Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
IEM 2ndterm SM Assignment (Sagnik Biswas)
Загружено:
Sagnik BiswasИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
IEM 2ndterm SM Assignment (Sagnik Biswas)
Загружено:
Sagnik BiswasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Institute of Engineering & Management
Software Project
Management
~Assignment
Faculty:
Santanu Mukherjee
Sagnik Biswas
Roll No. 27; Sec B
Minor: Systems
Software Management(SM-404) Home Assignment
2
nd
Term Full Marks: 40
IEM MBA 2
nd
Year Page 2
Answer the following questions. All question carry equal marks:
1. Time Management
a. Explain the concept of Critical Path Method and its components.
How does CPM help Project Manager to develop a project
schedule
The Critical Path Method or Critical Path Analysis is a mathematically
based algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is an important
tool for effective project management. It is commonly used with all forms of
projects, including construction, software development, research projects,
product development, engineering, and plant maintenance, among others.
Any project with interdependent activities can apply this method of
scheduling.
Components:-
A list of all activities required to complete the project (also known as
Work Breakdown Structure).
The time (duration) that each activity will take to complete.
The dependencies between the activities.
Each activity is represented as a node on the network, and connecting
lines are drawn to represent the time schedule to complete that activity.
Four parameters of each activity of the network are:-
Earliest start time (ES) = The earliest time an activity can start once the
previous dependent activities are over.
Earliest finish time (EF) = ES + activity duration.
Latest finish time (LF) = The latest time an activity can finish without
delaying the project.
Latest start time (LS) = LF - activity duration.
The float time for an activity is the time between the earliest (ES) and the
latest (LS) start time or between the earliest (EF) and latest (LF) finish
times.
CPM helps Project Manager to develop a project schedule in the
following ways-
It helps reduce project duration.
It helps reduce project costs.
It helps improve project efficiency.
It helps define multiple & critical paths.
It helps schedule, monitor and control projects.
It helps in organizing large projects.
It helps determine slack and float time.
It reveals all the dependencies in the organization.
Software Management(SM-404) Home Assignment
2
nd
Term Full Marks: 40
IEM MBA 2
nd
Year Page 3
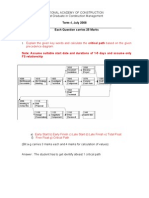
b. Consider the following table to answer the follow up questions:
Activity Preceding Activity Estimate
in Month
Start 0
D Start 4
A Start 6
F D, A 7
E D 8
G F, E 5
B F 5
H G 7
C H 8
End C, B 0
What is the duration of the critical path?
What is the float of activity B?
What is the float of activity E?
What is the float of activity D?
To shorten the length of the project, the sponsored has offered to
remove the work of activity E from the project, making D the
predecessor of activity G and F. What will be the effect?
Software Management(SM-404) Home Assignment
2
nd
Term Full Marks: 40
IEM MBA 2
nd
Year Page 4
2. Cost Management
a. Explain in detail the budget determination process in a software project
management situation
Planning, Scheduling, and Budgeting
The second section includes 10 guidelines that cover the basic requirements for
planning, scheduling, and establishing the time phased budgets for the tasks. The
integrated master schedule is the projects road map to meet contract objectives. This
schedule must be resource loaded to determine the budget for the work as scheduled.
The resource loaded schedule is the basis for the monthly budget, or BCWS, for each
task and thus the project. This time phased budget is the performance measurement
baseline (PMB). The total budget for each task, control account, or the entire project is
defined as the budget at complete (BAC).
Because most projects are initiated with some level of uncertainty; i.e. risk, project
managers typically set aside a portion of the total project value as a management
reserve (MR). MR added to the BAC equals the total project budgeted value, defined as
the contract budget base (CBB). This is illustrated below.
Establishing the baseline an Iterative, three step process
All of the budgets on any project should be logged for successful baseline control.
