Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Plain Bearing - CIP-JM Katalog
Загружено:
kazdanoИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Plain Bearing - CIP-JM Katalog
Загружено:
kazdanoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Laminate composite material
CIP bearings and wear pads
Catalog &
engineering manual
Laminates
composites
CIP Composite material is a laminated plastic mate-
rial made by impregnating fabric with thermosetting
resins. The physical and mechanical properties of all
grades of CIP make them excellent bearing materials.
CIP composites offer design engineers an attractive,
low cost alternative to the traditional materials used
throughout industry for bearings, wear pads and other
components.
CIP is only 1/6 the weight of steel, easily machined,
has good dimensional stability and contains no harm-
ful or toxic materials.
Advantages of
using CIP composites
Low maintenance, allows for reduction or elimina-
tion of wet lubrication.
Excellent electrical insulation and non-magnetic
series are available.
Excellent dimensional stability in water, corrosive
uids and chemical solutions.
Does not contain abrasive llers (no calcium carbon-
ate llers.)
High load capacity and shock load resistant.
Excellent mechanical strength.
Long life, wear resistant.
Non-abrasive to mating surfaces.
Applications
General purpose bearing & wear pad applications,
conveyor chain guides, electrical insulators, screw con-
veyor hanger bearings, hydraulic cylinder wear rings.
Linear slides or pivot points. Scissor lifts, bottle and
capping machinery.
Kiln cart bearings, wear strips on heat shrink seal-
ing machines, bearings in steel and aluminum plants,
high-temp hydraulic applications.
Ideal for pivoting and sliding applications where
thin wall bearings are required.
1. CIP Wear Rings
2. CIP Bearings &
Wear Pads
Cip series
100 series
Medium weave fabric with excellent mechanical
strength.
200 series
Medium weave fabric(100 series) crosswoven
with PTFE for a low coefcient of friction.
(Wrapped with series 100 material for walls
over 1/4 inch.(6.35mm))
300 series
High temperature fabric that can operate into
the 400 (204 C) range while maintaining its
high compressive strength.
400 series
Medium weave fabric (100 series) cross woven
with a PTFE textile for a low coefcient of fric-
tion in thin wall bearings. No additional series
wrap used.
Solid lubricants
All above series of CIP Composites are available
with solid lubricants incorporated. These can
be graphite, MOS2, or PTFE evenly dispersed
throughout the material. These materials are
recommended for use where other forms of lu-
bricants are undesirable, erratic or nonexistent.
These solid lubricants can substantially improve
performance where maintenance of wet lubrica-
tion lms is difcult.
CIP Material codes
Fabric Series
Polyester = 1
Poly & PTFE = 2
Nomex = 3
PTFE = 4
Additive
None = 0
Graphite = 1
Moly = 2
PTFE = 3
G & P = 4
M & P = 5
Resin
Standard = 1
Marine = 2
High Temp = 3
Advanced = A
Performance
Advanced = B
Performance Plus
Example: Polyester cloth, moly
lubrication additive, polyester resin
and Advanced Performance A =
Series 121A
Advanced performance CIP material
(example: 101a or 101b)
CIPs Advanced Performance material incorporates an additive that strengthens the resin to
enhance physical and mechanical properties. Dry lubricants may be used with this additive.
Advanced Performance Plus combines this additive with a lubricating enhancer.
Physical &
mechanical properties
Series 100 (dry running)
Compressive strength
Perpendicular to Laminate ...................................................35,000 PSI ............................241 N/mm
2
Perpendicular to Laminate (Breaking) ........................52,000 PSI ............................358 N/mm
2
Compressive strength (parallel) to Laminate..........13,500 PSI ............................93 N/mm
2
Tensile strength...................................................................................10,000 PSI ............................69 N/mm
2
Tensile Modulus of Elasticity ..................................................470,000 PSI .........................3,240 N/mm
2
Shear Strength .....................................................................................12,000 PSI ............................83 N/mm
2
Flexural Modulus of Elasticity ................................................280,000 PSI .........................1,930 N/mm2
Hardness Rockwell M ...................................................................100 ..............................................100
Density ......................................................................................................045 #/cu in ...........................1.2g/cm
3
Water Absorption .............................................................................<.1%
Dry applications are best suited to pivoting, linear or very slow rotational.
