Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Physics2013 hw5
Загружено:
Jake QiaoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics2013 hw5
Загружено:
Jake QiaoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Quantum mechancis
Homework 5
Zhihao Qiao
u5362850
Question 1
we know that
p
=
i
o
ox
the momentum operator
the expected value of momentum
< p
> =
]
o
o
-
|
i
]
o
ox
dx
d<p
>
dt
=
d
dt
]
o
o
-
|
i
]
o
ox
dx
d<p
>
dt
=
i
]
o
o d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] dx
Now we evaulate
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] first
By product rule
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] =
o
-
ot
o
ox
+
- o
ox
o
ot
By the TDSE
i
o
ot
=
2
2 m
o
2
ox
2
+V
o
ot
=
i
2 m
o
2
ox
2
i
o
-
ot
=
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
+
i
-
thus
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] =
o
-
ot
o
ox
+
- o
ox
o
ot
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] =
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
+
i
o
ox
+
- o
ox
i
2 m
o
2
ox
2
i
Now subsitute this into
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] to the integral
d<p
>
dt
=
i
]
o
o d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] dx
=
i
]
o
o
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
+
i
o
ox
+
- o
ox
i
2 m
o
2
ox
2
i
dx
=
i
]
o
o
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
+
i
-
o
ox
+
- i
2 m
o
ox
o
2
ox
2
i
- o
ox
|V
] dx
=
i
]
o
o
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
+
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx+
i
]
o
o i
-
V
o
ox
i
- o
ox
|V
]] dx
=
2
2 m
]
o
o
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx+
]
o
o
-
|V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
]] dx
we evaluate the first term firstly
2
2 m
]
o
o
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx
evaluate
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx by parts
let u =
o
ox
du =
o
2
ox
2
dv =
o
2
-
ox
2
v =
o
-
ox
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx =
o
ox
o
-
ox
j
o
o
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx since the particle cannot be at
infinity - boundary condition thus
o
ox
o
-
ox
j
o
o
= 0
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx =
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx
evaluate
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx by parts
let u =
-
du =
o
-
ox
dv =
o
ox
o
2
ox
2
v =
o
2
ox
2
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx = _
-
o
2
ox
2
o
o
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx since the particle cannot be
at infinity - boundary condition thus _
-
o
2
ox
2
o
o
= 0
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx =
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx
thus
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx =
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx =
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx terms cancel out
so
2
2 m
]
o
o
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx = 0
then back to the first integral
d<p
>
dt
=
i
]
o
o d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] dx
= 0+
]
o
o
-
|V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
]] dx
since
o
ox
|V
] = V
o
ox
+
oV
ox
thus V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
] =
oV
ox
d<p
>
dt
=
]
o
o
-
|V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
]] dx =
]
o
o
oV
ox
dx = <
oV
ox
>
thus we proved that
d<p
>
dt
= <
oV
ox
>
Question 2
Calculate the momentum operator
we can express any wavefunctions as a sum of the basis states and this
includes the wavefunction p
(z)
p
(z) = _
m
p
mn
mn
(z)
and we can find the coefficent
p
mn
=
]
0
L
m
-
(z) p
n
(z) dz
since the momentum operator
p
=
i
o
oz
thus
p
mn
=
2
L
]
0
L
m
-
(z)
i
o
oz
n
(z) dz
p
mn
=
i
2
L
]
0
L
m
-
(z)
o
oz
n
(z) dz
Which for the infinite square ware we can evaluate
For m=n.