Occasionally contracted tasks may be temporarily held in abeyance, not yet authorized
Software Management(SM-404) Home Assignment
2
nd
Term Full Marks: 40
IEM MBA 2
nd
Year Page 5
to a manager. When the project manager has yet to assign tasks and budgets to the
CAMs, such as an authorized, not yet negotiated additional work, the task and its budget
can be retained in undistributed budget (UB). These budget assignments, the WBS, and
the functional organizational identity of the managers can be captured in a matrix as
illustrated below.
Budget summary matrix
A very important aspect of the planning and budgeting process is to determine how
BCWP will be assessed. This determination begins with classifying work tasks as one of
three types: discrete, apportioned effort, or level of effort (LOE). From this initial
classification, for each discrete work effort work package, the CAM selects an earned
value technique such as milestones, 50/50, 0/100, or percent complete.
It must be stressed that work only begins when there is formal work authorization to
proceed. This requirement is a disciplined approach to clearly define work, schedule,
and budget before work commences and actual costs begin to accrue. The principles of
EVM are quite clear in this regard.
Software Management(SM-404) Home Assignment
2
nd
Term Full Marks: 40
IEM MBA 2
nd
Year Page 6
b. What do you understand by Earn Value Management? What are
the basic advantages of using EVM for project performance
management?
Earned value management is a project management technique for
measuring project performance and progress. It has the ability to combine
measurements of:
Scope
Schedule, and
Costs
In a single integrated system, Earned Value Management is able to provide
accurate forecasts of project performance problems, which is an important
contribution for project management.
The objectives of an EVM are to:
Relate time phased budgets to specific contract tasks and/or statements
of work.
Provide the basis to capture work progress assessments against the
baseline plan.
Relate technical, schedule, and cost performance.
Provide valid, timely, and auditable data/information for proactive
management action.
Supply managers with a practical level of summarization for effective
decision making.
Earned Value Management Advantages
1) As EVA is done periodically, management tries to make sure that all the project
parameters are on track.
2) It is probably the only system used at present which tracks the project in terms of
work, time and money.
3) Timely performance measurement makes sure that steps can be taken to the
bring project back on track before its too late.
Software Management(SM-404) Home Assignment
2
nd
Term Full Marks: 40
IEM MBA 2
nd
Year Page 7
c. Your project is running well. In the latest earn value report, you
see the CPI = 1.2, the SPI = 0.8, the PV = $600,000, and SV = -
$120,000. You cant find the CV in the report, so you calculate it
based on the information given. What is the CV?
Cost Performance Index (CPI) = 1.2
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) = 0.8
Planned Value (PV) = $ 6, 00, 000
Schedule Variance (SV) = -$ 1, 20, 000
Cost Variance (CV) measures how project is performing; productivity
measure. CV = EV AC (Positive Efficient, Negative Inefficient)
We know,
SV = EV PV, SPI = EV/PV
Therefore,
EV = SV + PV or EV = SPI * PV
EV = -$ 1, 20, 000 + $ 6, 00, 000 or EV = 0.8 * $ 6, 00, 000
EV = $ 4, 80, 000 in both the cases
Again,
CPI = EV/ AC
Therefore,
AC = EV / CPI
AC = $ 6, 00, 000 / 1.2 = $ 4, 00, 000
So,
Cost Variance (CV) = EV AC = $ (4, 80,000 4, 00,000) = $ 80, 000 (Ans.)
Software Management(SM-404) Home Assignment
2
nd
Term Full Marks: 40
IEM MBA 2
nd
Year Page 8
3. Quality Management
a. Explain the following Quality Control Tools with appropriate
examples
i. Cause and Effect Diagram
ii. Histogram
iii. Pereto Chart
iv. Run Chart
v. Scatter Diagram
vi. Control Chart
Cause and Effect Diagram
Helps the PM to look backwards at what has contributed to quality problems in
the project
Histogram
Displays data in the form of bars or columns.
Shows what problems are worth dealing with.