Please consult with Technical Services on rotary applications.
CIP Wear Pads
Tubes & sheets
Machining
CIP composite is readily machinable by con-
ventional machining techniques and, as a gen-
eral guide, may be treated as bronze but should
be machined dry without coolant.
For turning, tungsten carbide-tipped tools
should be used to obtain a ne nish. High-
speed steel tools can be used for machining
where accuracy below .005" (.12mm) is not
required and for small quantity production.
CIP composites are completely non-toxic.
It is advisable to use adequate dust extraction
when machining CIP composites.
Special products
Special components can be manufactured to
customers drawings from all grades of CIP. In
addition to special wear pads and bearings,
spherical bearings can be manufactured in CIP
Tubes & sheets
CIP tubes & sheets
Tube
Minimum bore ................. 3/8" (9.5mm)
Maximum bore ................. 54" (1371mm)
Standard lengths .............. 16",24",32"
(406mm),
(609mm),
(812mm)
Sheet
Minimum thickness ...... 1/16" (1.6mm)
Maximum thickness ..... 3" (76mm)
Standard size ....................... 16" x 24"
(406mm x 609mm),
to 32"x 60"
(812 x 1524 mm)
Custom Sizes available upon request
CIP Tubes & Sheets
to solve misalignment problems. Spheri-
cal bearing with metallic and CIP materials
combined can also be produced. Parts requir-
ing hex, square or irregular ID shapes can be
produced from mandrels made with the appro-
priate conguration. Please contact Columbia
Industrial Products Technical Service depart-
ment for special applications.
Standard CIP bearings
(Material grade 121)
Close-in on standard CIP bearing is
90-100%. Concentricity is held
to .002" (.05mm) max. 1/8" (3.1mm) wall
sections maximize load carrying capabilities
and minimize any thermal expansion problems.
This applies to both at and round
applications.
Standard laminate
composite bearings
Material grade 121
Standard thrust washers
Cip wear pads
CIP material is ideal for most wear pad applica-
tions. Its high compressive strength, dimension-
al stability and lubricity offer superior perfor-
mance when compared to PTFE, UHMW,
Cast Nylon or traditional Phenolics.
CIP can be provided from 1/16 to 3" (1.5mm
to 76mm) thick. Material can be bonded to
metal substrates or completely machined from
sheet to your specications. We invite you to
submit your wear pad applications for
consideration.
Installation
of CIP bearings
CIP bearings should be fully supported over
their loaded area, with uniform interference t.
A suitable lead-in chamfer should be provided in
the housing, and drawing or pressing-in meth-
ods should be used. Hammer blows should be
avoided. It is recommended that bearings be
retained by shoulders whenever possible.
CIP bearings close in between 90-100% of
their interference t. Flat components such as
wear pads can be retained by countersunk screws
and located by keeper plates where high lateral or
shearing loads are anticipated.
CIP material can also be bonded using two-
part epoxy resin adhesives, but manufacturers
recommendations must be strictly followed,
particularly with reference to pre-treatment of
the surfaces. Loctite grade 648 or Permabond
F246 are suggested adhesives. Where possible,
contaminating or corroding liquids should be
excluded from the bearing interface, unless they
are being used as lubricants. Sealing will also help
retain lubricants.
Mating surface
The surface nish of the mating component
has a major effect on the performance of the
bearing. Surface roughness should ideally be 32
microinches (0.8 Ra).
Suitable materials for shafts, thrust faces, etc.,
would be hardened steels or stainless. Hard
chrome plated steel surfaces cause high wear
rates under certain conditions, and burnishing
or other surface nish treatments should be
considered as an alternative.
The main criteria is that the mating surface
should be free from cutting edges. Journals
or thrust faces should be free of lubrication
grooves or holes.
Coefcient of
frictional values
LUBRICATION
Series 100
Series 200
GRADE
NONE WATER SOLUBLE OIL GREASE OIL
.18-.25 .01 .019 .013 .02
.18 .01 .019 .013 .02
.14 .01 .013 .013 .013
.05-.09 .01 .013 .013 .013
CIP 121
CIP 151
Electrical and
magnetic properties
All grades of CIP material are excellent insulat-
ing materials and may be used in many electri-
cal applications.
