Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MCDB 1A Midterm 1 2012
Загружено:
Kenji SoaresИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MCDB 1A Midterm 1 2012
Загружено:
Kenji SoaresАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name _________________________ TA ________________________
MCDB 1A Midterm 1
October 23, 2012
Scantron Instructions:
1. Use a #2 pencil to complete the form.
2. Write your name and fill in the appropriate bubbles.
3. Write your perm. number in the ID number box and fill in the bubbles.
4. Fill in the entire rectangle of the answer you choose.
5. Write the color of you exam below the ID box
READ ALL QUESTIONS THOROUGHLY----IN ALL CASES, PICK THE BEST ANSWER
30 Questions - 3 or 4 Points Each - as noted
1 Test Color Question - 1 point
1. Consider the following transcription bubble. If the region of DNA that needs to be
transcribed is to the right of the RNA Polymerase, which strand will be the template? (4
points)
A. bottom strand
B. top strand
C. insufficient information to answer the question
2. Which level of protein structure frequently uses both weak forces and covalent bonds?
(3 points)
A. secondary
B. primary
C. quaternary
D. tertiary
3. How many levels of protein structure (i.e., primary, secondary, tertiary and
quaternary) can involve covalent bonds? (3 points)
A. 1
B. 2
C. 0
D. 4
E. 3
MCDB 1A MT 1 Blue (5) Version: 1 Page: 1
4. How many fatty acids are typically in a phospholipid found in cellular membranes? (3
points)
A. 1
B. 0
C. 3
D. 2
E. some other number
5. Which of the following is part of a typical eukaryotic gene? (3 points)
A. introns
B. exons
C. both exons and introns are found in genes
6. What is the maximum number of amino acids that are loaded on a single tRNA prior to
its arrival at a ribosome? (3 points)
A. a very large number, since proteins can be thousands of amino acids long
B. 2
C. 1
D. 0
7. Which of the following enzymes does not add nucleotides to the growing chain during
replication? (4 points)
A. DNA ligase
B. DNA polymerase III
C. RNA primase
D. DNA polymerase I
E. all of the above add nucleotides to the growing chain
8. Which of the following amino acids is least likely to be found on the surface of a protein
floating freely in the cytoplasm? (3 points)
A. Amino Acid a
B. Amino Acid b
C. Amino Acid c
D. Amino Acid d
E. Amino Acid e
MCDB 1A MT 1 Blue (5) Version: 1 Page: 2
9. Which polymer has the highest molecular weight, i.e., which is the largest? (3 points)
A. an average DNA molecule
B. an average mRNA
C. cellulose
D. lipids
10. Imagine that you are doing the Meselson-Stahl experiment using N14 and N15 to
examine the mechanism of DNA replication. You grow the bacteria for many
generations in N14, spin down the cells and resuspend them in N15 media. Assuming
that replication proceeds by a semi-conservative mechanism, what would you observe
in the CsCl gradient after two rounds of replication? (4 points)
A. tube a
B. tube b
C. tube c
D. tube d
E. none of the above
11. Why do Chargaffs rules (A=T and C=G) hold for DNA but not for RNA? (3 points)
A. RNA is single stranded and DNA is double stranded
B. RNA has U instead of T
C. RNA has ribose instead of deoxyribose
D. RNA is much smaller than DNA
E. Some other reason is responsible for this fact
12. The overall reaction for the metabolic breakdown of glucose is: (4 points)
C
6
H
12
O
6
+6 O
2
--> 6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O
In which stage is the water actually formed?