p
mn
=
i
2
L
]
0
L
sin|
mz
L
]
o
oz
sin|
nz
L
] dz = <
m
p
n
>
p
mn
=
i
2
L
]
0
L
sin|
mz
L
]
n
L
cos|
nz
L
] dz
p
mn
=
2 n
L
2
i
]
0
L
sin|
mz
L
] cos|
nz
L
] dz
Thus
p
mn
=
2 n
L
2
i
_
L (mmCos[m] Cos[n ]n Sin[m] Sin[n ])
|m
2
n
2
]
When m
since m and n are natural numbers , so sin(m)=sin(n) = 0
so
p
mn
=
2 n
L
2
i
_
L (mmCos[m] Cos[n ])
|m
2
n
2
]
if m+n is even number then cos(m)cos(n) = 1
if m+n is odd number then cos(m)cos(n) = -1
thus Cos[m ] Cos[n ] = 1
m+n
so
p
mn
=
i
2 n
L
2
_
L |mm(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
p
mn
=
i
2 n
L
2
mL |1(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
p
mn
=
i
2 mn
L
|1(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
for m=n.
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
Quantum mechancis
Homework 5
Zhihao Qiao
u5362850
Question 1
we know that
p
=
i
o
ox
the momentum operator
the expected value of momentum
< p
> =
]
o
o
-
|
i
]
o
ox
dx
d<p
>
dt
=
d
dt
]
o
o
-
|
i
]
o
ox
dx
d<p
>
dt
=
i
]
o
o d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] dx
Now we evaulate
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] first
By product rule
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] =
o
-
ot
o
ox
+
- o
ox
o
ot
By the TDSE
i
o
ot
=
2
2 m
o
2
ox
2
+V
o
ot
=
i
2 m
o
2
ox
2
i
o
-
ot
=
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
+
i
-
thus
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] =
o
-
ot
o
ox
+
- o
ox
o
ot
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] =
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
+
i
o
ox
+
- o
ox
i
2 m
o
2
ox
2
i
Now subsitute this into
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] to the integral
d<p
>
dt
=
i
]
o
o d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] dx
=
i
]
o
o
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
+
i
o
ox
+
- o
ox
i
2 m
o
2
ox
2
i
dx
=
i
]
o
o
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
+
i
-
o
ox
+
- i
2 m
o
ox
o
2
ox
2
i
- o
ox
|V
] dx
=
i
]
o
o
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
+
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx+
i
]
o
o i
-
V
o
ox
i
- o
ox
|V
]] dx
=
2
2 m
]
o
o
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx+
]
o
o
-
|V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
]] dx
we evaluate the first term firstly
2
2 m
]
o
o
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx
evaluate
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx by parts
let u =
o
ox
du =
o
2
ox
2
dv =
o
2
-
ox
2
v =
o
-
ox
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx =
o
ox
o
-
ox
j
o
o
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx since the particle cannot be at
infinity - boundary condition thus
o
ox
o
-
ox
j
o
o
= 0
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx =
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx
evaluate
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx by parts
let u =
-
du =
o
-
ox
dv =
o
ox
o
2
ox
2
v =
o
2
ox
2
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx = _
-
o
2
ox
2
o
o
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx since the particle cannot be
at infinity - boundary condition thus _
-
o
2
ox
2
o
o
= 0
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx =
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx
thus
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx =
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx =
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx terms cancel out
so
2
2 m
]
o
o
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx = 0
then back to the first integral
d<p
>
dt
=
i
]
o
o d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] dx
= 0+
]
o
o
-
|V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
]] dx
since
o
ox
|V
] = V
o
ox
+
oV
ox
thus V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
] =
oV
ox
d<p
>
dt
=
]
o
o
-
|V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
]] dx =
]
o
o
oV
ox
dx = <
oV
ox
>
thus we proved that
d<p
>
dt
= <
oV
ox
>
Question 2
Calculate the momentum operator
we can express any wavefunctions as a sum of the basis states and this
includes the wavefunction p
(z)
p
(z) = _
m
p
mn
mn
(z)
and we can find the coefficent
p
mn
=
]
0
L
m
-
(z) p
n
(z) dz
since the momentum operator
p
=
i
o
oz
thus
p
mn
=
2
L
]
0
L
m
-
(z)
i
o
oz
n
(z) dz
p
mn
=
i
2
L
]
0
L
m
-
(z)
o
oz
n
(z) dz
Which for the infinite square ware we can evaluate
For m=n.
