Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
OSItables PDF
Загружено:
900913n008Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
OSItables PDF
Загружено:
900913n008Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
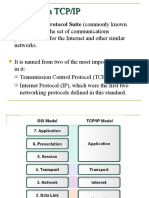
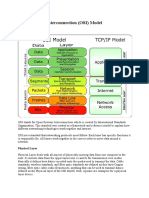
Layer Function
Example
Protocols
Hardware ( Lower
3 Levels)
Layer 7
Application
Gives user applications access to network.
This layer represents the services, that
directly support the user applications such
as software for web browsing, file
transfers, database access, and E-mail
FTP, HTTP, SMTP,
DNS, TFTP, NFS,
TELNET
Layer 6
Presentation
The presentation layer, usually part of an
operating system, converts incoming and
outgoing data from one presentation
format to another. Presentation layer
services include data encryption and text
compression.
ASCII, EBCDIC, MIDI,
MPEG, JPEG
Layer 5
Session
Opens, manages, and closes conversations
between two computers. It performs name
recognition and the functions such as
security, needed to allow two applications
to communicate over the network, also
provides error handling.
SQL, RPC
Layer 4
Transport
This layer provides transparent transfer of
data between end systems, or hosts, and is
responsible for end-to-end error recovery
and flow control. It ensures complete data
transfer.
Sequences data packets, and requests
retransmission of missing packets. It also
repackages messages for more efficient
transmission over the network.
TCP, UDP
Layer 3
Network
Establishes, maintains and terminates
network connections. Routes data packets
across network segments. Translates logical
addresses and names into physical
addresses.
IP, ICMP, ARP, PING Routers
Layer 2
Data Link
Transmits frames of data from computer to
computer on the same network segment.
Ensures the reliability of the physical link
established at layer 1. Standards define
how data frames are recognized and
provide the necessary flow control and
error handling at the frame set.
IEEE 802.2, 802.3,
802.5
Switches
Layer 1
Physical
The Physical layer defines all the electrical
and physical specifications for devices. This
includes the layout of pins, voltages, and
cable specifications. Hubs, repeaters and
network adapters are physical-layer
devices. Defines cabling and connections.
Transmits data over the physical media.
IEEE 802.2, 802.5 Cabling such Ethernet,
telephone, and patch
cables
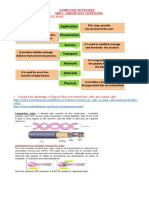
Layer Function Example Protocols
Layer 5
Application
This layer is the application software used by the network
user and includes much of what the OSI model contains
in the application, presentation, and session layers. It is
the user's access to the network. By using the application
software, the user defines what messages are sent over
the network.
HTTP, HTML,
Browsers(Internet
Explorer, Safari, Firefox),
Telnet, Messengers, Mail
Clients, SMTP, IMAP, POP
Layer 4
Transport
This layer is responsible for linking the application layer
software to the network and establishing end-to-end
connections between the sender and receiver when such
connections are needed. It is also responsible for
breaking long messages into several smaller messages to
make them easier to transmit and then recombining the
smaller messages back into the original larger message
at the receiving end. The transport layer can also detect
lost messages and request that they be resent
TCP, SPX, Windowing,
Packets
Layer 3
Network
This layer performs routing, in that it selects the next
computer to which the message should be sent. It can
also find the address of that computer if it doesn't already
know it.
IP, IPX, Gateways, Subnet
Masks, routers
Layer 2
Data Link
This layer is responsible for moving a message from one
computer to the next computer in the network path from
the sender to the receiver. It controls the physical layer by
deciding when to transmit messages over the media. It
formats the messages by indicating where they start and
end. It also detects and may correct any errors that have
occurred during transmission.
Ethernet, Frame relay, MAC
addresses, ARP( Address
Resolution Protocol),
Switches
Layer 1
Physical
This layer is the physical connection between the sender
and receiver. Its role is to transfer a series of electrical,
radio, or light signals through the circuit. The physical
layer includes all the hardware devices (e.g., computers,
modems, and switches) and physical media (e.g., cables
and satellites). The physical layer specifies the type of
connection and the electrical signals, radio waves, or light
pulses that pass through it.