A. electron transport/oxidative phosphoryation
B. the TCA cycle
C. the pre-entry reaction (pyruvate to acetyl CoA)
D. Glycolysis
E. none is a correct answer because water forms in all stages of metabolism
MCDB 1A MT 1 Blue (5) Version: 1 Page: 3
13. Which of the following polymers have branched chains? MARK ALL THAT APPLY (3
points)
A. cellulose
B. glycogen
C. DNA
D. starch
E. proteins
14. If you had a mutation that caused a codon to change from UAA to UAC, what would
you expect to happen? (4 points)
A. the mutant protein would be the same size as usual, just different in its composition
and perhaps its function
B. the mutant protein that would get synthesized would be longer than the normal
protein
C. the mutant protein that would get synthesized would be shorter than the normal
protein
D. more information is necessary to answer this question
15. Which new strand will be the lagging strand, i.e. which will be assembled
discontinuously? (3 points)
A. strand 1
B. strand 2
C. both strands
D. neither strand
16. Which is true about enzymes? (3 points)
A. enzymes speed up reactions by affecting the thermodynamics of a reaction
B. enzymes speed up reactions by affecting the overall change in the free energy of a
reaction
C. enzymes speed up reactions by affecting the activation energy of a reaction
MCDB 1A MT 1 Blue (5) Version: 1 Page: 4
17. In the 1944 Avery transformation experiment utilizing DNase, RNase and protease,
which of the following observations was the most important in supporting the
conclusion that DNA is genetic material? (4 points)
A. treatment of the extract with protease prevented transformation of R to S cells
B. treatment of the extract with DNase prevented transformation of R to S cells
C. treatment of the extract with RNase prevented transformation of R to S cells
18. Which part of an amino acid is involved in the hydrogen bonds that lead to the
formation of beta sheets? (3 points)
A. the alpha carbon
B. the R group
C. the core unit
D. some other part
19. Imagine that you have an mRNA molecule that encodes a protein 489 amino acids long.
Now, imagine that some errors occur during transcription. Which of the following
errors is likely to have the most severe consequences for the ability of the resulting
protein to function? (3 points)
A. the error is the deletion of one nucleotide in the 98th codon
B. the error is the replacement of one nucleotide for another in the 42th codon (not
creating a stop codon)
C. the error is the addition of one nucleotide in the 468th codon
D. all of these are equally likely to have severe consequences
20. Which of the following is not a part of the backbone of DNA or RNA? (3 points)
A. sugar
B. phosphate
C. aromatic base
D. all are part of the backbone
21. When a protein denatures, what kinds of bonds are disrupted? (4 points)
A. covalent bonds
B. weak bonds/forces
C. protein denaturation does not involve breaking of bonds
D. both weak bonds/forces and covalent bonds
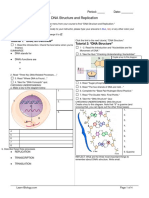
22. Consider the following mRNA.
5 CAGGUAAAUGCAGGGAAUGCUAAUAUAGUUACCCAG 3
What would be the identity of the 4th amino acid in the encoded protein? (3 points)
A. methionine
B. alanine
C. serine
D. leucine
E. some other amino acid
MCDB 1A MT 1 Blue (5) Version: 1 Page: 5
23. How many amino acids would be in the protein encoded by the RNA in the previous
question? (3 points)
A. 6
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
E. some other number
24. Is this the correct chemistry for peptide bond formation? (3 points)
A. yes
B. no
25. Which of the following amino acids can engage in disulfide bonding? (3 points)
A. amino acid a
B. amino acid b
C. amino acid c
D. amino acid d
E. amino acid e
26. What is a gene composed of? (3 points)
A. cheese
B. DNA
C. RNA
D. protein
MCDB 1A MT 1 Blue (5) Version: 1 Page: 6
27. THE GENETIC CODE TABLE IS NOT USEFUL FOR THIS QUESTION. THESE ARE
MADE UP DATA.
Imagine you were doing the experiments with bacterial extracts and synthetic RNAs
that were trying to figure out the genetic code. You do the following experiments and
get the following results:
When your synthetic RNA is polyU, you get a long chain of phenylalanine (poly-
phenylalanine).
When your synthetic RNA is polyC, you get a long chain of tryptophan (poly-
tryptophan).
When your synthetic RNA is ACACACACACACACACACACAC.., you get both
poly-serine and poly-leucine
When your synthetic RNA is AGCAGCAGCAGCAGCAGCAGC, you get three
products. One is a repeating polymer of leucine-alanine-proline, another is a repeating
polymer of tyrosine-valine-isoleucine and the third one is a repeating polymer of
asparagine-cysteine-glycine.
Which of the following is a plausible conclusion (4 points)?
