Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Cognitivist
Загружено:
Junitia Dewi Voa0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров3 страницы1. Cognitive theories of learning propose a four-stage encoding process for acquiring new information: selection, acquisition, construction, and integration.
2. Piaget's theory of cognitive development sees learning as an active process of discovery, not passive reception. He advocated for student-centered classrooms that facilitate learning through problem-solving.
3. Group discussion techniques can apply cognitive and Piagetian approaches. Students are organized into small groups, assigned roles like listener or problem-solver, and tasked with discussing a topic to promote active, collaborative learning.
Исходное описание:
Cognitive in sla, learning
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документ1. Cognitive theories of learning propose a four-stage encoding process for acquiring new information: selection, acquisition, construction, and integration.
2. Piaget's theory of cognitive development sees learning as an active process of discovery, not passive reception. He advocated for student-centered classrooms that facilitate learning through problem-solving.
3. Group discussion techniques can apply cognitive and Piagetian approaches. Students are organized into small groups, assigned roles like listener or problem-solver, and tasked with discussing a topic to promote active, collaborative learning.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров3 страницыCognitivist
Загружено:
Junitia Dewi Voa1. Cognitive theories of learning propose a four-stage encoding process for acquiring new information: selection, acquisition, construction, and integration.
2. Piaget's theory of cognitive development sees learning as an active process of discovery, not passive reception. He advocated for student-centered classrooms that facilitate learning through problem-solving.
3. Group discussion techniques can apply cognitive and Piagetian approaches. Students are organized into small groups, assigned roles like listener or problem-solver, and tasked with discussing a topic to promote active, collaborative learning.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
No.
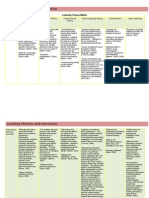
Theories of SLA Theories of Learning Activities in the
Classroom
1. The similar
Cognitive:
According to Weinstein and
Mayer (19!"# in this cognitive
$sychology $aradigm# ne%
information is ac&'ired
thro'gh a fo'r(stage encoding
$rocess involving selection,
acquisition, construction and
integration ()*Malley and
Chamot# 199+: 1,(1":
( Selection: in this
stage learners foc's
on s$ecific
information of interest
in the environment
and transfer that
information into
%or-ing memory.
( Acquisition: later#
learners actively
transfer information
from %or-ing
memory into long(
term(memory for
$ermanent storage.
( Construction: thirdly#
learners .'ild internal
connections .et%een
ideas contained in
%or-ing memory/ this
information can .e
'sed to enrich the
learner*s
'nderstanding or
retention of the ne%
ideas.
( Integration: in this
The similar
Cognitive:
0iaget (191" is re&'iring an
active learner# not a $assive
one# .eca'se $ro.lem(solving
s-ills cannot .e ta'ght# they
m'st .e discovered.
Cognitive models of learning
$ro$ose a different se&'ence
%hich incl'des (Madrid et al.
199":
( selecting information
from the environment#
( organizing the
information#
( relating it to %hat %e
already -no%#
( retaining %hat %e
consider to .e
im$ortant#
( using the information
in a$$ro$riate conte2ts
and sit'ations#
( reflecting on the
s'ccess of the learning
efforts and eval'ating
the effectiveness of
res'lts.
Piagets theory:
Within the classroom
learning sho'ld .e
st'dent centered a
accom$lished thro'gh
active discovery
learning. The role of
the teacher is to
facilitate learning#
rather than direct
t'ition. Therefore
teachers sho'ld
enco'rage the
follo%ing %ithin the
classroom:
o 3oc's on the $rocess
of learning# rather
than the end $rod'ct
of it.
o 4sing active
methods that re&'ire
rediscovering or
reconstr'cting
5tr'ths5.
o 4sing colla.orative#
as %ell as individ'al
activities (so children
can learn from each
other".
o 6evising sit'ations
that $resent 'sef'l
$ro.lems# and create
dise&'ili.ri'm in the
child.
o 7val'ate the level of
the child8s
develo$ment# so
s'ita.le tas-s can .e
final $rocess# the
learner searcher for
$rior -no%ledge in
long(term memory
and transfers this
-no%ledge to %or-ing
memory.
