Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Honors Economics Unit 1 Guide
Загружено:
John FlairИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Honors Economics Unit 1 Guide
Загружено:
John FlairАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name:
Date:
Hour:
Fundamentals of Economics
Unit One Review Guide:
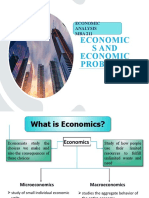
1) What is economics?
Study of choices people make to satisfy needs and events
2) What are the factors of production?
Natural resources, human resources, capital resources, and entrepreneurship
3) What is the goal of entrepreneurship?
To take a financial risk and start or improve a product
4) Why is scarcity a basic problem of economics?
Resources are limited, but wants are unlimited. Forces decisions on allocation of
resources.
5) What issues must producers address to distribute/allocate resources?
What to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce.
6) Why do producers study productivity?
To see if resources are being used wisely.
7) Why is sacrifice an important element of economic choice?
For each decision we make, there is a certain opportunity cost. We are sacrificing the
next best alternative each time. In production, resource causes opportunities sacrificed.
8) What assumptions are involved in creating a PPC?
Show all the possible combinations of two goods/services that can be produced
Assumes that available resources/technology is constant and that all resources are used in
most efficient manner possible.
9) Why might future production possibilities differ from current production
possibilities?
Increase in technology, change in resource availability, more efficient processes.
10) What are the difficulties associated with barter?
It is hard to give specific monetary values to each item. Therefore, money.
11) Why is true self sufficiency rare?
One would have to make everything one usesclothes, meals, food, shelter, computers,
any other materials. It is very difficult to provide all this for oneself.
12) What are the economic benefits of interdependence? What are the negatives?
Interdependence means that people can specialize and increase the efficiency and
productivity of processes. Negatives: everything is linked, so when something crashes,
everything crashes.
13) How are the three basic economic questions answered in traditional, command, and
market economies?
Traditional Economies: rural, non-developed countries. Customs govern economic
decisions. Tech not used widely. Farming, hunting/gathering. Focused on family unit.
For: family. What: basics. How: simple methods.
Command Economies: government makes decisions, allocates resources. Less individual
freedom, no competition, but not profit central (USSR). For: consumers: What: not
multiple brands. How: extensive regulation.
Market Economies: Resources are used and controlled by individuals. Decisions are
motivated by profit. More individual freedoms, competition. For: consumers. What:
everything, many types. How: profit-incentivized.
14) What are the roles of self-interest and incentives in a market economy?
Invisible hand: People will want to maximize their profits, and they usually get more
money by serving other people by producing the best products. It is in the best interest of
both producers and consumers. Incentive: maximize utility
15) What types of mixed economies exist today?
Mixed: government regulation in market economy. Individuals own means of production.
Protect from unfair things. Most effective. US and China.
16) What are the basic principles of free enterprise in the United States?
Resources, products, and money are exchanged.
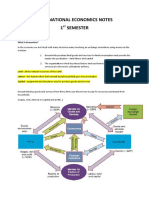
17) What are the two markets of the circular flow model?
Resource and product markets
18) List and explain the 5 sectors of the circular flow model discussed in class.
Homes: pay taxes, get products/services
Businesses: pay taxes, sell goods and services
Government: employer, exchanges money for labor. Consumer, purchases goods. Firm:
offers goods/services
Financial institutions: borrowing/lending money
International sector: global, makes an economy open
19) How does the circular flow model reflect exchange?
Each of the five sectors acts as both a resource and product consumer/seller. There is
constant exchange between the markets.
20) How do nations decide how to use scarce resources?
Allocation lol
21) What are the major goals of U.S. economic policy?
Freedom, efficiency, equity, security, stability, growth
22) Why do economic goals sometimes conflict?
Because different parties have different interests that get in the way of each other. No
growth without loss of stability and security. No equity with freedom.
