Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Utation: Big Picture
Загружено:
homamunfatИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Utation: Big Picture
Загружено:
homamunfatАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
B
i
o
l
o
g
y
D
i
s
c
l
a
i
m
e
r
:
t
h
i
s
s
t
u
d
y
g
u
i
d
e
w
a
s
n
o
t
c
r
e
a
t
e
d
t
o
r
e
p
l
a
c
e
y
o
u
r
t
e
x
t
b
o
o
k
a
n
d
i
s
f
o
r
c
l
a
s
s
r
o
o
m
o
r
i
n
d
i
v
i
d
u
a
l
u
s
e
o
n
l
y
.
Study Guides
Page 1 of 2
v1.1.11.2012
This guide was created by Amy Shen and Jin Yu. To learn more about the
student authors, visit http://www.ck12.org/about/about-us/team/interns.
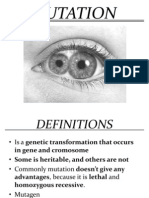
Germline mutations are serious because it can
be passed onto the offspring of the organism. Only
germline mutations can change offspring.
Somatic mutations are not as serious because
they can only occur in one cell and its daughter
cells. The mutation cannot be passed onto offspring.
Mutations affect the genetic material. The effect can
be a chromosomal alteration, point mutation, or
frameshift mutation.
Chromosomal alterations happen when part of a
chromosome breaks off and doesn't rejoin correctly.
Serious mutation: often result in death or serious
genetic disorder
Types of chromosomal alterations: deletion, duplica-
tion, inversion, insertion, translocation.
Mutations occur when mistakes are made during transcription or replication of DNA. There are several kinds of mutations
that occur in organisms. Mutations usually happen when chromosomes break or when nucleotides on a chromosome
are changed, inserted, or deleted. Everyone has mutations, and most mutations are harmless. However, there are
some mutations that can lead to serious illness or death.
Key Terms
Causes of Mutations
Mutation: A change in the bases of DNA/RNA.
Mutagen: Something that causes mutation.
Germline Mutation: A mutation in a gamete (can be passed onto offspring).
Somatic Mutation: Mutation that occurs in a somatic (non-gamete) cell.
Chromosomal Alteration: Mutation that changes chromosome structure.
Point Mutation: One nucleotide is changed.
Frameshift Mutation: When a nucleotide is deleted or inserted.
Genetic Disorder: Disease caused by gene mutations.
Big Picture
Most mutations are accidental and happen randomly as the result of mistakes during DNA replication or transcription
Example: ATGA ATCA
Mutations can also be caused by mutagens in the environment. Examples:
Chemicals
Cigarette smoke: contains dozens of mutagenic chemicals
Nitrate and nitrate Preservatives: in hotdogs and other processed meats
Barbecuing: create mutagenic chemicals in foods
Benzoyl peroxide: common ingredient in acne products
Infectious Agents
Helicobacter pylori: bacteria spread through contaminated food
Human papillomavirus (HIV): sexually transmitted virus
Radiation
UV radiation: both natural light and tanning beds
X-rays: medical, dental, airport security screening
Image credit: Dietzel65, Public Domain
Types of Mutations
Figure: Types of chromosomal alterations.
Mutation
Page 2 of 2
B
i
o
l
o
g
y
Effects of Mutations
Neutral mutations:
Most mutations do not have a negative or a positive effect
Many mutations are repaired before protein synthesis occurs
Cells containing DNA that cannot be repaired are usually prevented from dividing
Silent point mutations are also neutral mutations because the amino acids in the protein do not change
Benefcial mutations:
Mutations that have a positive effect
The new version of the protein helps the organism to adapt to changes in the environment
Benefcial mutations are necessary for evolution
Tend to be passed onto more offspring and become more common over time
Harmful mutations:
Mutations that have a negative effect
Result in genetic disorder or cancer
Cancer usually result from mutations in genes that regulate the cell cycle, which allow cells with damaged DNA
to continuously divide
Point mutations tend to be less serious, but the
effect depends on how the mutation changes the genetic
code.
