Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
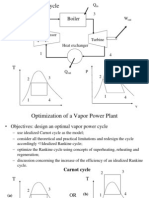
Vapour Power Cycle
Загружено:
lakshmikanth97Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Vapour Power Cycle
Загружено:
lakshmikanth97Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Vapor Power Systems
Power plants work on a cycle that produces net work
from a fossil fuel (natural gas, oil, coal) nuclear, or solar
input.
For Vapor power plants the working fluid, typically
water, is alternately vaporized and condensed.
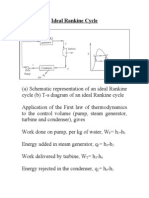
Consider the following Simple Vapor Power Plant
Consider subsystem A, each unit of mass periodically
undergoes a thermodynamic cycle as the working fluid
circulates through the four interconnected components
155
For the purpose of analyzing the performance of the
system, the following cycle describes the basic system
Consider each process separately applying conservation
of energy
For steady-state, neglecting KE and PE effects,
conservation of energy applied to a CV yields
) ( ) ( 2 / 1 ) (
1
2 2
out in out in out in
CV CV
z z g V V h h
m
W
m
Q
dt
dE
m
+ + + =
&
&
&
&
&
) ( 0
out in
CV CV
h h
m
W
m
Q
+ =
&
&
&
&
156
12 Turbine (adiabatic expansion)
) ( 0
2 1
h h
m
W
m
Q
out
+ =
&
&
&
&
) (
2 1
h h
m
W
w
out
out
= =
&
&
23 Condenser (no work)
) ( 0
3 2
h h
m
W
m
Q
out
+
=
&
&
&
&
1
) (+
out
W
&
2
) (
out
Q
&
2
) (
3 2
h h
m
Q
q
out
out
= =
&
&
3
157
34 Pump (Adiabatic)
) ( 0
4 3
h h
m
W
m
Q
in
+
=
&
&
&
&
3
4
) (
in
W
&
) (
3 4
h h
m
W
w
in
in
= =
&
&
41 Steam Generator (no work)
) (+
in
Q
&
1
) ( 0
1 4
h h
m
W
m
Q
in
+ =
&
&
&
&
) (
4 1
h h
m
Q
q
in
in
= =
&
&
4
Rankine Cycle Thermal Efficiency
( ) ( )
in
in out
in
in out
q
w w
m Q
m W m W
=
= =
&
&
&
&
&
&
/
/ /
input heat
out net work
4 1
3 4 2 1
) ( ) (
h h
h h h h
Rankine
=
158
Back Work Ratio (bwr)
2 1
3 4
/
/
(turbine) output work
(pump) input work
h h
h h
bwr
w
w
m W
m W
bwr
out
in
out
in
=
= = =
&
&
&
&
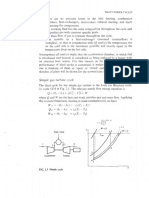
Ideal Rankine Cycle - no irreversibilities present in any
of the processes: no fluid friction so no pressure drop, and
no heat loss to surroundings
1. Steam generation occurs at constant pressure 41
2. Isentropic expansion in the turbine 12
3. Condensation occurs at constant pressure 23
4. Isentropic compression in the pump 34
P
boiler
With superheating
P
condenser
159
Note: For an ideal cycle no irreversibilities present so the
pump work can be evaluated by
4
3 int
vdP
m
W
rev
p
&
&
if the working fluid entering the pump at state 3 is pure
liquid, then
( )
= =
=
4
3
3 4 3
int
P P v vdP
m
W
w
rev
p
in
&
&
The negative sign has been dropped to be consistent with
previous use of w
in
160
Factors Affecting Cycle Efficiency
in
out
in
out in
in
in out
q
q
q
q q
q
w w
=
= 1
Recall: for a reversible heat addition process
= Tds q
Consider q
in
at the boiler and q
out
at the condenser
area shaded
1
4
1 4
=
= =
Tds q q
in T
in
q
in
1
4
T
s
Define mean temperature for process 4 1
4 1
1
4
s s
Tds
T
in
=
( )
4 1
1
4
1
4
s s T ds T Tds q
in in in
= = =
161
( )
area shaded
3 2
3
2
3 2
=
=
= =
s s T
Tds q q
out
out
3 2
q
out
T
T
out
s
Noting , the Ideal Rankine cycle thermal
efficiency is
4 1 3 2
s s s s =
in
out
in
out
in
out
Rankine
Ideal
T
T
s s T
s s T
q
q
=
= = 1
) (
) (
1 1
4 1
3 2
Note: this is identical to the Carnot Engine efficiency
which is also a reversible cycle
The back work ratio is
( )
( )
s out
in
Rankine
Ideal
h h
P P v
w
w
bwr
2 1
3 4 3
= =
162
Increase Rankine Cycle Efficiency
in
out
Rankine
Ideal
T
T
=1
Cycle efficiency can be improved by either:
- increasing the average temperature during heat
addition (
in
T )
- decreasing the condenser temperature (T
out
)
Increase the amount of superheat (41)
1
2