23) Discuss the determinants of Supply and Demand
Demand: Price, income, Price of related goods, Tastes, Expectations
Supply: Price, Input costs, Technology, Expectations
1. Economics: Study of choices to satisfy needs and wants
2. Economist: studies economics
3. Microeconomics: Study of choices in households, companies, and individual markets.
4. Macroeconomics: Entire economy, like uneployment.
5. Consumers: buy things
6. Producers: make things
7. Goods: things people purchase
8. Services: actions for fees
9. Resources: things needed for production
10. Factors of Production: natural/human/capital resources, entrepreneurship
11. Natural Resources: minerals, ore
12. Human Resources: labor
13. Capital Resources: infrastructure, machines, plants
14. Capital goods: machines for production
15. Consumer goods: things bought for consumption
16. Technology: increases supply, PPC.
17. Entrepreneurship: willingness/ability to take financial risk and start/improve a product
18. Entrepreneur: someone who does above
19. Scarcity: lack of resources (limited), but wants unlimited
20. Allocate: setting resources to certain uses
21. Productivity: Level of output from given input.
22. Efficiency: How effectively resources are being used.
23. Division of labor: Increases productivity, makes people do specific job
24. Specialization: people do specific job, increases productivity
25. Trade-off: if resource is used for certain thing, cant be used for something else
26. Opportunity cost: next best alternative that is given up for preferred item
27. Production possibilities curve (PPC): plots levels of two resources that can be produced.
28. Exchange: something given for something else
29. Barter: exchange of goods or services for other goods/services
30. Money: used as monetary value for goods/services, in exchange.
31. Utility: happiness
32. Self-sufficiency: producing everything one uses
33. Interdependence: everyone in world is dependent on products/goods from other places
34. Demand: how much of something is wanted
35. Supply: how much is available
36. Law of Supply: more price = more supply
37. Law of Demand: more price = less demand
38. Law of Supply and Demand: natural force of market pushes quantity supplied and
demanded to an equilibrium condition
39. Equilibrium: quantity supplied and demanded are equal.
Вам также может понравиться
- TermsДокумент3 страницыTermsToni Ann DunnОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 - Economic Issues and ConceptsДокумент87 страницLecture 1 - Economic Issues and ConceptsB-ton LimbeОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of EconomicsДокумент59 страницFundamentals of EconomicsUwuigbe UwalomwaОценок пока нет
- Economics: The Study of How Scarce, or Limited, Resources Are Used To Satisfy People's Unlimited Material Wants and NeedsДокумент15 страницEconomics: The Study of How Scarce, or Limited, Resources Are Used To Satisfy People's Unlimited Material Wants and NeedsNIKNISHОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1Документ26 страницLesson 1JAPSON, PRINCESS VОценок пока нет
- Toaz - Info CXC Economics Study Guide PRДокумент31 страницаToaz - Info CXC Economics Study Guide PRRickoy Playz100% (1)
- Micro 111 C1 by NayemДокумент10 страницMicro 111 C1 by NayemHasibul Hasan NayemОценок пока нет
- Economics NotesДокумент2 страницыEconomics Notesmalloi96Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 01 Principles of Economics Handout 1Документ42 страницыLesson 01 Principles of Economics Handout 1seyon sithamparanathanОценок пока нет
- Economics Notes: 1.1 - Basic Economic Problem: Choice and The Allocation of ResourcesДокумент52 страницыEconomics Notes: 1.1 - Basic Economic Problem: Choice and The Allocation of ResourcesMukmin Shukri100% (1)
- Applied Econ. Lesson 1Документ36 страницApplied Econ. Lesson 1Robert BalinoОценок пока нет
- Econ - C1 - Review GameДокумент2 страницыEcon - C1 - Review GameTARSEHSОценок пока нет
- Principles of Economics 1Документ36 страницPrinciples of Economics 1reda gadОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Exam Review Packet-RevisedДокумент6 страницUnit 1 Exam Review Packet-RevisedNoelia OliveroОценок пока нет