Types of point mutations:
Silent mutation: mutated codon codes for the same
amino acid (no effect on organism)
Several codons code for the same amino acid,
so if a point mutation changes CUU (leucine) to
CUG, CUA, or CUC, there is no effect because all
three also code for leucine
Missense: mutated codon codes for a different
amino acid
May have some effect on organism, but it de-
pends on the situation
Nonsense: mutated codon is a stop codon that stops
protein synthesis early
Usually this has a serious effect
Frameshift mutations can greatly affect protein
synthesis. Since codons are groups of 3 nucleotides,
adding/deleting a nucleotide shifts everything over and
changes every codon afterwards, which completely
changes the amino acids produced.
Example: AUG-ACU-UCG-GCC = start-threonine-
serine-alanine
Now, assume an insertion occurs in this sequence. Lets
say a C nucleotide is inserted after the start codon AUG:
AUG-CAC-UUC-GGC-C = start-histidine-
phenylalanine-glycine
The amino acid sequence changed dramatically even
though only one nucleotide was inserted.
Notes
Mutation cont.
Types of Mutations (cont.)
Вам также может понравиться
- What Is Mutation2Документ21 страницаWhat Is Mutation2Deepsnehil Dubey100% (2)
- MutationsДокумент29 страницMutationsiariajay100% (1)
- MutationДокумент62 страницыMutationAlan Syahputra100% (2)
- Gene Silencing: Presented byДокумент23 страницыGene Silencing: Presented byRouf Ahmad100% (1)
- The Plasma Proteins V5: Structure, Function, and Genetic ControlОт EverandThe Plasma Proteins V5: Structure, Function, and Genetic ControlFrank PutnamРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Types of MutationsДокумент25 страницTypes of Mutationsrohishaak100% (1)
- The Structure and Function of Animal Cell Components: An Introductory TextОт EverandThe Structure and Function of Animal Cell Components: An Introductory TextОценок пока нет
- Genetic MutationДокумент27 страницGenetic MutationKathleen JOy BiasUraОценок пока нет
- Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation: Receptors of Inflammatory Cells: Structure—Function RelationshipsОт EverandCellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation: Receptors of Inflammatory Cells: Structure—Function RelationshipsCharles G. CochraneОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Genetics PDFДокумент24 страницыBacterial Genetics PDFJaszmin Sonia KaurОценок пока нет
- Genetics 1.1 ResumeДокумент102 страницыGenetics 1.1 ResumemiertschinkОценок пока нет
- Gene MutationДокумент20 страницGene Mutationdheeresh aggarwalОценок пока нет
- DBT JRF in A NutshellДокумент29 страницDBT JRF in A NutshellVasu MathuraОценок пока нет
- Mutations ClassificationДокумент25 страницMutations ClassificationEdessa G. FlordelizОценок пока нет
- Linkage and Crossing OverДокумент8 страницLinkage and Crossing OverMahendra singh RajpurohitОценок пока нет
- Biology Genetic Mutation NotesДокумент1 страницаBiology Genetic Mutation NotesTiffany Gallina100% (2)
- Gene Silencing Gene Silencing: Niranjana.S.Karandikar Msc-I Roll No.12Документ21 страницаGene Silencing Gene Silencing: Niranjana.S.Karandikar Msc-I Roll No.12Niranjana KarandikarОценок пока нет
- MutationДокумент9 страницMutationsolgra100% (1)
- Genetic EngineeringДокумент19 страницGenetic EngineeringDo not ask meОценок пока нет
