Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Micro 4th Asessment Viral Hepatitis 2007
Загружено:
Adel SukerОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Micro 4th Asessment Viral Hepatitis 2007
Загружено:
Adel SukerАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Viral Hepatitis
Fourth Medical, 2007
Prof. Widad Al-Nakib, FRCPath.
Viral Hepatitis
Clinical Features
Hepatitis due to all thee !irue "ree#t
cli#icall$ i# a !er$ i%ilar fahio#, e"eciall$
duri#& the acute "hae of the ill#e. 'hu a
"ecific dia&#oi ca# o#l$ be %ade i# the
laborator$.
'he %a(orit$ of i#fectio# are totall$
asymptomatic, but co%%o# cli#ical
feature i#clude) anorexia, nausea,
vomiting, right upper quadrant pain and
raised liver enzymes AST and ALT.
Jaundice i the hall %ark of i#fectio#, but
te#d to de!elo" late.
A#icteric cae are alo !er$ co%%o#.
Jaundice
Viral Hepatitis - Historical
Perspective
A
A
Infectious
Infectious
Serum
Serum
Viral
Viral
hepatitis
hepatitis
Enterically
Enterically
transmitted
transmitted
Parenterally
Parenterally
transmitted
transmitted
F, G,
F, G,
other
other
E
E
!"!#
!"!#
B
B
D
D
C
C
Viral Hepatitis -
$vervie%
A B C D E
*ource of
!iru
fece
blood+
blood-deri!ed
bod$ fluid
blood+
blood-deri!ed
bod$ fluid
blood+
blood-deri!ed
bod$ fluid
fece
Route of
tra#%iio#
fecal-oral
"ercuta#euo
"er%ucoal
"ercuta#eou
"er%ucoal
"ercuta#eou
"er%ucoal
fecal-oral
Chro#ic
i#fectio#
#o $e $e $e #o
Pre!e#tio# "re+"ot-
e,"oure
i%%u#i-atio#
"re+"ot-
e,"oure
i%%u#i-atio#
blood do#or
cree#i#&.
rik beha!ior
%odificatio#
"re+"ot-
e,"oure
i%%u#i-atio#.
rik beha!ior
%odificatio#
e#ure afe
dri#ki#&
/ater
Type of Hepatitis
Two Types of Viral Hepatitis
ENTERICALL TRAN!"ITTED
HE#ATITI!$
A and E
#ARENTERALL TRAN!"ITTED
HE#ATITI! $
B and C
T%e Li&er is t%e Tar'et
Electron "icro'rap% of
Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
HAV
Caued b$ a "icor#a!iru, Entero&irus *+
'hi i a %all, #o#-e#!elo"ed icoahedral "article, 27
#% i# dia%eter, co#tai#i#& a ssRNA 'enome
Clinical Features
0#cubatio# "eriod ,-. wee/s 1%ea# 22 da$3
Milder dieae tha# 4e"atiti 5. a$%"to%atic i#fectio#
are !er$ co%%o#, e"eciall$ i# childre#.
Adult, e"eciall$ "re&#a#t /o%e#, %a$ de!elo" %ore
e!ere dieae
Althou&h co#!alece#ce %a$ be "rolo#&ed, there i no
c%ronic form of the dieae.
HAV
athogenesis
6iru e#ter !ia the &ut. re"licate i# the
ali%e#tar$ tract a#d "read to i#fect the li!er,
/here it %ulti"lie i# he"atoc$te.
Complications
Ful%i#a#t he"atiti i rare) 0.78 of cae
Viraemia is transient0
Virus is e1creted in t%e stools for two wee/s
precedin' t%e onset of symptoms.
HAV
!pidemiology
World-/ide ditributio#. endemic in most
countries. 'he i#cide#ce i# firt /orld cou#trie
i decli#i#&. 'here i a# e"eciall$ hi&h
i#cide#ce i# de!elo"i#& cou#trie a#d rural
area.
0# rural area of Africa, for e,a%"le, the
ero"re!ale#ce i 23340
HAV
Transmission " !nteric
9ar&e #u%ber of !iru "article are e,creted
i# tool, before the o#et of $%"to%.