Amount of superheating is limited by metallurgical
considerations of the turbine (T
1
< 670C)
Added benefit is that the quality of the steam at the
turbine exit is higher
163
Increase boiler pressure (4 1)
Disadvantages:
- Requires more robust equipment
- Vapor quality at 2 lower than at 2
164
Decrease Condenser Pressure (2 3)
T
out
is limited to the temperature of the cooling medium
(e.g., lake at 15C need 10C temperature difference for
heat transfer so T
out
>25C)
Disadvantages:
- Note: for water P
sat
(25C)= 3.2 kPa lower than
atmospheric, possible air leakage into lines
- Vapor quality lower at lower pressure not good for
turbine
165
The most common method to increase the cycle thermal
efficiency is to use a two-stage turbine and reheat the
steam in the boiler after the first stage
( )
( )
3 2 1 6
6 5 4 3 2 1
input heat
out net work
+
+
=
= =
q q
w w w
q
w w
in
in out
( ) ( )
2 3 6 1
5 6 4 3 2 1
/
) ( ) ( ) (
h h h h
h h h h h h
reheat w
Rankine
+
+
=
166
Вам также может понравиться
- Ideal Rankine CycleДокумент27 страницIdeal Rankine Cycleslv_prasaadОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic CyclesДокумент32 страницыThermodynamic CyclessunitbhaumikОценок пока нет
- Deal With Systems That Produce Power in Which The Working Fluid Remains A Gas Throughout The Cycle, I.e., No Change in PhaseДокумент22 страницыDeal With Systems That Produce Power in Which The Working Fluid Remains A Gas Throughout The Cycle, I.e., No Change in PhasePushpa Mohan RajОценок пока нет
- AERO ENGINE ch2-1Документ40 страницAERO ENGINE ch2-1Dennis Padec BwochengoОценок пока нет
- KD PDFДокумент46 страницKD PDFAnonymous XynN1g6GDОценок пока нет
- Diesel CycleДокумент20 страницDiesel CycleShafiq ShapianОценок пока нет
- Internal Combustion Engines: LecturДокумент32 страницыInternal Combustion Engines: LecturPuneet GargОценок пока нет
- Motor Bakar Minggu-11Документ45 страницMotor Bakar Minggu-11setoОценок пока нет
- Vapour Cycles GoodДокумент19 страницVapour Cycles GoodParameswararao Billa100% (1)
- Chapter RankineДокумент32 страницыChapter RankineZack ZukhairiОценок пока нет
- Unit - 2 Vapour Power Cycle - Theory - NotesДокумент14 страницUnit - 2 Vapour Power Cycle - Theory - Notes1DS19ME136-Shivam KumarОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 Air CyclesДокумент32 страницыLecture 3 Air CyclesMemo KhalidОценок пока нет
- A Vapor Power Cycle: BoilerДокумент14 страницA Vapor Power Cycle: BoilerRohan RustagiОценок пока нет
- Gas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyДокумент68 страницGas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyManjunatha TnОценок пока нет
- Analisa Siklus OttoДокумент9 страницAnalisa Siklus OttochandraОценок пока нет
- Internal Combustion EngineДокумент5 страницInternal Combustion EnginenidhidarklordОценок пока нет
- Gas - Turbine - CycleДокумент41 страницаGas - Turbine - CycleKalpaniОценок пока нет
- Stirling Heat Engine - Internal Combustion Engine (Otto Cycle) - Diesel Engine - Steam Engine (Rankine Cycle) - Kitchen RefrigeratorДокумент11 страницStirling Heat Engine - Internal Combustion Engine (Otto Cycle) - Diesel Engine - Steam Engine (Rankine Cycle) - Kitchen RefrigeratormarzinusОценок пока нет
- Principle of TurbomachineryДокумент159 страницPrinciple of TurbomachinerySharath ChandraОценок пока нет
- Otto Diesel Dual Ideal Cycle - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Документ16 страницOtto Diesel Dual Ideal Cycle - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Danang Wahdiat Aulia Ishaq0% (1)
- Vapour Power SystemДокумент12 страницVapour Power SystemluriahОценок пока нет
