Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Static Timing Analysis: January 05
Загружено:
Sandeep PatilИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Static Timing Analysis: January 05
Загружено:
Sandeep PatilАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Static Timing Analysis
January 05
222 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Goals for today
Introduction to STA and the basic idea behind
the process.
STA inputs and outputs.
Defining and applying constraints.
Analyze the results of STA.
Saple STA run and reports
!!! Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Synchronous Design
In Synchronous Design Cloc" Controls the
Dataflo#$$$
On %&ery Cloc" Tic" data o&es fro one
State to Another
'ogic Delay bet#een t#o state has to be
'ess then cloc" (eriod
Alost all ASICs are Synchronous Designs
))) Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Synchronous Design: Example
Out * +,b+ if -A./01-C.D0 else +,b2
A
B
D
l!
"ut
Add
Add
omp#
333 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Timing Analysis
'ogic delay bet#een any t#o 4lops
need to be saller then Cloc" (eriod
There are T#o #ays to &erify
5
Dynaic Tiing analysis
5
Static Tiing analysis
666 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Dynamic Timing analysis
Tiing siulation #ith Series of
4unctional &ectors
Siulator #ill ta"e in netlist7 8ate
delays
Chec" if there is any Tiing 9iolations
::: Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Dynamic Timing analysis
;ea"ness of DTA
5
It is difficult to generate &ectors #hich
co&er all cobinations of logic
5
<e=uires huge C(> and ?eory
5
Tie consuing
@@@ Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Static Timing Analysis
Design is bro"en do#n in sets of tiing
paths
Delay of each path is calculated
Copare path delay to constraints
chec" if they ha&e been et
;hy is it called STA$
AAA Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Static timing analysis: Ad$antages
Do not re=uire any &ectors
<uns &ery fast
?ore efficient in C(> and ?eory
usage
+2 +2 +2 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
%hat STA chec!s
If design Can #or" at gi&en ?aB 4re=uency
If Design can #or" in different operating
-(9T0 conditions
If Design Satisfies %lectrical constraints
-Trans7 cap7 fanout etc0
Signal Integrity of routing
++ ++ ++ Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Timing &aths
Design is bro"en do#n in sets of signal
paths
%ach path has startpoint and %ndpoint
Startpoint is (riary Input or Cloc"
pins of <egister
%ndpoint is (riary output or D pins of
registers
<egister is a cell #ith setupCDold tie
re=uireent e.g 4lop7 ?eory etc.
+2 +2 +2 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Timing path Types
+! +! +! Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Timing path Types cont'
&rimary input to register
5
Start (rom )nput &in* Ends at +egister
5
Example )n, to ((,
5
+e-uires Setting input delay at input
pin relati$e to cloc!
+) +) +) Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Timing path Types cont'
+egister to register
5
Start from loc! pin of +egister
5
Ends at D pin of +egister
5
Example: &ath .et/een ((, to ((0
5
onstrained .y specification of the
cloc!
+3 +3 +3 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Timing path Types cont'
+egister to output
5
Start from loc! pin of +egister
5
Ends at "utput &in
5
Example: &ath .et/een ((0 to "ut,
5
onstrained .y specification "utput
delay on output port
+6 +6 +6 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Timing path Types cont'
)nput to output
5
Start from )nput &in
5
Ends at "utput &in
5
Example: &ath .et/een )n0 to "ut0
5
onstrained .y specification "utput
delay on output port and input delay
on input port
+: +: +: Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
&ath Groups
(aths are grouped according to cloc"s
controlling their endpoints
Set of paths associated #ith a cloc" is
called as path group
All paths #ith no particular cloc" goes
to default path group
+@ +@ +@ Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Timing hec!s
Typical Tiing chec"s done are
5
Setup and Dold
5
<eco&ery and <eo&al
5
?iniu pulse #idth
5
8litch detection -cloc" gating0
+A +A +A Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Setup and 1old
?iniu tie that a data input pin of
a Se=uential cell ust be stable Before
Cloc" Transition.