As bearings and thrust washers CIP material
is suitable for use in dynamos, electric motors,
generators, etc.
As at laminate, it can be used in heavy
switchgear, transformers, insulating chassis and
as general construction
material.
Sliprings and other current transfer devices
can also be manufactured from CIP.
CIP is non-magnetic and does not build-up
static charges. These properties may often be
exploited to advantage where interference with
Insulation Resistance (Megohms)
BSS.2782 (Pt. 2) ...........................................................................2,000
Electrical Strength at 194 F (90 C)
BSS.2782 (Pt.2) Flatwise (Volts/mil) ...........................210
Edgewise (kv/inch - kv/mm) ..............................................47 (1.85kv/mm)
Power Factor (1 M/c per sec) 0.021
Permittivity (1 M/c per sec) 3.1
Hydraulic Wear Rings
Conditions: Standard CIP grades running
against stainless steel mating surface. This data
was generated by testing at these extreme speci-
cations.
Bearing pressure: 2,000 PSI (13.7 N/mm
2
)
Surface speed: 90 SFM (v =4.5 m/s)
Hydraulic Wear Rings
Thermal properties
Operating temperature range
Standard Series 100 & 200 grades ...........................................-40 / +250 F (121C)
Series 300 grade ......................................................................................-40 / +400 F (204)
Linear coefcient of thermal expansion
(68 O F - 212 O F) (20C - 100OC) per degree F
Standard Series 100 & 200 grades
Normal to laminate (bearing diameter) ................................6.7 x 10-5 (1.7 x 10-3mm)
Parallel to laminate (bearing length) .......................................3.8 x 10-5 (9.6 x 10-4mm)
Series 300
Normal to laminate (bearing diameter) ...............................3.0 x 10-5 (7.1 x 10-4mm)
Parallel to laminate (bearing length) .......................................1.6 x 10-5 (4.0 x 10-4mm)
CIP Special Bearings
For operating temperatures exceeding Series
100 & 200 grades, use Series 300 to 400 F
(204C) with a compressive strength of 35,000
PSI (241 MPA). Series 300 is available with the
same solid lubricants as the standard grades.
As is common with all resin bonded fabrics
CIP has a low thermal conductivity. Under
normal circumstances frictional heat is removed
via the mating metal surface. However, in cases
where shafts or housings are conducting heat to
the bearing assembly, the lubricant must be suf-
cient to remove both frictional and conducted
heat.
The removal of frictional heat may be im-
proved particularly in dry running applications,
by using the housing as the main heat conduc-
tor. The wall thickness of bearings should be
kept to a minimum in order to improve heat
dissipation.
Thermal expansion of CIP material is greater
than that of most metal alloy bearings and the
characteristic must be taken into account in
designs for higher temperature applications.
For applications where there will be a temper-
ature change of > 60 F (15C), please consult
with Columbia Industrial Products for correct
running clearance.
Chemical and
corrosion resistance
S = Satisfactory L = Satisfactory for limited service U = Unsatisfactory
Although the utmost care is taken to ensure the accuracy of data supplied and ad-
vice or opinions given by the company and to maintain the highest possible quality
of the Companys products and the materials used therein, the supply of such data,
the giving of such advice or opinions and the sale of the Companys products are
subject to the condition that in no circumstances is the Company to be under any
liability for any injury, expense, loss or damage whatsoever arising or alleged to
arise directly or indirectly as a result of the adoption of data supplied or advice or
opinions given or the use to the Companys products except in so far as the Compa-
nys conditions of sale expressly otherwise provided.
This table refers in particular to Series 100
CIP. CIP does not corrode and is unaffected
by many solvents, inorganic solutions, fats and
weak acids. It should be noted that water and
chemical liquids often act as lubricants on the
material giving low coefcients of friction and
thereby eliminating the problems commonly
encountered by metal bearings. Composites
are attacked by ketones, chlorinated solvents,
strong alkalis, hot strong oxidizing agents.