Cat 5 cabling, Fiber Optic
Cabling
1. By OSI Layer, which group sets the standards for each OSI layer?
Application: W3C/IETF
Presentation: Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG), CompuServe (GIF), Various
Vendors for video and audio codecs, W3C
Session: IETF
Transport: IETF
Network: IETF
Data link: IEEE
Physical: ANSI(American National Standards Institute)/TIA (Telecommunications
Industry Association)/EIA (Electronic Industries Alliance)
2. Describe, by device, how information from your computers keyboard at home gets out to the
Internet. Specifically, briefly describe each device and its function.
a. the keyboard sends data in forms of 1s and 0s to the operating system
b. the modem receives a request to connect to the internet from the operating system
c. the router sends information through networks to the internet
3. Go to speedtest.net and test your Internet connection speed. Report that on your assignment.
Вам также может понравиться
- Networking Chapter 2: OSI LAYER Chapter 2 OSI LAYERДокумент4 страницыNetworking Chapter 2: OSI LAYER Chapter 2 OSI LAYERRaymart BuendiaОценок пока нет
- CCENT Notes Part-1Документ56 страницCCENT Notes Part-1davidvhallОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ8 страницLecture 2jasmhmyd205Оценок пока нет
- 7-Layer OSI MODELДокумент11 страниц7-Layer OSI MODELBabu CamОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Device Configuration PDFДокумент24 страницыChapter 1 Device Configuration PDFShambel WorkuОценок пока нет
- Osi Model LanДокумент8 страницOsi Model LanRenegade DiverОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1: Computer Networks LabДокумент11 страницAssignment 1: Computer Networks LabNickОценок пока нет
- Assignment 4Документ10 страницAssignment 4anil rajputОценок пока нет
- Communications Layers SummaryДокумент7 страницCommunications Layers SummaryKarthickmanikandan GОценок пока нет
- Computer Networks Set 1Документ20 страницComputer Networks Set 1madhavibandari609Оценок пока нет
- OSI ModelДокумент6 страницOSI ModelmushahidОценок пока нет
- The OSI Reference ModelДокумент21 страницаThe OSI Reference ModelNaureen HossainОценок пока нет
- DAY1 01 Networking FundamentalsДокумент29 страницDAY1 01 Networking FundamentalsPrashant C KadatareОценок пока нет
- NetworksДокумент8 страницNetworksGaby MbuguaОценок пока нет
- Week 3Документ5 страницWeek 3hiren_keepsmilingОценок пока нет
- The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model and Network ProtocolsДокумент148 страницThe Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model and Network Protocolswfidayu100% (1)
- CCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasДокумент42 страницыCCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasAnas ElgaudОценок пока нет
- Data Communication & Networking Dr/Abdulmajeed Abdulrazag Student/ Loai Khalifa ID/IBB058Документ7 страницData Communication & Networking Dr/Abdulmajeed Abdulrazag Student/ Loai Khalifa ID/IBB058Abdulhadi KhalifaОценок пока нет
- Shubham KhedekarДокумент25 страницShubham KhedekarSasi KumarОценок пока нет
- Chap5 Osi 2015Документ20 страницChap5 Osi 2015semakulaОценок пока нет
- Computer Networks-Module1Документ34 страницыComputer Networks-Module1Sreedevi YashpalОценок пока нет
- OSI ModelДокумент32 страницыOSI ModelBhanu Singh0% (1)
- OSI LayersДокумент2 страницыOSI Layersnlly4uОценок пока нет
- Computer Network Layers CIS748 Class NotesДокумент9 страницComputer Network Layers CIS748 Class NotesSuresh KumarОценок пока нет
- T OSI: He Seven Layers of The ModelДокумент4 страницыT OSI: He Seven Layers of The Modellolimazn1Оценок пока нет
- Introduction TCP/IPДокумент23 страницыIntroduction TCP/IPSasi KumarОценок пока нет