Selection and ac&'isition
determine ho% m'ch is
learned# %hereas constr'ction
and integration determine %hat
is learned and ho% it is
organi9ed.
3aerch and :as$er (191#
19," %ere the first to a$$ly
this conce$t to the field of SLA.
They stated that the learner8s
declarative knowledge
consisted of internali9ed inter(
lang'age r'les and memori9ed
ch'n-s of lang'age %hereas
$roced'ral -no%ledge %ere
those strategies and $roced'res
'sed .y the learner to $rocess
L; information for ac&'isition
and 'se. According to 3aerch
and :as$er# $roced'ral
-no%ledge can .e
differentiated into five se$arate
com$onents ()*Malley and
Chamot# 199+:1(19":
1" Reception procedures#
s'ch as the 'se of
inference to e2tra$olate
meaning.
;" Production
procedures, s'ch as
$lanning and
monitoring s$eech
set.
6oing gro'$
disc'ssion
3irst# the teacher
stim'lates the
st'dents*
-no%ledge .y
as-ing some
&'estions a.o't
the to$ic that %ill
.e disc'ssed
<n the %hilst
activities# the
teacher as-s the
st'dents to ma-e a
gro'$ %hich
consists of fo'r
st'dents. The
teacher gives the
to$ic disc'ssion
=.iling'al
ed'cation sho'ld
.e a$$lied in
<ndonesia>. The
teacher as-s the
st'dents to read a
short story .ased
on the to$ic. The
teacher decides
for each gro'$
that ; mem.ers in
the gro'$ sho'ld
.e the listeners
and the last ;
mem.ers sho'ld
.e a $ro.lem
solver. The
listeners have to
chec- and see
$rod'ction.
?" Conversational
procedures, s'ch as
follo%ing ling'istic
$rinci$les that $rod'ce
coherent te2ts.
@" Communication
strategies# %hich are
intended to solve
$ro.lems in s$eech
com$rehension.
1" Learning procedures,
s'ch as the develo$ment
of inter(lang'age
-no%ledge thro'gh
hy$othesis formation
and testing.
Вам также может понравиться
- Assure Model Cyberbullying Online LessonДокумент6 страницAssure Model Cyberbullying Online Lessonapi-250108894Оценок пока нет
- Lesson For ProfileДокумент5 страницLesson For Profileapi-242127878Оценок пока нет
- Mentor Observation FormДокумент3 страницыMentor Observation Formapi-252935769Оценок пока нет
- Assessment of Young ChildrenДокумент15 страницAssessment of Young ChildrenMeis MalirmaseleОценок пока нет
- Supervisor Eval 2Документ5 страницSupervisor Eval 2api-267446628Оценок пока нет
- Hclark Gifted Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыHclark Gifted Lesson Planapi-253519526Оценок пока нет
- Iscuss HOW YOU MAY Create A Learning Organization Through THE Effective Development OF A Training PlanДокумент8 страницIscuss HOW YOU MAY Create A Learning Organization Through THE Effective Development OF A Training PlanAmanda MaharajОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 7Документ4 страницыLesson Plan 7api-253738102Оценок пока нет
- Mathematics Lesson PlancritiqueДокумент7 страницMathematics Lesson Plancritiqueapi-254356567Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 2Документ7 страницLesson Plan 2api-246027187Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 11Документ118 страницChapter 11RasyidSyechbubakarОценок пока нет
- 50 Crazy Ideas To Change EducationДокумент7 страниц50 Crazy Ideas To Change EducationBudi TirtanaОценок пока нет
