Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Immobilized Enzyme Systems: Enzyme Immobilization: To Restrict Enzyme Mobility in A Fixed Space
Загружено:
lovehopeОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Immobilized Enzyme Systems: Enzyme Immobilization: To Restrict Enzyme Mobility in A Fixed Space
Загружено:
lovehopeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Immobilized Enzyme Systems
Enzyme Immobilization:
To restrict enzyme mobility in a fixed space.
UNITIII
R.KAVITHA,M.PHARM
LECTURER,
DEPARTMENTOFPHARMACUTICS
SRMCOLEGEOFPHARMACY
SRMUNIVERITY
ImmobilizedEnzymeSystems
EnzymeImmobilization:
Easyseparationfromreactionmixture,providingtheabilityto
controlreactiontimesandminimizetheenzymeslostinthe
product.
Reuseofenzymesformanyreactioncycles,loweringthetotal
productioncostofenzymemediatedreactions.
Abilityofenzymestoprovidepureproducts.
Possibleprovisionofabetterenvironmentforenzymeactivity
Diffusionallimitation
Immobilized Enzyme Systems
Methods of Enzyme Immobilization:
- Entrapment
- Surface Immobilization
- Cross-linking
EntrapmentImmobilization isbasedonthe
localizationofanenzymewithinthelatticeof
apolymermatrixormembrane.
retainenzyme
allowthepenetrationofsubstrate.
Itcanbeclassifiedintomatrixandmicro
capsuletypes.
Immobilized Enzyme Systems
Immobilized Enzyme Systems
Entrapment
- Matrix Entrapment - Membrane Entrapment
(microencapsulation)
Immobilized Enzyme
Systems
Matrix Materials:
Organics: polysaccharides, proteins, carbon, vinyl and
allyl polymers, and polyamides. e.g. Ca-alginate, agar,
K-carrageenin, collagen
Immobilization procedures:
Enzyme + polymer solution polymerization
extrusion/shape the particles
Inorganics: activated carbon, porous ceramic.
Shapes: particle, membrane, fiber
Immobilized Enzyme Systems
Entrapment
challenges:
- enzyme leakage into solution
- diffusional limitation
- reduced enzyme activity and stability
- lack of control micro-environmental
conditions.
It could be improved by modifying matrix or
membrane.
Immobilized Enzyme Systems
Surface immobilization
According to the binding mode of the enzyme, this
method can be further sub-classified into:
- Physical Adsorption: Van der Waals
Carriers: silica, carbon nanotube, cellulose, etc.
Easily desorbed, simple and cheap,
enzyme activity unaffected.
- Ionic Binding: ionic bonds
Similar to physical adsorption.
Carriers: polysaccharides and synthetic polymers
having ion-exchange centers.
Immobilized Enzyme Systems
Surface immobilization
- Covalent Binding: covalent bonds
Carriers: polymers contain amino, carboxyl,
sulfhydryl, hydroxyl, or phenolic groups.
- Loss of enzyme activity
- Strong binding of enzymes
Immobilized Enzyme Systems
Cross-linking is to cross link enzyme
molecules with each other using agents
such as glutaraldehyde.
Features: similar to covalent binding.
Several methods are combined.
Summaryof
ImmobilizationMethods
MethodsofEnzymeimmobilization:
Entrapment
matrix
membrane(microencapsulation)
Surfaceimmobilization
physicaladsorption
ionicbinding
covalentbinding
Crosslinking
Recycle packed column reactor:
- allow the reactor to operate at high fluid velocities.
ImmobilizedEnzymeReactors
Fluidized Bed Reactor:
- a high viscosity substrate solution
- a gaseous substrate or product in a continuous reaction system
- care must be taken to avoid the destruction and
decomposition of immobilized enzymes
- An immobilized enzyme tends to decompose
upon physical stirring.
- The batch system is generally suitable for the production
of rather small amounts of chemicals.
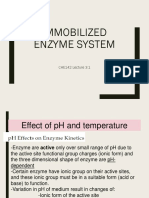
FactorsAffectingEnzymeKinetics
pHeffects
onenzymes
enzymeshaveionicgroupsontheiractivesites.