Software Management(SM-404) Home Assignment
2
nd
Term Full Marks: 40
IEM MBA 2
nd
Year Page 9
Pareto Chart
Pareto chart is a type of histogram
It arranges results from most frequent to less frequent to identify which root
causes resulting into most problems.
Run Chart
To look at history and see a pattern of variation
Provide trends
Scatter Diagram
Tracks two variables to see if they are related
Software Management(SM-404) Home Assignment
2
nd
Term Full Marks: 40
IEM MBA 2
nd
Year Page 10
Control Charts
Are set up during Plan Quality Process as part of the effort to determine what
will be the quality of the project.
They are utilized Perform Quality Control to help PM determine if a process is
within acceptable limits.
Example:
Manufacturing of doors.
Control charts help identify if door samples measurement are within the specified range.
Control charts can also be used to monitor project performance figures such as
cost and schedule variables.
Most commonly control charts are used to monitor production and other
processes to see if the processes are within acceptable limits.
Control Charts Upper and Lower Limits
These limits are acceptable range of variation of a process.
They are often shown as two dashed lines on a control chart.
The acceptable range of measurements between upper and lower control limits
is set by the PM and Stakeholders based on the organizations quality standards.
Normally the range is calculated based on +/- 3 sigma or standard deviations.
Data points within the ranges are considered within control.
Example: Control limits for delivery of a work packet
Вам также может понравиться
- Primavera FinalДокумент22 страницыPrimavera FinalHaneef MohamedОценок пока нет
- Performance Evaluation Parameters For Projects and Non-ProfitsДокумент58 страницPerformance Evaluation Parameters For Projects and Non-ProfitsAnjali Angel Thakur93% (14)
- Network TopologyДокумент26 страницNetwork Topologyvijaysingh100% (25)
- Englishix Reading PartialiiiДокумент4 страницыEnglishix Reading PartialiiiCesar UA100% (1)
- GRADUATE SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT EXAMДокумент7 страницGRADUATE SCHOOL OF MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT EXAMShivaani AggarwalОценок пока нет
- Environmental Management System ISO 14001 - 9519499903Документ110 страницEnvironmental Management System ISO 14001 - 9519499903Nelson Alejandro Fierro100% (2)
- Earned Value ManagementДокумент17 страницEarned Value ManagementwaterОценок пока нет
- MBA Project ManagementДокумент29 страницMBA Project ManagementGokaSinghОценок пока нет
- Earned Value-Microsoft ProjectДокумент12 страницEarned Value-Microsoft ProjectJadong KimОценок пока нет
- Basic Statistics in Bio MedicalДокумент271 страницаBasic Statistics in Bio Medicalifai.gs7487100% (2)
- Business Plan (Details)Документ26 страницBusiness Plan (Details)Sagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Socioeconomic Impact StudyДокумент15 страницSocioeconomic Impact StudyAngeline Sampaga100% (2)
- Payroll ManagementДокумент14 страницPayroll ManagementMercy Smarty50% (4)
- Schedule Hierarchy - An OverviewДокумент3 страницыSchedule Hierarchy - An OverviewBTconcordОценок пока нет
- Research Holds The Following Significant DataДокумент2 страницыResearch Holds The Following Significant Datarhomelyn malana100% (1)
- Five Key Project Metrics for Successful ExecutionДокумент7 страницFive Key Project Metrics for Successful ExecutionNaokhaiz AfaquiОценок пока нет
- Chapter5 Project PlanningДокумент38 страницChapter5 Project PlanningSanchit BatraОценок пока нет
- Software ManagementДокумент37 страницSoftware ManagementSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Primavera Final PPT - ClassДокумент22 страницыPrimavera Final PPT - Classsatish230289100% (1)
