Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ITIL Service Design Poster
Загружено:
Dominic Benedito100%(6)100% нашли этот документ полезным (6 голосов)
2K просмотров1 страницаITIL Service design poster
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документITIL Service design poster
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(6)100% нашли этот документ полезным (6 голосов)
2K просмотров1 страницаITIL Service Design Poster
Загружено:
Dominic BeneditoITIL Service design poster
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
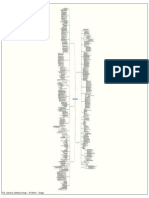
SERVICE DESIGN INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Business Requirements Stage should consist of:
Appointment of a Project Manager
Identification of Stakeholders
Requirements analysis, prioritization, agreement
and documentation
Determination and agreement of outline budgets
and business benefits
Resolution of potential conflict between business
units and agreement on corporate requirements
Sign-off process for the agreed requirements
Development of a customer engagement plan
Information on Requirements of NewServices
Facilities/ Features and Functionality required (Utility)
Management Information and Management needs required
Business Processes supported, Dependencies, Priorities,
Criticality and Impact
Business Cycles and Seasonal Variations
SLRs and Service Level Targets (Warranty)
Business Transaction Levels, numbers and types of users +
future growth
Business justification, including Financial and Strategic
aspects
Level of business capability or support to be provided
MANAGEMENT OF DATA AND
INFORMATION
Defining tool
requirements:
Tools Selection
Implementation
considerations:
Evaluation
process &
criteria:
Heading
DELIVERY MODEL OPTIONS
Delivery
Strategies
Insourcing
Outsourcing
Application
Service provision
Partnership
Co-sourcing or
multisourcing
Business process
outsourcing(BPO)
Knowledge
process
outsourcing
(KPO) Cloud
Description
Utilize internal organization resources
Utilize external organization resources
Provide shared computer-based
services
2 or more organizations working
together to design, develop, transition,
maintain, operate and support IT
services
Combination of insourcing and
outsourcing
Relocating entire business functions
using formal agreements
Provide domain-based process and
business expertise
Offer specific pre-defined services but
can be customized for a specific
organization
Advantages
Direct Control
Freedom of choice
Purchased expertise
Support for transient
needs
Low-cost location
Support and upgrades
included
Market expansion/
entrance
Competitive response
Time to market
Control
Single point of
responsibility
Access to specialist skills
Significant cost savings
Low-cost location
Services are easily defined
Sourcing is straightforward
Disadvantages
Scale limitations
Cost and time to market
Less direct control
Exit barriers
Usage-based charging models
Access to facilities only
Intellectual property and
copyright protection
Project complexity
Culture clash between
companies
Loss of business knowledge
Loss of relationship with the
business
Loss of internal expertise
Culture clash between
companies
Internal clouds are complex
Coordinating insourced
offerings with external cloud
services
Multi-vendor
sourcing
Sourcing different sources from
different vendors
Organization is not tied to
a single vendor
Coordinating different vendors
activities and services
SERVICE DESIGN
MODELS
Design and
Development
approaches
Main input required for newor changed services
Main outputs is the service design package
SERVICE LEVEL MANAGEMENT
Provide a point of regular
contact and communication
to the customers and
business managers
IT services are delivered.
