Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hatching Quality Chicks: Clear Eggs With No Embryonic Development (Infertiles)
Загружено:
Bari Shobari0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
21 просмотров10 страницThis document discusses common symptoms of incubation failures and their probable causes and recommended corrective measures. It lists symptoms such as clear eggs with no development, blood rings, dead embryos, chicks dying before or after hatching, early or late hatching, crippled chicks, and more. For each symptom, it identifies likely causes such as improper incubation temperatures, humidity, ventilation, egg storage or handling, diseases, or nutritional deficiencies in breeders. It recommends solutions like adjusting incubation conditions, improving sanitation, using healthy breeding stock, or modifying management practices. The goal is to diagnose problems and prevent failures in egg incubation and hatchability.
Исходное описание:
egg incuubator
Оригинальное название
Pengaturan penetasan
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document discusses common symptoms of incubation failures and their probable causes and recommended corrective measures. It lists symptoms such as clear eggs with no development, blood rings, dead embryos, chicks dying before or after hatching, early or late hatching, crippled chicks, and more. For each symptom, it identifies likely causes such as improper incubation temperatures, humidity, ventilation, egg storage or handling, diseases, or nutritional deficiencies in breeders. It recommends solutions like adjusting incubation conditions, improving sanitation, using healthy breeding stock, or modifying management practices. The goal is to diagnose problems and prevent failures in egg incubation and hatchability.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
21 просмотров10 страницHatching Quality Chicks: Clear Eggs With No Embryonic Development (Infertiles)
Загружено:
Bari ShobariThis document discusses common symptoms of incubation failures and their probable causes and recommended corrective measures. It lists symptoms such as clear eggs with no development, blood rings, dead embryos, chicks dying before or after hatching, early or late hatching, crippled chicks, and more. For each symptom, it identifies likely causes such as improper incubation temperatures, humidity, ventilation, egg storage or handling, diseases, or nutritional deficiencies in breeders. It recommends solutions like adjusting incubation conditions, improving sanitation, using healthy breeding stock, or modifying management practices. The goal is to diagnose problems and prevent failures in egg incubation and hatchability.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 10
Pengaturan penetasan
Poultry: Reproduction & Incubation
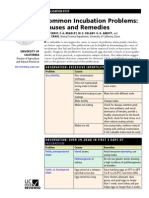
Trouble Shooting Failures with Egg Incubation
When incubation of eggs fails, indications are often available that a well trained professional
uses for diagnosing the causes for failure. The information listed below includes the more
common symptoms for incubation failures, the causes for each symptom, and the recommended
corrective measures. A good incubation publication is available from your local County Agent's
office or the Poultry Extension Department at Mississippi State University to help in analyzing
the incubation procedure. It explains the artificial incubating process more in detail. Ask for
MCES Publication 1182, Hatching Quality Chicks.
Symptoms of incubation/breeder management problems include:
Clear eggs with no visible embryonic development.
Blood rings in incubated eggs.
Many dead embryos at an early stage.
Chicks fully formed, but dead without pipping.
Pipped eggs, but died without hatching.
Early hatching.
Late hatching or not hatching uniformly.
Sticky embryos.
Embryos sticking or adhering to shell.
Crippled and malformed chicks.
Abnormal, weak, or small chicks.
Chicks with labored breathing.
Large, soft-bodied mushy chicks.
Rough or unhealed navels on chicks.
Short down on chicks.
Excessive yellow down color.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective
Measures
Clear Eggs with no embryonic
development (infertiles)
Males undernourished Follow a
recommended
feeding program
to provide
adequate
nutrition.
Replace
underweight
males with
vigorous ones
Too few males Increase the
number of males
in the flock.
Seasonal decline in fertility Use young
cockerels more
resistant to
environmental
stress.
Competition among breeding males Do not use too
many males.
Rear all males
together. Place
temporary
partitions within
large pens.
Diseased flock Conduct an
approved disease
control program.
Frozen combs and wattles Provide
comfortable
housing. Properly
select and
maintain
drinking
fountains.
Old males Replace with
younger males.
Selected mating in pens Artificially
inseminate
infertile hens.
Replace males in
the pen/house.
Male sterility Replace males in
the pen/house.
Crowded breeders Provide
recommended
floor space, at
least 3 ft/bird.
Improper artificial insemination techniques
or use of old/over-diluted semen.