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Ms. Rita A. MapacpacДокумент3 страницыMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Ms. Rita A. MapacpacJohnKennethPrescillaSilloriquezОценок пока нет
- Big Picture in Focus: Ulob Metalanguage: Develop Work Breakdown StructureДокумент7 страницBig Picture in Focus: Ulob Metalanguage: Develop Work Breakdown StructureArthur LeywinОценок пока нет
- Project Planing & SchedulingДокумент6 страницProject Planing & Schedulingnagarkar_123Оценок пока нет
- The Factors Affecting The Academic Performance of The Working Students at Dela Salle John Bosco College (DLS-JBC) S.Y. 2018 - 2019Документ50 страницThe Factors Affecting The Academic Performance of The Working Students at Dela Salle John Bosco College (DLS-JBC) S.Y. 2018 - 2019Shun Dee Lebico100% (3)
- 5 Major Outputs and DeliverablesДокумент17 страниц5 Major Outputs and DeliverablesShepherd NhangaОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Project Management: The Quick Reference HandbookОт EverandIntroduction to Project Management: The Quick Reference HandbookОценок пока нет
- Software Project ManagementДокумент14 страницSoftware Project Managementmohd zuberОценок пока нет
- Earned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamОт EverandEarned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (15)
- Question Paper - PrimaveraДокумент6 страницQuestion Paper - Primaveramahesh_ch1224100% (1)
- Storage Area Network SANДокумент39 страницStorage Area Network SANSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- MB0049Документ21 страницаMB0049Dipika KumariОценок пока нет
- Case Study: Why Agile Goes AwryДокумент13 страницCase Study: Why Agile Goes AwryMohd NizamОценок пока нет
- Cost controlling in construction using earned valueДокумент9 страницCost controlling in construction using earned valueMohammed Zubair100% (1)
- The Application EVM-NNДокумент16 страницThe Application EVM-NNAlfin SuprayugoОценок пока нет
- CM 1 WBS PartthДокумент21 страницаCM 1 WBS PartthPartth JayyОценок пока нет
- © 2009, Ing. Rodolfo Ambriz, PMP, MCTS, MCITP - 1Документ9 страниц© 2009, Ing. Rodolfo Ambriz, PMP, MCTS, MCITP - 1Lê Tiến TrungОценок пока нет
- UNIT-5-5-1-NOTESДокумент8 страницUNIT-5-5-1-NOTESSarthak kadamОценок пока нет
- Questions - Task 2Документ5 страницQuestions - Task 2Alessandro FonsecaОценок пока нет
- ERP ImplementationsДокумент12 страницERP Implementationsuser44448605Оценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Cpm/pert and Eva Analysis On Project ManagementДокумент8 страницEvaluation of Cpm/pert and Eva Analysis On Project Managementajie wahyujatiОценок пока нет
- MB0049-Project Management Semester - 2: Q.1 Describe in Detail The Various Phases of Project Management Life CycleДокумент12 страницMB0049-Project Management Semester - 2: Q.1 Describe in Detail The Various Phases of Project Management Life CycleCharmi M ParikhОценок пока нет
- SEN-UNIT-5-5-2Документ11 страницSEN-UNIT-5-5-2Sarthak kadamОценок пока нет
- AMSDAC Specification and FeaturesДокумент38 страницAMSDAC Specification and FeaturesfaisalОценок пока нет
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)Документ5 страницWork Breakdown Structure (WBS)Nipuni MaduwanthiОценок пока нет
- Project Management FinalДокумент102 страницыProject Management FinalManikantan PrakashОценок пока нет
- 5 Major Outputs and DeliverablesДокумент17 страниц5 Major Outputs and Deliverablessajith2702Оценок пока нет
- LBNL EVMS Reference Guide Final Rev0Документ22 страницыLBNL EVMS Reference Guide Final Rev0orjuanОценок пока нет
- Topic Review 2Документ24 страницыTopic Review 2LHОценок пока нет
- Earned Value Analysis SoftwareДокумент9 страницEarned Value Analysis SoftwareosemavОценок пока нет
- Supply Chain Management in Tourism and Hospitality Project ManagementДокумент7 страницSupply Chain Management in Tourism and Hospitality Project ManagementMarcillan MarquezОценок пока нет