?iniu tie that a data input pin of
a Se=uential cell ust be stable After
Cloc" Transition.
22 22 22 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
2+ 2+ 2+ Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
+eco$ery and +emo$al
<eco&eryE ?iniu tie
that an asynchronous
control input pin ust be
stable after deserted and
before neBt cloc" edge
<eo&alE ?iniu tie
that an asynchronous
input pin ust be stable
before being deserted and
after the pre&ious cloc"
edge
Reset
Reset
Clock
Clock
Recovery
Removal
22 22 22 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
2inimum loc! &ulse %idth
?iniu Aount of tie bet#een t#o
consecuti&e <ise and fall edge of the cloc"
Minimum High
Pulse width
Minimum Low
Pulse width
2! 2! 2! Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Glitch Detection -Cloc" getting chec"0
+
Flip Flop
CLK
En
Clk
Clk
En
FF.Clk
2) 2) 2) Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
onstraints
Constraints are Designer,s goals
<estriction put by technology library
also =ualify as constraints
STA easures if these goals are et.
Typical constraints are cloc"7 inputCout
put delays7 design specific tiing
re=uireents
23 23 23 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Types "f onstraints
26 26 26 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Defining cloc!
Defines #hich are the cloc" ports and the
cloc" attributes
createFcloc" Gperiod +2n G#a&efor H2 3I G
nae cl"
;a&efor starts at 2 #ith 32J duty cycle
2: 2: 2: Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Generated3Deri$ed cloc!
Internal cloc" is di&ide by )
createFgeneratedFcloc"
2@ 2@ 2@ Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
4irtual cloc!
This path is constrained by a cloc" -cl"0
outside of chip
2A 2A 2A Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
loc! Distri.ution
!2 !2 !2 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
loc! &arameters
Cloc" s"e#
Cloc" uncertainty
Cloc" insertion delay
Cloc" Kitter
Ideal and propagated cloc"
Do# this paraeters affects
!+ !+ !+ Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
loc! s!e/
!2 !2 !2 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
loc! 5itter
!! !! !! Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
loc! latency3delay
!) !) !) Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
)deal and computed loc!
Off chip cloc" effects are fiBed throughout
a. Source latency
b. Litter
On chip routing is estiated for ideal cloc"
a. /udgeted net#or" latency
b. /udgeted s"e#
On chip routing is coputed after CTS
a. Actual insertion delay
b. Actual s"e#
!3 !3 !3 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Setting )nput Delay
Input signal arri&es at 2.3ns after rising
edge of CM
SetFinputFdelay
!6 !6 !6 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Setting "utput Delay
Output signal needs to arri&e tie at O after
By ns
SetFoutputFdelay
!: !: !: Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
)nput Dri$e strength
Along #ith tiing constraints one needs to
specify design en&ironent
SetFdri&ingFcell
!@ !@ !@ Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
"utput load
Setting output load
SetFdri&ingFcell
!A !A !A Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
hec! 6 hec!7 hec!
Chec"Ftiing #ill chec" if e&ery thing
is constrained
)2 )2 )2 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Timing onstraints Tutorial
Deri&e top 'e&el SDC fro 8i&en
Data
)+ )+ )+ Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
(alse &ath
A false path is a tiing path that cannot
propagate a signal.
A path ay eBist in the circuit but ne&er
be used
A functional path ay eBist but the
tiing is &ery slo# or irrele&ant
A path ay eBist in the circuit but no
cobination of input &ectors ay e&er
eBercise it
)2 )2 )2 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
(alse path Example
)! )! )! Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
(alse path Example:
&aths Bet/een T/o cloc!s
)) )) )) Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
2ultiycle &ath
A ulticycle path is a tiing path that is not
eBpected to propagate a signal in one cycle.
Norally7 all paths are constrained for
single-cycle tiing.
?ulticycle paths are eBceptions to the
default single-cycle tiing..
?ulticycle paths are defined by coand
setFulticycleFpath.