Follow
recommendations
of primary
breeder
company.
Eggs damaged by environment Gather eggs
frequently (at
least once daily).
Eggs stored too long or incorrectly Store eggs at 50-
60 degrees F. and
60% relative
humidity.
Incubate eggs
within 7 days of
lay.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective Measures
Blood rings Improper storage Follow recommended egg storage and
gathering recommendations.
Improper incubation temperatures Check thermometer accuracy and
incubator functions. Follow
recommended temperature settings.
Improper breeder nutrition Feed breeders a diet with balanced
nutrient levels.
Improper fumigation Follow fumigation recommendations.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective
Measures
Many dead embryos at early
stages
Improper incubation temperatures (usually too
high)
Follow
recommended
incubation
temperatures.
Improper egg turning Turn at least 3
times daily.
Inherited low hatchability Avoid cross
breeding. May
need to secure
different
breeding
stock.
Improper ventilation Increase
ventilation
rate in
incubator
and/or room,
but avoid
drafts. Add
oxygen at high
altitudes.
Pullorum disease or other salmonelloses Use eggs from
disease-free
sources. Have
NPIP
representatives
blood-test the
breeder flock.
Improper nutrition of breeders Provide a
well-balanced
nutritional diet
to breeders.
Symptoms Probable Cause
Corrective
Measures
Pipped eggs, but died without
hatching
Insufficient moisture Increase
humidity
(wet-bulb
temperature)
during the
hatching
period.
Improper ventilation Increase
ventilation
rate in
incubator
and/or
room, but
avoid drafts.
Improper setting of eggs causing malpositioned
embryos
Set eggs
with small
end down.
Turn eggs
properly but
avoid
turning
within 3
days of
hatching.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective Measures
Early hatching (may have bloody navels) High incubation temperatures Follow recommended
incubation
temperatures. Check
equipment for proper
function. Guard
against electrical
surges or high
incubator room
temperatures.
Improper egg storage Store eggs at 50-60
degrees F. and 60%
R.H. Turn at least 3
times daily.
Symptoms
Probable Cause Corrective
Measures
Late hatching or not hatching
uniformly
Low incubation temperatures Follow
recommended
incubation
temperatures.
Warm and cool spots in incubator due to
faulty design
Contact
incubator
company or
obtain a
different
incubator
design.
Old or improperly stored eggs Gather eggs
frequently,
cool
immediately
and store
eggs
properly. Do
not store
longer than 7
days.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective
Measures
Sticky embryos (embryos may be smeared with
egg contents)
High average incubation
humidity
Follow
recommended
incubation
humidity.
Check size of
air cell as an
indicator for
adjusting
humidity
condition.
Low incubation temperature Follow
recommended
temperature
settings.
Lethal genes Avoid cross
breeding.
May need to
secure
different
breeding
stock.
Inadequate ventilation Increase
ventilation
rate in
incubator
and/or room,
but avoid
drafts.
Improper fumigation of eggs Fumigate
eggs by
following the
procedure
carefully.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective
Measures
Embryos sticking or adhering to
shell
Low incubation humidity (especially during
hatching)
Increase
incubation
humidity by
increasing
water
evaporation.
Embryos
dried too
much.
Excessive ventilation rate Reduce
ventilation
rate but
maintain
minimum
air
exchange to
prevent
suffocation
of embryos.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective
Measures
Crippled and malformed
chicks
Improper incubation temperatures (usually too
high)
Follow
recommended
incubation
temperatures.
Low incubation humidity Increase
incubation
humidity by
increasing
water
evaporation.
Embryos
dried too
much.
Improper egg setting position or turning during
incubation
Set eggs with
small ends
down. Turn
eggs at least 3
times daily.
Do not turn
eggs within 3
days of
hatching.
Heredity Proper
culling and
breeding
practices will
reduce
problems.
Slick hatching trays Use trays
with wire
floors or
place
crinoline on
hatching
surface.
Improper nutrition of breeders Provide a
well-balanced
nutritional
diet to
breeders.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective
Measures
Abnormal, weak, or small chicks High incubation or hatching temperatures Follow
recommended
incubation
temperatures.
Small eggs hatch small chicks Set only
standard or
large sized
eggs.
Insufficient incubation humidity Maintain
recommended
humidity for
species of bird
incubated..
Improper ventilation in hatcher unit Increase
ventilation rate,
but avoid drafts.