For acidic and alkaline applications, refer to
Columbia Industrial Products for recommenda-
tions.
Satisfactory means that the material retains
50% or over of its original dry strength after
immersion for at least six months.
Engineering
manual
The information guide in this engineering sec-
tion enables the designer to establish parameters
which will provide maximum performance of a
bearing in his application. Also we will provide
assistance on material selection and ts.
During composite bearing selection there are
many effects on the bearing to take into consid-
eration. Composite bearings operate at different
press ts and running clearances than bronze or
other metal bearings. Composite bearings re-
quire a heavier press t to retain the bearing in
the housing. The running clearances are larger
in order to reduce heat buildup in the bearing.
Shaft material should be stainless steel or
hardened steel. The minimum hardness sug-
gested is Rockwell 45C. The surface nish
should be from 8-32 microinches (0.2 - 0.8 Ra).
CIP Bearings & Wear Pads
Hard chrome plating may cause premature wear
and should be avoided. Holes in the shaft for
greasing should also be avoided as the edge of
the hole could cut the bearing.
The bearing housing should have a chamfer
for lead-in. The installer should use a press-in
or Drawin method. Do not hammer or the
bearing could be damaged.
Bearing wall thickness is very important.
The correct wall thickness gives the bearing the
proper strength to stay in the housing. Use table
E as a guide for wall thickness.
The following calculation page and tables will
guide you through sizing a composite bearing.
The rst step in sizing a bearing is to gather the
correct information. Use the Application Ques-
tions sheet for this task.
Application questions
Bearing size calculations
Thermal expansion of CIP composites
When composites are used in elevated temperatures they expand. This expansion is seen as a reduc-
tion in the bore diameter of a bearing installed in a housing. In sizing a bearing we must add ad-
ditional clearances to the bore so the shaft will run free at the elevated temperatures. The following
is an example of this calculation.
Series 100 & 200 are used up to 200F (94C) continuous. Above 200F (94C), use CIP Series
300. The coefcients of linear expansion follow.
Linear expansion for Series 100 & 200 = .00006" (.0015mm)/deg over 68F (20C)
Linear expansion for Series 300 = .00003" (.0007mm)/deg over 68F (20C)
Calculations for bearings operating above 68F (20C)
Assume we are using CIP 100 Series material
Assume a bearing running at 200F (94C)
Assume a wall thickness on .250 (6.35mm)
Calculate the delta T, or difference between 68F (20C) and the 200F (94C)
200F (94C) minus 68F (20C) equals 132 (55C) of temperature change
The formula to determine additional clearance is:
2 x Wall Thickness x Coefcient x Delta T = Clearance
2 x .250 (6.35mm) x .00006 (.0015mm) x 132F (56C) = .0039" (.099mm)
Cutting Angles of Turning
Top Rake - 0 to 6 Side Rake - 5 to 8 Front Rake - 4 to 5
Speeds for Cutting
Normal Surface nish 22 to 26 feet/second (6.7/7.9 m/s)
Speeds for Feed
First pass/roughing .015 to .035 inches per revolution (.38mm/.88mm)
Last pass/nishing .010 to .015 inches per revolution (.38mm/.88mm)
Machining cip composites
CIP Composite materials are easily machined
by using conventional tooling and methods.
You can use the same methods as you would
for Aluminum or Brass. CIP Composites are
machined dry. A dust mask and or work area
suction is suggested.
For lathe work, carbide or diamond tipped
tools can be used to generate a ne surface
nish. Diamond tool tips do not produce as
much heat when cutting and are suggested for
best results. CIP Composites are 100% bearing
material with no llers.
Sample application questions
32 microinches (0.8 Ra) or Better
Sample bearing
calculations
Johnson Metall is Scandinavias largest
producer of plain bearings, bars, tubes
and castings in bronze. Production
facilities can be found in Sweden
and Finland, sales company in
Denmark and Norway.
Headquarters is located in rebro,
Sweden. Over two hundred people work
here and accounted for sales of SEK 250
million in 2005.
Altogether, the JM Group employs
about 300 people (2005) and has a sales
of SEK 360 million (2005).
Johnson Metall AB is a wholly owned
subsidiary of Hexagon AB.