)3 )3 )3 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
2ultiycle &aths
)6 )6 )6 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
(unctional 2odes
CopleB Designs can ha&e ultiple Tie
paths that are dependent on the enabled
functional odes
%.g Noral 4unctional ode and Debug
?ode
Case analysis pro&ides a eans of setting
constant paths that you #ant the tool to
ignore during tiing analysis
): ): ): Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
"perating onditions
The operating conditions of a design usually
include the process7 &oltage7 and
teperature ranges a design encounters.
Operating conditions are defined in a
technology library in an operatingFconditions
group.
Oou can choose operation condition by
setFoperatingFcondition
)@ )@ )@ Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
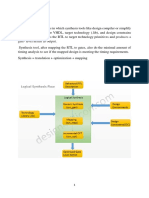
Specify Design data
and libraries
Specify
Interconnect
Specify Clocks
Specify
Input/Output
Delays
Specify
Timing
Exceptions
ASIC
Netlist
ASIC
Liarary
SP!"
#ire Load
Models
$ack%
annotated
STA 2ethodology
)A )A )A Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
STA 2ethodology
Ceck Timing
!pdate Timing
"enerate
#eports
Constraints
&iolators
Path
'iming
$ottleneck
Re(orts
32 32 32 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Delays
Total Delay * Cell Delay . Interconnect
Delay
Cell Delay depend upon Input
transition and output cap.
Interconnect Delay depends upon
capacitance and resistance
>ser need to pro&ide Interconnect <7 C
3+ 3+ 3+ Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Specify )nterconnect
Standard parasitic %Bchange forat
-S(%40 file
5
%Btracted < and C
Standard Delay 4orat -SD40
5
Accurate tiing inforation fro Delay
calculation tool
;ireload ?odels
5
(re-layout net delay estiates
32 32 32 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
&ath Delay
Actual path delay is su of net and
cell delays along tiing the path
3! 3! 3! Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
8et Delays
Is the total tie need to charge or
discharge all the parasites of a Net
Net parasites depends up on
5
Net 'ength
5
Net <outing
5
Net 4anout
3) 3) 3) Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
"n7hip $ariation
Intra die &ariation and intra #afer process
&ariations.
Teperature and &oltage &ariation on the
die.
Deration of the appropriate path for the
analysis so that additional argin is
obtained.
33 33 33 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
S) effects
%ffect of signal propagation on one net7
affecting another adKacent net.
Causes delay push out and glitch in the
&icti net.
(T-SI analysis
36 36 36 Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
STA /al! through
3: 3: 3: Open-Silicon Confidential Open-Silicon Confidential
Goals for today
Introduction to STA and the basic idea behind
the process.
STA inputs and outputs.
Defining and applying constraints.
Analyze the results of STA.
Saple STA run and reports
Вам также может понравиться
- Static Timing Analysis - MaharshiДокумент29 страницStatic Timing Analysis - MaharshiSatish Yada100% (1)
- Logic Equivalence CheckДокумент34 страницыLogic Equivalence CheckROBI PAUL100% (2)
- Asic Design Flow:: Specification FloorplanДокумент9 страницAsic Design Flow:: Specification Floorplanp gangadhar KumarОценок пока нет
- It Is A Process To Convert RTL Code Into Design ImplementationДокумент5 страницIt Is A Process To Convert RTL Code Into Design ImplementationsrajeceОценок пока нет