- S (Hot Reservoir) - Q S (Cold Reservoir) + - Q: - / T - / T S (Engine) 0 (Cyclic Process)Документ51 страницаS (Hot Reservoir) - Q S (Cold Reservoir) + - Q: - / T - / T S (Engine) 0 (Cyclic Process)കൂട്ടുകാരിയെ സ്നേഹിച്ച കൂട്ടുകാരൻОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Gas Power CyclesДокумент48 страницIntroduction To Gas Power CyclesN S SenanayakeОценок пока нет
- Diesel CycleДокумент7 страницDiesel CycleJayaprakash S MechОценок пока нет
- Web6 Combuction SystemДокумент11 страницWeb6 Combuction SystemeswarbobbyОценок пока нет
- Cycle EfficiencyДокумент17 страницCycle Efficiencyrashm006ranjanОценок пока нет
- Stirling EngineДокумент11 страницStirling EngineMario MikulandraОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics of Internal Combustion EngineДокумент66 страницThermodynamics of Internal Combustion EnginealagurmОценок пока нет
- A True Concept of Blue Printing .: Study & Analysis of Carnot's Model For Ideal MachineДокумент19 страницA True Concept of Blue Printing .: Study & Analysis of Carnot's Model For Ideal Machine012345543210Оценок пока нет
- Gas Power Cycle - Part 1Документ46 страницGas Power Cycle - Part 1Shahran IezzatОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics II - Lecture 03 - 27 SepДокумент25 страницMechanical Engineering Thermodynamics II - Lecture 03 - 27 SepThineshraaj Naidu Jaya RamanОценок пока нет
- Brayton CycleДокумент15 страницBrayton CycleMarion Villamor100% (1)
- MUCLecture 2022 123134814Документ17 страницMUCLecture 2022 123134814Raja ArifОценок пока нет
- DS1 2023 Vapour Power Cycle Part 1Документ27 страницDS1 2023 Vapour Power Cycle Part 1Tommba TommyОценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент26 страницThermodynamicsManikanta Reddy100% (1)
- Gas Power CyclesДокумент76 страницGas Power CyclesJuan JoseОценок пока нет
- Air Standard CyclesДокумент28 страницAir Standard CyclesAditya Krishnakumar100% (1)
- 4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics: Unit I. Earth, Air, Fire, and WaterДокумент11 страниц4200:225 Equilibrium Thermodynamics: Unit I. Earth, Air, Fire, and WaterRiky IkhwanОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Internal Combustion EnginesДокумент26 страницThermodynamic Analysis of Internal Combustion EnginesKatu2010Оценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic CyclesДокумент30 страницThermodynamic CyclesRudra PratapОценок пока нет
- Gas Cycles Otto, Diesel, Dual CyclesДокумент43 страницыGas Cycles Otto, Diesel, Dual Cyclesprasad5034100% (1)
- Gas Power Cycles: Final State Gaseous State All ThroughtДокумент26 страницGas Power Cycles: Final State Gaseous State All Throughtboj VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- CH 13Документ32 страницыCH 13hirenpatel_universalОценок пока нет
- Jet Aircraft Propulsion Example QuestionДокумент19 страницJet Aircraft Propulsion Example Questionlittlemerf2100% (1)
- Gas Power Cycles: Cengel & BolesДокумент18 страницGas Power Cycles: Cengel & BoleskishoremarОценок пока нет
- Brayton CycleДокумент5 страницBrayton CycleAnonymous yorzHjDBd100% (1)
- Outline: Unit Eleven - Cycle AnalysisДокумент5 страницOutline: Unit Eleven - Cycle AnalysisbarelihbОценок пока нет
- Brayton Cycle PDFДокумент22 страницыBrayton Cycle PDFBiswajeet MaharanaОценок пока нет
- Power PlantДокумент63 страницыPower PlantSatheesh Sekar100% (4)
- Chapter 9,10,11Документ50 страницChapter 9,10,11myra091100% (1)
- Vapor Power CyclesДокумент48 страницVapor Power CyclesJames WankerОценок пока нет
- Lec 15 16 - CH 9 BRAYTON TurbineДокумент17 страницLec 15 16 - CH 9 BRAYTON Turbinesamhameed2100% (1)
- Gas Turbine Theory by Hih Saravanamuttoo, H. Cohen & GFC RogersДокумент11 страницGas Turbine Theory by Hih Saravanamuttoo, H. Cohen & GFC RogersduccОценок пока нет
- Advanced Thermodynamics Production of Power From HeatДокумент27 страницAdvanced Thermodynamics Production of Power From HeatPappuRamaSubramaniam100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Engine Cycles 2Документ18 страницChapter 3 - Engine Cycles 2Zaidan AlsallalОценок пока нет