p
mn
=
i
2
L
]
0
L
sin|
mz
L
]
o
oz
sin|
nz
L
] dz = <
m
p
n
>
p
mn
=
i
2
L
]
0
L
sin|
mz
L
]
n
L
cos|
nz
L
] dz
p
mn
=
2 n
L
2
i
]
0
L
sin|
mz
L
] cos|
nz
L
] dz
Thus
p
mn
=
2 n
L
2
i
_
L (mmCos[m] Cos[n ]n Sin[m] Sin[n ])
|m
2
n
2
]
When m
since m and n are natural numbers , so sin(m)=sin(n) = 0
so
p
mn
=
2 n
L
2
i
_
L (mmCos[m] Cos[n ])
|m
2
n
2
]
if m+n is even number then cos(m)cos(n) = 1
if m+n is odd number then cos(m)cos(n) = -1
thus Cos[m ] Cos[n ] = 1
m+n
so
p
mn
=
i
2 n
L
2
_
L |mm(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
p
mn
=
i
2 n
L
2
mL |1(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
p
mn
=
i
2 mn
L
|1(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
for m=n.
2 physics2013_hw5.nb
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
Quantum mechancis
Homework 5
Zhihao Qiao
u5362850
Question 1
we know that
p
=
i
o
ox
the momentum operator
the expected value of momentum
< p
> =
]
o
o
-
|
i
]
o
ox
dx
d<p
>
dt
=
d
dt
]
o
o
-
|
i
]
o
ox
dx
d<p
>
dt
=
i
]
o
o d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] dx
Now we evaulate
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] first
By product rule
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] =
o
-
ot
o
ox
+
- o
ox
o
ot
By the TDSE
i
o
ot
=
2
2 m
o
2
ox
2
+V
o
ot
=
i
2 m
o
2
ox
2
i
o
-
ot
=
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
+
i
-
thus
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] =
o
-
ot
o
ox
+
- o
ox
o
ot
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] =
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
+
i
o
ox
+
- o
ox
i
2 m
o
2
ox
2
i
Now subsitute this into
d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] to the integral
d<p
>
dt
=
i
]
o
o d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] dx
=
i
]
o
o
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
+
i
o
ox
+
- o
ox
i
2 m
o
2
ox
2
i
dx
=
i
]
o
o
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
+
i
-
o
ox
+
- i
2 m
o
ox
o
2
ox
2
i
- o
ox
|V
] dx
=
i
]
o
o
i
2 m
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
+
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx+
i
]
o
o i
-
V
o
ox
i
- o
ox
|V
]] dx
=
2
2 m
]
o
o
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx+
]
o
o
-
|V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
]] dx
we evaluate the first term firstly
2
2 m
]
o
o
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx
evaluate
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx by parts
let u =
o
ox
du =
o
2
ox
2
dv =
o
2
-
ox
2
v =
o
-
ox
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx =
o
ox
o
-
ox
j
o
o
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx since the particle cannot be at
infinity - boundary condition thus
o
ox
o
-
ox
j
o
o
= 0
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx =
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx
evaluate
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx by parts
let u =
-
du =
o
-
ox
dv =
o
ox
o
2
ox
2
v =
o
2
ox
2
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx = _
-
o
2
ox
2
o
o
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx since the particle cannot be
at infinity - boundary condition thus _
-
o
2
ox
2
o
o
= 0
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx =
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx
thus
]
o
o o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
dx =
]
o
o
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx =
]
o
o o
-
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx terms cancel out
so
2
2 m
]
o
o
o
2
-
ox
2
o
ox
- o
ox
o
2
ox
2
dx = 0
then back to the first integral
d<p
>
dt
=
i
]
o
o d
dt
|
-
|
o
ox
] ] dx
= 0+
]
o
o
-
|V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
]] dx
since
o
ox
|V
] = V
o
ox
+
oV
ox
thus V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
] =
oV
ox
d<p
>
dt
=
]
o
o
-
|V
o
ox
o
ox
|V
]] dx =
]
o
o
oV
ox
dx = <
oV
ox
>
thus we proved that
d<p
>
dt
= <
oV
ox
>
Question 2
Calculate the momentum operator
we can express any wavefunctions as a sum of the basis states and this
includes the wavefunction p
(z)
p
(z) = _
m
p
mn
mn
(z)
and we can find the coefficent
p
mn
=
]
0
L
m
-
(z) p
n
(z) dz
since the momentum operator
p
=
i
o
oz
thus
p
mn
=
2
L
]
0
L
m
-
(z)
i
o
oz
n
(z) dz
p
mn
=
i
2
L
]
0
L
m
-
(z)
o
oz
n
(z) dz
Which for the infinite square ware we can evaluate
For m=n.