A. the genetic code is based on the number 4
B. the genetic code is based on the number 3
C. the genetic code is based on the number 2
D. the genetic code is based on the number 1
E. not enough information to make an educated guess
28. Imagine that you are a hungry cell and acquire a big supply of 1,3-biphosphoglycerate.
How many ATPs can you get from the complete oxidation of each molecule of 1,3-
biphosphoglycerate to CO
2
and water, including from the NADH and FADH
2
that are
generated along the way. (3 points)
A. 17
B. 26
C. 34
D. 13
E. some other number
29. In the Hershey-Chase experiment using radioactive S35 and P32, what did the S35
label? (4 points)
A. protein because S is present in a couple of amino acids
B. protein because S is present in all amino acids
C. DNA because S is present in pyrimidines
D. DNA because S is present in purines
E. none of the above is a correct answer
30. Imagine that you are working on the protein DNA Polymerase, which is synthesized
on ribosomes like all proteins and then gets transported to the nucleus because it has a
nuclear localization signal. What is a nuclear localization signal made of? (4 points)
A. a combination of two of the above answers
B. carbohydrates attached to the protein
C. fatty acids attached to the protein
D. amino acids within the DNA polymerase protein itself
MCDB 1A MT 1 Blue (5) Version: 1 Page: 7
End of Exam. Please return your test and scantron to your TA.
If you don't have a TA, give your exam and scantron to Dr. Bush near to the podium
on stage.
MCDB 1A MT 1 Blue (5) Version: 1 Page: 8
G
e
n
e
t
i
c
C
o
d
e
Вам также может понравиться
- UIUC MCB 150 Practice Exam 02 Fall 2009Документ15 страницUIUC MCB 150 Practice Exam 02 Fall 2009Carlos GuiterizОценок пока нет
- 2012 Bio 93 Final Exam Lecture D Version B KEYДокумент11 страниц2012 Bio 93 Final Exam Lecture D Version B KEYHyds HshsОценок пока нет
- MCDB !B Midterm 1 KeyДокумент8 страницMCDB !B Midterm 1 KeyKenji SoaresОценок пока нет
- Mock FinalДокумент19 страницMock Finalbuddybbuddy100% (1)
- Cell TestttДокумент22 страницыCell TestttMark Soto100% (2)
- MCDB 1B 2010 FinalДокумент10 страницMCDB 1B 2010 Finaleddie_solis_4Оценок пока нет
- Dna and Rna StructureДокумент63 страницыDna and Rna StructureKhaled DabourОценок пока нет
- Protein Synthesis Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Документ6 страницProtein Synthesis Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Tia wkwk100% (1)
- Quiz 1 Answers Protein FoldingДокумент7 страницQuiz 1 Answers Protein FoldingJeevikaGoyalОценок пока нет
- BIO 361 Exam 4 ReviewДокумент45 страницBIO 361 Exam 4 ReviewNigel Zhang100% (1)
- PCB3103C Exam 2 (Take-Home)Документ5 страницPCB3103C Exam 2 (Take-Home)Pmorris1898Оценок пока нет
- Biocomp Exam 2013Документ11 страницBiocomp Exam 2013e100% (1)
- 6.6.Q BANK SLdocxДокумент20 страниц6.6.Q BANK SLdocxNaz Gümüşlüoğlu100% (1)
- Lab - 1.09 - DNA Replication - Lab - BR2016 PDFДокумент4 страницыLab - 1.09 - DNA Replication - Lab - BR2016 PDFBeth RobeliaОценок пока нет
- FGIKReplication Student HandoutДокумент16 страницFGIKReplication Student Handoutnj saim100% (1)
- Exam Questions 1. A Level Biology, AQA, Unit 2, June 2015Документ19 страницExam Questions 1. A Level Biology, AQA, Unit 2, June 2015Ryan JamesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 BB QA (Corrected)Документ6 страницChapter 16 BB QA (Corrected)Rafael G. Garcia SanchezОценок пока нет
- 9700 w15 QP 13Документ16 страниц9700 w15 QP 13Hew Li Yang100% (1)
- 10 - Genetics and Evolution (Worksheet)Документ8 страниц10 - Genetics and Evolution (Worksheet)Lim YH100% (1)
- B1001A Practice+Midterm+Exam 2023Документ15 страницB1001A Practice+Midterm+Exam 2023ye100% (1)
- The Cell Cycle & CANCERДокумент17 страницThe Cell Cycle & CANCERjesuslovers100% (1)