- Effective Study Skills 3Документ4 страницыEffective Study Skills 3aamir.saeedОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan-Something From NothingДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan-Something From Nothingapi-241102275Оценок пока нет
- Curriculum Planning Process Context of Schooling Instructional Variables Planning Considerations Planning For Classroom InstructionsДокумент17 страницCurriculum Planning Process Context of Schooling Instructional Variables Planning Considerations Planning For Classroom InstructionsJuliet CintaОценок пока нет
- The Action ResearchДокумент75 страницThe Action ResearchRomelyn LaguraОценок пока нет
- Educ 302lesson Plan Form Lesson 1Документ3 страницыEduc 302lesson Plan Form Lesson 1api-240595879Оценок пока нет
- M HussainДокумент38 страницM HussainSOHEL BANGIОценок пока нет
- Good Math Lesson PlansДокумент36 страницGood Math Lesson PlansZulsubhaDaniSiti100% (1)
- Workshops Are Intended To Develop In-Depth Knowledge, Skills, And/or SpecificДокумент7 страницWorkshops Are Intended To Develop In-Depth Knowledge, Skills, And/or SpecificsuparswaОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 6Документ4 страницыLesson Plan 6api-253738102Оценок пока нет
- Final Exam Rubric: Name: DateДокумент14 страницFinal Exam Rubric: Name: Dateselrach00Оценок пока нет
- Edited Nursing Research PaperДокумент20 страницEdited Nursing Research PaperMaria VisitacionОценок пока нет
- PlanДокумент3 страницыPlanTotztutz Togodunz Tonztunz100% (1)
- Lesson Planning Form For Accessible Instruction - Calvin College Education ProgramДокумент3 страницыLesson Planning Form For Accessible Instruction - Calvin College Education Programapi-252008448Оценок пока нет
- Current Events3 MihaДокумент7 страницCurrent Events3 MihaIin KoboОценок пока нет
- Current Events3 MihaДокумент7 страницCurrent Events3 Mihakimshine2Оценок пока нет
- Supervisor Eval 1Документ5 страницSupervisor Eval 1api-267446628Оценок пока нет
- Key Assessment Part 1: Identification of Learning ProblemДокумент32 страницыKey Assessment Part 1: Identification of Learning ProblemJoeyJohnsonОценок пока нет
- Tressel Final EvalДокумент5 страницTressel Final Evalapi-242814807Оценок пока нет
- Learning Theories MatrixДокумент6 страницLearning Theories MatrixFonzy Garcia100% (1)
- Case Studies Revisited: What Can Activity Theory Offer?Документ8 страницCase Studies Revisited: What Can Activity Theory Offer?Marc CRОценок пока нет
- 20 - Vuong Ut Bach LanДокумент15 страниц20 - Vuong Ut Bach LanLan VuongОценок пока нет
- Interview Report and Reflection PaperДокумент6 страницInterview Report and Reflection PaperDương DươngОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 3Документ4 страницыLesson Plan 3api-253738102Оценок пока нет
- Adult LearnersДокумент8 страницAdult LearnersCheri HoОценок пока нет
- Medical Education 2010: 44: 440-448: ObjectivesДокумент9 страницMedical Education 2010: 44: 440-448: ObjectivesneetamoniОценок пока нет
- Workshop 1 AsdfДокумент3 страницыWorkshop 1 AsdfRoberto As DfОценок пока нет
- Social StructureДокумент3 страницыSocial Structureapi-244894096Оценок пока нет
- Economics Lesson PlanДокумент6 страницEconomics Lesson Planapi-556755635Оценок пока нет
- 7 Components of CTLДокумент3 страницы7 Components of CTLM. Hilmi Abdul AzizОценок пока нет