VariationofpHchangestheionicform oftheactive
sites.
pHchangesthethreeDimensionalstructureof
enzymes.
onsubstrate
somesubstratescontainionicgroups
pHaffectstheionicformofsubstrate
affectstheaffinityofthesubstratetothe enzyme.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Kinetics
Temperature
- on the rate of enzyme catalyzed reaction
k2=A*exp(-Ea/R*T)
T k2
- enzyme denaturation
T
] [
] [
2
ES k
dt
P d
v = =
v
] [
] [
E
d
k
dt
E d
=
Denaturation rate:
k
d
=A
d
*exp
(-Ea/R*T)
k
d
: enzyme denaturation rate constant;
E
a
: deactivation energy
Вам также может понравиться
- 3 Biochemical Engineering CH 3Документ36 страниц3 Biochemical Engineering CH 3yordanos gulilatОценок пока нет
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- L3.1 - Enzyme Immobilization SystemsДокумент60 страницL3.1 - Enzyme Immobilization SystemsRalph EvidenteОценок пока нет
- Organized Multienzyme Systems: Catalytic PropertiesОт EverandOrganized Multienzyme Systems: Catalytic PropertiesG. Rickey WelchОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes-Enzyme-immobilization of EnzymeДокумент16 страницLecture Notes-Enzyme-immobilization of EnzymeShashank Khare100% (2)
- Immobilised EnzymesДокумент39 страницImmobilised EnzymesSwathin NaikОценок пока нет
- ImmobilizationДокумент25 страницImmobilizationNikki ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Enzyme ImmobilizationДокумент73 страницыEnzyme ImmobilizationDaniel Pulido RojasОценок пока нет
- Bahir Dar Institute of Technology: Department of Chemical EngineeringДокумент44 страницыBahir Dar Institute of Technology: Department of Chemical Engineeringjust loughОценок пока нет
- Vidhi A. Modh Assistant Professor at SSSCP, ZundalДокумент30 страницVidhi A. Modh Assistant Professor at SSSCP, ZundalVidhi ModiОценок пока нет
- Biochemisty: Immobilization of EnzymesДокумент24 страницыBiochemisty: Immobilization of EnzymesAnubhuti JhaОценок пока нет
- Lec10 Immobilized Enzymes BiosensorsДокумент35 страницLec10 Immobilized Enzymes Biosensorschintan kapadiaОценок пока нет
- Ankita Gupta: M.Pharm (1 Year) Psit - KanpurДокумент25 страницAnkita Gupta: M.Pharm (1 Year) Psit - Kanpurmonamoname2Оценок пока нет
- CAIE Biology A-Level: Topic 3: EnzymesДокумент4 страницыCAIE Biology A-Level: Topic 3: EnzymesChinguun MunkhtsetsegОценок пока нет
- Enzymes:: Commented (1) : Im Going To Add The Notes From TheДокумент5 страницEnzymes:: Commented (1) : Im Going To Add The Notes From TheSarahОценок пока нет
- Practice 5 VerdeДокумент17 страницPractice 5 Verdeantonio salasОценок пока нет
- Enzyme ImmobilisationДокумент10 страницEnzyme ImmobilisationSaurabh MandalОценок пока нет
- Immobilized EnzymesДокумент9 страницImmobilized EnzymesNITIN100% (1)
- Presented To:: Dr. Manisha Bhardwaj Presented By: Prerna (M.SC Biochemistry)Документ15 страницPresented To:: Dr. Manisha Bhardwaj Presented By: Prerna (M.SC Biochemistry)Anubhuti JhaОценок пока нет
- Course Subject: Biochemistry Course Topic: EnzymesДокумент5 страницCourse Subject: Biochemistry Course Topic: EnzymesAgyao Yam FaithОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Immobilization Can Be Defined As "The Imprisonment of AДокумент14 страницEnzyme Immobilization Can Be Defined As "The Imprisonment of AAnjali YadavОценок пока нет
- Enzymes:: The Nature's CatalystsДокумент51 страницаEnzymes:: The Nature's Catalystskrk100% (1)
- 634904411345780000Документ24 страницы634904411345780000chintan kapadiaОценок пока нет
- Enzyme and Cell Immobilization and Its Applications: Course Title: Industrial Production of Secondary MetabolitesДокумент27 страницEnzyme and Cell Immobilization and Its Applications: Course Title: Industrial Production of Secondary MetabolitesPrerna GuptaОценок пока нет
- Enzymes:: Catabolic ReactionsДокумент5 страницEnzymes:: Catabolic ReactionsSarahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Enzymes: MetabolismДокумент11 страницChapter 4: Enzymes: MetabolismChong HyenОценок пока нет