To monitor and measure
services given to
customers and maintained
by the organization
Provide a reliable
communication channel
and a trusted relationship
with customers and
business representatives
Provide key information
on operational services,
targets, achievements and
breaches
Service provider should
establish clear policies for
the conduct of the SLM
process. The required and
cost-justifiable service
quality is maintained and
gradually improved
CSF Based on the objective of a
process
KPI Developed to organizations
appropriate level of maturity, CSF and
particular circumstances
Identifying suitable customer
representatives to negotiate with
Bypassing the use of
the SLMprocesses
Lack of appropriate
tools and resources
IDENTIFYING & DOCUMENTING
BUSINESS REQUIREMENTS &
DRIVERS
Information on Requirements of Retiring Services
Exact Scope of Retirement
Business justification, Financial and Strategic Aspects
What would replace the retiring service
Interfaces and Dependencies with other services
Disposal and/or re-use requirements for service assets
and configuration items associated with Retiring
Services
Archiving Strategy for any business data
Information on Requirements of Existing Services
New Facilities/ Features and Functionality Requirements
Changes in Business Processes, Dependencies, Priorities,
Criticality and Impact
Changes in volumes of Service Transition
Increased Service Levels and Service Level Targets
Business Justification, including Financial and Strategic
aspects
ITIL SERVICE DESIGN
Benedito, Christian, Kara, Abrahams, Peters, Smith, Nombewu
Inputs to various Design Activities are:
All constraints, financial budgets
and plans
Service Management visions,
strategies, policies, objectives and
plans
The Service Portfolio
Design activities are triggered by
changes in business needs or
service improvements. A
structured approach to the design
activities should be adopted to
ensure consistency and integration
is achieved.
Deliverables fromthe Design Activities:
Suggested revisions to IT strategies and
policies
Designs for new or changed services
Process review and analysis report
Designs for revised measurement
methods and processes
DESIGN ACTIVITIES
Key Factors for successful Data Management:
All users have ready access to the
information they need to do their jobs
Data assets are fully exploited through data
sharing
Data assets are protected and secured with
IT security policies
Quality of organizations data is maintained
at an acceptable level
MANAGING DATA ASSETS
Improving quality of Data:
Add value to the services delivered to customers
Reduce risks in the business
Reduce costs of business processes
Stimulate innovation in internal business processes
SCOPE OF DATA MANAGEMENT
Four areas of Management included within Data/
Information Management:
Management of Data Resources
Management of Data/Information Technology
Management of Information Processes
Management of Data Standards and Policies
Data/Information Management is how an
organization plans, collects, creates,
organizes, uses, controls, disseminates and
disposes of its Data/Information.
DESIGN COORDINATION
Purpose Scope Challenges & Risks Policies, Principles & basic concepts Valuing the business Process activities, methods & techniques
S
E
R
V
I
C
E
C
A
T
A
L
O
G
U
E
M
A
N
A
G
E
M
E
N
T
IMPLEMENTING SERVICE
DESIGN
Business Impact Analysis
Ascertain the business needs,
impacts and risks.
Enable organization to define
Critical services
Acceptable levels and times of service outage
Critical business and service periods
Cost of loss of service
Security implications to the loss of a service
2 Areas
Business management
Service Management
Six Sigma (DMADV)
used to develop new
processes.
Six Sigma (DMADV)
used to develop new
processes.
Prerequisites for success
Clearly define goals and objectives
Understanding of processes, procedures, functions,
roles and responsibilities
Understanding of interfaces and dependencies
Understanding of business needs
Develop measurement and analysis technologies
Required metrics to evaluate health of service design
Review of measurement programme
CAPACITY
MANAGEMENT
Purpose and Objectives
Produce and maintain an
appropriate up to date capacity
plan
Scope
Undertaking tuning activities to make
the most efficient use of existing IT
resources
Value to Business
Ensuring required capacity and
performance are provided
Policies, Principles and
Concepts
Balancing cost against
demands
Processes, Activities, Methods
and Techniques
Improving service performance
wherever it is cost justifiable
Trigger, Inputs, Outputs and
Interfaces
Periodic trending and modelling
Information Management
Business Data
Financial Data
Critical Success Factors and Key
Performance Indicators
CSF- accurate business forecast
KPI accurate forecast of planned
expenditure
Challenges and Risks
Persuading the business to provi de I
formation on its strategic business plan IDENTIFYING SERVICE
REQUIREMENTS
SD must consider all elements. Approach
should consider service + its constitution
components.
Requirements:
Scalability
Business processes + business units
IT service + agreed business requirements
Service itself + its SLR or SLA
Techinlogy components used to deploy + deliver Service
Internally delivered supporting services
Externally supplied supporting services
Performance measurements + metrics required
Legislated or required security levels.
