Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Mid Year Physics f4 p2
Загружено:
MadAm JaJaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Mid Year Physics f4 p2
Загружено:
MadAm JaJaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PEPERIKSAAN PERTENGAHAN TAHUN TINGKATAN 4 2014
FIZIK
KERTAS 2
Dua jam tiga puluh minit
(Anda dinasihatkan untuk memperuntukkan masa 90 minit untuk Bahagian A,
30 minit untuk Bahagian B dan 30 minit untuk Bahagian C)
JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI SEHINGGA DIBERITAHU.
Prepared by,
..
PN NOR JAMALIAH
Checked by,
..
MR. TOH HONG MEO
Untuk Kegunaan Pemeriksa
Bahagian Soalan Markah
Penuh
Markah
A
1 4
2 5
3 6
4 7
5 8
6 8
7 10
8 12
Jumlah Bahagian A 60
B
B
9 20
10 20
C
C
11 20
12 20
Jumlah Besar
1. Kertas soalan ini mengandungi tiga bahagian : Bahagian A,
Bahagian B dan Bahagian C
2. Jawab semua soalan dalam Bahagian A, satu soalan
daripada Bahagian B dan satu soalan daripada Bahagian C.
3. Jawapan kepada ketiga-tiga bahagian ini hendaklah
diserahkan bersama-sama.
4. Jawapan kepada Bahagian A hendaklah ditulis dalam ruang
yang disediakan dalam kertas soalan.
Nama : ........................ Tingkatan :
4531/2
Fizik
Kertas 2
MEI
2014
2 Jam
SULIT
SECTION A/BAHAGIAN A
Answer all questions in answer provided. Jawab semua soalan di ruangan yang disediakan
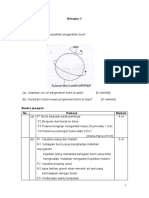
1 The figures below show a vernier caliper used to measure the diameter of a metal ball.
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan angkup vernier yang digunakan untuk mengukur diameter
sebiji bola logam.
Figure 1.1 shows the position of the vernier scale when the jaws are closed.
Rajah 1.1 menunjukkan keadaan skala vernier apabila jaws ditutup
Figure 1.2 shows the position of the vernier scale when a metal ball is put between the
jaws of the vernier calipers.
Rajah 1.2 menunjukkan keadaan skala vernier apabila bola logam diletakkan diantara
jaws angkup vernier.
a) What is the zero error of the vernier calipers?
Nyatakan ralat sifar bagi angkup vernier?
[ 1 mark]
b) What is the reading of the vernier calipers as shown in Figure 1.2?
Nyatakan bacaan angkup vernier seperti rajah 1.2
[ 1 mark]
c) Calculate the diameter of the metal ball.
Hitung diameter bola logam
[ 1 mark]
d) If the device used is replaced by a micrometer screw gauge, which device is more
sensitive?
Jika alat yang digunakan digantikan dengan tolok skru micrometer, alat
pengukuran yang manakah lebih sensitive?
[ 1 mark]
2 Rajah 2.1(a) menunjukkan sebuah lori pengangkut. Rajah 2.1(b) menunjukkan lori
pengangkut yang sama membawa kontena barangan
Diagram 2.1(a) shows an empty pickup truck. Diagram 2.1(b) shows the same pickup
truck carrying a crate.
(a) Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan inertia?
What is meant by inertia?
..
..
[1 mark] / [1 markah]
(b) Bandingkan jisim lori pengangkut dalam rajah 2.1(a) dengan jisim lori pengangkut
beserta kontena barangan dalam rajah 2.1(b).
Compare the mass of the pickup truck in diagram 2.1(a) with the total mass of the
pickup truck and crate in diagram 2.1(b).
.
[1 mark] / [1 markah]
(c) Bandingkan inertia lori pengangkut dalam rajah 2.1(a) dengan inertia lori pengangkut
dan kontena barangan dalam rajah 2.1(b)
Compare the inertia of pickup truck in diagram 2.1(a) with inertia of pickup truck and
crate in diagram 2.1(b)
.
.