- Computer Network Layers CIS748 Class NotesДокумент10 страницComputer Network Layers CIS748 Class Notesanon-54811Оценок пока нет
- CSC Unit-3Документ21 страницаCSC Unit-3Smita AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Networking Basics & OSI Reference ModelДокумент79 страницNetworking Basics & OSI Reference Modelwisedotblue100% (1)
- Computer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222Документ13 страницComputer Networking Refers To Connected Computing Devices 222RAY COOLОценок пока нет
- OSI ModelДокумент32 страницыOSI ModelNathenael Yimer DametewОценок пока нет
- 7 Layers of OSIДокумент4 страницы7 Layers of OSIMayank JhaОценок пока нет
- EthernetДокумент5 страницEthernetRiti NayyarОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 DCN Lecture Notes 10 22Документ21 страницаUnit 2 DCN Lecture Notes 10 22arun kaushikОценок пока нет
- Assignment-Cn: Syeda Pakiza ImranДокумент5 страницAssignment-Cn: Syeda Pakiza Imrannauman tariqОценок пока нет
- Cisco: Sritrusta SukaridhotoДокумент34 страницыCisco: Sritrusta SukaridhotoAhmad SahalОценок пока нет
- Computer Networks: Instructor: Maqsood RaziДокумент83 страницыComputer Networks: Instructor: Maqsood RaziIqbal Uddin KhanОценок пока нет
- DC and CN Chapt-5-1Документ88 страницDC and CN Chapt-5-1habtamud655Оценок пока нет
- MOdel OSI NoteДокумент7 страницMOdel OSI NoteZulfadli HanaffiОценок пока нет
- Net 102 Prelim ModulesДокумент36 страницNet 102 Prelim ModulesNovy Airhris MianaОценок пока нет
- Capture All HTTP Packets by Using Wireshark and Try To Fetch All HTTP Usernames & PasswordsДокумент38 страницCapture All HTTP Packets by Using Wireshark and Try To Fetch All HTTP Usernames & PasswordsCandy AngelОценок пока нет
- Network Models: Ambo University Woliso Campus Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceДокумент73 страницыNetwork Models: Ambo University Woliso Campus Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaОценок пока нет
- OSI Model Data Unit Layer Function: ApplicationДокумент6 страницOSI Model Data Unit Layer Function: ApplicationSanyam JainОценок пока нет
- E-Commerce Chapter 2: E-Mail and Internet 2.1 Computer Communication SystemДокумент10 страницE-Commerce Chapter 2: E-Mail and Internet 2.1 Computer Communication Systemshravan1108Оценок пока нет
- Data CommunicationДокумент3 страницыData CommunicationKarunakaran RameshОценок пока нет
- 1.0 The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) ModelДокумент5 страниц1.0 The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Modelvickypatel_63873791100% (1)
- Networking Basics: Dept. of Computer Science Faculty of Science and TechnologyДокумент33 страницыNetworking Basics: Dept. of Computer Science Faculty of Science and TechnologyMahmud Ridwan JoyОценок пока нет
- Layer OSIДокумент3 страницыLayer OSIClarence Joy BautistaОценок пока нет
- Report About " OSI Model "Документ9 страницReport About " OSI Model "mahamd saiedОценок пока нет
- Network Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of EngineeringДокумент22 страницыNetwork Models: Dept. of Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineeringআসিফ রেজাОценок пока нет
- Important Questions For MID I CNДокумент14 страницImportant Questions For MID I CN20H51A0540-NAKKA SREEKAR B.Tech CSE (2020-24)Оценок пока нет
- Ccna Icnd1 Study NotesДокумент187 страницCcna Icnd1 Study NotesRohitSinghОценок пока нет
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1От EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyОт EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisОт EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisОценок пока нет