- BVB College of Engineering and Technology Department of Civil EngineeringДокумент12 страницBVB College of Engineering and Technology Department of Civil EngineeringVinayakОценок пока нет
- Robel Asfaw Id 1102401Документ13 страницRobel Asfaw Id 1102401Robel AsfawОценок пока нет
- Bsbpmg514 TestДокумент5 страницBsbpmg514 Testsita maharjanОценок пока нет
- Project Production Planning and Control MethodsДокумент29 страницProject Production Planning and Control MethodsDivyanshuPandeyОценок пока нет
- Cost Management: Project Management and SAPДокумент37 страницCost Management: Project Management and SAPthi.morОценок пока нет
- This Document Contains "Project Management Plan" of Project School Management SystemДокумент8 страницThis Document Contains "Project Management Plan" of Project School Management SystemHafiz Usman InayatОценок пока нет
- 212 Download Annual Report 2017-18Документ8 страниц212 Download Annual Report 2017-18avdesh7777Оценок пока нет
- The Management Spectrum: People, Product, Process and Project in Software EngineeringДокумент9 страницThe Management Spectrum: People, Product, Process and Project in Software EngineeringPoonam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Project Management: A Managerial Approach: by Lalit Kumar SharmaДокумент26 страницProject Management: A Managerial Approach: by Lalit Kumar SharmaUjjwal ShresthaОценок пока нет
- PAE Ch-3 Project-PlanningДокумент39 страницPAE Ch-3 Project-PlanningProf. Dr. Anbalagan ChinniahОценок пока нет
- Course Mba - 2 Semester Subject Assignment MB0049 - Set1: Project ManagementДокумент37 страницCourse Mba - 2 Semester Subject Assignment MB0049 - Set1: Project ManagementMaheder AdmassuОценок пока нет
- Program Management - Overview - 18 Jan 2013Документ26 страницProgram Management - Overview - 18 Jan 2013venkat4Оценок пока нет
- An Overview of Project PlanningДокумент24 страницыAn Overview of Project PlanningTanmoy Chakraborty0% (1)
- University-Of-Phoenix CMGT 410 Week 1 Assignment 1Документ5 страницUniversity-Of-Phoenix CMGT 410 Week 1 Assignment 1justquestionanswerОценок пока нет
- Project SchedulingДокумент17 страницProject SchedulingSolomon W. DemissieОценок пока нет
- PM Techniques for Leading ProjectsДокумент22 страницыPM Techniques for Leading ProjectsLaxmi Prakash SubediОценок пока нет
- Software Project Management Chap - 4Документ29 страницSoftware Project Management Chap - 4Roast CrispОценок пока нет
- BPE-Lec 1Документ69 страницBPE-Lec 1hadich5066Оценок пока нет
- IRJET Time and Cost Control Using EarnedДокумент9 страницIRJET Time and Cost Control Using EarnedWong KenFОценок пока нет
- Earned Value Management (EVM)Документ10 страницEarned Value Management (EVM)Faisal Al QadriОценок пока нет
- SPM NotesДокумент10 страницSPM NotesSrikanth DeivasigamaniОценок пока нет
- Time Management CollegeДокумент2 страницыTime Management CollegeSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Financial Institutes & Markets: 2010 MBA (N)Документ4 страницыFinancial Institutes & Markets: 2010 MBA (N)Sagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- IfДокумент4 страницыIfSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- International FinanceДокумент2 страницыInternational FinanceSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- IfДокумент4 страницыIfSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Financial Institutes and MarketsДокумент7 страницFinancial Institutes and MarketsSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Financial Ratios Analysis for March 2013 and March 2012Документ13 страницFinancial Ratios Analysis for March 2013 and March 2012Sagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Managing India's Current Account DeficitДокумент3 страницыManaging India's Current Account DeficitSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- ABCДокумент6 страницABCSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Business Plan (Details)Документ24 страницыBusiness Plan (Details)Sagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- IntroductionДокумент17 страницIntroductionSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Automatic Speech RecognitionДокумент34 страницыAutomatic Speech RecognitionRishabh PurwarОценок пока нет