HEXAGON AB
JOHNSON METALL AB
Sweden
Scandinavias Largest
E
d
i
t
i
o
n
6
2
0
0
5
Head office rebro
Stlgatan 15
P.O. Box 1513
SE-701 15 REBRO, SWEDEN
Phone +46 19 17 51 00
Fax +46 19 14 83 40
E-mail: sales.orebro@johnson-metall.com
Internet: www.johnson-metall.com
Denmark
Johnson Metal A/S
Nyholms All 20
DK-2610 RDOVRE, DENMARK
Phone +45 36 70 00 44
Fax +45 36 70 80 50
E-mail: j-m@johnson-metal.dk
Internet: www.johnson-metall.com
Finland
OY Johnson Metall
Turkkirata 14
FI-33960 PIRKKALA 6, FINLAND
Phone +358 33 42 77 00
Fax +358 33 42 77 28
E-mail: myynti@johnson-metall.fi
Norway
Johnson Metall AS
Katfos Nringspark
N-3360 GEITHUS, NORWAY
Phone +47 32 78 32 00
Fax +47 32 78 32 01
E-mail: sales.geithus@johnson-metall.com
Internet: www.johnson-metall.com
T
e
t
a
b
,
r
e
b
r
o
Hexagon
Polymers
Hexagon
Engineering
OY JOHNSON METALL
Finland
JOHNSON METALL AS
Norway
JOHNSON METAL A/S
Denmark
Measurement
Technology
Hexagon
Johnson Metall is Scandinavias largest
producer of plain bearings, bars, tubes
and castings in bronze. Production
facilities can be found in Sweden
and Finland, sales company in
Denmark and Norway.
Headquarters is located in rebro,
Sweden. Over two hundred people work
here and accounted for sales of SEK 250
million in 2005.
Altogether, the JM Group employs
about 300 people (2005) and has a sales
of SEK 360 million (2005).
Johnson Metall AB is a wholly owned
subsidiary of Hexagon AB.
HEXAGON AB
JOHNSON METALL AB
Sweden
Scandinavias Largest
E
d
i
t
i
o
n
6
2
0
0
5
Head office rebro
Stlgatan 15
P.O. Box 1513
SE-701 15 REBRO, SWEDEN
Phone +46 19 17 51 00
Fax +46 19 14 83 40
E-mail: sales.orebro@johnson-metall.com
Internet: www.johnson-metall.com
Denmark
Johnson Metal A/S
Nyholms All 20
DK-2610 RDOVRE, DENMARK
Phone +45 36 70 00 44
Fax +45 36 70 80 50
E-mail: j-m@johnson-metal.dk
Internet: www.johnson-metall.com
Finland
OY Johnson Metall
Turkkirata 14
FI-33960 PIRKKALA 6, FINLAND
Phone +358 33 42 77 00
Fax +358 33 42 77 28
E-mail: myynti@johnson-metall.fi
Norway
Johnson Metall AS
Katfos Nringspark
N-3360 GEITHUS, NORWAY
Phone +47 32 78 32 00
Fax +47 32 78 32 01
E-mail: sales.geithus@johnson-metall.com
Internet: www.johnson-metall.com
T
e
t
a
b
,
r
e
b
r
o
Hexagon
Polymers
Hexagon
Engineering
OY JOHNSON METALL
Finland
JOHNSON METALL AS
Norway
JOHNSON METAL A/S
Denmark
Measurement
Technology
Hexagon
Johnson Metall is Scandinavias largest
producer of plain bearings, bars, tubes
and castings in bronze. Production
facilities can be found in Sweden
and Finland, sales company in
Denmark and Norway.
Headquarters is located in rebro,
Sweden. Over two hundred people work
here and accounted for sales of SEK 250
million in 2005.
Altogether, the JM Group employs
about 300 people (2005) and has a sales
of SEK 360 million (2005).
Johnson Metall AB is a wholly owned
subsidiary of Hexagon AB.