- MBO07Документ432 страницыMBO07Sanjana Srivastava100% (1)
- TOPIC 3.5 - Photosynthesis (AP Bio) Student Learning Guide, (2021)Документ6 страницTOPIC 3.5 - Photosynthesis (AP Bio) Student Learning Guide, (2021)L Chan100% (1)
- Topic K Respiration H1 H2 2017 Tutorial QNДокумент11 страницTopic K Respiration H1 H2 2017 Tutorial QNliang yi choo100% (1)
- 2012 Bio 93 Final Exam Lecture C Version A KEY PDFДокумент11 страниц2012 Bio 93 Final Exam Lecture C Version A KEY PDFHyds Hshs100% (1)
- Evolution ReviewДокумент3 страницыEvolution ReviewJenna Vong100% (1)
- MT Sep 2021-22 XII Bio QP 004 FinalДокумент10 страницMT Sep 2021-22 XII Bio QP 004 FinalKalpna Rani100% (1)
- Enzyme ProtocolДокумент6 страницEnzyme Protocoltapas kunduОценок пока нет
- TOPIC 3.4, 3.6 - Cellular Respiration Student Learning Guide (AP Bio)Документ8 страницTOPIC 3.4, 3.6 - Cellular Respiration Student Learning Guide (AP Bio)L Chan100% (1)
- Sat II Real Evolution QuestionsДокумент3 страницыSat II Real Evolution QuestionsMido MidoОценок пока нет
- MCQ Chapter 1 Page 2Документ27 страницMCQ Chapter 1 Page 2Leen Alodat100% (1)
- Cell Communication Packet 1Документ20 страницCell Communication Packet 1jade20090106100% (1)
- 9 Csomes DNAДокумент6 страниц9 Csomes DNAKenth Roger A. MaquilingОценок пока нет
- 2009 MidtermI Form1Документ12 страниц2009 MidtermI Form1svОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates NotesДокумент5 страницCarbohydrates NotesWutWut100% (1)
- 1.5 Nucleic Acids QPДокумент17 страниц1.5 Nucleic Acids QPHuseyn AgazadeОценок пока нет
- Khan Academy DNA Technology QuestionsДокумент4 страницыKhan Academy DNA Technology QuestionsLoraОценок пока нет
- Preparatory Exam Nov-Dec 2023Документ15 страницPreparatory Exam Nov-Dec 2023Dr. M. Prince100% (1)
- H2 Evolution QuestionsДокумент27 страницH2 Evolution QuestionsWesley Tan100% (1)
- Lecture 2 Membrane Transport & Cell Signaling - QuestionsДокумент6 страницLecture 2 Membrane Transport & Cell Signaling - Questions中华雅思王Оценок пока нет
- TOPIC 6.1 - 6.2 - DNA Structure and Replication, Student Learning GuideДокумент4 страницыTOPIC 6.1 - 6.2 - DNA Structure and Replication, Student Learning GuideL ChanОценок пока нет
- Energy and Ecosystems Part 2Документ16 страницEnergy and Ecosystems Part 2dfq67gtkqs100% (1)
- L Energy and Respiration I PDFДокумент12 страницL Energy and Respiration I PDFMichelle Yeap67% (3)
- Bio Exam ZsmuДокумент84 страницыBio Exam ZsmuManthan Patil100% (1)
- IBO 2008 Theory Part A - CCLДокумент67 страницIBO 2008 Theory Part A - CCLOmala100% (1)
- 4 RespirationДокумент80 страниц4 RespirationTori Hop Along Clinch100% (1)
- Full Length Practice Test - 01Документ20 страницFull Length Practice Test - 01Abhishek AroraОценок пока нет
- 23 How To Do Hardy Weinberg ProblemsДокумент5 страниц23 How To Do Hardy Weinberg ProblemstsrifОценок пока нет
- 2 Mem TransДокумент6 страниц2 Mem TransPhuong DoanОценок пока нет
- ECOLOGY TEST Mhs JusanДокумент4 страницыECOLOGY TEST Mhs Jusannatukundajoshua42Оценок пока нет
- Edexcel A-LEVEL BIO4 June 2005 QPДокумент20 страницEdexcel A-LEVEL BIO4 June 2005 QPapi-3726022100% (1)
- 4.3 Classification and EvolutionДокумент109 страниц4.3 Classification and Evolutiontaaniya sadiq100% (1)
- Ecology: B Division E BДокумент15 страницEcology: B Division E BVeena Agaram100% (1)
- IB Biology G Assess WSSДокумент3 страницыIB Biology G Assess WSSHellö Pëach100% (1)
- Recombinant DNA MCQДокумент6 страницRecombinant DNA MCQChaze WaldenОценок пока нет
- Ls3 Midterm I Exam: InstructionsДокумент8 страницLs3 Midterm I Exam: InstructionsArmaanGurayaОценок пока нет
- Midterm 2 Review QuestionsДокумент23 страницыMidterm 2 Review QuestionshamoudyelmouallemОценок пока нет
- Transcription and Translation - QuestionsДокумент8 страницTranscription and Translation - QuestionsoceanblueeyesОценок пока нет