- 3 Genetic Engineering LECДокумент14 страниц3 Genetic Engineering LECCipriano N TucayОценок пока нет
- Genetech 1 - 11'12 Sem 2Документ31 страницаGenetech 1 - 11'12 Sem 2gajenraoОценок пока нет
- Types of MutationsДокумент11 страницTypes of MutationsnsjunnarkarОценок пока нет
- Measure of Central TendencyДокумент16 страницMeasure of Central Tendencydr.neupane27Оценок пока нет
- Prodcut of Recombinat DNA TechnologyДокумент9 страницProdcut of Recombinat DNA TechnologySHOAIB NAVEEDОценок пока нет
- Characteristics and Genotyping (Semi-Automated and Automated), Apparatus Used in GenotypingДокумент45 страницCharacteristics and Genotyping (Semi-Automated and Automated), Apparatus Used in GenotypingKhalid HameedОценок пока нет
- Eukaryotic Cell OrganellesДокумент7 страницEukaryotic Cell OrganellesMary100% (2)
- Lab Report 1Документ6 страницLab Report 1Margarita Kotsev100% (1)
- Dna, Rna, Transcription, Translation & Protein Synthesis PDFДокумент14 страницDna, Rna, Transcription, Translation & Protein Synthesis PDFSaeed Khan100% (1)
- R DNA TchnologyДокумент32 страницыR DNA TchnologyReena GuptaОценок пока нет
- Mutation: Neeraj Kumar Maurya Environmental BiotechnologyДокумент24 страницыMutation: Neeraj Kumar Maurya Environmental BiotechnologyNeeraj MauryaОценок пока нет
- Nucleic Acids & Their MetabolismДокумент62 страницыNucleic Acids & Their MetabolismPURSUIT OF SUCCESSОценок пока нет
- Bio MajorДокумент4 страницыBio MajorAnna LiОценок пока нет
- Light Reaction ReflectionДокумент2 страницыLight Reaction ReflectionMARK BRIAN FLORESОценок пока нет
- Pedigree AnalysisДокумент18 страницPedigree AnalysisSanjeet YadavОценок пока нет
- Gene Therapy InfoДокумент3 страницыGene Therapy InfoShailendra Singh KhichiОценок пока нет
- Genetic Engineering: Junalyn Gale D. TapayaДокумент27 страницGenetic Engineering: Junalyn Gale D. TapayaKyle Refugio100% (1)
- What Is DNAДокумент4 страницыWhat Is DNApranav shuklaОценок пока нет
- Mutations NotesДокумент4 страницыMutations NotesYukiichris Lam0% (1)
- Genetics, Lecture 11 (Lecture Notes)Документ16 страницGenetics, Lecture 11 (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-QudsiОценок пока нет
- Antisense RNA TherapyДокумент17 страницAntisense RNA TherapyGuleRia ShiVani100% (1)
- Medical BiotechnologyДокумент34 страницыMedical Biotechnologyalfi alfathanaОценок пока нет
- Genetics LectureДокумент30 страницGenetics Lectureapi-295463484Оценок пока нет
- C11 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF DNA AND RNA Concepts of Genetics 12ed (Brooker)Документ21 страницаC11 MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF DNA AND RNA Concepts of Genetics 12ed (Brooker)Catalina CristinaОценок пока нет
- DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESISДокумент60 страницDNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESISathirah100% (1)
- Recombinant Dna TechnologyДокумент3 страницыRecombinant Dna TechnologyAeron Jade ParenaОценок пока нет
- Central Dogma of Molecular GeneticsДокумент3 страницыCentral Dogma of Molecular GeneticsDiana RomeroОценок пока нет
- Genetics NotesДокумент28 страницGenetics NotesjasОценок пока нет
- Gene Regulation of Prokaryotic TranscriptionДокумент17 страницGene Regulation of Prokaryotic TranscriptionAyu Tri AgustinОценок пока нет