AVAILABILITY
MANAGEMENT
Information Management:
Process should maintain an
AIMS that contains all of the
measurements + information
required to complete the
availability management
process + provide
appropriate information.
Triggers, inputs, outputs +
interfaces:
Events trigger availability
managements activities
Sources of information are
relevant to availability
managements.
Value to business:
Availability of systems +
services matches evolving
agreed needs of business.
Policies, principles + basic
concepts:
Continually trying to ensure
all operational services meet
their agreed availability
targets.
Critical success factors + key
performance indicators:
Each org should identify
appropriate CSFs based on its
objectives for the process.
Challenges + Risks:
Main challenge to meet and
manage expectations of the
customers.
Risks:
Lack of commitment
Lack of senior management
commitment
Labour-intensive reporting
process.
BALANCED
DESIGN:
SERVICE DESIGN
TOOLS
Enable: Useful in:
SERVICE
MANAGEMENT
TOOLS
Data structure
Conformity to international open
standards
Flexibility in implementation, usage
and data sharing.
Support for monitoring service
levels.
Consideration must be given to
platform on which tool wil be
expected to operate.
During early stages think about
vendor and tool credibility.
Asses trading needs of
organisation.
Tool has to be implemented.
Hardware platform has been
prepared and software loaded:
data population has to be
considered.
Out of the box
Configuration
Custimization
Service
Design
5 Main
Aspects
Service solutions for new
or changed services
Management
information and tools
Technology
architectures and
management
architectures
The process required
Measurement
methods and metrics
Purpose + Objective:
Level of availability delivered
in all IT services meets
agreed availability.
Scope:
Covers the design,
implementation,
measurement, management
and improvement of IT
service
DESIGN
CONSTRAINTS
All design activities
operate within many
constraints
This means that designers are
not always free to design
most desirable solutions
The primary constraints that determine the
boundaries of a service solution design are the
utility and warranty desired by the customer
The most obvious
additional constraints is
the financial one
MANAGEMENT OF
APPLICATIONS
To fully implement management of applications companies use SDLC
The application
portfolio This is simply a full record of
all applications
Application
frameworks This covers all management and
operational aspects and provides
solutions
Design of specific
applications
The most important phase,
ensures that an application is
conceived with operability and
management
Managing trade-offs
Balancing the relationship
among resources
Design patterns
General, repeatable solution to a commonly
occurring problem
Templates and code
generation
A number of development tools provide variety of templates for
creating common application components
Rapid
Application
Design (RAD)
Off-the-shelf
solutions
Purpose and objective
Scope
Value to the business Information
management
Policies principles and
basic concepts
Critical success factors and Key
performance indicators
Challenges Risks
Valuing Data
Classifying
Data
Data
Ownership
Data Migration
Data retrieval
& usage
Data Capture
Data Storage
Data Integrity
Data related
issues
Purpose to provide and maintain a single source of
consistent info on all operational services.
Scope To provide and maintain accurate info on all
services being transitioned to the live environment.
Value to the business Provides a central source of info on the
IT services delivered by the service provider catalogue.
Policies/Principles/Basic Concepts - To be fully active demand
needs to be active throughout the whole lifecycle.
Information Management - The service Portfolio and Customer
Portfolio Minutes of meetings between business relationship managers
and customers
Risks - Lack of, or inaccurate configuration management information, which results
on the impact of changing demand on the service providers infrastructure and
applications.
Challenges - The customer might find it difficult to break down
individual activities that make sense to the service provider.
Activities/Methods/
Techniques
Business Plans
Marketing Plans
Sales Forecast
Objective - Ensures high level of customer satisfaction making sure
that the customers needs are met to the requirement
Service Level Requirements
Service level requirement s for all
services are ascertained
Ability to deliver against these
requirements is assessed
Risk to the Services
and processes
Considered during
production and
preferred solution is
selected.
Where do we start?