- AP Biology Unit 5 ExamДокумент13 страницAP Biology Unit 5 ExamLana Sage CummingsОценок пока нет
- Exam 4 Study Guide Spring 2023Документ5 страницExam 4 Study Guide Spring 2023Masai PaceОценок пока нет
- Bioremediation of PesticidesДокумент3 страницыBioremediation of PesticidesSunil VohraОценок пока нет
- Drosophilia Lab ReportДокумент5 страницDrosophilia Lab ReportMaddie BleaseОценок пока нет
- Fig.1: Vegetative Morphology of EctocarpusДокумент21 страницаFig.1: Vegetative Morphology of EctocarpusAmrit Mund EducationalОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis (KEY)Документ6 страницPhotosynthesis (KEY)kylevОценок пока нет
- AP Bio Essay #29Документ2 страницыAP Bio Essay #29Elioth Gomez100% (1)
- EBMT 2021 ProgramДокумент288 страницEBMT 2021 Programtirillas101Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemДокумент12 страницChapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine System蔡旻珊Оценок пока нет
- SCP Production NotesДокумент4 страницыSCP Production Notessaurabh pandeyОценок пока нет
- Anaphy 8-12 LabДокумент11 страницAnaphy 8-12 LabKrisha Mae PascuaОценок пока нет
- Activity Sheet in PhotosynthesisДокумент3 страницыActivity Sheet in PhotosynthesisKenneth Roy BalangueОценок пока нет
- AnaPhy - Digestive SystemДокумент11 страницAnaPhy - Digestive SystemGia P. de VeyraОценок пока нет
- Compost Tea Brewing ManualДокумент91 страницаCompost Tea Brewing ManualJanetS14338100% (1)
- Tititititi DORA 2Документ2 страницыTititititi DORA 2Isaiah MaglambayanОценок пока нет
- Godbout, J. P., & Glaser, R. (2006) - Stress-Induced Immune Dysregulation. Implications For Wound Healing, Infectious Disease and CancerДокумент7 страницGodbout, J. P., & Glaser, R. (2006) - Stress-Induced Immune Dysregulation. Implications For Wound Healing, Infectious Disease and CancerFranco Paolo Maray-GhigliottoОценок пока нет
- November 2006 MS - Paper 3 CIE Biology IGCSEДокумент6 страницNovember 2006 MS - Paper 3 CIE Biology IGCSEUzair ZahidОценок пока нет
- Rainsure Company, Instrument and Assays Introduction CLVДокумент61 страницаRainsure Company, Instrument and Assays Introduction CLVMohammed H. KeshtaОценок пока нет
- Food Chains and Food WebsДокумент2 страницыFood Chains and Food WebsBoey Soo YinОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis PDFДокумент22 страницыPhotosynthesis PDFbhaskar rayОценок пока нет
- Cognitive Power of WomenДокумент4 страницыCognitive Power of WomenEditor IJRITCCОценок пока нет
- Nitrobacter WinogradskyДокумент7 страницNitrobacter WinogradskyFerryKurniawanОценок пока нет
- Topical Test Biology Form 4Документ14 страницTopical Test Biology Form 4Siti Wahida SuleimanОценок пока нет
- Course HeroДокумент17 страницCourse HeroBalОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Manual and GuidelineДокумент27 страницLaboratory Manual and GuidelineFatih Rushdi100% (1)
- Digestion and Absorption 111Документ6 страницDigestion and Absorption 111Brijesh BalachandranОценок пока нет
- Winter Course Allocation Report (Updated On 18dec2015)Документ274 страницыWinter Course Allocation Report (Updated On 18dec2015)ASEEMОценок пока нет
- CSEC Biology June 2002 P1 Specimen PaperДокумент13 страницCSEC Biology June 2002 P1 Specimen PaperJoy BoehmerОценок пока нет
- Alee - Ecological Animal Geography (1951)Документ749 страницAlee - Ecological Animal Geography (1951)caegeospОценок пока нет
- All About CellДокумент5 страницAll About CellShane LaluОценок пока нет
- Patient's Name:: Ms. Bharti PorwalДокумент1 страницаPatient's Name:: Ms. Bharti PorwalHimanshuОценок пока нет
- Glutamate Excitotoxicity in The Cerebellum Mediated by IL-1: Journal ClubДокумент3 страницыGlutamate Excitotoxicity in The Cerebellum Mediated by IL-1: Journal ClubJar JarОценок пока нет