- MutationДокумент26 страницMutationKyraMicaEllaFloresОценок пока нет
- Structure and Function of ChromosomesДокумент12 страницStructure and Function of ChromosomesArvind ChavanОценок пока нет
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyДокумент18 страницRecombinant DNA TechnologyZachary Vincent PetallarОценок пока нет
- Genetic TerminologyДокумент6 страницGenetic TerminologyMuthu KaruppanОценок пока нет
- This Video: To Do: Watch To Complete This TableДокумент1 страницаThis Video: To Do: Watch To Complete This TableLaura Cormane100% (1)
- Gene Mutation: Genomes 3Документ72 страницыGene Mutation: Genomes 3Abdus SubhanОценок пока нет
- Module Mol Chapter 7Документ78 страницModule Mol Chapter 7eyoelОценок пока нет
- Plant Molecular Farming For Recombinant Therapeutic ProteinsДокумент61 страницаPlant Molecular Farming For Recombinant Therapeutic Proteinsnitin_star2010Оценок пока нет
- Polymerase Chain ReactionДокумент22 страницыPolymerase Chain ReactionPoornaBasuri100% (1)
- Molecular BiologyДокумент9 страницMolecular Biologyrifat RasheedОценок пока нет
- 7.2 Gene /point Mutation: Learning OutcomeДокумент28 страниц7.2 Gene /point Mutation: Learning OutcomebedahОценок пока нет
- MutationsДокумент22 страницыMutationsMadhuОценок пока нет
- GCSE ELIT REVISED Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard MayJune Series 2011 9983Документ16 страницGCSE ELIT REVISED Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard MayJune Series 2011 9983homamunfatОценок пока нет
- 50 Word Story TellingДокумент1 страница50 Word Story TellinghomamunfatОценок пока нет
- B. Red, Yellow, and Blue Can Be Mixed Together To Make Secondary ColorsДокумент1 страницаB. Red, Yellow, and Blue Can Be Mixed Together To Make Secondary ColorshomamunfatОценок пока нет
- Every Child Matters: Change For Children: in Social CareДокумент16 страницEvery Child Matters: Change For Children: in Social CarehomamunfatОценок пока нет
- Colors: Lesson Ten: The Three Primary Colors Are Red, Yellow, and Blue. They CanДокумент1 страницаColors: Lesson Ten: The Three Primary Colors Are Red, Yellow, and Blue. They CanhomamunfatОценок пока нет
- 18 Yatcb Lesson Plans Complete Book FINALДокумент146 страниц18 Yatcb Lesson Plans Complete Book FINALhomamunfatОценок пока нет
- 16.1 Questioning John ProctorДокумент2 страницы16.1 Questioning John ProctorhomamunfatОценок пока нет
- B. Write The Following Information On The Calendar On Page 10. Write SmallДокумент1 страницаB. Write The Following Information On The Calendar On Page 10. Write SmallhomamunfatОценок пока нет
- 13.05.15 Prepostions of PlaceДокумент1 страница13.05.15 Prepostions of PlacehomamunfatОценок пока нет
- 15.1 Speaking and Listening Assessment - Role PlayingДокумент2 страницы15.1 Speaking and Listening Assessment - Role PlayinghomamunfatОценок пока нет
- To Be or Not To Be Haben and SeinДокумент1 страницаTo Be or Not To Be Haben and SeinhomamunfatОценок пока нет
- St. Benedict's College - Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыSt. Benedict's College - Lesson PlanhomamunfatОценок пока нет
- 6 HATS - What Are They SayingДокумент1 страница6 HATS - What Are They SayinghomamunfatОценок пока нет
- Thinking Skills & Discussion SkillsДокумент6 страницThinking Skills & Discussion SkillshomamunfatОценок пока нет