Diseased or poorly conditioned breeder flock Use eggs from
disease-free
sources only.
Have NPIP
representatives
blood-test the
breeder flock.
Improper nutrition of breeders Provide a well-
balanced
nutritional diet
to breeders
(especially
vitamin levels).
Excessive fumigation in hatcher Fumigate using
proper
procedures.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective Measures
Chicks with labored breathing Excessive use of fumigant Follow recommended fumigation
procedures.
Respiratory diseases Check disease status of breeder
flock. Conduct a thorough cleanup
and disinfection of incubator and
hatching facilities.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective Measures
Large, soft-bodied mushy chicks;
dead on trays; bad odor
Low average incubation
temperaturePoor ventilation
Follow
recommended
incubation
temperatures.Increase
ventilation rate in
incubator and/or
room, but avoid
drafts.
Navel infection (Omphalitis) Clean and disinfect
incubator and
hatching units
between settings of
eggs. Maintain dry
hatching trays.
Properly store and
fumigate eggs.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective Measures
Rough or unhealed navels Improper incubation temperatures Follow recommended incubation
temperatures.
High hatching humidity Maintain proper humidity.
Navel infection (Omphalitis) Clean and disinfect incubator and
hatching units between settings of
eggs. Maintain dry hatching trays.
Properly store and fumigate eggs.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective Measures
Short down on chicks High incubation temperatures Follow recommended
incubation
temperatures.
Low incubation humidity
Follow suggestions to
correct insufficient
humidity.
Excessive ventilation Reduce vent openings
to restrict but maintain
adequate air exchange.
Holding chicks in hatcher too long after hatching Remove all chicks as
soon as fluffy but
within 24 hours after
hatching.
Symptoms Probable Cause Corrective
Measures
Excessive yellow coloring of
down
Improper and excessive fumigation in hatcher
unit
Follow
recommended
fumigation
procedures.
Вам также может понравиться
- How To Preserve Eggs: Freezing, Pickling, Dehydrating, Larding, Water Glassing, & MoreОт EverandHow To Preserve Eggs: Freezing, Pickling, Dehydrating, Larding, Water Glassing, & MoreРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Common Incubation Problems: Causes and Remedies: Publication 8127Документ0 страницCommon Incubation Problems: Causes and Remedies: Publication 8127Dani GarnidaОценок пока нет
- Egg Incubation for the Poultry Keeper - A Collection of Articles on the Methods and Equipment of Natural and Artificial IncubationОт EverandEgg Incubation for the Poultry Keeper - A Collection of Articles on the Methods and Equipment of Natural and Artificial IncubationОценок пока нет
- 003 Ilmu Ternak Unggas Kuliah 2012Документ16 страниц003 Ilmu Ternak Unggas Kuliah 2012JafarОценок пока нет
- IncubationДокумент8 страницIncubationMP2013100% (1)
- Lee Cartwright Incubating and Hatching EggsДокумент15 страницLee Cartwright Incubating and Hatching EggscallantagОценок пока нет
- EPS 001 Incubating and Hatching EggsДокумент13 страницEPS 001 Incubating and Hatching EggsSamuel Ivan NganОценок пока нет
- MTJ Raise Organic Chicken - SAGДокумент97 страницMTJ Raise Organic Chicken - SAGMarvin Rivero100% (1)
- Poultry Science of Livestock and Non Ruminants: Practical Report 2016Документ13 страницPoultry Science of Livestock and Non Ruminants: Practical Report 2016Pavithra Morgan100% (2)
- Trouble Shooting Failures With Egg Incubation: Hatching Quality ChicksДокумент8 страницTrouble Shooting Failures With Egg Incubation: Hatching Quality Chickst0mpr1c3Оценок пока нет
- IncubationДокумент9 страницIncubationoluchukwu u.Оценок пока нет
- Incubation and TroubleshootingДокумент3 страницыIncubation and TroubleshootingJohn Baldo FriasОценок пока нет
- Identifying Good Layer From Non LayerДокумент24 страницыIdentifying Good Layer From Non Layergemma salomonОценок пока нет