- Serial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsОт EverandSerial Port Complete: COM Ports, USB Virtual COM Ports, and Ports for Embedded SystemsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (9)
- Networking 1Документ77 страницNetworking 1Prashant ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Ndubuisi Agomoh CVДокумент10 страницNdubuisi Agomoh CVAda AnyaОценок пока нет
- Cisco 02Документ4 страницыCisco 02Zelop DrewОценок пока нет
- HCIA - DATACOM Single ChoiceДокумент143 страницыHCIA - DATACOM Single Choicemulte123100% (3)
- HP Switching What They SellДокумент64 страницыHP Switching What They SellneelОценок пока нет
- HC900 ControllerДокумент75 страницHC900 Controllerthanh_cdt01Оценок пока нет
- 4 The Medium Access Control SublayerДокумент6 страниц4 The Medium Access Control SublayermonkeygrОценок пока нет
- Alcatel Lucent OmniSwitch 6450 10Документ6 страницAlcatel Lucent OmniSwitch 6450 10ScribdUser250Оценок пока нет
- CIA - MikroTik Pricelist Jun 2023Документ1 страницаCIA - MikroTik Pricelist Jun 2023Horas Computer555Оценок пока нет
- 17 Micom C264-Brochure PokДокумент8 страниц17 Micom C264-Brochure PokFahd SaeedОценок пока нет
- SPA9000userguide PDFДокумент129 страницSPA9000userguide PDFrigofsОценок пока нет
- PT5 Laboratory Exercise 5Документ14 страницPT5 Laboratory Exercise 5Sandy GorricetaОценок пока нет
- Huawei CloudEngine 12800 Series Switches Data SheetДокумент21 страницаHuawei CloudEngine 12800 Series Switches Data Sheetalmamartinez27Оценок пока нет
- HP ProCurve 2915-8G-PoE SwitchДокумент9 страницHP ProCurve 2915-8G-PoE SwitchGusОценок пока нет
- Question Bank For Signal EngineerДокумент20 страницQuestion Bank For Signal EngineerVikas Srivastav81% (21)
- Switch Catalyst - 3650Документ34 страницыSwitch Catalyst - 3650Aldrin Krujer Cayetano CornelioОценок пока нет
- Huawei LTE Outdoor CPE B2368-22 Product Description Draft A (20180111)Документ32 страницыHuawei LTE Outdoor CPE B2368-22 Product Description Draft A (20180111)JoelMalangОценок пока нет
- Innova Central Quick Guide Rev 1 1 1Документ6 страницInnova Central Quick Guide Rev 1 1 1api-3705913Оценок пока нет
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Документ3 страницыNetwork Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Roxanne EspirituОценок пока нет
- Networking Questions PDFДокумент38 страницNetworking Questions PDFAdam DanielОценок пока нет
- En Dsmbisp PT SLM v41Документ114 страницEn Dsmbisp PT SLM v41Kenneth_Patten_3257100% (1)
- Solo MOTOMESH Solo 2 2 Network Setup and Installation GuideДокумент142 страницыSolo MOTOMESH Solo 2 2 Network Setup and Installation Guidelanceloth741671100% (1)
- Examples For WEB ConfigurationsДокумент46 страницExamples For WEB ConfigurationsmalakОценок пока нет
- Broadcom Networking Overview - For JP Morgan-20210111-FINALДокумент33 страницыBroadcom Networking Overview - For JP Morgan-20210111-FINALMohsen GoodarziОценок пока нет
- EN Datasheet TEG-30262 (v1.0R)Документ3 страницыEN Datasheet TEG-30262 (v1.0R)karlk tosОценок пока нет
- Eswitching Chapter2: Ccna Exploration 3 Answers Chapter 2Документ4 страницыEswitching Chapter2: Ccna Exploration 3 Answers Chapter 2JuliandersonPereiraОценок пока нет
- SpiderCloud System Commissioning Guide (LCI) Release 3.1Документ76 страницSpiderCloud System Commissioning Guide (LCI) Release 3.1Hector Solarte50% (2)
- Packet Tracer - Implement Vlans and Trunking: Addressing TableДокумент5 страницPacket Tracer - Implement Vlans and Trunking: Addressing TableThịnh TrầnОценок пока нет
- Network Solutions For Tunnel Automation 1614004261Документ77 страницNetwork Solutions For Tunnel Automation 1614004261mykillerdroneОценок пока нет
- Topic 1: Easy QuestionsДокумент38 страницTopic 1: Easy QuestionsTetelo VincentОценок пока нет