HEXAGON AB
JOHNSON METALL AB
Sweden
Scandinavias Largest
E
d
i
t
i
o
n
6
2
0
0
5
Head office rebro
Stlgatan 15
P.O. Box 1513
SE-701 15 REBRO, SWEDEN
Phone +46 19 17 51 00
Fax +46 19 14 83 40
E-mail: sales.orebro@johnson-metall.com
Internet: www.johnson-metall.com
Denmark
Johnson Metal A/S
Nyholms All 20
DK-2610 RDOVRE, DENMARK
Phone +45 36 70 00 44
Fax +45 36 70 80 50
E-mail: j-m@johnson-metal.dk
Internet: www.johnson-metall.com
Finland
OY Johnson Metall
Turkkirata 14
FI-33960 PIRKKALA 6, FINLAND
Phone +358 33 42 77 00
Fax +358 33 42 77 28
E-mail: myynti@johnson-metall.fi
Norway
Johnson Metall AS
Katfos Nringspark
N-3360 GEITHUS, NORWAY
Phone +47 32 78 32 00
Fax +47 32 78 32 01
E-mail: sales.geithus@johnson-metall.com
Internet: www.johnson-metall.com
T
e
t
a
b
,
r
e
b
r
o
Hexagon
Polymers
Hexagon
Engineering
OY JOHNSON METALL
Finland
JOHNSON METALL AS
Norway
JOHNSON METAL A/S
Denmark
Measurement
Technology
Hexagon
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- ComprehensiverangeДокумент4 страницыComprehensiverangekazdanoОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- GE - SX-GE - AX Thrust Plain Spherical BearingsДокумент1 страницаGE - SX-GE - AX Thrust Plain Spherical BearingskazdanoОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Earth Boss: - Provides Preferential Equipotential Bonding Connection PointДокумент1 страницаEarth Boss: - Provides Preferential Equipotential Bonding Connection PointkazdanoОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- LB-Buch-Conventional-Hardness (Rockwel Shore)Документ23 страницыLB-Buch-Conventional-Hardness (Rockwel Shore)kazdanoОценок пока нет
- ISO 3601 G Measurements in Millimeters Measurements in Inches ISO 3601 G Size ID CS ID CS SizeДокумент8 страницISO 3601 G Measurements in Millimeters Measurements in Inches ISO 3601 G Size ID CS ID CS SizekazdanoОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- KTF-standard ENGДокумент60 страницKTF-standard ENGkazdanoОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
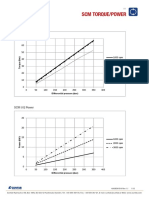
- SCM Torque and Power 151019Документ12 страницSCM Torque and Power 151019kazdanoОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- High Strength Fine Grained Structural Steel, Quenched and TemperedДокумент6 страницHigh Strength Fine Grained Structural Steel, Quenched and TemperedkazdanoОценок пока нет
- SCM 012-130 SaeДокумент12 страницSCM 012-130 SaekazdanoОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- SCM Torque and Power 151019Документ12 страницSCM Torque and Power 151019kazdanoОценок пока нет
- SCM 025-108 M2Документ8 страницSCM 025-108 M2kazdanoОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- 42 CR Mo 4Документ4 страницы42 CR Mo 4kazdanoОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
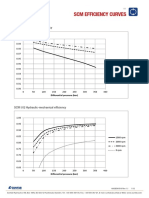
- SCM Efficiency Curves SCM Efficiency CurvesДокумент12 страницSCM Efficiency Curves SCM Efficiency CurveskazdanoОценок пока нет
- Product: CatalogueДокумент38 страницProduct: CataloguekazdanoОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- CH3 1 Welding Joint SymbolsДокумент32 страницыCH3 1 Welding Joint SymbolskazdanoОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Class Equip Lifting Mach enДокумент9 страницClass Equip Lifting Mach enerzengenhariaОценок пока нет
- G G GE EEN N NE EER R RA Aalll P PPU U UR R RP PPO O OS SSE EE E EEN N NC C Clllo O OS SSU U UR R RE EES SSДокумент37 страницG G GE EEN N NE EER R RA Aalll P PPU U UR R RP PPO O OS SSE EE E EEN N NC C Clllo O OS SSU U UR R RE EES SSkazdanoОценок пока нет