- Incubating Eggs: Phillip J. Clauer, Poultry Extension Specialist, Animal and Poultry SciencesДокумент5 страницIncubating Eggs: Phillip J. Clauer, Poultry Extension Specialist, Animal and Poultry SciencesDalida BehiterОценок пока нет
- 18 Common Problems With Hatching Eggs (And How To Fix Them)Документ4 страницы18 Common Problems With Hatching Eggs (And How To Fix Them)pushpen5115Оценок пока нет
- Hand Rearing Cockatiels: Housing and Ambient TemperatureДокумент3 страницыHand Rearing Cockatiels: Housing and Ambient TemperatureJake MangahasОценок пока нет
- Aviagenbrief: Best Practice Management in The Absence of Antibiotics at The HatcheryДокумент5 страницAviagenbrief: Best Practice Management in The Absence of Antibiotics at The HatcherymahmudОценок пока нет
- Hatching Chickens. Incubating Eggs For Raising Baby ChickensДокумент11 страницHatching Chickens. Incubating Eggs For Raising Baby ChickensMichael HeidbrinkОценок пока нет
- Goat Production Technologies 2Документ7 страницGoat Production Technologies 2Shiela SalvosaОценок пока нет
- Incubator BasicsДокумент13 страницIncubator BasicsSelva Mara CoutoОценок пока нет
- Porcine Infertility: Prof G N PurohitДокумент25 страницPorcine Infertility: Prof G N PurohitgnpobsОценок пока нет
- Porcine Infertility: Prof G N PurohitДокумент25 страницPorcine Infertility: Prof G N PurohitgnpobsОценок пока нет
- EPS 001 Incubating and Hatching Eggs1 PDFДокумент13 страницEPS 001 Incubating and Hatching Eggs1 PDFsanthoshОценок пока нет
- 1 Perform PreДокумент13 страниц1 Perform PreRomally Antonette TagnipezОценок пока нет
- Raise Organic Chickens (Reviewer NG OAP NCII) (AutoRecovered)Документ3 страницыRaise Organic Chickens (Reviewer NG OAP NCII) (AutoRecovered)SittieОценок пока нет
- Hatchery ManagmentДокумент25 страницHatchery ManagmentMuhammad AwaisОценок пока нет
- KW Poultry Unit PPДокумент115 страницKW Poultry Unit PPLaila UbandoОценок пока нет
- Achieving High YieldsДокумент34 страницыAchieving High YieldsAciОценок пока нет
- Core Competencies: 1. Maintain Poultry EnvironmentДокумент51 страницаCore Competencies: 1. Maintain Poultry EnvironmentCharlton Benedict BernabeОценок пока нет
- SgaДокумент4 страницыSgaLovely Princess Balaba ToraynoОценок пока нет
- Cookey 10 q1 Module 1 4Документ12 страницCookey 10 q1 Module 1 4rainepoblete07Оценок пока нет
- Raise Organic ChickenДокумент32 страницыRaise Organic ChickenBernardo Lacaza Juvita JR.Оценок пока нет
- Is The Feed Readily Accessible?: Low Egg ProductionДокумент2 страницыIs The Feed Readily Accessible?: Low Egg ProductionTakougalamoОценок пока нет
- What Is Chronic Egg Laying?Документ2 страницыWhat Is Chronic Egg Laying?SarchizianОценок пока нет
- Incubation HandbookДокумент77 страницIncubation HandbookDr. Md Aminul IslamОценок пока нет
- Agriculture Form 4 NotesДокумент68 страницAgriculture Form 4 NotesKenzo DickenzОценок пока нет
- Egg Baby Project: Buenasher Learning Academy IncДокумент11 страницEgg Baby Project: Buenasher Learning Academy IncEl CruzОценок пока нет
- GALLINAS REPRODUCTORAS DE ENGORDE AcostaДокумент3 страницыGALLINAS REPRODUCTORAS DE ENGORDE AcostaAndres De la rosaОценок пока нет
- Introduction Japanese QuailДокумент9 страницIntroduction Japanese QuailJelena Petrović Ex MaslaćОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 2: Egg InoculationДокумент15 страницExperiment No. 2: Egg InoculationILHAM BAGUS DARMA .NОценок пока нет
- Module 34 Tle 10Документ13 страницModule 34 Tle 10redox franciscoОценок пока нет
- Incubating / Hatching Procedure, Process: IncubationДокумент8 страницIncubating / Hatching Procedure, Process: Incubationhik hokОценок пока нет
- Storageand Handlingof EggsДокумент2 страницыStorageand Handlingof EggsHenri PurnomoОценок пока нет
- Egg BindingДокумент3 страницыEgg BindingEmprit SaktiОценок пока нет
- Breeding, Gestation, & Farrowing: Lesson IntroductionДокумент12 страницBreeding, Gestation, & Farrowing: Lesson Introductionorases_papreferredОценок пока нет