- SynopsysДокумент3 страницыSynopsysGowtham VeeramalluОценок пока нет
- Designing robust clock trees for complex SoCsДокумент9 страницDesigning robust clock trees for complex SoCsStudent100% (1)
- Notes7 Applying Synthesis ConstraintsДокумент18 страницNotes7 Applying Synthesis ConstraintsravishopingОценок пока нет
- STAДокумент31 страницаSTAdasari pavan tejaОценок пока нет
- SPN RtutorialДокумент33 страницыSPN RtutorialSiva kumar100% (1)
- Low Power PDFДокумент42 страницыLow Power PDFMayur AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Team VLSIДокумент3 страницыTeam VLSINaganithesh GhattamaneniОценок пока нет
- SYNTHESIS-sparc by RajeshДокумент20 страницSYNTHESIS-sparc by RajeshRajesh PerlaОценок пока нет
- Typical ASIC design flow synthesis constraintsДокумент134 страницыTypical ASIC design flow synthesis constraintsMark Ting-Min LinОценок пока нет
- Timing ClosureДокумент23 страницыTiming ClosureSasank VenkataОценок пока нет
- Automatic Clock Tree Synthesis for ASIC DesignsДокумент21 страницаAutomatic Clock Tree Synthesis for ASIC DesignsROBI PAULОценок пока нет
- Clock GateДокумент19 страницClock Gateamma4manuОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Digital Flow in Mixed Environment (2 - Back End)Документ89 страницIntroduction To The Digital Flow in Mixed Environment (2 - Back End)Nguyen Van ToanОценок пока нет
- Team VLSI TCLДокумент7 страницTeam VLSI TCLNaganithesh GhattamaneniОценок пока нет
- IDDQ TestingДокумент38 страницIDDQ TestingVeeranjaneyulu DhikondaОценок пока нет
- Negative Skew For Setup: Propagation Delays Load Delays Interconnect DelaysДокумент25 страницNegative Skew For Setup: Propagation Delays Load Delays Interconnect DelaysRajni100% (1)
- PD Flow I - FloorplanДокумент25 страницPD Flow I - FloorplansudhirОценок пока нет
- PT Lab1 FlowДокумент22 страницыPT Lab1 FlowJenniferPeterОценок пока нет
- PrimeTime: Specifying Timing ExceptionsДокумент24 страницыPrimeTime: Specifying Timing ExceptionsAnonymous CTRhtz94Оценок пока нет
- Team VLSI SDCДокумент11 страницTeam VLSI SDCNaganithesh GhattamaneniОценок пока нет
- Lin TingДокумент87 страницLin TingVeeresh TangadgiОценок пока нет
- Boundary-Scan DFT GuidelinesДокумент63 страницыBoundary-Scan DFT GuidelinesSambhav VermanОценок пока нет
- Testing and Design-for-Testability (DFT) For Digital Integrated CircuitsДокумент95 страницTesting and Design-for-Testability (DFT) For Digital Integrated Circuitsnagabhairu anusha100% (1)
- In Genus, the command to read HDL files is:read_hdl -format <format> <file_name>For example:read_hdl -format verilog top.vThis will read the Verilog file top.v into the current designДокумент98 страницIn Genus, the command to read HDL files is:read_hdl -format <format> <file_name>For example:read_hdl -format verilog top.vThis will read the Verilog file top.v into the current designROBI PAUL100% (1)
- Standard CellДокумент53 страницыStandard CellShwethОценок пока нет
- UncertaintyДокумент24 страницыUncertaintyramana459Оценок пока нет
- Sharif Digital Flow Introduction Part I: Synthesize & Power AnalyzeДокумент128 страницSharif Digital Flow Introduction Part I: Synthesize & Power AnalyzejohnmechanjiОценок пока нет
- Mentor Graphics Simulation Tools ASIC Design FlowДокумент45 страницMentor Graphics Simulation Tools ASIC Design FlowKapasi TejasОценок пока нет
- Fundamental of Loic SynthesisДокумент105 страницFundamental of Loic SynthesisyaminiОценок пока нет