- Cours Immobilisation Enzymatique Partie Génie Biochimique Et Enzymatique 2023-2024 IAA2Документ79 страницCours Immobilisation Enzymatique Partie Génie Biochimique Et Enzymatique 2023-2024 IAA2ghislain22.kevinОценок пока нет
- UNIT V Enzyme ImmobilizationДокумент32 страницыUNIT V Enzyme ImmobilizationmurgulwarshitalОценок пока нет
- Enzymes, Enzymes Kinetics and Enzymes ImmobilisationДокумент65 страницEnzymes, Enzymes Kinetics and Enzymes ImmobilisationKaycee ChirendaОценок пока нет
- Immobilized Enzyme: Engr. Vera Marie L. LanariaДокумент16 страницImmobilized Enzyme: Engr. Vera Marie L. LanariaAldu BebsОценок пока нет
- Ch-Immobilization of Enzyme PDFДокумент92 страницыCh-Immobilization of Enzyme PDFVОценок пока нет
- Study On EnzymesДокумент21 страницаStudy On EnzymesPragyan Kumar PradhanОценок пока нет
- Summary Notes (2019-2021 Syllabus) 3Документ4 страницыSummary Notes (2019-2021 Syllabus) 3Muhammad Bin AqeelОценок пока нет
- Report BiotechДокумент6 страницReport Biotechnica roseОценок пока нет
- 3.5 Enzymes 2Документ64 страницы3.5 Enzymes 2Alondra SagarioОценок пока нет
- EnzymeДокумент11 страницEnzymewyniel lipanglipangОценок пока нет
- Enzyme ImmobilizationДокумент27 страницEnzyme Immobilizationsabuz pataОценок пока нет
- Content 5 (Immobilized Enzymes and Cells)Документ10 страницContent 5 (Immobilized Enzymes and Cells)Chala KelbessaОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Immobilized EnzymeДокумент3 страницыEnzyme Immobilized EnzymeDivya TripathyОценок пока нет
- BCH 4211 Lecture NoteДокумент22 страницыBCH 4211 Lecture NoteMusa AbubakarОценок пока нет
- Immobilization of Enzymes and CellsДокумент14 страницImmobilization of Enzymes and CellsTayyaba FatimaОценок пока нет
- The Preparation and Kinetics of Immobilised EnzymesДокумент60 страницThe Preparation and Kinetics of Immobilised EnzymesRajashekhar BogarajulaОценок пока нет
- Chapter-3 - Enzyme Kinetics-Part-4 PDFДокумент20 страницChapter-3 - Enzyme Kinetics-Part-4 PDFShivam AnandОценок пока нет
- E-Mail: E-Mail:: Lemessa - Etana@aait - Edu.et Lemessa - Etana@aait - Edu.etДокумент47 страницE-Mail: E-Mail:: Lemessa - Etana@aait - Edu.et Lemessa - Etana@aait - Edu.etdesalegn abera100% (1)
- Criteria For Selection of Enzymatic ReactorДокумент5 страницCriteria For Selection of Enzymatic ReactorParnnika BaroliaОценок пока нет
- Topic4 Enzyme TechnologyДокумент79 страницTopic4 Enzyme Technologymunyee91Оценок пока нет
- ERT211 CHP 1-2 PDFДокумент27 страницERT211 CHP 1-2 PDFsobiyamaragathavelОценок пока нет
- Enzymes in FoodДокумент53 страницыEnzymes in FoodHồ Xuân AnОценок пока нет
- BCH 407 (Enzymology)Документ26 страницBCH 407 (Enzymology)idriscognitoleadsОценок пока нет
- EnzymeДокумент16 страницEnzymesalcedocedmerkОценок пока нет
- ImmobilizationДокумент16 страницImmobilizationDavid Muñoz HuachuhuillcaОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Are The Tools of LifeДокумент31 страницаEnzymes Are The Tools of LifedrhydrogenОценок пока нет
- 3 MTCHM3 LEC EnzymesДокумент8 страниц3 MTCHM3 LEC EnzymesMahal BarrosoОценок пока нет
- An Assignment On "Immobilization of Cell and Enzymes" in Subject MBB 603 Advances in Microbial BiotechnologyДокумент20 страницAn Assignment On "Immobilization of Cell and Enzymes" in Subject MBB 603 Advances in Microbial Biotechnologychintan kapadiaОценок пока нет
- Enzymes (As Biology)Документ42 страницыEnzymes (As Biology)Muhtasim FarhanОценок пока нет
- Enzymes 1Документ6 страницEnzymes 1zarszОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry 1: - Biochemistry of Amino Acids - Biochemistry of Proteins - Portrait of Allosteric ProteinДокумент55 страницBiochemistry 1: - Biochemistry of Amino Acids - Biochemistry of Proteins - Portrait of Allosteric ProteinHiba N IkhmyesОценок пока нет
- BiochemicalДокумент17 страницBiochemicalYonas TarekegnОценок пока нет
- 4 Industrial EnzymesДокумент2 страницы4 Industrial EnzymesNicolas JayОценок пока нет