- Strategies For The Differentiated ClassroomДокумент13 страницStrategies For The Differentiated ClassroomAmin MofrehОценок пока нет
- Developmental Reading TCE 583, Three Credits: Winograk@orst - EduДокумент12 страницDevelopmental Reading TCE 583, Three Credits: Winograk@orst - EduCymon DazОценок пока нет
- Pilgrims Lesson3Документ4 страницыPilgrims Lesson3api-240589503Оценок пока нет
- Aaryaveer An Effective SchoolДокумент22 страницыAaryaveer An Effective SchoolArya SamajОценок пока нет
- Form 3 MothsДокумент4 страницыForm 3 Mothsapi-252172239Оценок пока нет
- Michelle Lep Numeracy At1Документ4 страницыMichelle Lep Numeracy At1api-219265938Оценок пока нет
- Ce175 4C E01 CW1 2017141692 Resurreccion LalaineДокумент3 страницыCe175 4C E01 CW1 2017141692 Resurreccion LalaineMa. Lalaine Nicole ResurreccionОценок пока нет
- fs2 Episode1 130322235456 Phpapp01Документ6 страницfs2 Episode1 130322235456 Phpapp01Jeanne May Marcos SantosОценок пока нет
- Iq A ProceedingДокумент6 страницIq A Proceedingainainsyirah91Оценок пока нет
- Pre OralДокумент10 страницPre OralSky ChingОценок пока нет
- Effectiveness of Teaching Strategies To Senior High School Students of First City Providential CollegeДокумент13 страницEffectiveness of Teaching Strategies To Senior High School Students of First City Providential CollegeMarilyn Tamboon100% (2)
- Using Metacognitive To Promote LearningДокумент9 страницUsing Metacognitive To Promote LearningNuraihan HashimОценок пока нет
- Assignment: A Conceptual Analysis of Classroom ManagementДокумент13 страницAssignment: A Conceptual Analysis of Classroom ManagementTenisha KnowlesОценок пока нет
- Instructional Software Lesson Idea Template2022 SimonsДокумент3 страницыInstructional Software Lesson Idea Template2022 Simonsapi-618157398Оценок пока нет
- PlpinnahamiltonДокумент3 страницыPlpinnahamiltonapi-256164112Оценок пока нет
- Mid Term Project BilingualismДокумент2 страницыMid Term Project BilingualismJunitia Dewi VoaОценок пока нет
- Science Bilingual Grd. 3Документ1 страницаScience Bilingual Grd. 3Junitia Dewi VoaОценок пока нет
- RPP englisXI 2Документ68 страницRPP englisXI 2Junitia Dewi VoaОценок пока нет
- Cross Cultural UnderstandingДокумент2 страницыCross Cultural UnderstandingJunitia Dewi VoaОценок пока нет
- BehaviourismДокумент3 страницыBehaviourismJunitia Dewi VoaОценок пока нет
- ChomskyДокумент48 страницChomskyJunitia Dewi VoaОценок пока нет
- Story THe Frog FamilyДокумент1 страницаStory THe Frog FamilyJunitia Dewi VoaОценок пока нет
- History of DramaДокумент3 страницыHistory of DramaJunitia Dewi VoaОценок пока нет
- Ethnography PDFДокумент26 страницEthnography PDFJunitia Dewi VoaОценок пока нет
- When I Was One and TwentyДокумент1 страницаWhen I Was One and TwentyJunitia Dewi VoaОценок пока нет
- O19 Btech 5 1016Документ249 страницO19 Btech 5 1016Anish SachdevaОценок пока нет
- Spring Boot AnnotationsДокумент12 страницSpring Boot AnnotationsMedNejjarОценок пока нет
- Rainfall Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыRainfall Lesson Planapi-241808531Оценок пока нет
- Law Student Government: Ateneo de Naga UniversityДокумент1 страницаLaw Student Government: Ateneo de Naga UniversityFbarrsОценок пока нет
- Alessi and Trollips Model 2011Документ3 страницыAlessi and Trollips Model 2011Anonymous HBT778cОценок пока нет