- Microeconomics By: Zemach Lemecha (M.SC, Asst. Prof.) : Semester I, 2015Документ251 страницаMicroeconomics By: Zemach Lemecha (M.SC, Asst. Prof.) : Semester I, 2015Binkisa Billo0% (1)
- AP Macro - 1.25.24Документ97 страницAP Macro - 1.25.24M KОценок пока нет
- SIU Principles Of: EconomicsДокумент48 страницSIU Principles Of: EconomicsMohammed YassinОценок пока нет
- Unit 1: Introduction, Economics AS A Social Science AND THE Economic ProblemsДокумент3 страницыUnit 1: Introduction, Economics AS A Social Science AND THE Economic ProblemsMelannyОценок пока нет
- Resource Utilization and EconomicsДокумент5 страницResource Utilization and EconomicsmalindaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Economics: Cindy QuaileДокумент29 страницIntroduction To Economics: Cindy QuaileMary Elizabeth ApolonioОценок пока нет
- Intro To Economics 2013Документ28 страницIntro To Economics 2013John Louis PulidoОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Agricultural Economics (AEB 212) : Group: Student Numbers: VENUE: Lecture Theatre 311/003Документ46 страницIntroduction To Agricultural Economics (AEB 212) : Group: Student Numbers: VENUE: Lecture Theatre 311/003Thabo ChuchuОценок пока нет
- Economics Scarce Resources: Labor, Capital, and Entrepreneurship Will Lead To The Production of ApplesДокумент6 страницEconomics Scarce Resources: Labor, Capital, and Entrepreneurship Will Lead To The Production of ApplesEmilio JacintoОценок пока нет
- Rift Valley University Harar Campus Introduction To EcononicsДокумент23 страницыRift Valley University Harar Campus Introduction To EcononicsUkash sukarmanОценок пока нет
- Econ Unit 1 Fundamentals NotesДокумент6 страницEcon Unit 1 Fundamentals NotesClive BurnettОценок пока нет
- Definitions of Ten Different Authors of EconomicДокумент5 страницDefinitions of Ten Different Authors of EconomicGames destroyerОценок пока нет
- 3 B Revision NotesДокумент169 страниц3 B Revision NotesAurelia KimОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Business and Its EnvironmentДокумент28 страницUnit 1 Business and Its EnvironmentMaham ButtОценок пока нет
- Macroeconomics: 1. MicroeconomicsДокумент30 страницMacroeconomics: 1. MicroeconomicsVictoria GalenkoОценок пока нет
- Learning Module: Prepared byДокумент23 страницыLearning Module: Prepared bySachi UncianoОценок пока нет
- Applied Economics Module 1Документ23 страницыApplied Economics Module 1Sachi UncianoОценок пока нет
- Bab 1Документ28 страницBab 1Anonymous nxJ50dОценок пока нет
- Foundation of Economics PDFДокумент6 страницFoundation of Economics PDFgabytjintjelaarОценок пока нет
- Micro Econ. 1Документ42 страницыMicro Econ. 1ELIANA PAULОценок пока нет
- Economics Unit 1Документ30 страницEconomics Unit 1Aishvariya SОценок пока нет
- Allocation of ResourcesДокумент14 страницAllocation of ResourcesAzar Anjum RiazОценок пока нет
- Basic Economic ConceptsДокумент18 страницBasic Economic ConceptsShakarim AubakirovОценок пока нет
- Introduction Into Economics - Content NotesДокумент19 страницIntroduction Into Economics - Content Notescameron.d.newtonОценок пока нет
- Notes - EconomicsДокумент69 страницNotes - EconomicsHaktan OdabasiОценок пока нет
- Managerial Ecomomics CH-1Документ34 страницыManagerial Ecomomics CH-1Lemlem DejeneОценок пока нет
- Econs SummaryДокумент139 страницEcons SummaryNica PolicarpioОценок пока нет
- Unit 2. ActivitiesДокумент3 страницыUnit 2. Activitieswho is sheeeОценок пока нет
- Microeconomics Exam NotesДокумент11 страницMicroeconomics Exam NotesRobin SminesОценок пока нет
- Mb1102 Me - Unit 1 - Dr.R.R.ArunДокумент24 страницыMb1102 Me - Unit 1 - Dr.R.R.ArunDr. R. ArunОценок пока нет
- Micro Lect 1Документ66 страницMicro Lect 1Pakistani FriendsОценок пока нет
- EconomicsДокумент36 страницEconomicsAbdataОценок пока нет
- Abm Lesson 2Документ40 страницAbm Lesson 2Robert BalinoОценок пока нет
- ST Roop Convent School Class 12-Commerce Subject: EconomicsДокумент6 страницST Roop Convent School Class 12-Commerce Subject: EconomicsBerryОценок пока нет
- De Cuong Tieng AnhДокумент7 страницDe Cuong Tieng AnhNgọc NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Health Economics 2Документ71 страницаHealth Economics 2NICHOLAS KAUMBAОценок пока нет