2) Case-to-case via faecal-oral route.
:utbreak i# cr;che are !er$ co%%o#.
+) Contamination of food or water wit%
sewa'e
0#fected food ha#dler
*hell fih &ro/# i# e/a&e-"olluted /ater
Geo&raphic 'istri(ution of H"V
Infection
Anti-HAV #re&alence
Hi'%
Intermediate
Low
Very Low
"&e-specific )ortality 'ue to
Hepatitis "
"&e &roup
*years+
,ase-Fatality
*per -...+
<
5
3.0
5-14 1.6
15-29
1.6
30-49 3.8
>49 17.5
Total 4.1
*ource) 6iral 4e"atiti *ur!eilla#ce Pro&ra%, 7<2=-7<2<
HAV
#iagnosis
6iru ca##ot be cultured in vitro fro%
cli#ical %aterial, a#d dia&#oi i %ade o#
the "ree#ce of HAV-specific I'" i# the
"atie#t> blood
HAV
HAV
revention
7) assive immunisation -
Nor%al i%%u#o&lobuli# &i!e# to)
'ra!eller to third /orld cou#trie
4ouehold co#tact of acute cae
+) Active $mmunization
0#acti!ated cell culture-deri!ed !acci#e ha rece#tl$
beco%e a!ailable. #ot i# &e#eral ue
/ecommended 'oses and
Schedules
of Hepatitis " Vaccine
5roup A'e
No0
Doses EL0607 (ml)
!c%edule
(mont%s)
C%ildren and
Adolescents
+-28 years
, ,93 (30.) 3: 2: 9-2+
Adults ;28 years
+
2:<<3 (203)
3: 9-2+
Doses
HAVRI=
?@90*A u#it
Hepatitis E Virus (HEV)
Rece#tl$ ide#tified caue of e#tericall$
tra#%itted #o#-A, #o#-5 1NAN5) he"atiti
Calici&irus
"herical, #o# e#!elo"ed, 27-=A #% "article
co#tai#i#& a RNA &e#o%e.
Electron "icro'rap% of HEV
HEV
Clinical Features
0#cubatio# "eriod =0-A0 da$
Acute, elf li%iti#& he"atiti, #o chro#ic
carrier tate
A&e) "redo%i#a#tl$ $ou#& adult, 7B-A0
$ear
Complications
Ful%i#a#t he"atiti i# "re&#a#t /o%e#.
Mortalit$ rate i hi&h 1 u" to A08 3
Hepatitis E Virus Infection
0ypical Serolo&ic ,ourse
1ee2s after
E3posure
0
i
t
e
r
Symptom
s
"40
I&G anti-HEV
I&) anti-HEV
Virus in stool
. - 5 6 7 8 9 : ; < -
.
-
-
-
5
-
6
HEV
athogenesis
*i%ilar to he"atiti A. !iru re"licate i#
the &ut i#itiall$, before i#!adi#& the li!er,
a#d !iru i hed i# the tool "rior to the
o#et of $%"to%.
6irae%ia i tra#ie#t. A lar&e i#oculu% of
!iru i #eeded to etablih i#fectio#.
Geo&raphic 'istri(ution of
Hepatitis E
HEV
!pidemiology
9ittle i k#o/# $et. 'he i#cide#ce of i#fectio#
a""ear to be lo/ i# firt /orld cou#trie.
2) Lar'e out>rea/s ha!e bee# decribed i#
0#dia, Me,ico a#d North Africa /here the
ource of i#fectio# i uuall$ &ro faecal
co#ta%i#atio# of dri#ki#& /ater u""lie.
+) Case-to-case transmission to houehold
co#tact a""ear to be u#co%%o#. 'hi
u&&et that a lar&e i#oculu% i #eeded to
etablih i#fectio#.
HEV
#iagnosis
No routi#e laborator$ tet are a!ailable a $et.
6iru ca##ot be cultured in vitro.