- Uttar Pradesh Voluntary Action NetworkДокумент3 страницыUttar Pradesh Voluntary Action NetworklovehopeОценок пока нет
- 2014 - 13 - Article 5Документ4 страницы2014 - 13 - Article 5lovehopeОценок пока нет
- SolutionsДокумент14 страницSolutionsHazem DiabОценок пока нет
- Pharmaceutical Science 2014Документ24 страницыPharmaceutical Science 2014lovehope100% (1)
- 106720070205Документ8 страниц106720070205lovehopeОценок пока нет
- Obstetric Nursing Sample ChapterДокумент14 страницObstetric Nursing Sample ChapterlovehopeОценок пока нет
- Bytes October 13-65-88 - FinalДокумент24 страницыBytes October 13-65-88 - FinallovehopeОценок пока нет
- J. Org. Chem., 1962, 27 (9), PP 3236-3239Документ4 страницыJ. Org. Chem., 1962, 27 (9), PP 3236-3239lovehopeОценок пока нет
- Introduction of PharmacologyДокумент10 страницIntroduction of PharmacologylovehopeОценок пока нет
- A C A D e M I C S C I e N C e SДокумент5 страницA C A D e M I C S C I e N C e SlovehopeОценок пока нет
- Academic Sciences: Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical ResearchДокумент4 страницыAcademic Sciences: Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical ResearchlovehopeОценок пока нет
- Chemistry ExpДокумент4 страницыChemistry ExplovehopeОценок пока нет
- Attachment C454ea4cДокумент32 страницыAttachment C454ea4clovehopeОценок пока нет
- Exp't 61: 1,4-Di-T-Butylbenzene Via Friedel-Crafts AlkylationДокумент6 страницExp't 61: 1,4-Di-T-Butylbenzene Via Friedel-Crafts AlkylationlovehopeОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of NMR - James PDFДокумент31 страницаFundamentals of NMR - James PDFSoundarya ChandramouleeswaranОценок пока нет
- J Jep 2005 01 031Документ2 страницыJ Jep 2005 01 031lovehopeОценок пока нет
- SolubilityДокумент10 страницSolubilityOmar S. SalihОценок пока нет
- Exp't 42: Two Easy Diels-Alder PuzzlesДокумент5 страницExp't 42: Two Easy Diels-Alder Puzzleslovehope0% (1)
- PeetersДокумент5 страницPeeterslovehopeОценок пока нет
- J Biomaterials 2012 03 046Документ18 страницJ Biomaterials 2012 03 046lovehopeОценок пока нет
- Exp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzeneДокумент4 страницыExp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzenelovehopeОценок пока нет
- Drying Evaporation EnglishДокумент1 страницаDrying Evaporation EnglishlovehopeОценок пока нет
- Exp't 42: Two Easy Diels-Alder PuzzlesДокумент5 страницExp't 42: Two Easy Diels-Alder Puzzleslovehope0% (1)
- Exp 11Документ4 страницыExp 11lovehopeОценок пока нет
- Exp 11Документ4 страницыExp 11lovehopeОценок пока нет
- Exp't 13: Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylation of Diethyl MalonateДокумент5 страницExp't 13: Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylation of Diethyl MalonatelovehopeОценок пока нет
- Exp't 41: The Reaction of Maleic Anhydride and CycloheptatrieneДокумент5 страницExp't 41: The Reaction of Maleic Anhydride and CycloheptatrienelovehopeОценок пока нет
- Exp 4Документ4 страницыExp 4lovehopeОценок пока нет
- Exp 31Документ4 страницыExp 31lovehopeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Introduction - The Nature of Drugs & Amp Drug Development & Amp RegulationДокумент27 страницChapter 1 - Introduction - The Nature of Drugs & Amp Drug Development & Amp RegulationarifpharmjuОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 AnswersДокумент3 страницыChapter 4 AnswersMatt Wong100% (2)
- 2020 Microencapsulation of Essential Oils by Complex CoacervationДокумент21 страница2020 Microencapsulation of Essential Oils by Complex CoacervationNguyễn Trần Hòa HợpОценок пока нет
- 18 - Chemistry in Everyday Life (New) PDFДокумент17 страниц18 - Chemistry in Everyday Life (New) PDFthinkiit60% (10)
- Coan & Shoichet, 2008 Stoichiometry and Physical Chemistry of Promiscuous AggregatorsДокумент7 страницCoan & Shoichet, 2008 Stoichiometry and Physical Chemistry of Promiscuous AggregatorsKonkmanОценок пока нет
- Métodos de Acoplamiento Automatizado Ligando-Receptor (Docking)Документ24 страницыMétodos de Acoplamiento Automatizado Ligando-Receptor (Docking)Amina BourОценок пока нет