Assessment should be
taken to ascertain strengths
and weaknesses may
include customer
satisfaction surveys, talking
to staff, analysing processes
in action
Starting point is wherever
the organisation is in terms
of IT service management
maturity
Methods of
Measurement of
service Design
Define
Measure
Analyse
Design
Verify
Define
Measure
Analyse
Improve
Control
Delicate Balancing
act ensuring
functionality +
targets are met
Concept extremely
important to service design
activities + to balance
between effort spent in
design, development and
delivery of service
Hardware
Design
Software
Design
Environmental
Design
Process
Design
Data Design
Ensuring standards and
conventions are followed
Offering
prototyping
Management
of service cost
Offering modelling and
simulation facilities.
Speeding up
design
process
Functionality:
Service or product and everything
that is part of the service and its
provision
Resources:
People, technology +
money available for
effort
Service design main purpose is the design
of new or changes services for
implementation in live enviroment
Key output for service design is to design
solutions to meet the changing requirements
of the business
Triggers
Triggers are changes in the business requirements
and services
Outputs
*A comprehensive and
consistent set of services
*A revised enterprise
architecture
*Service portfolio updates
Interfaces
The principle interfaces to the adjacent stages of
the life-cycle
*Service strategy : using information contained
within it strategy
*Service transition : with the handover of the
design of the service solutions within the SDP
* Also interfaces with all processes that include
service design activity
Inputs
A number of sources of information relevant to
design process
*service charter for new or changed services
*Change requests from any stage of service life-
cycle
*Governance required
*Corporate, legal and regulatory polices
requirements
SERVICE-
ORIENTED
ARCHITECTURE
It is strongly recommended
that a business process and
solutions should be designed
and developed by a SOA
SOA is defined by OASIS and is
considered best practise used by many
organizations
SOA brings value and agility to the
development of self-contained services
that are reuasble
When SOA principles are used by
the IT service provider organization,
it is critical that a accurate service
catalogue Is maintained as part of
an overall service portfolio and
CMS
SERVICE DESIGN GOALS
*Design service to satisfy business objectives based on
quality, compliance, risk and security requirements
*Design a service that can be easily and efficiently
developed and reduce, minimize or constrain long term
costs of service provision
*Contribute to the improvement of the IT service
Value creation
through services
Determine
Вам также может понравиться
- Organizing Itsm: Transitioning the It Organization from Silos to Services with Practical Organizational ChangeОт EverandOrganizing Itsm: Transitioning the It Organization from Silos to Services with Practical Organizational ChangeОценок пока нет
- ITIL Service Strategy Poster PDFДокумент1 страницаITIL Service Strategy Poster PDFDominic Benedito100% (4)
- Service Integration and Management (SIAM™) Professional Body of Knowledge (BoK), Second editionОт EverandService Integration and Management (SIAM™) Professional Body of Knowledge (BoK), Second editionОценок пока нет
- Materna ITIL Poster v4.0.0Документ2 страницыMaterna ITIL Poster v4.0.0desertedtweek93% (15)