2) E"- By demonstratin' calici&irus-li/e particles
in t%e stool: >y electron microscopy
+) Virus-!pecific I'" in serum
,) #CR - HEV-specific se?uences in stool
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
Hepadna &irus
A2 #% 6irio# 1alo k#o/# a CDa#e
"articleC3 co#tai# a circular dDNA &e#o%e
HBV Anti'ens
HBsA' E urface 1coat3 "rotei#
"roduced i# e,ce a %all "here a#d tubule
HBcA' E i##er core "rotei#
HBeA' E ecreted "rotei#. fu#ctio# u#k#o/#
Electron "icro'rap% of HBV
HBV
Clinical Features
0#cubatio# "eriod 2 - B %o#th
0#idiou o#et of $%"to%.
'e#d to caue a %ore e!ere dieae tha#
4e"atiti A.
A$%"to%atic i#fectio# occur freFue#tl$.
HBV
athogenesis
0#fectio# i parenterally transmitted. 'he
!iru re"licate i# the li!er a#d !iru "article,
a /ell a e,ce !iral urface "rotei#, are
hed i# lar&e a%ou#t i#to the blood.
6irae%ia i "rolo#&ed a#d the >lood of
infected indi&iduals is %i'%ly infectious.
Course of HBV Infection
HBV C%ronic Hepatitis
HBV
Complications
2) #ersistant infection)-
Follo/i#& acute i#fectio#, a""ro,i%atel$ B8 of
i#fected i#di!idual fail to eli%i#ate the !iru
co%"letel$ a#d beco%e persistently i#fected.
'hoe /ho are at particular ris/ include)
babie, $ou#& childre#
i%%u#oco%"ro%ied "atie#t
%ale G fe%ale
'he !iru "erit in the he"atoc$te a#d o#-
&oi#& li!er da%a&e occur becaue of the hot
i%%u#e re"o#e a&ai#t the i#fected li!er cell0
HBV
C%ronic infection %a$ take o#e of two
for%)
Chronic persistent %epatitis - the !iru
"erit, but there i %i#i%al li!er da%a&e
Chronic Active %epatitis - 'here i
a&&rei!e detructio# of li!er tiue a#d
ra"id "ro&reio# to cirrhoi or li!er failure
HBV
+) Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)0
Patie#t /ho beco%e "erite#tl$ i#fected are at rik of
de!elo"i#& HCC0
HBV i thou&ht to "la$ a role i# the de!elo"%e#t of thi
%ali&#a#c$ becaue)
a3 208 of "atie#t /ith 4CC are carrier of he"atiti 5.
b3 6iru DNA ca# be ide#tified i# he"atocellular carci#o%a
cell.
c3 6iru DNA ca# i#te&rate i#to the hot chro%oo%e.
,) @ulminant Hepatitis
Rare. accou#t for 78 of i#fectio#.
Hpatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
HBV
!pidemiology
#re&alence of disease
World-/ide there are AB0 %illio# "erita#t carrier of
he"atiti 5, B0 %illio# of /hich are i# Africa. Carria&e
rate !ar$ %arkedl$ i# differe#t area. 0# Africa, i#fectio#
i %uch %ore co%%o# i# rural co%%u#itie tha# i# the
citie.
2) Blood$
5lood tra#fuio#, eru% "roduct,
*hari#& of #eedle, ra-or
'attooi#&, acu"u#cture
Re#al dial$i
:r&a# do#atio#
HBV
+) !e1ual intercourse
,) HoriAontal transmission i# childre#, fa%ilie, >cloe
"ero#al co#tact>.
'hi i the %a(or %ode of tra#%iio# i# Africa /here
the %a(orit$ of i#di!idual beco%e i#fected at bet/ee#
three a#d #i#e $ear of a&e.
4ori-o#tal tra#%iio# alo occur i# childre#>
i#titutio# a#d %e#tal ho%e.