- Clockgate Enable Path Timing: - TypeДокумент5 страницClockgate Enable Path Timing: - TypeSandeep PatilОценок пока нет
- What Is STA ?Документ13 страницWhat Is STA ?veeru100% (1)
- MbistДокумент38 страницMbistNaga NitheshОценок пока нет
- DFT Compiler Lab 1: Insert Scan Chain: Computer-Aided VLSI System DesignДокумент4 страницыDFT Compiler Lab 1: Insert Scan Chain: Computer-Aided VLSI System DesignMani KandanОценок пока нет
- Upf PresentationДокумент30 страницUpf PresentationAnupam Gajendra Narayan ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- On Chip VariationДокумент29 страницOn Chip Variationgpraveenroy100% (1)
- Static Timing Analysis in VLSI CircuitsДокумент16 страницStatic Timing Analysis in VLSI CircuitseeshgargОценок пока нет
- #STA #Constraint #Set Clock Groups #Static Timing AnalysisДокумент3 страницы#STA #Constraint #Set Clock Groups #Static Timing AnalysisFeroz AhmedОценок пока нет
- StaДокумент91 страницаStaMohd Mayur100% (1)
- Prime Time FeaturesДокумент15 страницPrime Time FeaturesPruthwish PatelОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 STAДокумент55 страницLecture 3 STAAn HuynhОценок пока нет
- 1 DFT Coding RulesДокумент22 страницы1 DFT Coding RulesKshitij GurjarОценок пока нет
- CPF Tutorial 2007 12 06Документ55 страницCPF Tutorial 2007 12 06LoiLeVanОценок пока нет
- Synthesis AlДокумент7 страницSynthesis AlAgnathavasiОценок пока нет
- Reduce Congestion With IC CompilerДокумент9 страницReduce Congestion With IC Compilermaharajm98Оценок пока нет
- Extensive Application Notes On Clocks in PrimetimeДокумент39 страницExtensive Application Notes On Clocks in PrimetimevikkisachdevaОценок пока нет
- Lab2 Synopsys DCДокумент12 страницLab2 Synopsys DCkrunalОценок пока нет
- Scan Chain Insertion and ATPG Using Design Compiler and TetraMAXДокумент47 страницScan Chain Insertion and ATPG Using Design Compiler and TetraMAXLakshmi PrasadОценок пока нет
- Power Analysis and Ir Drop Analysis FlowДокумент18 страницPower Analysis and Ir Drop Analysis FlowMayur AgarwalОценок пока нет
- SynthesisДокумент18 страницSynthesissrajeceОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Design CompilerДокумент9 страницTutorial Design Compilermmorsy1981Оценок пока нет
- Clock Tree Synthesis - Why Clock Tree Synthesis Is Necessary - CSDN BlogДокумент21 страницаClock Tree Synthesis - Why Clock Tree Synthesis Is Necessary - CSDN BlogAgnathavasiОценок пока нет
- VLSI Test Principles and Architectures: Design for TestabilityОт EverandVLSI Test Principles and Architectures: Design for TestabilityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- System-on-Chip Test Architectures: Nanometer Design for TestabilityОт EverandSystem-on-Chip Test Architectures: Nanometer Design for TestabilityОценок пока нет
- Collections LabsДокумент23 страницыCollections LabsSandeep PatilОценок пока нет
- ESE570 Lab112Документ4 страницыESE570 Lab112Sandeep PatilОценок пока нет
- Debugging Clock Trees Will Now Be Easier: Cadence Cdnlive! 2007 Emea Conference in MunichДокумент22 страницыDebugging Clock Trees Will Now Be Easier: Cadence Cdnlive! 2007 Emea Conference in MunichSandeep PatilОценок пока нет
- Clockgate Enable Path Timing: - TypeДокумент5 страницClockgate Enable Path Timing: - TypeSandeep PatilОценок пока нет
- FilterДокумент4 страницыFilterSandeep PatilОценок пока нет
- Mallika Ancient Indian HistoryДокумент36 страницMallika Ancient Indian HistorySandeep PatilОценок пока нет