- 4 Lecture - Incubation, Hatching, Egg Structure and Formation.Документ45 страниц4 Lecture - Incubation, Hatching, Egg Structure and Formation.Arpan ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- 4.form Four NotesДокумент71 страница4.form Four Noteskinsley wandaОценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting Egg Quality: R. Scott Beyer - Poultry SpecialistДокумент4 страницыFactors Affecting Egg Quality: R. Scott Beyer - Poultry SpecialistMaamar AmamraОценок пока нет
- Commercial Broiler Breeds in The PhilippinesДокумент22 страницыCommercial Broiler Breeds in The PhilippineskevinОценок пока нет
- Development Embrio, Incubation and HechingДокумент25 страницDevelopment Embrio, Incubation and HechingGian Apriansya AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Brooding ManagementДокумент20 страницBrooding ManagementRonabelle Montojo Villanueva - GumalinggingОценок пока нет
- Raising Japanese QuailДокумент5 страницRaising Japanese QuailJafar Khan100% (1)
- Florida: Hatchability Problem AnalysisДокумент1 страницаFlorida: Hatchability Problem AnalysisMacovei MihaelaОценок пока нет
- In Vitro FertilizationДокумент34 страницыIn Vitro FertilizationShally May Estrella OrozcoОценок пока нет
- PoultryДокумент11 страницPoultryTawanda MandazaОценок пока нет
- Egg Safety and The Backyard FlockДокумент3 страницыEgg Safety and The Backyard FlockVisvendra SinghОценок пока нет
- Incubating Eggs of Domestic Birds: EC 530 Rev. October 1996Документ14 страницIncubating Eggs of Domestic Birds: EC 530 Rev. October 1996Xialin ZhangОценок пока нет
- Oksa ANSI-9013 1996-06Документ4 страницыOksa ANSI-9013 1996-06Redel AlaОценок пока нет
- Swine 1Документ54 страницыSwine 1Keegan McElroyОценок пока нет
- CertificateДокумент3 страницыCertificateRathnayaka NewilОценок пока нет
- Science in The Art of Osteopathy PDFДокумент378 страницScience in The Art of Osteopathy PDFPetru Acozmei100% (5)
- Psychological Well Being - 18 ItemsДокумент5 страницPsychological Well Being - 18 ItemsIqra LatifОценок пока нет
- Meghan Baxendell Resume January 2017 OnlineДокумент3 страницыMeghan Baxendell Resume January 2017 Onlineapi-323081470Оценок пока нет
- ObamaDeception SupplementalBookletДокумент34 страницыObamaDeception SupplementalBookletAccurateHistorian100% (4)
- Training Report BorocapsДокумент20 страницTraining Report BorocapsCrimson TienОценок пока нет
- Relationship of Chronic Disease With Psychososial Problems in Patients in Gunung Jati Hospital CirebonДокумент7 страницRelationship of Chronic Disease With Psychososial Problems in Patients in Gunung Jati Hospital CirebonSitti AuraОценок пока нет
- Risk Assessment: Severity (1, 2 or 3)Документ1 страницаRisk Assessment: Severity (1, 2 or 3)Ulviyye ElesgerovaОценок пока нет
- 12 Compulsive Activities ChecklistДокумент8 страниц12 Compulsive Activities ChecklistShrey BadrukaОценок пока нет
- NBME 16 Complete PDFДокумент112 страницNBME 16 Complete PDFSilar Khan67% (18)
- Slu Brochure Ay 2014-2015Документ2 страницыSlu Brochure Ay 2014-2015Michael BermudoОценок пока нет
- 9700 w14 QP 21Документ16 страниц9700 w14 QP 21rashmi_harryОценок пока нет
- Jurnal PsikiatriДокумент4 страницыJurnal PsikiatriSri SiswatiОценок пока нет
- Caroline O'Mahony Caroline's Fit PlanДокумент30 страницCaroline O'Mahony Caroline's Fit PlanGizem MutluОценок пока нет
- 2016 Article InternationalEcoHealthOneHealtДокумент139 страниц2016 Article InternationalEcoHealthOneHealtMauricio FemeníaОценок пока нет
- Your Wellness Profile: Laboratory ActivitiesДокумент4 страницыYour Wellness Profile: Laboratory Activitiesdusty kawiОценок пока нет
- Daftar Pustaka: PenyakitДокумент9 страницDaftar Pustaka: Penyakitmagdalena kristantiОценок пока нет
- Tranexamic Acid MouthwashДокумент1 страницаTranexamic Acid MouthwashTalal MazharОценок пока нет
- Reflection Essay - HRM533Документ9 страницReflection Essay - HRM533Mazatul NadirahОценок пока нет
- BISWAS Vol 3, Issue 2Документ225 страницBISWAS Vol 3, Issue 2Vinayak guptaОценок пока нет
- Henry Schein Orthodontics Catalog - General SuppliesДокумент8 страницHenry Schein Orthodontics Catalog - General SuppliesOrtho OrganizersОценок пока нет