<) Vertical transmission - "eri#atal tra#%iio# fro% a
carrier %other to her bab$
tra#"lace#tal 1rare3
duri#& deli!er$
"ot #atal , HHbreat feedi#& , HHcloe co#tact
Hi'% (84)$ AB8 of &lobal "o"ulatio#
I
lifeti%e rik of i#fectio# GJ08
I
earl$ childhood i#fectio# co%%o#
Intermediate (+4-*4)$ A=8 of &lobal
"o"ulatio#
I
lifeti%e rik of i#fectio# 208-J08
I
i#fectio# occur i# all a&e &rou"
Low (B+4)$ 728 of &lobal "o"ulatio#
I
lifeti%e rik of i#fectio# K208
I
%ot i#fectio# occur i# adult rik &rou"
Glo(al Patterns of ,hronic H#V
Infection
Geo&raphic 'istri(ution of ,hronic
H#V Infection
HBsA' #re&alence
84 - Hi'%
+-*4 - Intermediate
B+4 - Low
HBV 5enotypes
Acute Hepatiti B !i"u #$%ectio$ &it'
(eco)e"*
1ee2s after
E3posure
0iter
!ymptoms
HBeA' anti-HBe
Total anti-HBc
I'" anti-HBc
anti-HBs
HBsA'
3 < 8 2+ 29 +3 +< +8 ,+ ,9 .+ 233
+"o,"eio$ to C'"o$ic Hepatiti B !i"u
#$%ectio$
1ee2s after
E3posure
0iter
I'" anti-HBc
Total anti-
HBc
HBsA'
Acute
(9 mont%s)
HBeA'
C%ronic
(ears)
anti-HBe
3 < 8 2+ 29 +3 +< +8 ,+ ,9 .+
ears
Interpretation of !erolo'ical "ar/ers of
HBV
/is2 Factors for "cute
Hepatitis #
=nited States
7 Includes se1ual contact wit% acute cases: carriers: and multiple partners0
!ource$ CDC !entinel Counties !tudy of Viral Hepatitis
Heterose1ual7
(<24)
Homose1ual Acti&ity
(C4)
House%old Contact
(+4)
Healt% Care Employment
(24)
Dt%er (24)
6n/nown (,24)
InEectin'
Dru' 6se
(2.4)
-
+"e)e$t c'"o$ic HB! #$%ectio$
-
+"e)e$t c'"o$ic li)e" .ieae
-
+"e)e$t p"i/a"* 'epatocellula"
ca"ci$o/a
-
+"e)e$t acute */pto/atic HB!
i$%ectio$
Elimination of Hepatitis # Virus
0ransmission (y Vaccination
Objectives
-
+"e)e$t pe"i$atal HB! t"a$/iio$
-
(outi$e )acci$atio$ o% all i$%a$t
-
!acci$atio$ o% c'il."e$ i$ 'i,'-"i0 ,"oup
-
!acci$atio$ o% a.olece$t
1
all u$)acci$ate. c'il."e$ at 11-12 *ea" o%
a,e
1
2'i,'-"i03 a.olece$t at all a,e
-
!acci$atio$ o% a.ult i$ 'i,'-"i0 ,"oup
Ho% ,an 1e Eliminate Hepatitis #
Virus 0ransmission
Strategy
HBV
#re&ention
2) Acti&e ImmuniAation
Two t$"e of &accine are a!ailable)
2) !erum deri&ed - "re"ared fro% 45A& "urified fro%
the eru% of 456 carrier
+) Recom>inant HBsA' - %ade b$ &e#etic e#&i#eeri#& i#
$eat
5oth !acci#e are eFuall$ afe a#d effecti!e. 'he
ad%i#itratio# of three doe i#duce "rotecti!e le!el of
a#tibodie i# <B8 of !acci#e reci"ie#t.
L#i!eral i%%u#i-atio# of i#fa#t /a i#troduced i# A"ril
7<<B. Infants recei&e , doses at 9: 23 and 2< wee/s
of a'e
HBV
6acci#e hould be ad%i#itered to "eo"le at
F%i'% ris/G of i#fectio# /ith 456)
2) Healt% care wor/ers
+) !e1ual partners of c%ronic carriers
,) Infants of HBV carrier mot%ers
HBV
+) #assi&e Anti>ody
High titer hepatitis B specific immune globulin
hould be ad%i#itered to #o# i%%u#e
i#di!idual follo/i#& i#&le e"iode e,"oure to
456-i#fected blood.