- AbstractДокумент1 страницаAbstractSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Technical Seminar on Ad-Hoc NetworksДокумент20 страницTechnical Seminar on Ad-Hoc NetworksSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Smart CardДокумент1 страницаSmart CardSagnik BiswasОценок пока нет
- Market Research Brief Pet Shops (Cartimar)Документ2 страницыMarket Research Brief Pet Shops (Cartimar)Perry YapОценок пока нет
- The Impact of Participatory Management On Employees' PerformanceДокумент15 страницThe Impact of Participatory Management On Employees' PerformanceKAYODE OLADIPUPOОценок пока нет
- In School, Family, & Community Connections: Emerging IssuesДокумент76 страницIn School, Family, & Community Connections: Emerging Issuesirinad_7Оценок пока нет
- Extensional Flow Properties of Polymers Using Stretching Flow MethodsДокумент78 страницExtensional Flow Properties of Polymers Using Stretching Flow MethodsRobin ChenОценок пока нет
- Module 1 - Introduction To Managerial EconomicsДокумент18 страницModule 1 - Introduction To Managerial EconomicsAmeen MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Business Statistics CourseplanДокумент3 страницыBusiness Statistics CourseplanRottenHelloОценок пока нет
- Wind Power Operating Cost in UsДокумент28 страницWind Power Operating Cost in UsByambaa BattulgaОценок пока нет
- ARI Varmam Therapy Mail Today Article 25jan 2011Документ1 страницаARI Varmam Therapy Mail Today Article 25jan 2011Arts Research InstituteОценок пока нет
- Stress Analysis of Steam Generator Shell Nozzle Junction For Sodium Cooled Fast Breeder ReactorДокумент9 страницStress Analysis of Steam Generator Shell Nozzle Junction For Sodium Cooled Fast Breeder ReactorVinh Do Thanh100% (1)
- Brand Positioning StrategiesДокумент5 страницBrand Positioning StrategiesRajОценок пока нет
- Gender Race and Class in Media A Critical Reader 5th Edition Dines Test BankДокумент8 страницGender Race and Class in Media A Critical Reader 5th Edition Dines Test Bankkathleenbaileytcgsrikobx100% (24)
- Architect's Role in Rural Community DevelopmentДокумент32 страницыArchitect's Role in Rural Community DevelopmentedrizhОценок пока нет
- A Case Study of Amul CoДокумент1 страницаA Case Study of Amul CoNeysa ElizabethОценок пока нет
- Direction of Industry A Literature Review On Industry 40Документ10 страницDirection of Industry A Literature Review On Industry 40Marko BrkicОценок пока нет
- I. Local Hero Project RESEACHERS: Melchor G. Dullao, Carites B. SangmayaoДокумент3 страницыI. Local Hero Project RESEACHERS: Melchor G. Dullao, Carites B. SangmayaomelchieОценок пока нет
- Appreciative Learning Program ProposalДокумент28 страницAppreciative Learning Program ProposalMuhammad Arif ButtОценок пока нет
- Technical Writing AssignmentДокумент3 страницыTechnical Writing AssignmentJamshidОценок пока нет
- Modern SCADA for Power GridsДокумент14 страницModern SCADA for Power GridsVasluianuОценок пока нет
- NColge - 1372 - Industrial and Organisational PsychologyДокумент242 страницыNColge - 1372 - Industrial and Organisational PsychologyPrince SinghОценок пока нет
- RANSTUDYДокумент9 страницRANSTUDYClaire TacanОценок пока нет
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: SOCIOLOGY 9699/12Документ4 страницыCambridge International AS & A Level: SOCIOLOGY 9699/12Noor Ul ainОценок пока нет
- Process Capability Analysis ExplainedДокумент60 страницProcess Capability Analysis ExplainedSrikar RenikindhiОценок пока нет