[1 mark] / [1 markah]
(d) Apabila lori pengangkut dalam rajah 2.1(b) bergerak kehadapan tibatiba, kontena
barangan akan bergerak ke belakang. Terangkan mengapa
When pickup truck in diagram 2.1(b) suddenly moves forwards, the crate will move
backwards. Explain why.
[1 mark] / [ 1 markah]
(e) Nyatakan satu contoh kesan inertia yang positif
Give one example of positive effect of inertia.
[1 mark] / [1 markah]
3 Diagram 3 shows a section of ticker tape obtained from the motion of a battery-driven toy
car using a ticker-timer of frequency 50 Hz.
Rajah 3 menunjukkan satu keratan pita detik yang diperolehi daripada pergerakan
sebuah kereta mainan yang digerakkankan oleh tenaga bateri menggunakan jangka masa
detik berfrekuensi 50 Hz.
Diagram 3
a) What is the time, in second, represented by each tick?
Berapakah masa, dalam saat, yang diwakili oleh setiap detik?
...................................................................................................
[1 mark]
b) How would you describe the motion of the toy car?
Bagaimanakah anda boleh terangkan mengenai pergerakan kereta mainan
tersebut
.....................................................................................................
[1 mark]
c) Based on Diagram 3, calculate the average velocity of the toy car at the instances
when the displacements are as labeled.
Berdasarkan Rajah 3, kirakan halaju purata kereta mainan tersebut pada sesaran
seperti dilabelkan
(i) 0.8 cm
[1 mark]
(ii) 2.0 cm
[1 mark]
d) Based on the answers in 3(c)(i) and 3(c)(ii), calculate the acceleration of the toy
car.
Berdasarkan jawapan pada 3(c)(i) dan 3(c)(ii), kirakan pecutan kereta mainan
tersebut
[2 marks]
4 Diagram 4.1 shows a car moving from P to R. The thrust of the cars engine is constant
throughout PQR. [Ignore the frictional force]
Rajah 4.1 menunjukkan sebuah kereta bergerak daripada P ke R. Tujahan enjin kereta
adalahtetap di sepanjang PQR. ( Abaikan daya geseran )
Diagram 4.2 shows a graph of velocity against time for the motion of the car.
Rajah 4.2 menunjukkan graf halaju melawan masa bagi pergerakan kereta tersebut.
( a ) What is meant by velocity?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan halaju?
.
[1 mark]
( b ) Using diagram 4.2,
Menggunakan Rajah 4.2 ,
( i ) State the physical quantity represented by the area under the graph.
Nyatakan kuantiti fizik yang diwakili oleh luas di bawah graf.
...........
[1 mark]
( ii ) describe the motion of the car from p to q.
huraikan gerakan kereta itu dari P ke Q.
.
[1mark]
( iii ) What is the distance from P to Q ?
Berapakah jarak dari P ke Q ?
...................................................................................................................
[1mark]
( iv ) calculate the deceleration of the car from Q to R
hitungkan nyahpecutan kereta dari Q ke R.
[2marks]
( c ) Explain why the car decelerates while moving up the slope even though it is acted
upon by a constant thrust.
Terangkan mengapa kereta mengalami nyahpecutan semasa menaiki cerun
walaupun tujahan enjin kerata yang bertindak adalah tetap.
.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
[1marks]
5
Diagram 5/Rajah 5
( a ) Diagram 5 shows a rocket moves upward with an acceleration.
Rajah 5 menunjukkan sebuah roket bergerak ke atas dengan pecutan.
( i ) Mark and label the forces acting on the rocket.
Tanda dan labelkan daya-daya yang bertindak ke atas roket tersebut.
[2 marks]
( ii ) State the relationship between the forces in ( a )( i ). Give a reason for your
answer.
Nyatakan hubungan antara daya-daya di ( a )( i ). Beri sebab bagi jawapan
anda.
. .
..............................................................................................................................
[2 marks]
( b ) A rocket moves with upward force of 10 000 N. The mass of the rocket is 800
kg.(gravitational acceleration ,g = 10 N kg
-1
)
Sebuah roket bergerak dengan daya tujah ke atas 10 000 N. Jisim roket tersebut
adalah 800 kg. ( pecutan graviti, g = 10 N kg
-1
)
( i ) What is the net upward force acting on the rocket ?