For e,a%"le) #eedle tick i#(urie
HBV
73 0#terfero# alp%a or >eta
23 9a%i!udi#e 1='C3
=3 Adefo!ir a#d other M#e/N a#ti!iral
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
'he %a(or caue of parenterally transmitted
non A non B %epatitis. 0t eluded ide#tificatio# for
%a#$ $ear. 0# 7<2<, the &e#o%e /a clo#ed
fro% the eru% of a# i#fected chi%"a#-ee.
&irology
HCV i a Fla!i!iru.
'hu "robabl$ e#!elo"ed.
4a a RNA &e#o%e
Doe #ot &ro/ i# cell culture, but ca# i#fect
Chi%"a#-ee
HCV
Incu>ation period
Incu>ation period
A&era'e 9-* w/s
A&era'e 9-* w/s
Ran'e +-+9
Ran'e +-+9
Acute illness (Eaundice)
Acute illness (Eaundice)
"ild (
"ild (
B
B
+34)
+34)
Case fatality rate
Case fatality rate
Low
Low
C%ronic infection
C%ronic infection
*.4-8.4
*.4-8.4
C%ronic %epatitis
C%ronic %epatitis
*34 (most as1)
*34 (most as1)
Cirr%osis
Cirr%osis
234-+34
234-+34
"ortality from CLD
"ortality from CLD
24-.4
24-.4
HCV
Clinical Features
0#cubatio# "eriod J-2 /eek
Caue a %ilder for% of acute he"atiti tha#
doe he"atiti 5
5ut B08 i#di!idual de!elo" chro#ic i#fectio#,
follo/i#& e,"oure.
Complications
73 Chro#ic li!er dieae
23 4e"atocellular carci#o%a
Serologic Pattern of Acute HCV Infection
with Recovery
Symptoms +/-
ime after
!"posure
i
t
e
r
anti-
HCV
A#
$ormal
% & ' ( ) * + & ' ( )
,ears -onths
HCV R$A
Serologic Pattern of Acute HCV Infection with
Progression to Chronic Infection
Symptoms +/-
ime after
!"posure
i
t
e
r
anti-
HCV
A#
$ormal
% & ' ( ) * + & ' ( )
,ears -onths
HCV R$A
HCV Transmission
#ercutaneous
I
Clotti#& factor before !iral i#acti!atio#
I
'ra#fuio#, tra#"la#t fro% i#fected do#or
I
'hera"eutic 1co#ta%i#ated eFui"%e#t, u#afe
i#(ectio# "ractice3
I
:ccu"atio#al 1#eedletick3
#ermucosal
I
Peri#atal
I
0#(ecti#& dru& ue
I
*e,ual
C%ronic Hepatitis C
@actors #romotin' #ro'ression or !e&erity
0#creaed alcohol i#take
A&e G A0 $ear at ti%e of i#fectio#
406 co-i#fectio#
H:ther
Male &e#der
:ther co-i#fectio# 1e.&., 4563
*ource) *e#ti#el Cou#tie, CDC
!ources of Infection for
#ersons wit% Hepatitis C
Se"ual &*.
/ther0 *.
1n2nown &%.
In3ecting 4rug use +%.
ransfusion &%.
56efore screening7
0$osocomial8 Health-care wor28 Perinatal
HCV Dia'nosis
2) !erolo'y
Reliable erolo&ical tet ha!e o#l$ rece#tl$
beco%e a!ailable. Pree#ce of HCV-specific
I'5 i#dicate e1posure but #ot infecti&ity
+) Viral RNA Detection
#CR detect &iral RNA 1&e#o%e3 i# "atie#t>
eru%. Pree#ce of HCV RNA i# the blood
i#dicate current or c%ronic infections
HCV Treatment
2) Recom>inant interferon H Ri>a&irin
+) #e'ylated interferon H Ri>a&irin
Hepatitis Delta Virus (HDV)
Defecti&e &irus /hich reFuire 4e"atiti 5 a a
hel"er !iru i# order to re"licate. 0#fectio#
therefore only occurs in patients 'ho are
already in(ected 'ith %epatitis ).