- Freud's Psychosexual Stages of DevelopmentДокумент30 страницFreud's Psychosexual Stages of DevelopmentjessaОценок пока нет
- Transcript Emily Fletcher Greater Sex Better Sleep With Ziva Meditation 224 PDFДокумент40 страницTranscript Emily Fletcher Greater Sex Better Sleep With Ziva Meditation 224 PDFLacramioara Ionescu100% (1)
- Risk Factors of Internet Addiction Among AdolescentsДокумент14 страницRisk Factors of Internet Addiction Among AdolescentsM. F. MubinОценок пока нет
- FV2113 Short Note Student Copy Assignmnet 1 (1) 2000Документ9 страницFV2113 Short Note Student Copy Assignmnet 1 (1) 2000Nadia RiazОценок пока нет
- Restobar FSДокумент58 страницRestobar FSGabrielle Alonzo100% (1)
- Health Promotion and MaintenanceДокумент170 страницHealth Promotion and Maintenancepopota100% (1)
- Personal Finance Canadian 2nd Edition Madura Test BankДокумент48 страницPersonal Finance Canadian 2nd Edition Madura Test Bankannabellaauroravb5cf100% (22)
- Biological Basis of HomosexulaityДокумент22 страницыBiological Basis of HomosexulaityDhimitri BibolliОценок пока нет
- ShowfileДокумент19 страницShowfileiyalazhaguОценок пока нет
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignОт EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (138)
- Bridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsОт EverandBridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (16)
- Carpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresОт EverandCarpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (2)
- Art of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionОт EverandArt of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Working Guide to Pump and Pumping Stations: Calculations and SimulationsОт EverandWorking Guide to Pump and Pumping Stations: Calculations and SimulationsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Exposure: Poisoned Water, Corporate Greed, and One Lawyer's Twenty-Year Battle Against DuPontОт EverandExposure: Poisoned Water, Corporate Greed, and One Lawyer's Twenty-Year Battle Against DuPontРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- Non-destructive Testing and Evaluation of Civil Engineering StructuresОт EverandNon-destructive Testing and Evaluation of Civil Engineering StructuresJean-Paul BalayssacОценок пока нет
- Piping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsОт EverandPiping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Onshore Structural Design Calculations: Power Plant and Energy Processing FacilitiesОт EverandOnshore Structural Design Calculations: Power Plant and Energy Processing FacilitiesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (13)
- Waste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretОт EverandWaste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Did Your Can of Soda Kill A Whale? Water Pollution for Kids | Children's Environment BooksОт EverandDid Your Can of Soda Kill A Whale? Water Pollution for Kids | Children's Environment BooksОценок пока нет
- Principles of direct and superior responsibility in international humanitarian lawОт EverandPrinciples of direct and superior responsibility in international humanitarian lawОценок пока нет
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignОт EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (19)
- Earthquake-Resistant Structures: Design, Build, and RetrofitОт EverandEarthquake-Resistant Structures: Design, Build, and RetrofitРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (8)
- Deepwater Deception: The Truth about the Tragic Blowout & Perversion of American JusticeОт EverandDeepwater Deception: The Truth about the Tragic Blowout & Perversion of American JusticeОценок пока нет
- Reduce, Reuse and Recycle : The Secret to Environmental Sustainability : Environment Textbooks | Children's Environment BooksОт EverandReduce, Reuse and Recycle : The Secret to Environmental Sustainability : Environment Textbooks | Children's Environment BooksОценок пока нет