- Cot - English 4-Q4-WK 10-Gary C. RodriguezДокумент5 страницCot - English 4-Q4-WK 10-Gary C. Rodriguezjerick de la cruzОценок пока нет
- IMSДокумент19 страницIMSSIDDHANTОценок пока нет
- Dokumen Penjajaran Kurikulum Bahasa Inggeris Tingkatan 2 KSSMДокумент7 страницDokumen Penjajaran Kurikulum Bahasa Inggeris Tingkatan 2 KSSMQhairunisa HinsanОценок пока нет
- B2016 Interpersonal and Intrapersonal Expectancies, Trusz ROUTLEDGEДокумент203 страницыB2016 Interpersonal and Intrapersonal Expectancies, Trusz ROUTLEDGEricОценок пока нет
- CV BlackrockДокумент2 страницыCV BlackrockWasif Al WazedОценок пока нет
- DisneyДокумент6 страницDisneyz.kОценок пока нет
- PSYC 4110 PsycholinguisticsДокумент11 страницPSYC 4110 Psycholinguisticsshakeelkhanturlandi5Оценок пока нет
- Pooja Raut Resume - Java DeveloperДокумент3 страницыPooja Raut Resume - Java DeveloperVaibhav PahuneОценок пока нет
- Japan: Geography and Early HistoryДокумент29 страницJapan: Geography and Early HistoryXavier BurrusОценок пока нет
- Gambaran Pengelolaan Emergency Kit (Trolley) Di Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah (RSUD) Dr. Hasri Ainun HabibieДокумент10 страницGambaran Pengelolaan Emergency Kit (Trolley) Di Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah (RSUD) Dr. Hasri Ainun HabibieRutharyantiSihotangОценок пока нет
- DLL 2Документ7 страницDLL 2Jonathan LilocanОценок пока нет
- The Use of Mind Mapping in The Teaching of Reading A Procedure TextДокумент12 страницThe Use of Mind Mapping in The Teaching of Reading A Procedure TextMuhammad Hidayatul Rifqi100% (1)
- POEMS Syndrome - A Report of 14 Cases and Review of The LiteratureДокумент6 страницPOEMS Syndrome - A Report of 14 Cases and Review of The LiteratureHabib G. Moutran BarrosoОценок пока нет
- L&T Limited: About The CompanyДокумент2 страницыL&T Limited: About The CompanySai SanjeevareddyОценок пока нет
- Airport ContextДокумент2 страницыAirport Contextcaro alvaradoОценок пока нет
- Power BI Vs Tableau - Which One Is Right For YouДокумент9 страницPower BI Vs Tableau - Which One Is Right For Youboo ajuОценок пока нет
- Wandering Minds Mobile ExhibitДокумент3 страницыWandering Minds Mobile ExhibitMichelleTurla-MacarayoОценок пока нет
- Features of 21st Century HRD and Training ProgramsДокумент9 страницFeatures of 21st Century HRD and Training Programstvglacaba1213100% (1)
- Module 7Документ4 страницыModule 7trishia marie monteraОценок пока нет
- The Role of Autonomy Support and Autonomy Orientation in Prosocial Behavior EngagementДокумент25 страницThe Role of Autonomy Support and Autonomy Orientation in Prosocial Behavior EngagementtrandavescuОценок пока нет
- SED LIT 2 Chapter 3 ActivitiesДокумент4 страницыSED LIT 2 Chapter 3 ActivitiesSylvia DanisОценок пока нет
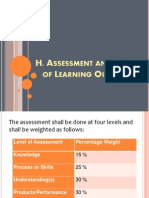
- Assessment and Rating of Learning OutcomesДокумент28 страницAssessment and Rating of Learning OutcomesElisa Siatres Marcelino100% (1)
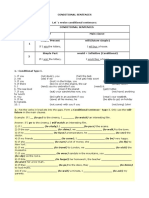
- Conditional Sentences 4º EsoДокумент4 страницыConditional Sentences 4º EsoLorenaОценок пока нет
- Course ContentsДокумент2 страницыCourse ContentsAreef Mahmood IqbalОценок пока нет
- Test A NN4 2020-2021Документ2 страницыTest A NN4 2020-2021Toska GilliesОценок пока нет