- Mel712 29Документ28 страницMel712 29Sharath ChandraОценок пока нет
- PpeДокумент7 страницPpeChristopher YsitОценок пока нет
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGОт EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGОценок пока нет
- 37 - Weldability and Performance of AHSSДокумент27 страниц37 - Weldability and Performance of AHSSsivaОценок пока нет
- Phystcs B (Advancing Physics) U Nderstanding Processes: Friday AfternoonДокумент21 страницаPhystcs B (Advancing Physics) U Nderstanding Processes: Friday AfternoonKelen KawasakiОценок пока нет
- Chandan Matty Theory CompleteДокумент199 страницChandan Matty Theory Completemir zainОценок пока нет
- 121Документ39 страниц121Hendra RuhunussaОценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower Side Stream FiltrationДокумент5 страницCooling Tower Side Stream FiltrationChandrakant JuikarОценок пока нет
- Cremophor A GradesДокумент8 страницCremophor A GradesMd.ali-bin-saifullah100% (4)
- Chemistry Sba LabДокумент5 страницChemistry Sba LabTawayna HemmingsОценок пока нет
- Permian Rod Operations - Sucker Rod Identification Chart PDFДокумент1 страницаPermian Rod Operations - Sucker Rod Identification Chart PDFMinimaxou78Оценок пока нет
- D. Types of Tests On SandДокумент9 страницD. Types of Tests On SandSandeepОценок пока нет
- Is Alcohol in Skincare Products Bad For Your Skin in The Long TermДокумент6 страницIs Alcohol in Skincare Products Bad For Your Skin in The Long TermgaladrielinОценок пока нет
- h2 Physics DefinitionsДокумент7 страницh2 Physics DefinitionsJerald LimОценок пока нет
- Separation TechniquesДокумент4 страницыSeparation TechniquesNicola Faye BronОценок пока нет
- Uni of Frankfurt - Thermodynamic PotentialsДокумент15 страницUni of Frankfurt - Thermodynamic PotentialstaboogaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 PDFДокумент81 страницаChapter 5 PDFKarthik Teja MummareddiОценок пока нет
- Out 3Документ24 страницыOut 3aminbm.pt24Оценок пока нет
- DJ 10 CM Plate: MJ MJДокумент9 страницDJ 10 CM Plate: MJ MJredspidey13100% (2)
- ABS Polar Ice Class Ship Structure DesignДокумент48 страницABS Polar Ice Class Ship Structure Designronny-suОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Schemes Form 1Документ4 страницыChemistry Schemes Form 1NZURE NJOKAОценок пока нет
- C. Graciano A. Ayestarán - Steel Plate Girder Webs Under Combined Patch Loading, Bending and SheДокумент11 страницC. Graciano A. Ayestarán - Steel Plate Girder Webs Under Combined Patch Loading, Bending and SheAsdrubal AyestaránОценок пока нет
- Isolation and Alkaline Hydrolysis of The Protein GlutenДокумент5 страницIsolation and Alkaline Hydrolysis of The Protein GlutenTiffany EspirituОценок пока нет
- Physics Form 5Документ4 страницыPhysics Form 5Kaiwen ChinОценок пока нет
- Cu (II) Complex v3 011809Документ7 страницCu (II) Complex v3 011809shahera rosdiОценок пока нет
- Roof Bolting AKMДокумент81 страницаRoof Bolting AKMNutan PrakashОценок пока нет
- Ece PDFДокумент36 страницEce PDFGnaneshwar KandukuriОценок пока нет
- Non-Ideal Reactors: Deviations From Ideal Reactor BehaviorДокумент8 страницNon-Ideal Reactors: Deviations From Ideal Reactor BehaviorrawadОценок пока нет
- Alchemy at The Crowning of NatureДокумент30 страницAlchemy at The Crowning of NatureMano DasruthiОценок пока нет
- أجهزة قياس درجة الحرارة المستخدمة في دوائر التحكم الأوتوماتيكي PDFДокумент10 страницأجهزة قياس درجة الحرارة المستخدمة في دوائر التحكم الأوتوماتيكي PDFعيسى محمد حسنОценок пока нет
- Physics Folio... Simple2 Yg MungkinДокумент15 страницPhysics Folio... Simple2 Yg MungkinMuhammad HaikalОценок пока нет