Berapakah daya tujah bersih ke atas yang bertindak pada roket itu ?
[2 marks]
( ii ) Calculate the acceleration of the rocket.
Hitungkan pecutan roket itu.
[2 marks]
6 Rajah 6.1 menunjukkan seorang budak , berjisim 40 kg berlari kea rah 2 kg papan luncur dengan
halaju 20 ms
-1.
Budak itu kemudian melompat ke atas panapan luncur dan bergerak ke depan.
Diagram 6.1 shows a boy, whose mass is 40 kg is running towards a 2 kg skateboard with
a velocity of 20 ms
-1
. The boy then jumps onto the skateboard and moves forward.
Rajah 6.2 menunjukkan seekor katak berjisim 100g dalam keadaan pegun di atas 10 g daun yang
pegun. Katak itu melompat dari daun ke tebing sungai
Diagram 6.2 shows a frog with a mass of 100 g which is at rest on a 10 g stationary leaf.
The frog then jumps from the leaf to the river bank.
.
Diagram 6.1
Diagram 6.2
a) Perhatikan Rajah 6.1 dan Rajah 6.2 dan bandingkan jenis pergerakan budak itu selepas
melompat ke atas papan luncur dan katak selepas melompat ke tebing sungai Observe
Diagram 6.1 and Diagram 6.2 and compare the type of movement of the boy after
jumping onto the skateboard and the frog after jumping from the leaf to the river
bank.
[2 marks]
b) (i) Bandingkan jumlah momentum budak itu sebelum dan selepas dia melompat ke
papan luncur.
Compare the total momentum for the boy before and after he jumps onto the
skateboard.
[1mark]
(ii) Kira halaju budak itu selepas dia melompat ke atas papan luncur.
Calculate the velocity of the boy after he jumps onto the skateboard.
[2marks]
(iii)State the principle involved.
Nyatakan prinsip yang terlibat
[1mark]
c) Seorang budak perempuan berjisim 30 kg berlari dengan velocity 20 ms
-1
pada papan luncur
yang sama pada Rajah 6.1
A girl whose mass is 30 kg runs with the velocity of 20 ms
-1
to the identical skateboard
as shown in Diagram 6.1.
Kirakan momentum budak perempuan itu.
Calculate the momentum of the girl.
[2marks]
7 Rajah 7.1(a) menunjukkan Ali sedang menendang bola dan rajah 7.1(b) menunjukkan Ali
sedang menendang satu batu
Diagram 7.1(a) shows Ali kicking a football and diagram 7.1(b) shows Ali kicking a rock.
Rajah 7.1/Diagram 7.1
(a) Takrifkan daya impuls.
Define impulsive force.
.
[1 mark ]/[1 markah]
(b) Bola dalam rajah 7.1(a) berjisim 1.5 kg. Apabila Ali menendang bola itu, ia bergerak
dengan halaju 20ms-1 dari keadaan pegun dalam masa 0.2 s. Hitung daya impuls yang
dikenakan Ali ke atas bola itu.
The ball in diagram 7.1(a) has a mass of 1.5 kg. When Ali kicks the ball, it moves from
rest to 20 ms-1 in 0.2 s. Calculate the impulsive force that Ali exerted on the ball.
[2 marks] / [2 markah]
(c) Batu dalam rajah 7.1(b) mempunyai jisim yang sama dengan bola (1.5 kg). Apabila
Ali menendang batu itu, ia bergerak dengan halaju yang sama dengan bola (20ms
-1
) dari
keadaan pegun. Walaubagaimana pun, disebabkan kekerasan batu, masa kaki Ali
bersentuh dengan batu hanyalah 0.02 s. Hitung daya impuls yang dikenakan Ali ke atas
batu itu
The rock in diagram 7.1(b) has the same mass with the ball (1.5 kg). When Ali kicks the
rock, it moves from rest to the same velocity as the ball ( 20 ms-1 ). However,due to the
rigidity of the rock, the time which Alis foot is in contact with the rock is only 0.02 s.
Calculate the impulsive force that Ali exerted on the rock.
[2 marks] / [2 markah]
(d) Bandingkan masa perlanggaran dalam raja 7.1(a) dengan rajah 7.1(b).