p
mn
=
i
2
L
]
0
L
sin|
mz
L
]
o
oz
sin|
nz
L
] dz = <
m
p
n
>
p
mn
=
i
2
L
]
0
L
sin|
mz
L
]
n
L
cos|
nz
L
] dz
p
mn
=
2 n
L
2
i
]
0
L
sin|
mz
L
] cos|
nz
L
] dz
Thus
p
mn
=
2 n
L
2
i
_
L (mmCos[m] Cos[n ]n Sin[m] Sin[n ])
|m
2
n
2
]
When m
since m and n are natural numbers , so sin(m)=sin(n) = 0
so
p
mn
=
2 n
L
2
i
_
L (mmCos[m] Cos[n ])
|m
2
n
2
]
if m+n is even number then cos(m)cos(n) = 1
if m+n is odd number then cos(m)cos(n) = -1
thus Cos[m ] Cos[n ] = 1
m+n
so
p
mn
=
i
2 n
L
2
_
L |mm(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
p
mn
=
i
2 n
L
2
mL |1(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
p
mn
=
i
2 mn
L
|1(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
for m=n.
SetAttributesm, Constant
physics2013_hw5.nb 3
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
SetAttributesn, Constant
SetAttributesL, Constant
IntegrateSinm
z
L
Cosn
z
L
, z, 0, L
L m m Cosm Cosn n Sinm Sinn
m
2
n
2
For m = n
p
mn
=
2 n
L
2
i
]
0
L
sin|
nz
L
] cos|
nz
L
] dz
p
mn
=
L Sinn
2
2 n
since n is a natural number sin(n) always = 0
thus
p
mn
= 0 when m = 0
IntegrateSinn
z
L
Cosn
z
L
, z, 0, L
L Sinn
2
2 n
PART b
The particle in the infinite well which is the superposition with probability
1
3
being in the first state, probability 0 being in the second state and
probability
2
3
being in the third state
we know that the coeffiecnt is
p
mn
=
i
2 mn
L
|1(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
take m be the row and n be the coloum
The 3x3 matrix form of expectation values
p =
0
8
i3L
0
8
i3L
0
24
i5L
0
24
i5L
0
thus the mean value of momentum is
<p> =
1
3
e
iE
1
tf
0 e
iE
2
tf
2
3
e
iE
3
tf
0
8
i3L
0
8
i3L
0
24
i5L
0
24
i5L
0
1
3
e
iE
1
tf
0 e
iE
2
tf
2
3
e
iE
3
tf
=
0
8
i3 3 L
e
iE
1
tf
+
2 24
3 i5L
e
iE
3
tf
0
1
3
e
iE
1
tf
0 e
iE
2
tf
2
3
e
iE
3
tf
= 0
The mean value of momentum is zero and the time depend term is also 0
(c) calculate the expectation value of momentum if the state vector is a equal
superposition of second and third ISW eigenstates
That means the Pr for the first state is 0, for the second state is
1
2
and for the
third state is
1
2
since the 3x3 matrix is the same thus
p =
0 e
iE
1
tf 1
2
e
iE
2
tf
1
2
e
iE
3
tf
0
8
i3L
0
8
i3L
0
24
i5L
0
24
i5L
0
0 e
iE
1
tf
1
2
e
iE
2
tf
1
2
e
iE
3
tf
=
8
i 2 3 L
e
iE
2
tf 24
i5 2 L
e
iE
3
tf
24
i5 2 L
e
iE
2
tf
0 e
iE
1
tf
1
2
e
iE
2
tf
1
2
e
iE
3
tf
=
12
i5L
e
iE
3
tf
e
iE
2
tf
12
i5L
e
iE
2
tf
e
iE
3
tf
let E
3
t f =
3
E
2
t f =
2
=
12
i5L
e
iE
3
tf
e
iE
2
tf
12
i5L
e
iE
2
tf
e
iE
3
tf
=
12
i5L
[(cos
3
+isin
3
) (cos
2
isin
2
) (cos
2
+isin
2
) (cos
3
isin
3
)]
=
12
i5L
[2 isin
2
cos
3
+2 isin
3
cos
2
]
=
12
i5L
[2 isin
2
cos
3
+2 isin
3
cos
2
]
=
24
5 L
[sin
2
cos
3
+sin
3
cos
2
]
=
24
5 L
sin(
3
2
)
Hence we have