Clinical Features
0#creaed e!erit$ of li!er dieae i# 4e"atiti 5
HDV
&irology
!iru "article =J #% i# dia%eter
e#ca"ulated /ith 45A&, deri!ed fro% 456
delta a#ti&e# i aociated /ith !iru "article
RNA &e#o%e
!pidemiology
0de#tified i# i#tra-!e#ou dru& abuer i# 0tal$.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- A Brief List of Old Wives TalesДокумент3 страницыA Brief List of Old Wives TalesMelissaОценок пока нет
- About VaginaДокумент13 страницAbout VaginaRazend Muhd0% (1)
- Toolbox Talk CylindersДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk CylindersAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- Toolbox Talk CylindersДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk CylindersAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- قواعد الانجليزية كاملة اهداء صفحة المدرس بوكДокумент40 страницقواعد الانجليزية كاملة اهداء صفحة المدرس بوكboudekhanaОценок пока нет
- Toolbox Talk ConstructionДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk ConstructionAdel Suker100% (1)
- Toolbox Talk ErgonomicsДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk ErgonomicsAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- Toolbox Talk Fire SafetyДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk Fire SafetyAdel Suker0% (1)
- Bott Mech Toolbox TalksДокумент266 страницBott Mech Toolbox TalksAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- F. Y. B. Sc. (Zoology) Question BankДокумент51 страницаF. Y. B. Sc. (Zoology) Question BankHassan Ahmed100% (2)
- Incident Report of BP TexasДокумент341 страницаIncident Report of BP TexasUmar Khan100% (1)
- Case Presentation PreeclampsiaДокумент41 страницаCase Presentation PreeclampsiaJomari Zapanta50% (2)
- Toolbox Talk DrivingДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk DrivingAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- Toolbox Talk DrivingДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk DrivingAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- Toolbox Talk ElectricalДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk ElectricalAdel Suker100% (1)
- Classification of Neutrophilic Granulocytes 2000Документ1 страницаClassification of Neutrophilic Granulocytes 2000Gregorio De Las Casas100% (1)
- Oil and Gas Revision 2Документ11 страницOil and Gas Revision 2Adel SukerОценок пока нет
- National Geographic Little Kids - 03 2019 - 04 2019Документ35 страницNational Geographic Little Kids - 03 2019 - 04 2019florenciaОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 Admission Procedure of Women in LabourДокумент30 страницUnit 3 Admission Procedure of Women in LabourNishaThakuriОценок пока нет
- ImpressionДокумент7 страницImpressionAnnisa Nur AmalaОценок пока нет
- GRI 2: General Disclosures 2021: Universal StandardДокумент58 страницGRI 2: General Disclosures 2021: Universal StandardAlfita PutrimasiОценок пока нет
- Vacuum Leak Test ProcedureДокумент6 страницVacuum Leak Test ProcedureTomy George100% (4)
- Modelconfspace PDFДокумент13 страницModelconfspace PDFAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- TENSESДокумент9 страницTENSESworld of innovationОценок пока нет
- Tenses TableДокумент5 страницTenses Tableapi-314670535Оценок пока нет
- Indg402 PDFДокумент7 страницIndg402 PDFKheireddine AounallahОценок пока нет
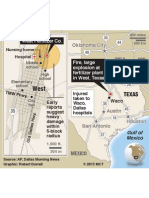
- Location of West, Texas, Plant ExplosionДокумент1 страницаLocation of West, Texas, Plant ExplosionThe State Newspaper0% (1)
- IOC Fire IncidentДокумент32 страницыIOC Fire Incidentnimesh_patel_indira101Оценок пока нет