Compare time of impact in diagram 7.1(a) with diagram 7.1(b).
...............................................................................................................
[1 mark]/[1 markah]
(e) Bandingkan daya impuls dalam rajah 7.1(a) dengan rajah 7.1(b).
Compare the impulsive force in diagram 7.1 (a) with diagram 7.1(b).
...............................................................................................................
[1 mark]/[1 markah]
(f) Bandingkan kesakitan yang dialami Ali dalam rajah 7.1(a) dengan rajah 7.1(b).
Compare the pain experience by Ali in diagram 7.1(a) with diagram 7.1(b).
.................................................................................................................
[1 mark]/[ 1 markah ]
(g) Berdasarkan jawapan anda dalam (d), (e) dan (f), nyatakan hubungan antara masa
perlanggaran, daya impuls dan kesakitan yang dialami Ali.
Based on your answers in (d), (e) and (f), state the relationship between time of
impact, impulsive force and pain experienced by Ali.
........................................................
[1 mark] / [ 1 markah]
(h) Cadangkan satu cara bagaimana Ali dapat mengurangkan kesakitannya dalam rajah
7.1(b)
Suggest one way how Ali could reduce his pain in diagram 7.1(b).
[1 mark]/[ 1 markah]
8 Jadual 8.1 menunjukkan tiga jenis kereta mainan kawalan jauh dan ciri-cirinya.
Table 8.1 shows three types of remote control toy car and their characteristics
(a) (i) Berdasarkan jadual 8.1, kereta mainan yang manakah mempunyai pecutan yang
paling tinggi?
Based on Table 8.1, which car toy will accelerate more?
...............................................................................................................................
[1 markah]
(ii) Berikan satu sebab kepada jawapan di 8(a) dan nyatakan hubungan di antara sebab
dan konsep fizik yang terlibat.
Give the reason for your answer in 8(a) and state the relationship between the
reason and physics concept involved
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
[2 markah]
(b) Rajah 8.2 menunjukkan seorang pelajar sedang menolak kotak 5.0kg dengan daya-
daya yang berbeza di atas permukaan kasar tiga jenis satah kayu, P, Q, R.
Diagram 8.2 shows a student is pushing a 5.0 kg box with difference forces on three
types of rough surface on wooden plan P, Q, R.
Jadual 8.2 menunjukkan magnitude pecutan a, dan daya F yang digunakan untuk
menolak kotak tersebut di atas setiap permukaan kayu.
Table 8.2 shows the magnitude of acceleration a, and force applied F, to push the box
on each surface of wooden plane.
Jadual 8.2/Table 8.2
i) Apakah maksud daya geseran?
What is the meaning of frictional force?
..............................................................................................................................
[1 markah]
(c) Hitung daya geseran untuk setiap permukaan satah kayu
Calculate the frictional force of each surface on wooden plane
(i) Satah Kayu P
Wooden plane P
[2 markah]
(ii) Satah kayu Q
Wooden plane Q
[1 markah]
(iii) Satah kayu R
Wooden plane R
[1 markah]
(d) Tentukan satah permukaan yang paling sesuai untuk membina gelongsong di
taman permainan. Berikan satu sebab.
Determine the most suitable surface of wooden plan to build a slide at childrens
playground. Give a reason.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
[2 markah]
(e) Nyatakan dua pengubahsuaian yang boleh dilakukan untuk mengurangkan geseran
Name two modification should be added to reduce the friction
..
..
[2 marks]
SECTION B/BAHAGIAN B
[ 20 marks]
Answer any one question from this section/Jawab mana-mana satu soalan dari bahagian ini.
9 Figure 9 (a) shows the reading of an ammeter before any current is connected to it.
Rajah 9(a) menunjukkan bacaan ammeter sebelum disambungkan dengan arus.
Diagram 9(a)/Rajah 9(a)
a) Explain the meaning of systematic errors. Give two examples of systematic
errors.
Terangkan maksud ralat sistematik. Berikan dua contoh ralat sistematik
[5 marks]
b) A student used the above ammeter to measure current in electrical circuit. Figure
9(b) shows the reading of the current from his experiment
Seorang pelajar menggunakan ammeter di atas untuk mengukur arus dalam litar
elektrik. Rajah 9(b) menunjukkan bacaan arus daripada eksperimennya.