<p(t)> =
24
5 L
sin(
3
2
) where E
3
t f =
3
E
2
t f =
2
4 physics2013_hw5.nb
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
PART b
The particle in the infinite well which is the superposition with probability
1
3
being in the first state, probability 0 being in the second state and
probability
2
3
being in the third state
we know that the coeffiecnt is
p
mn
=
i
2 mn
L
|1(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
take m be the row and n be the coloum
The 3x3 matrix form of expectation values
p =
0
8
i3L
0
8
i3L
0
24
i5L
0
24
i5L
0
thus the mean value of momentum is
<p> =
1
3
e
iE
1
tf
0 e
iE
2
tf
2
3
e
iE
3
tf
0
8
i3L
0
8
i3L
0
24
i5L
0
24
i5L
0
1
3
e
iE
1
tf
0 e
iE
2
tf
2
3
e
iE
3
tf
=
0
8
i3 3 L
e
iE
1
tf
+
2 24
3 i5L
e
iE
3
tf
0
1
3
e
iE
1
tf
0 e
iE
2
tf
2
3
e
iE
3
tf
= 0
The mean value of momentum is zero and the time depend term is also 0
(c) calculate the expectation value of momentum if the state vector is a equal
superposition of second and third ISW eigenstates
That means the Pr for the first state is 0, for the second state is
1
2
and for the
third state is
1
2
since the 3x3 matrix is the same thus
p =
0 e
iE
1
tf 1
2
e
iE
2
tf
1
2
e
iE
3
tf
0
8
i3L
0
8
i3L
0
24
i5L
0
24
i5L
0
0 e
iE
1
tf
1
2
e
iE
2
tf
1
2
e
iE
3
tf
=
8
i 2 3 L
e
iE
2
tf 24
i5 2 L
e
iE
3
tf
24
i5 2 L
e
iE
2
tf
0 e
iE
1
tf
1
2
e
iE
2
tf
1
2
e
iE
3
tf
=
12
i5L
e
iE
3
tf
e
iE
2
tf
12
i5L
e
iE
2
tf
e
iE
3
tf
let E
3
t f =
3
E
2
t f =
2
=
12
i5L
e
iE
3
tf
e
iE
2
tf
12
i5L
e
iE
2
tf
e
iE
3
tf
=
12
i5L
[(cos
3
+isin
3
) (cos
2
isin
2
) (cos
2
+isin
2
) (cos
3
isin
3
)]
=
12
i5L
[2 isin
2
cos
3
+2 isin
3
cos
2
]
=
12
i5L
[2 isin
2
cos
3
+2 isin
3
cos
2
]
=
24
5 L
[sin
2
cos
3
+sin
3
cos
2
]
=
24
5 L
sin(
3
2
)
Hence we have
<p(t)> =
24
5 L
sin(
3
2
) where E
3
t f =
3
E
2
t f =
2
physics2013_hw5.nb 5
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
PART b
The particle in the infinite well which is the superposition with probability
1
3
being in the first state, probability 0 being in the second state and
probability
2
3
being in the third state
we know that the coeffiecnt is
p
mn
=
i
2 mn
L
|1(1)
m+n
]
|m
2
n
2
]
take m be the row and n be the coloum
The 3x3 matrix form of expectation values
p =
0
8
i3L
0
8
i3L
0
24
i5L
0
24
i5L
0
thus the mean value of momentum is
<p> =
1
3
e
iE
1
tf
0 e
iE
2
tf
2
3
e
iE
3
tf
0
8
i3L
0
8
i3L
0
24
i5L
0
24
i5L
0
1
3
e
iE
1
tf
0 e
iE
2
tf
2
3
e
iE
3
tf
=
0
8
i3 3 L
e
iE
1
tf
+
2 24
3 i5L
e
iE
3
tf
0
1
3
e
iE
1
tf
0 e
iE
2
tf
2
3
e
iE
3
tf
= 0
The mean value of momentum is zero and the time depend term is also 0
(c) calculate the expectation value of momentum if the state vector is a equal
superposition of second and third ISW eigenstates