- ASCO Final v1 ColorДокумент10 страницASCO Final v1 ColorAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- Toolbox Talk BiospillДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk BiospillAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- Toolbox Talk ConfspaceДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk ConfspaceAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- Toolbox Talk BiospillДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk BiospillAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- tbt3 TДокумент1 страницаtbt3 TAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- Toolbox Talk BicycleДокумент1 страницаToolbox Talk BicycleAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- Conabeare Acoustics Tool Box Talks July 2010Документ126 страницConabeare Acoustics Tool Box Talks July 2010Adel SukerОценок пока нет
- NZ Fire Behaviour Toolkit: User Guide and Technical: June 2008Документ32 страницыNZ Fire Behaviour Toolkit: User Guide and Technical: June 2008Adel SukerОценок пока нет
- Special Edition Fire BehaviorДокумент11 страницSpecial Edition Fire BehaviorAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- HK Ocean Park (Wednesday 8am) (Read-Only)Документ22 страницыHK Ocean Park (Wednesday 8am) (Read-Only)Ajay GopalОценок пока нет
- 2.movers Pratice Test - RW Part 1 - 2Документ20 страниц2.movers Pratice Test - RW Part 1 - 2Ngoc Huyen HoangОценок пока нет
- Ang Inahing Manok at Ang Kanyang Mga SisiwДокумент13 страницAng Inahing Manok at Ang Kanyang Mga SisiwKaren Kichelle Navarro EviaОценок пока нет
- The Revision Test 2014Документ3 страницыThe Revision Test 2014Danang SatrioОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент41 страницаUntitledReham Ricka ValmonteОценок пока нет
- Articles, Determiners & Quantifiers Set 1Документ25 страницArticles, Determiners & Quantifiers Set 1fatoОценок пока нет
- Activity Book 1º - EstudianteДокумент89 страницActivity Book 1º - EstudianteJULIO CESARОценок пока нет
- Budidaya Maggot Lalat Black Soldier Flies (BSF) Sebagai Pakan TernakДокумент5 страницBudidaya Maggot Lalat Black Soldier Flies (BSF) Sebagai Pakan TernakMiqdadОценок пока нет
- Topic PPT Bone StructureДокумент14 страницTopic PPT Bone StructureMoonОценок пока нет
- Exam (1) On Unit (1) :: Connect Plus 4 - 1st TermДокумент12 страницExam (1) On Unit (1) :: Connect Plus 4 - 1st TermHassan k1455 rashidОценок пока нет
- Mixed Dentition AnalysisДокумент6 страницMixed Dentition AnalysisJess JesiОценок пока нет
- Learn English Podcasts Elementary 01 02 TranscriptДокумент5 страницLearn English Podcasts Elementary 01 02 TranscriptrosebudkstОценок пока нет
- Types of Reproduction: Sexual AsexualДокумент45 страницTypes of Reproduction: Sexual AsexualasdОценок пока нет
- Chapter-2 Profile of Karbi Anglong DistrictДокумент37 страницChapter-2 Profile of Karbi Anglong DistrictDiganta Kumar GogoiОценок пока нет
- Animals SimilesДокумент1 страницаAnimals SimilesacademiaedelОценок пока нет
- a hero of our time (当代英雄)Документ165 страницa hero of our time (当代英雄)JingОценок пока нет
- Hydrocoele PDFДокумент1 страницаHydrocoele PDFSaugat PantОценок пока нет
- The Warm-Up: Sabina Rubio SánchezДокумент19 страницThe Warm-Up: Sabina Rubio Sánchezsabirubiosa5741Оценок пока нет
- TESTДокумент5 страницTESTnoralizaaliОценок пока нет
- L4 Directed Writing Insert ZooparkДокумент4 страницыL4 Directed Writing Insert ZooparkPranavОценок пока нет
- Family Members Possessive CaseДокумент6 страницFamily Members Possessive CaseClaudia SamfiraОценок пока нет
- Clavus, Ingrown Nail, Skin Epithelial CystsДокумент11 страницClavus, Ingrown Nail, Skin Epithelial CystsRafiОценок пока нет