- MethodsДокумент11 страницMethodsNguyễn Hiếu HiềnОценок пока нет
- Advance Pharmacology: Lab Worksheet: Practical 1Документ3 страницыAdvance Pharmacology: Lab Worksheet: Practical 1Wincent HuangОценок пока нет
- Enzyme InhibitionДокумент8 страницEnzyme InhibitionfayeОценок пока нет
- LEC - 5 - Complexation and Protein BindingДокумент50 страницLEC - 5 - Complexation and Protein BindingGRACE MAR CABAHUGОценок пока нет
- NTA SensorДокумент6 страницNTA SensorMritunjay Singh YadavОценок пока нет
- Full Download Book Basic Clinical Pharmacology 15Th Edition PDFДокумент41 страницаFull Download Book Basic Clinical Pharmacology 15Th Edition PDFalvin.vincent421100% (15)
- Chemometric Guided Isolation of New Triterpenoid Saponins As Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors From Achyranthes Bidentata BlumeДокумент39 страницChemometric Guided Isolation of New Triterpenoid Saponins As Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors From Achyranthes Bidentata BlumeIoОценок пока нет
- Atomevo: A Web Server Combining Protein Modelling, Docking, Molecular Dynamic Simulation and MMPBSA Analysis of CandidaДокумент14 страницAtomevo: A Web Server Combining Protein Modelling, Docking, Molecular Dynamic Simulation and MMPBSA Analysis of CandidaLeandro AlvesОценок пока нет
- Enzyme/Receptor-Ligand Interactions and Its AnalysisДокумент20 страницEnzyme/Receptor-Ligand Interactions and Its AnalysisRaman ChandelОценок пока нет
- Principles of Plant Nutrition Mengel, KirkbyДокумент846 страницPrinciples of Plant Nutrition Mengel, KirkbyMadeli Villanueva Quispe100% (6)
- Alchemical Free Energy Calculation With GromacsДокумент55 страницAlchemical Free Energy Calculation With GromacsReinaldo Oliveira JúniorОценок пока нет
- J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3353-3361Документ9 страницJ. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3353-3361VeronicaIguarbeMontalbanОценок пока нет
- Computational Biology and Chemistry: Research ArticleДокумент10 страницComputational Biology and Chemistry: Research ArticleNAMIRA TANIYA TASYA TARADIFAОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 - ComplexationДокумент48 страницTopic 2 - ComplexationLokesh JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Review Principles of Protein-Protein Interactions: Susan Jones and Janet M. ThorntonДокумент8 страницReview Principles of Protein-Protein Interactions: Susan Jones and Janet M. ThorntoncocogolОценок пока нет
- Drug Receptor InteractionsДокумент29 страницDrug Receptor InteractionscsujithaОценок пока нет
- Biology Extended Essay Madeeha Kalsekar: (I) State A Null Hypothesis That The Student Could Make For This InvestigationДокумент6 страницBiology Extended Essay Madeeha Kalsekar: (I) State A Null Hypothesis That The Student Could Make For This InvestigationMadeeha KalsekarОценок пока нет
- Jensenone From Eucalyptus Essential Oil As A Potential Inhibitor of COVID 19 Corona Virus InfectionДокумент9 страницJensenone From Eucalyptus Essential Oil As A Potential Inhibitor of COVID 19 Corona Virus InfectionSilvia MariluzОценок пока нет
- MDPI DockingДокумент222 страницыMDPI DockingFoxiTriggerBoy52Оценок пока нет
- ITC200 Training PDFДокумент87 страницITC200 Training PDFHumberto FreitasОценок пока нет
- Hitrap BlueДокумент8 страницHitrap BlueQi ChaoОценок пока нет
- Molecular Story Further Studies: Carvedilol CYP2D6 Interaction: A Patient Case Related To Medicinal ChemistryДокумент1 страницаMolecular Story Further Studies: Carvedilol CYP2D6 Interaction: A Patient Case Related To Medicinal ChemistryjovanaОценок пока нет
- It C Book ChapterДокумент13 страницIt C Book Chaptergo4tidalОценок пока нет
- Affinity Selection-Mass Spectrometry Screening Techniques For Small Molecule Drug DiscoveryДокумент9 страницAffinity Selection-Mass Spectrometry Screening Techniques For Small Molecule Drug DiscoveryFábio Teixeira da SilvaОценок пока нет