Diagram 9(b)/Rajah 9(b)
i) There is a mirror near ammeter scale. Explain the function of the mirror.
Terdapat cermin berhampiran skala ammeter. Terangkan fungsi cermin tersebut.
[4 marks]
ii) Using Figure 9(a) and Figure 9(b), shows the steps to get the actual reading of the
current.
Menggunakan Rajah 9(a) dan Rajah 9(b), tunjukkan langkah-langkah untuk
mendapatkan bacaan sebenar arus tersebut.
[4 marks]
c) Suggest ways to improve the accuracy of measurement in any instruments used
in the laboratory.
Cadangkan cara-cara untuk meningkatkan kejituan dalam pengukuran peralatan
di dalam makmal.
[4 marks]
d) Explain the meaning of the following
Terangkan maksud dibawah:
i) Consistency
Kepersisan
ii) Accuracy
Kejituan
[3 marks]
10 a) Two importance aspects are involved in the description of a physical quantity.
What are these two aspects?
Dua aspek penting yang terlibat dalam menerangkan kuantiti fizik. Nyatakan
aspek tersebut?
[2 marks]
b) i) What is the difference between base quantities and derived quantities?
Nyatakan perbezaan antara kuantiti asas dan kuantiti terbitan?
[2 marks]
ii)Name the five base quantities and state their SI units
Namakan lima kuantiti asas dan SI unit
[5 marks]
iii) State the unit of force in terms of base SI unit.
Nyatakan unit bagi daya dalam asas SI unit
[1 mark]
c) List in correct order the steps involved in the process of scientific investigation.
Senaraikan mengikut susunan yang betul langkah-langkah dalam penyiasatan
proses sains.
[10 marks]
SECTION C/BAHAGIAN C
[ 20 marks]
Answer any one question from this section.
11 Diagram 11 (a) shows two identical eggs being released from the same height onto two
different surfaces
Rajah 11(a) menunjukkan dua biji telur yang sama dilepaskan pada ketinggian yang
sama ke atas dua permukaan yang berbeza.
Diagram 11 (b) shows the conditions of the egg after they hit the concrete floor and the
sponge. It is observed that the egg stops faster when it hits the concrete floor.
Rajah 11(b) menunjukkan keadaan telur selepas perlanggaran dengan lantai konkrit
dan span. Berdasarkan pemerhatian, telur berhenti dengan cepat apabila berlanggar
dengan lantai konkrit.
a) i) What is meant by impulse?
Apakah maksud impuls?
[1 mark]
ii) Based on Diagram 11(a) and 11(b), compare the condition of the eggs, the surface of
the concrete floor and the surface of the sponge and when the eggs hits the surfaces.
Relate the change in the conditions of the eggs and the surfaces to deduce a relevant
physics concept.
Berdasarkan Rajah 11(a) dan 11(b), bandingkan keadaan telur, permukaan lantai
konkrit dan permukaan span dan apabila telur tersebut berlanggar dengan
permukaan. Hubungkaitkan perubahan keadaan telur dan permukaan untuk membuat
satu kesimpulan tentang satu konsep fizik
[5 marks]
b) Explain the change in energy that occurs from the point where the egg is released
until it reaches the position in Diagram 11 (b).
Terangkan perubahan tenaga yang berlaku dari titik telur dilepaskan sehingga
mencapai keadaan pada Rajah 11(b).
[4 marks]
c)
Diagram 11(c)
Diagram 11(c) shows four tankers, P, Q, R and S, with different specifications.
You are required to determine the most suitable tanker to deliver oil safetly.
Study the specifications of all the four tankers from the following aspects:
Rajah 11(c) menunjukkan empat lori tangki, P, Q, R, dan S, dengan spesifikasi yang
berbeza.
Anda dikehendaki menentukan lori tangki yang paling sesuai digunakan untuk
menghantar minyak dengan selamat.
Kaji spesifikasi keempat-empat lori itu dari aspek berikut:
- The type of brakes
Jenis brek
- The number of tyres
Bilangan tayar
- The number and size of the tanks
Bilangan dan saiz tangki
- The distance between the trailer and the tractor
Jarak antara treler dan kepala lori
Explain the suitability of the aspects.