- ITIL® Guide to Software and IT Asset Management - Second EditionОт EverandITIL® Guide to Software and IT Asset Management - Second EditionРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- ITIL Service Transition Poster PDFДокумент1 страницаITIL Service Transition Poster PDFDominic Benedito100% (6)
- ITIL Lifecycle Essentials: Your essential guide for the ITIL Foundation exam and beyondОт EverandITIL Lifecycle Essentials: Your essential guide for the ITIL Foundation exam and beyondОценок пока нет
- ITIL Service Operation Poster PDFДокумент1 страницаITIL Service Operation Poster PDFDominic Benedito100% (7)
- Implementing Itsm: From Silos to Services: Transforming the It Organization to an It Service Management Valued PartnerОт EverandImplementing Itsm: From Silos to Services: Transforming the It Organization to an It Service Management Valued PartnerОценок пока нет
- Implementing ITILДокумент27 страницImplementing ITILvimpat100% (3)
- CMDB Systems: Making Change Work in the Age of Cloud and AgileОт EverandCMDB Systems: Making Change Work in the Age of Cloud and AgileОценок пока нет
- Building IT and Digital Excellence With ITIL 4Документ5 страницBuilding IT and Digital Excellence With ITIL 4carl0sm0ra100% (1)
- Pragmatic Application of Service Management: The Five Anchor ApproachОт EverandPragmatic Application of Service Management: The Five Anchor ApproachОценок пока нет
- Itil4 A Pocket Guide Jan Van BonДокумент21 страницаItil4 A Pocket Guide Jan Van BonEngineer & MBA32% (19)
- IT Services Core Services CatalogueДокумент138 страницIT Services Core Services CatalogueHello Word :-)100% (3)
- High Velocity Itsm: Agile It Service Management for Rapid Change in a World of Devops, Lean It and Cloud ComputingОт EverandHigh Velocity Itsm: Agile It Service Management for Rapid Change in a World of Devops, Lean It and Cloud ComputingОценок пока нет
- ITIL® v3 - The Big PictureДокумент1 страницаITIL® v3 - The Big Picturelaszlosomogyi@chellohu100% (3)
- IT for Business (IT4B): From Genesis to Revolution, a business and IT approach to digital transformationОт EverandIT for Business (IT4B): From Genesis to Revolution, a business and IT approach to digital transformationОценок пока нет
- Infographic 7 Guiding Principles of ITIL 4Документ1 страницаInfographic 7 Guiding Principles of ITIL 4eirudОценок пока нет
- Practical IT Service Management: A concise guide for busy executivesОт EverandPractical IT Service Management: A concise guide for busy executivesОценок пока нет
- AXELOS SIAM WhitepaperДокумент24 страницыAXELOS SIAM WhitepaperSurya Prakash Garg100% (1)
- Itil Cobit Mapping TemplateДокумент6 страницItil Cobit Mapping Templategobits100% (3)
- ITIL4 Summary PDFДокумент16 страницITIL4 Summary PDFAhmed AbdelFatah100% (1)
- IT Service Management Implementation OverviewДокумент60 страницIT Service Management Implementation OverviewAlan McSweeney100% (1)
- Architecting Itsm: A Reference of Configuration Items and Building Blocks for a Comprehensive It Service Management InfrastructureОт EverandArchitecting Itsm: A Reference of Configuration Items and Building Blocks for a Comprehensive It Service Management InfrastructureОценок пока нет
- ITIL+Service Operation 1203Документ49 страницITIL+Service Operation 1203Андрей ИвановОценок пока нет
- ROI of ITSMДокумент20 страницROI of ITSMSourabh MishraОценок пока нет
- ITIL+4 HandsOnДокумент45 страницITIL+4 HandsOnKathia Lissbeth Rodriguez100% (1)
- Itil 4 and IT4IT: Rob AkershoekДокумент25 страницItil 4 and IT4IT: Rob Akershoekfalcon.peregrine7775100% (1)
