan (Subject: SCIENCE)Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Intensive 4 Page 3 PDFДокумент1 страницаIntensive 4 Page 3 PDFRenu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Intensive 3 Page 2Документ1 страницаIntensive 3 Page 2Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Intensive 4 Page 4Документ1 страницаIntensive 4 Page 4Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Form 2 - Page 2Документ1 страницаForm 2 - Page 2Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- School Culture Climate & AchievementДокумент13 страницSchool Culture Climate & AchievementPutra Rahmat ArmyОценок пока нет
- Form 1 Assessment OCTOBER 2015 Form 1 Science: (Duration: 25 Minutes)Документ8 страницForm 1 Assessment OCTOBER 2015 Form 1 Science: (Duration: 25 Minutes)Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Teacher Leaders Impacting School CultureДокумент10 страницTeacher Leaders Impacting School CultureYugesh D PANDAYОценок пока нет
- The Significance of Assumptions Underlying School Culture in The Process of ChangeДокумент6 страницThe Significance of Assumptions Underlying School Culture in The Process of ChangeRenu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Form 1 Assessment OCTOBER 2015 Form 1 Science: (Duration: 25 Minutes)Документ8 страницForm 1 Assessment OCTOBER 2015 Form 1 Science: (Duration: 25 Minutes)Renu SekaranОценок пока нет
- Venturi Meter and Orifice Plate Lab ReportДокумент11 страницVenturi Meter and Orifice Plate Lab Reportprajwal m100% (1)
- 2022 - Hyd 443 - 1Документ201 страница2022 - Hyd 443 - 1api-620585842Оценок пока нет
- Energetics: Pharmaceutical Enzymes Kraft PulpingДокумент6 страницEnergetics: Pharmaceutical Enzymes Kraft Pulping박우진Оценок пока нет
- Sewage Treatment PlantДокумент32 страницыSewage Treatment Plantjamroze496114100% (2)
- Fluids Lec1 Pump TurbinesДокумент46 страницFluids Lec1 Pump TurbinesPrem LoveОценок пока нет
- 1 - Intro + Basic ConceptsДокумент48 страниц1 - Intro + Basic ConceptsShawki BsatОценок пока нет
- Abstractions From Precipitation: AbstractionДокумент10 страницAbstractions From Precipitation: AbstractionmarkhanОценок пока нет
- MAN Energy Develops IMOKAT II Catalyst To Reduce Methane SlipДокумент10 страницMAN Energy Develops IMOKAT II Catalyst To Reduce Methane Slipali.khalifaОценок пока нет
- 1E ME0084RevDДокумент12 страниц1E ME0084RevDkarthickmectrОценок пока нет
- ARTESA 394 - 01-25-17 - 12-46-38PM - ACU - ReportДокумент1 страницаARTESA 394 - 01-25-17 - 12-46-38PM - ACU - ReportPedro Antonio Mejia SuarezОценок пока нет
- Topic 1 ACMVДокумент21 страницаTopic 1 ACMVEmi ArisОценок пока нет
- 30J - APCI LNG Liquefaction ProcessesДокумент27 страниц30J - APCI LNG Liquefaction ProcessesPutu Indra Mahatrisna100% (2)
- CV Prop - Termof PG 518-19-20Документ3 страницыCV Prop - Termof PG 518-19-20MargaritaОценок пока нет
- Entry Exam - M.Sc. / 2015-2016 Chemical Engineering Department University of Baghdad Date 13/8/2015 Time: 3 HrsДокумент5 страницEntry Exam - M.Sc. / 2015-2016 Chemical Engineering Department University of Baghdad Date 13/8/2015 Time: 3 Hrshiba thamirОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Fusion: Advantages of Fusion PowerДокумент2 страницыIntroduction To Fusion: Advantages of Fusion PowerThe milk goes firstОценок пока нет
- T10206 XG02 P1PGB - 110001 - Pid CCWДокумент1 страницаT10206 XG02 P1PGB - 110001 - Pid CCWtuyencntnОценок пока нет
- Ch. 1 Particulate Nature of MatterДокумент10 страницCh. 1 Particulate Nature of MatterهندОценок пока нет
- SURGE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS - Part 7Документ2 страницыSURGE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS - Part 7Ali QureshiОценок пока нет
- Hoshizaki IM-500SAA Icemaker Service ManualДокумент39 страницHoshizaki IM-500SAA Icemaker Service ManualBenjamin DoverОценок пока нет
- Surface WaterДокумент22 страницыSurface WaterLuis MenendezОценок пока нет
- Default Separator CalculationДокумент209 страницDefault Separator CalculationzamijakaОценок пока нет
- Compressed Air Process FiltrationДокумент20 страницCompressed Air Process FiltrationOgut AjaОценок пока нет
- Note Ideal Gas TutorialДокумент5 страницNote Ideal Gas TutorialGnabryОценок пока нет
- Amine TreatmentДокумент2 страницыAmine TreatmentEmamokeОценок пока нет
- 006 Intro To BHS (Cased Hole)Документ17 страниц006 Intro To BHS (Cased Hole)VanVietRoanОценок пока нет
- Gas Laws Problem Set (Edited)Документ2 страницыGas Laws Problem Set (Edited)Kurt Bidua0% (1)
- Water Lect 2 - Project CyclesДокумент70 страницWater Lect 2 - Project CyclesNur Hazirah Sadon100% (1)
- VCS Guidelines Rev 10 01 2Документ15 страницVCS Guidelines Rev 10 01 2DMYTRO STRYZHKOVОценок пока нет
- Cien 30143 - Hydraulics 2Документ44 страницыCien 30143 - Hydraulics 2VincentОценок пока нет
- Oct27 2012Документ1 страницаOct27 2012pribhor2Оценок пока нет