Justify your choice.
Terangkan kesesuaian aspek-aspek itu.
Beri sebab bagi pilihan anda.
[ 10 marks / 10 markah]
12 a) The ticker-tape P, Q and R shown in the Diagram 12 (a) are produced by three trolleys
pulling the tapes through a ticker timer operating at 50 Hz.
Pita detik P, Q, R ditunjukkan dalam Rajah 12(a) diperoleh daripada tiga troli.
i) Describe the motion represented by each of the tape P, Q and R.
Terangkan pergerakan yang ditunjukkan pada setiap pita detik P, Q dan R.
[6 marks]
ii) Find the average velocity of the trolley that produces tape P.
Cari halaju purata troli bagi pita P
[2 marks]
iii) Find the average acceleration of the trolley that produces tape R.
Cari pecutan troli bagi pita Q
[3 marks]
b) A bullet of mass 20 g is fired from 2 kg riffle with a velocity of 20 ms-1 towards 3 kg
block of wood. The block of wood is suspended from the ceiling as shown in Diagram
12 (b)
i) Find the recoil velocity of the rifle.
Hitung halaju lentingan senapang itu
[3 marks]
ii) Find the maximum height reached by the block of wood after the bullet is
embedded in it.
Hitung ketinggian maksimum bagi blok kayu selepas peluru menembusinya
[3 marks]
iii) Name the principle used in obtaining the answer to (b)(ii)
Namakan prinsip yang digunakan di (b)(i)
[1 mark]
iv) What energy changes occur when the bullet hits the block of wood?
Apakah perubahan tenaga yang berlaku apabila peluru melanggar blok
kayu?
[2 marks]
Вам также может понравиться
- Soalan K2Документ9 страницSoalan K2Amirudin Md IsaОценок пока нет
- Fizik Tingkatan 4 Kertas 2 2018Документ23 страницыFizik Tingkatan 4 Kertas 2 2018MadAm JaJa100% (3)
- k2 FizikДокумент16 страницk2 FizikHatena ContennaОценок пока нет
- Fizik Kertas 2Документ24 страницыFizik Kertas 2abnu980% (1)
- Ulangkaji Tingkatan 2 Set 2Документ9 страницUlangkaji Tingkatan 2 Set 2Siti Aminah HubadillahОценок пока нет
- Percubaan Fizik 2 Kertas 2Документ29 страницPercubaan Fizik 2 Kertas 2tini277Оценок пока нет
- Modul 1 Master Math Tingkatan 3Документ4 страницыModul 1 Master Math Tingkatan 3zain93Оценок пока нет
- Modul Mudah Maths TG 3 - Bab 01Документ21 страницаModul Mudah Maths TG 3 - Bab 01NOR ANIZAN BINTI MAT HASAN MoeОценок пока нет
- Kertas Objektif SainsДокумент1 страницаKertas Objektif SainsMie MfmОценок пока нет
- Ujian Akhir Tahun Pendidikan Moral Tingkatan 1 KSSMДокумент6 страницUjian Akhir Tahun Pendidikan Moral Tingkatan 1 KSSMdayangОценок пока нет
- Kedah Trial Fizik Kertas 2 SPMДокумент22 страницыKedah Trial Fizik Kertas 2 SPMfarahibbОценок пока нет
- Fizik Kertas 2Документ15 страницFizik Kertas 2Roslina ZakariaОценок пока нет
- KSSM T2 MTДокумент9 страницKSSM T2 MTNiksuryati NikkubОценок пока нет
- Kimia SPM Kimia k2 Set 2Документ15 страницKimia SPM Kimia k2 Set 2api-3841296Оценок пока нет
- 3 Formula Dan Persamaan KimiaДокумент20 страниц3 Formula Dan Persamaan KimiawannwaОценок пока нет
- BRG ElaunДокумент3 страницыBRG ElaunIsmail Baihaqie MYОценок пока нет