- Old Q.papers M.tech I SemДокумент15 страницOld Q.papers M.tech I SemallakagopichandОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
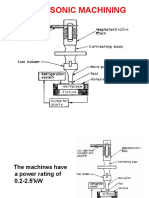
- Ultrasonic Machining (USM)Документ19 страницUltrasonic Machining (USM)RakeshSaini100% (2)
- Final Thesis On CNCДокумент56 страницFinal Thesis On CNCSundeep Kumar100% (1)
- Boring BarsДокумент27 страницBoring BarsSurjeet Singh SaranОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Micro MachiningДокумент302 страницыMicro Machiningapulavarty100% (2)
- Toolrec UGДокумент9 страницToolrec UGrolandОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Different Types of FixturesДокумент20 страницChapter 2 Different Types of FixturesaragawОценок пока нет
- Locating DevicesДокумент7 страницLocating DevicesRavi Arjun KumarОценок пока нет
- Reacondicionamiento de Bloque de Cilindros PDFДокумент37 страницReacondicionamiento de Bloque de Cilindros PDFJavier Hector CayaОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Cad CamДокумент6 страницCad CamC1DA20ME030 Hemanth SОценок пока нет
- Ultrasonic MachiningДокумент21 страницаUltrasonic MachiningMuhd Nur JihadОценок пока нет
- B FeelerДокумент8 страницB FeelerharisОценок пока нет
- SF-2012AH-QG User' S ManualДокумент61 страницаSF-2012AH-QG User' S Manualkamal hasan0% (1)
- H - Additional MachiningДокумент51 страницаH - Additional MachiningedsaregОценок пока нет
- VARGUS - Industrial Solutions - MetricДокумент20 страницVARGUS - Industrial Solutions - MetricGilberto ManhattanОценок пока нет
- Group Technology & CappДокумент43 страницыGroup Technology & CappSubbu SuniОценок пока нет
- BBN - Hot Forged Bolts - Machined Parts Main CatalogueДокумент31 страницаBBN - Hot Forged Bolts - Machined Parts Main CatalogueKapil Enterprises BigboltnutОценок пока нет
- Asientos de Valvulas RectificadorasДокумент2 страницыAsientos de Valvulas RectificadorasJuan Pablo Ramirez GiraldoОценок пока нет
- Unit I 1-Cutting Tool Angles and Their SignificanceДокумент48 страницUnit I 1-Cutting Tool Angles and Their Significanceprof_panneer50% (2)
- Chip Formation 2Документ8 страницChip Formation 2Ebrahim Abdullah HanashОценок пока нет
- Manual GuideДокумент6 страницManual GuideDeysi CardenasОценок пока нет
- SolidCAM Back Spindle Guide PDFДокумент32 страницыSolidCAM Back Spindle Guide PDFNguyen Quoc TuanОценок пока нет
- Turning and Drilling PPT MFG Chapter23 FinalДокумент78 страницTurning and Drilling PPT MFG Chapter23 FinalRavichandran GОценок пока нет
- 165 Kostadin Cukor Jurkovic CIM2017Документ6 страниц165 Kostadin Cukor Jurkovic CIM2017Kenan MuhamedagicОценок пока нет
- Electrical Discharge Machining: Various Electric Discharge MachinesДокумент40 страницElectrical Discharge Machining: Various Electric Discharge MachinesArun PrasadОценок пока нет
- Ch-5 DrillingДокумент41 страницаCh-5 DrillingakshayОценок пока нет
- ShaftДокумент15 страницShaftj sОценок пока нет
- Mori Seiki ZT 1000 y enДокумент16 страницMori Seiki ZT 1000 y enOswald muñoz100% (1)
- Mechanics of The Metal Cutting Process. I. Orthogonal Cutting and A Type 2 ChipДокумент15 страницMechanics of The Metal Cutting Process. I. Orthogonal Cutting and A Type 2 ChipJosé María Flores RojasОценок пока нет
- Effect of Cutting Edge Preparation On Tool Performance in Hard-Turning of DF-3 Tool Steel With Ceramic ToolsДокумент11 страницEffect of Cutting Edge Preparation On Tool Performance in Hard-Turning of DF-3 Tool Steel With Ceramic ToolsKrebs_1977Оценок пока нет