- 6 Areas Mindmap - OurselvesДокумент1 страница6 Areas Mindmap - OurselveshomamunfatОценок пока нет
- SB Roadmap B1 1Документ161 страницаSB Roadmap B1 1Carmen Flores AloyОценок пока нет
- Pro Con ChartДокумент3 страницыPro Con Chartapi-461614875Оценок пока нет
- Concept of ConstitutionДокумент32 страницыConcept of ConstitutionDorepe Icon0% (1)
- Omran WalidДокумент196 страницOmran WalidDébora AmougouОценок пока нет
- Crowd Management - Model Course128Документ117 страницCrowd Management - Model Course128alonso_r100% (4)
- Tadano450xl PDFДокумент12 страницTadano450xl PDFmunawar0% (1)
- Light Design by Anil ValiaДокумент10 страницLight Design by Anil ValiaMili Jain0% (1)
- Tasha Giles: WebsiteДокумент1 страницаTasha Giles: Websiteapi-395325861Оценок пока нет
- Bob Jones: This CV Template Will Suit Jobseekers With Senior Management ExperienceДокумент3 страницыBob Jones: This CV Template Will Suit Jobseekers With Senior Management ExperienceDickson AllelaОценок пока нет
- Inner DriveДокумент51 страницаInner DriveShaurya VajhulaОценок пока нет
- 100 IELTS Essay Topics For IELTS Writing - My IELTS Classroom BlogДокумент16 страниц100 IELTS Essay Topics For IELTS Writing - My IELTS Classroom BlogtestОценок пока нет
- ĐÁP ÁN ĐỀ THI THỬ SỐ 03 (2019-2020)Документ8 страницĐÁP ÁN ĐỀ THI THỬ SỐ 03 (2019-2020)Đào VânОценок пока нет
- 0 - Danica Joy v. RallecaДокумент2 страницы0 - Danica Joy v. RallecaRandy Jake Calizo BaluscangОценок пока нет
- CE - 441 - Environmental Engineering II Lecture # 11 11-Nov-106, IEER, UET LahoreДокумент8 страницCE - 441 - Environmental Engineering II Lecture # 11 11-Nov-106, IEER, UET LahoreWasif RiazОценок пока нет
- Berghahn Dana ResumeДокумент2 страницыBerghahn Dana ResumeAnonymous fTYuIuK0pkОценок пока нет
- Reading in MCJ 216Документ4 страницыReading in MCJ 216Shela Lapeña EscalonaОценок пока нет
- Letter For LACДокумент7 страницLetter For LACDahlia G. MaglasangОценок пока нет
- Hurricanes Reading Comprehension FreebieДокумент20 страницHurricanes Reading Comprehension FreebieAlex WaddellОценок пока нет
- The Mutant Epoch Mature Adult Content Mutations v1Документ4 страницыThe Mutant Epoch Mature Adult Content Mutations v1Joshua GibsonОценок пока нет
- Variables in The EquationДокумент3 страницыVariables in The EquationfiharjatinОценок пока нет
- Accuracy of Transferring Analog Dental Casts To A Virtual ArticulatorДокумент9 страницAccuracy of Transferring Analog Dental Casts To A Virtual ArticulatorNetra TaleleОценок пока нет
- Cot 4 Mapeh (Health)Документ15 страницCot 4 Mapeh (Health)RELYN LUCIDOОценок пока нет
- Unit 9 TelephoningДокумент14 страницUnit 9 TelephoningDaniela DanilovОценок пока нет
- User Manual ManoScanДокумент58 страницUser Manual ManoScanNurul FathiaОценок пока нет
- Calgary Project Consultants, DubaiДокумент18 страницCalgary Project Consultants, DubaiManish GuptaОценок пока нет
- A3 Report Template Checklist - SafetyCultureДокумент4 страницыA3 Report Template Checklist - SafetyCulturewarriorninОценок пока нет
- 热虹吸管相变传热行为CFD模拟 王啸远Документ7 страниц热虹吸管相变传热行为CFD模拟 王啸远小黄包Оценок пока нет
- Lier Upper Secondary SchoolДокумент8 страницLier Upper Secondary SchoolIES Río CabeОценок пока нет
- Pay Scale WorkshopДокумент5 страницPay Scale WorkshopIbraОценок пока нет
- Think Feel DoДокумент3 страницыThink Feel DoHardik MehtaОценок пока нет