- Hala Tuju Selepas Tingkatan 3 - Aliran SBPДокумент1 страницаHala Tuju Selepas Tingkatan 3 - Aliran SBPemramyunusОценок пока нет
- Skema Ujian Lisan Mendengar Set 1Документ1 страницаSkema Ujian Lisan Mendengar Set 1juliaОценок пока нет
- Soalan Ulangkaji Sains Tingkatan 2 Bab 5Документ3 страницыSoalan Ulangkaji Sains Tingkatan 2 Bab 5Shila AshilaОценок пока нет
- Science Quest 2019Документ29 страницScience Quest 2019PPD MELAKA TENGAH-CM8 Moe0% (1)
- Chemistry Paper 2 Trial Set8Документ18 страницChemistry Paper 2 Trial Set8marina_zaineeОценок пока нет
- Latih Tubi Sains Pt3Документ7 страницLatih Tubi Sains Pt3Anonymous fBxwaWRCОценок пока нет
- Pat Sains Ting 2 2019Документ24 страницыPat Sains Ting 2 2019Azlin ShahОценок пока нет
- Asas KelestarianДокумент7 страницAsas Kelestarianazwantalib87Оценок пока нет
- Tugasan Geografi Tingkatan 3 Minggu 23Документ2 страницыTugasan Geografi Tingkatan 3 Minggu 23Cik NescAfeОценок пока нет
- Soalan Sains T4 Bab 5 (BM)Документ9 страницSoalan Sains T4 Bab 5 (BM)Abdullah Yusof Azzam100% (2)
- BAB 9 Lukisan Berskala Form 3Документ6 страницBAB 9 Lukisan Berskala Form 3hazrizal_84Оценок пока нет
- Soalan GKT MPP3 2023Документ12 страницSoalan GKT MPP3 2023liyanaОценок пока нет
- Teks Mc-Pengawas (Tanpa Majlis)Документ7 страницTeks Mc-Pengawas (Tanpa Majlis)umiadeebОценок пока нет
- Excel in Geografi TG 2 - Nota ExcelДокумент18 страницExcel in Geografi TG 2 - Nota Excelnarrowone bpОценок пока нет
- Jawapan Modul PBD Geografi Tingkatan 1: Bab: 1 Arah TP 3&4 (M/s 5)Документ16 страницJawapan Modul PBD Geografi Tingkatan 1: Bab: 1 Arah TP 3&4 (M/s 5)Nur balqis123 BT MOHD SAFARОценок пока нет
- Kalkulator Maths SPM 2017Документ30 страницKalkulator Maths SPM 2017Azuin Hashim0% (1)
- GM Math Section CДокумент3 страницыGM Math Section CSITI NUR LYANA BINTI YAHYA MoeОценок пока нет
- Pat Matematik Tingkatan 1 2020Документ13 страницPat Matematik Tingkatan 1 2020Mohd Fadli Bakar KedahОценок пока нет
- Bio T4 (K2)Документ18 страницBio T4 (K2)Sharifah Izyan Al-QudryОценок пока нет
- Soalan Esei Bahagian C PT3 - 4Документ2 страницыSoalan Esei Bahagian C PT3 - 4HELLINA BERAYUОценок пока нет
- Karnival Koakademik Bahasa Cina Peringkat Kebangsaan Tahun 2023Документ2 страницыKarnival Koakademik Bahasa Cina Peringkat Kebangsaan Tahun 2023Ti Yee SanОценок пока нет
- Buku Teks Bab 8 Lokus Dalam Dua DimensiДокумент16 страницBuku Teks Bab 8 Lokus Dalam Dua DimensiMiNH Hayat100% (1)
- JAWAPAN - Tatabahasa & RumusanДокумент27 страницJAWAPAN - Tatabahasa & RumusanKungHie TiongОценок пока нет
- Latihan Fizik Kuantum SabahДокумент13 страницLatihan Fizik Kuantum SabahZaidah MYОценок пока нет
- Modul Topikal Kbat Matematik Tingkatan 2 (BM)Документ60 страницModul Topikal Kbat Matematik Tingkatan 2 (BM)Helen PappuОценок пока нет
- Skema Jawapan PBD Tingkatan 1Документ6 страницSkema Jawapan PBD Tingkatan 1Suhaimi Omar RamihОценок пока нет