That means the Pr for the first state is 0, for the second state is
1
2
and for the
third state is
1
2
since the 3x3 matrix is the same thus
p =
0 e
iE
1
tf 1
2
e
iE
2
tf
1
2
e
iE
3
tf
0
8
i3L
0
8
i3L
0
24
i5L
0
24
i5L
0
0 e
iE
1
tf
1
2
e
iE
2
tf
1
2
e
iE
3
tf
=
8
i 2 3 L
e
iE
2
tf 24
i5 2 L
e
iE
3
tf
24
i5 2 L
e
iE
2
tf
0 e
iE
1
tf
1
2
e
iE
2
tf
1
2
e
iE
3
tf
=
12
i5L
e
iE
3
tf
e
iE
2
tf
12
i5L
e
iE
2
tf
e
iE
3
tf
let E
3
t f =
3
E
2
t f =
2
=
12
i5L
e
iE
3
tf
e
iE
2
tf
12
i5L
e
iE
2
tf
e
iE
3
tf
=
12
i5L
[(cos
3
+isin
3
) (cos
2
isin
2
) (cos
2
+isin
2
) (cos
3
isin
3
)]
=
12
i5L
[2 isin
2
cos
3
+2 isin
3
cos
2
]
=
12
i5L
[2 isin
2
cos
3
+2 isin
3
cos
2
]
=
24
5 L
[sin
2
cos
3
+sin
3
cos
2
]
=
24
5 L
sin(
3
2
)
Hence we have
<p(t)> =
24
5 L
sin(
3
2
) where E
3
t f =
3
E
2
t f =
2
6 physics2013_hw5.nb
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
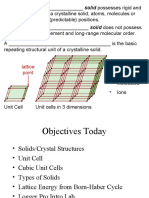
- HW 5Документ4 страницыHW 5Jake QiaoОценок пока нет
- Diet Coke and Mentos: What Is Really Behind This Physical Reaction?Документ7 страницDiet Coke and Mentos: What Is Really Behind This Physical Reaction?OrdoviciumОценок пока нет
- Problems On Stat Phys - Pag45Документ290 страницProblems On Stat Phys - Pag45Marco Antonio Reyes GarciaОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Physics2020 Week1Документ10 страницPhysics2020 Week1Jake QiaoОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition: X H A TДокумент3 страницыPrinted by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition: X H A TJake QiaoОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- IB Physics Practical Repor2Документ2 страницыIB Physics Practical Repor2Jake QiaoОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- AP Godse EDCДокумент35 страницAP Godse EDCSasi DharanОценок пока нет
- Iiser K SOP PDFДокумент2 страницыIiser K SOP PDFsaawanОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Skills Annexe and Epitome of WisdomДокумент102 страницыSkills Annexe and Epitome of WisdomsuhailfarhaanОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Suspension: Course Name: Pharmaceutical Technology-I Course Code: PHRM 3125Документ45 страницSuspension: Course Name: Pharmaceutical Technology-I Course Code: PHRM 3125Masum HossinОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Science 9 - Q2 - Mod3 - IONS-HOW-ARE-THEY-FORMED - VerFinalДокумент23 страницыScience 9 - Q2 - Mod3 - IONS-HOW-ARE-THEY-FORMED - VerFinalAbel Emmanuel Solitario CabralesОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Chem 2 Q1 Module 1 Attractive ForcesДокумент9 страницChem 2 Q1 Module 1 Attractive ForcesPrincess Venita BerganteОценок пока нет