- Mallika Ancient Indian HistoryДокумент36 страницMallika Ancient Indian HistorySandeep PatilОценок пока нет
- TminДокумент17 страницTminhanaОценок пока нет
- Veritas Certification: Exam Preparation GuideДокумент6 страницVeritas Certification: Exam Preparation GuideMustapha ASSILAОценок пока нет
- GIT Basics PDFДокумент126 страницGIT Basics PDFCosticã Pardaillan Lupu100% (1)
- Bed AllocationДокумент32 страницыBed AllocationTaj SОценок пока нет
- Power DUO Source 200 W USB-C PD Reference Design: TI Designs: TIDA-050012Документ24 страницыPower DUO Source 200 W USB-C PD Reference Design: TI Designs: TIDA-050012Alex LuzОценок пока нет
- Signals and SystemsДокумент174 страницыSignals and Systemsjale charitha reddy50% (2)
- Maharana Pratap College of Technology, Gwalior: Seminar File ONДокумент18 страницMaharana Pratap College of Technology, Gwalior: Seminar File ONJaiHanumankiОценок пока нет
- Compensators - ControllersДокумент22 страницыCompensators - ControllersPrasanth Kumar0% (1)
- Ar8600mk2 Manual AДокумент147 страницAr8600mk2 Manual ACoba LahОценок пока нет
- ScriptДокумент189 страницScriptspoolОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 OoadДокумент22 страницыChapter 3 Ooadsujitha14Оценок пока нет
- Internship Post - Frontend Development InternДокумент2 страницыInternship Post - Frontend Development InternAris ManouguianОценок пока нет
- Project Report of Gym WebsiteДокумент84 страницыProject Report of Gym WebsiteGower100% (2)
- Geethanjali ECE Virtual Lab Software ListДокумент2 страницыGeethanjali ECE Virtual Lab Software ListSuneelkrishna RallabhandiОценок пока нет
- Comparative Analysis of Commercial and OpenSource Mobile Device Forensic ToolsДокумент6 страницComparative Analysis of Commercial and OpenSource Mobile Device Forensic ToolsKhalid OsmanОценок пока нет
- Resume - Joseph ArrigoДокумент1 страницаResume - Joseph Arrigoapi-414632733Оценок пока нет
- Next Generation Innovation Technologies: ..We CommitДокумент52 страницыNext Generation Innovation Technologies: ..We CommitDonna WalterОценок пока нет
- Computer Architecture McqsДокумент10 страницComputer Architecture McqsSatsshhОценок пока нет
- How To Fix Cisco Router Lost Config After RebootДокумент3 страницыHow To Fix Cisco Router Lost Config After RebootW Banu WidodoОценок пока нет
- Zdlra 2020 V2Документ53 страницыZdlra 2020 V2Tran Quoc DungОценок пока нет
- QT Designer WidgetsДокумент128 страницQT Designer WidgetsTadeu FelixОценок пока нет
- IC200ALG260Документ1 страницаIC200ALG260ahmedОценок пока нет
- 01-05 Overall QoS ProcessДокумент22 страницы01-05 Overall QoS Processmanojsingh474Оценок пока нет
- RS PRO Bench Power Supply 180W 2-OutputДокумент5 страницRS PRO Bench Power Supply 180W 2-OutputGuillaume FoubertОценок пока нет
- Network Lab by ArmstrongДокумент52 страницыNetwork Lab by Armstrongarmstrongjoseph1908Оценок пока нет
- A Guide To Ddos Protection: Choosing The Right ModelДокумент11 страницA Guide To Ddos Protection: Choosing The Right ModelriyaОценок пока нет
- SW DK TM4C129X Ug 2.1.4.178 PDFДокумент54 страницыSW DK TM4C129X Ug 2.1.4.178 PDFTân PhanОценок пока нет
- MarkSheet & Calculator Program PDFДокумент8 страницMarkSheet & Calculator Program PDFGhulam Ali BhangwarОценок пока нет
- Pin Configuration of IC 7447Документ2 страницыPin Configuration of IC 7447Ahmar Niazi100% (1)
- Expert Python and Django developer seeking challenging roleДокумент1 страницаExpert Python and Django developer seeking challenging roleSuvojit MondalОценок пока нет