- Problem Management - ItilДокумент27 страницProblem Management - ItilivofabiorodriguesОценок пока нет
- Itil Poster The Big Picture CFN PeopleДокумент1 страницаItil Poster The Big Picture CFN PeopleFabrizio MachadoОценок пока нет
- Itil v3 Service Design GuidelinesДокумент72 страницыItil v3 Service Design GuidelineslatifahmadpoorОценок пока нет
- Itil v3 Process ModelДокумент2 страницыItil v3 Process ModelMahya Bagheri100% (1)
- Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL)Документ65 страницInformation Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL)Wong Chan WengОценок пока нет
- Implementing ItsmДокумент1 страницаImplementing ItsmnihadnagiОценок пока нет
- Sample Metrics For ITIL ProcessesДокумент3 страницыSample Metrics For ITIL ProcessessantuchetuОценок пока нет
- IT Service Catalogue GuidelinesДокумент10 страницIT Service Catalogue GuidelinesmusabqОценок пока нет
- Itil V4Документ44 страницыItil V4Jesús Hurtado Gonzales94% (17)
- ITSM Reference Architecture v1 PDFДокумент42 страницыITSM Reference Architecture v1 PDFvenky95100% (1)
- ITIL Service Management AwarenessДокумент15 страницITIL Service Management AwarenessManoj KulkarniОценок пока нет
- Checklist of Recommended ITIL Documents For Processes and Functions enДокумент18 страницChecklist of Recommended ITIL Documents For Processes and Functions enFeleke AfeworkОценок пока нет
- ITIL Process Map WallchartДокумент2 страницыITIL Process Map Wallchartphilmeyer100% (3)
- Monitoring and Event Management: ITIL® 4 Practice GuideДокумент33 страницыMonitoring and Event Management: ITIL® 4 Practice GuideNeuta Harol100% (2)
- ITIL Service DesignДокумент64 страницыITIL Service DesignemedinillaОценок пока нет
- ITIL Process Maturity Assessment and Roadmap v5Документ38 страницITIL Process Maturity Assessment and Roadmap v5danrodd100% (1)
- ITIL Service DeliveryДокумент1 страницаITIL Service DeliverygringoricanОценок пока нет
- ITIL KPIs and The IT Balanced ScorecardДокумент37 страницITIL KPIs and The IT Balanced Scorecardtobitobsen_20013953100% (11)
- ITIL Process Assessment Framework - MacDonaldДокумент42 страницыITIL Process Assessment Framework - MacDonaldNikos NikakisОценок пока нет
- Lean ITSM Whitepaper PDFДокумент60 страницLean ITSM Whitepaper PDFfabioos0% (1)
- The IT Service ManagementДокумент167 страницThe IT Service ManagementEdi MahdiОценок пока нет
- ITSM Assessment ReportДокумент175 страницITSM Assessment Reportmarcelo_linero100% (1)
- Togaf&itil PDFДокумент12 страницTogaf&itil PDFpolen chheangОценок пока нет
- ITIL 4 Specialist - CDS in 1000 Words - DIGITAL PDFДокумент5 страницITIL 4 Specialist - CDS in 1000 Words - DIGITAL PDFĐoàn Đức Đề100% (1)
- IT Operations Management GuideДокумент136 страницIT Operations Management Guideneal_kir100% (3)
- One Future.: Own ItДокумент11 страницOne Future.: Own ItSurabhi PrakashОценок пока нет
- ITSM Best PracticesДокумент1 страницаITSM Best PracticesАлексей Лукацкий0% (1)
- Ccna 4 Case StudyДокумент3 страницыCcna 4 Case StudyDominic BeneditoОценок пока нет
- Practice Skills AssessmentДокумент5 страницPractice Skills AssessmentDominic BeneditoОценок пока нет
- WCI1600 Assignment 3 MemoДокумент3 страницыWCI1600 Assignment 3 MemoDominic BeneditoОценок пока нет
- Practical 11 of 2012 SolutionДокумент5 страницPractical 11 of 2012 SolutionDominic Benedito0% (1)
- CCNA2 - 1 - Configuring Network Devices and Introduction To RoutingДокумент60 страницCCNA2 - 1 - Configuring Network Devices and Introduction To RoutingDominic BeneditoОценок пока нет