- Properties of SolidsДокумент3 страницыProperties of SolidsJashmin LarozaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Lect-5Material Science SRM 1st Year Unit 1 LECTURE NOTES-6Документ54 страницыUnit 1 Lect-5Material Science SRM 1st Year Unit 1 LECTURE NOTES-6ECE A SRM VDP100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- RietveldДокумент25 страницRietveldTino RMFCОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Nonlinear Peltier Effect in Semiconductors.Документ4 страницыNonlinear Peltier Effect in Semiconductors.danielglezaОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Engineering Physics SemiconductersДокумент110 страницEngineering Physics SemiconductersGanguОценок пока нет
- QMДокумент92 страницыQMt ElderОценок пока нет
- Intro SolidsДокумент25 страницIntro SolidsCQChoongОценок пока нет
- Introduction of Physics ElectronicsДокумент263 страницыIntroduction of Physics ElectronicsChayito HerreraОценок пока нет
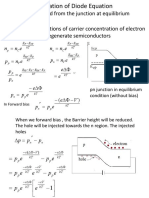
- Derivation of Diode EquationДокумент7 страницDerivation of Diode EquationSatyaОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Pilani Campus: Birla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniДокумент2 страницыPilani Campus: Birla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniANSHUMAN MISHRAОценок пока нет
- Chapter Two, The Structure of Crystalline Solids PDFДокумент23 страницыChapter Two, The Structure of Crystalline Solids PDFOmar Abu MahfouthОценок пока нет
- Inorganic Chemistry Chem-318 Lec 3Документ24 страницыInorganic Chemistry Chem-318 Lec 3Mahnoor ShakeelОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Endsem 2010Документ2 страницыEndsem 2010Prithviraj NetkeОценок пока нет
- Quantum MirageДокумент17 страницQuantum MirageajeshsvОценок пока нет
- QC DissertationДокумент85 страницQC DissertationAhmed MahmoudОценок пока нет
- Effect of Substitution of MN With Fe or CR in Heusler Alloy of Co2MnsnДокумент11 страницEffect of Substitution of MN With Fe or CR in Heusler Alloy of Co2MnsnΙήήΘςέήτ βόγОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Crystal Structure and Unit CellsДокумент8 страницCrystal Structure and Unit CellsChristianne Evarientos100% (1)
- DPP 20220411175616686155Документ52 страницыDPP 20220411175616686155Ronit NigamОценок пока нет
- LECTURE 06 - Latent Image FormationДокумент22 страницыLECTURE 06 - Latent Image FormationPradeepОценок пока нет
- RembertDuine SpintronicsДокумент81 страницаRembertDuine SpintronicsKirthi RkОценок пока нет
- Defects and Transport in Crystalline SolidsДокумент209 страницDefects and Transport in Crystalline SolidsKhánhОценок пока нет
- Elementary ParticlesДокумент23 страницыElementary ParticlesWarrior DroyОценок пока нет
- HW 4Документ2 страницыHW 4Saied Aly SalamahОценок пока нет
- Phase DiagramДокумент36 страницPhase DiagramMobashawir AlamОценок пока нет