- Ujian Geografi Ting.1Документ4 страницыUjian Geografi Ting.1Anonymous Uw55I3hVkОценок пока нет
- Modul Sejarah Tingkatan 3Документ5 страницModul Sejarah Tingkatan 3Gely MandusОценок пока нет
- m26 Theorem Pitagoras PentaksiranДокумент25 страницm26 Theorem Pitagoras PentaksiranZarina IdrisОценок пока нет
- PAT BM T2 (Murid)Документ6 страницPAT BM T2 (Murid)FREDA WONG CHEN SING MoeОценок пока нет
- Jsu FizikДокумент3 страницыJsu FizikAzrul AkmarОценок пока нет
- Sains t3 2017Документ20 страницSains t3 2017Mona Mohtar0% (1)
- Soalan Bab 2 Kimia Tingkatan 4Документ2 страницыSoalan Bab 2 Kimia Tingkatan 4nor hafizahОценок пока нет
- MODUL 1 SKEMA e Akademik 2021Документ21 страницаMODUL 1 SKEMA e Akademik 2021Yusa YusufОценок пока нет
- Trial Pt3 Bahagian B GeografiДокумент8 страницTrial Pt3 Bahagian B GeografiNor Kamarul AshikinОценок пока нет
- Tg2 Praktis JawapanДокумент6 страницTg2 Praktis JawapancorneliaОценок пока нет
- Penilaian Pentaksiran Sejarah Tingkatan 1 (Ujian Penggal Kedua)Документ6 страницPenilaian Pentaksiran Sejarah Tingkatan 1 (Ujian Penggal Kedua)Naziah SalehatОценок пока нет
- Bab 8 - Garis Dan Sudut (Tingkatan 1)Документ4 страницыBab 8 - Garis Dan Sudut (Tingkatan 1)FirdausSupianОценок пока нет
- Cara Menjawab Soalan SejarahДокумент41 страницаCara Menjawab Soalan SejarahSanthiya PerisamyОценок пока нет
- Trial Fizik KBSMДокумент15 страницTrial Fizik KBSMNurul Nabisah Haji MohamadОценок пока нет
- Edit k2 FZ t5Документ14 страницEdit k2 FZ t5norizah mohd satariОценок пока нет
- Lembaran Kerja Kelas Tambahan Isnin 28 Ogos 2023Документ17 страницLembaran Kerja Kelas Tambahan Isnin 28 Ogos 2023sarina sangkalaОценок пока нет
- Program Pacuan Gemilang 2021Документ141 страницаProgram Pacuan Gemilang 2021FATIN NABILAH BINTI ABDUL RAZAK MoeОценок пока нет
- Skema Soalan Ramalan K2 SPM Set 1 2023Документ25 страницSkema Soalan Ramalan K2 SPM Set 1 2023Gan Hock KiamОценок пока нет
- Section AДокумент14 страницSection AprebasubahОценок пока нет
- RPT Physics Form 4 2019Документ14 страницRPT Physics Form 4 2019MadAm JaJaОценок пока нет
- K1 F4 2019Документ14 страницK1 F4 2019MadAm JaJaОценок пока нет
- Fizik Tingkatan 4 Kertas 3 2018Документ10 страницFizik Tingkatan 4 Kertas 3 2018MadAm JaJa100% (2)
- Ahli Jawatankuasa BBMДокумент1 страницаAhli Jawatankuasa BBMMadAm JaJaОценок пока нет
- Ahli Jawatankuasa Bilik TayangДокумент1 страницаAhli Jawatankuasa Bilik TayangMadAm JaJaОценок пока нет
- Paper 2Документ19 страницPaper 2MadAm JaJaОценок пока нет
- Physics Monthly Test Form 4 2017Документ2 страницыPhysics Monthly Test Form 4 2017MadAm JaJaОценок пока нет
- Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun Tingkatan 5: Sulit 4531/2Документ26 страницPeperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun Tingkatan 5: Sulit 4531/2MadAm JaJaОценок пока нет
- Paper 2Документ34 страницыPaper 2MadAm JaJaОценок пока нет
- Laporan Egg ParachuteДокумент3 страницыLaporan Egg ParachuteMadAm JaJaОценок пока нет