- 5 - Handbook On TCAS - An Indigenous ATP System - April 2021Документ150 страниц5 - Handbook On TCAS - An Indigenous ATP System - April 2021AliveluОценок пока нет
- Eap5-0623-2 - Research Essay - 22002463 - Nguyễn Hồng Khánh NgọcДокумент9 страницEap5-0623-2 - Research Essay - 22002463 - Nguyễn Hồng Khánh NgọcKhánh NgọcОценок пока нет
- Network Forensic Log AnalysisДокумент5 страницNetwork Forensic Log AnalysisEditor IJRITCCОценок пока нет
- Circuit 1B: Potentiometer: Parts NeededДокумент6 страницCircuit 1B: Potentiometer: Parts NeededDarwin VargasОценок пока нет
- 1-CC-Link IE TSN Na EngДокумент71 страница1-CC-Link IE TSN Na EngThanh Kieu Nguyen ThiОценок пока нет
- How To Execute Linux Command by ABAP ProgramДокумент3 страницыHow To Execute Linux Command by ABAP ProgramEEEОценок пока нет
- LP Fujitsu 1din2014Документ11 страницLP Fujitsu 1din2014Anonymous 4MLEo9TVQОценок пока нет
- LPG 2015 e CompleteДокумент489 страницLPG 2015 e CompleteJose MolinaОценок пока нет
- Unit 2: Introduction To The Engineering Profession: Engr. Roman M. Richard, MengДокумент13 страницUnit 2: Introduction To The Engineering Profession: Engr. Roman M. Richard, MengRoman MarcosОценок пока нет
- LAB3.2 - Connecting Windows Host Over iSCSI With MPIOДокумент13 страницLAB3.2 - Connecting Windows Host Over iSCSI With MPIOwendy yohanesОценок пока нет
- Intelligent Reflecting Surface Practical Phase ShiftДокумент5 страницIntelligent Reflecting Surface Practical Phase ShiftVarsha SinghОценок пока нет
- Mobile Application Development at Android: A Crash Course For BeginnersДокумент13 страницMobile Application Development at Android: A Crash Course For BeginnersWasimОценок пока нет
- Mini-Link™ PT 6010 Etsi: Microwave Packet Terminal For High CapacitiesДокумент4 страницыMini-Link™ PT 6010 Etsi: Microwave Packet Terminal For High CapacitiesTafadzwa Comfort NyambiraОценок пока нет
- Fawde 20 KvaДокумент4 страницыFawde 20 KvatritiluОценок пока нет
- Motor Es CatДокумент42 страницыMotor Es CatfelixezamoraОценок пока нет
- PIN Diagram of Intel 8085 Microprocessor - Lecture 3Документ14 страницPIN Diagram of Intel 8085 Microprocessor - Lecture 3ojasbhosale07Оценок пока нет
- Manufacturing Capabilities in Microsoft Dynamics NAVДокумент3 страницыManufacturing Capabilities in Microsoft Dynamics NAVAtanacia Ilagan100% (1)
- 2 Module No. 1 The Field of Engineering ManagementДокумент4 страницы2 Module No. 1 The Field of Engineering ManagementAdrian LequironОценок пока нет
- Baseband AudioДокумент48 страницBaseband Audiorahul09990Оценок пока нет
- Le Veritable Dragon RougeДокумент142 страницыLe Veritable Dragon RougeDavid GourmetОценок пока нет
- Listening Test 25% Intento 1Документ11 страницListening Test 25% Intento 1Adriana LoaizaОценок пока нет
- Search: Skip To Content Using Gmail With Screen ReadersДокумент11 страницSearch: Skip To Content Using Gmail With Screen ReadersKavitha100% (1)
- B230/B237/D042 Service ManualДокумент1 312 страницB230/B237/D042 Service ManualSutan HarrymanОценок пока нет
- 12 CS - SQPДокумент5 страниц12 CS - SQPkumaran mudОценок пока нет
- WellheadДокумент2 страницыWellheadRicardo Paz SoldanОценок пока нет
- Andheri WestДокумент60 страницAndheri WestNikunj VaghasiyaОценок пока нет
- FoxitДокумент13 страницFoxitFariz DaffaОценок пока нет
- Endress-Hauser Cerabar PMP11 ENДокумент4 страницыEndress-Hauser Cerabar PMP11 ENSensortecsa SensortecsaОценок пока нет
- Rohit Bhai RateДокумент3 страницыRohit Bhai RateYogesh AryaОценок пока нет
- Library Management SystemДокумент10 страницLibrary Management SystemMickey VillaflorОценок пока нет