- Economics&Economic ProblemsДокумент22 страницыEconomics&Economic ProblemsRhocel TolenadaОценок пока нет
- Module APPLIED EcoДокумент39 страницModule APPLIED EcoAngelyn LingatongОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Economics - ppt1Документ13 страницIntroduction To Economics - ppt1Akshay HemanthОценок пока нет
- H2 Economics Detailed SummaryДокумент84 страницыH2 Economics Detailed Summaryragul96100% (1)
- Good Intro To Economics FINALДокумент54 страницыGood Intro To Economics FINALShaswat AgarwalОценок пока нет
- IBDP Economics HL Chapter 1 NotesДокумент6 страницIBDP Economics HL Chapter 1 NotesAditya Rathi100% (1)
- BusinessДокумент64 страницыBusinessVlad KaneОценок пока нет
- Summary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESОт EverandSummary Of "Economics, Principles And Applications" By Mochón & Becker: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESОценок пока нет
- Jataka Tales - The Crane and The CrabДокумент5 страницJataka Tales - The Crane and The Crabshahrajan2k1Оценок пока нет
- 7A Detailed Lesson Plan in Health 7 I. Content Standard: Teacher's Activity Students' ActivityДокумент10 страниц7A Detailed Lesson Plan in Health 7 I. Content Standard: Teacher's Activity Students' ActivityLeizel C. LeonidoОценок пока нет
- Potato Lab ReportДокумент10 страницPotato Lab ReportsimplylailaОценок пока нет
- MidtermДокумент8 страницMidtermBrian FrenchОценок пока нет
- 7 Critical Reading StrategiesДокумент1 страница7 Critical Reading StrategiesWilliam Holt100% (2)
- 400 Series Turbo App Chart 2Документ5 страниц400 Series Turbo App Chart 2Abi ZainОценок пока нет
- Persephone by Julia Donaldson: (A Meadow. Enters Persephone, Picking The Petals of A Daisy.)Документ10 страницPersephone by Julia Donaldson: (A Meadow. Enters Persephone, Picking The Petals of A Daisy.)Dobler Liliana100% (1)
- List of Least Learned Competencies MAPEH7 1st To 3rd QuarterДокумент3 страницыList of Least Learned Competencies MAPEH7 1st To 3rd QuarterMark Dexter MejiaОценок пока нет
- Student Handbook MCCДокумент32 страницыStudent Handbook MCCeyusuf74Оценок пока нет
- Mech302hw5s 2Документ11 страницMech302hw5s 2priyadarshini212007Оценок пока нет
- D78846GC20 sg2Документ356 страницD78846GC20 sg2hilordОценок пока нет
- SD OverviewДокумент85 страницSD OverviewSamatha GantaОценок пока нет
- Chapter (1) The Accounting EquationДокумент46 страницChapter (1) The Accounting Equationtunlinoo.067433100% (3)
- Uprooted Radical Part 2 - NisiOisiN - LightДокумент307 страницUprooted Radical Part 2 - NisiOisiN - LightWillОценок пока нет
- Bonus Masters and InspiratorsДокумент73 страницыBonus Masters and InspiratorsGrosseQueue100% (1)
- Razom For UkraineДокумент16 страницRazom For UkraineАняОценок пока нет
- Young Entrepreneurs of IndiaДокумент13 страницYoung Entrepreneurs of Indiamohit_jain_90Оценок пока нет
- Bragg Waveguide and Its DescriptionДокумент22 страницыBragg Waveguide and Its DescriptionPratibha Karki RawatОценок пока нет
- You Are Loved PDFДокумент4 страницыYou Are Loved PDFAbrielle Angeli DeticioОценок пока нет
- Adult Consensual SpankingДокумент21 страницаAdult Consensual Spankingswl156% (9)
- FR-A800 Plus For Roll To RollДокумент40 страницFR-A800 Plus For Roll To RollCORTOCIRCUITANTEОценок пока нет
- Rule 107Документ8 страницRule 107AlexОценок пока нет
- Voucher-Zona Wifi-@@2000 - 3jam-Up-764-04.24.24Документ10 страницVoucher-Zona Wifi-@@2000 - 3jam-Up-764-04.24.24AminudinОценок пока нет
- Procedures: Step 1 Freeze or Restrain The Suspect/sДокумент5 страницProcedures: Step 1 Freeze or Restrain The Suspect/sRgenieDictadoОценок пока нет
- 001 Ipack My School BagДокумент38 страниц001 Ipack My School BagBrock JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Nurse Implemented Goal Directed Strategy To.97972Документ7 страницNurse Implemented Goal Directed Strategy To.97972haslinaОценок пока нет
- 4.1 Genetic Counselling 222Документ12 страниц4.1 Genetic Counselling 222Sahar JoshОценок пока нет
- School of ApologeticsДокумент104 страницыSchool of ApologeticsSAMSONОценок пока нет
- 3.1 Learning To Be A Better StudentДокумент27 страниц3.1 Learning To Be A Better StudentApufwplggl JomlbjhfОценок пока нет