Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ME 201 Basics
Загружено:
mz_haqАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ME 201 Basics
Загружено:
mz_haqАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
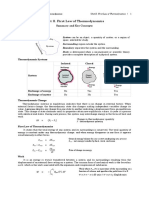
Thermodynamic System
Basic Concepts & Terminology
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
Professor
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET)
Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh
T006
A thermodynamic system is simply any object, quantity of
matter, or region of space that has been selected for study.
zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/
Everything that is not part of the system is referred to as the
surroundings or environment.
ME 201: Basic Thermodynamics
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
Boundary or control surface (CS) separates the system from
its surroundings.
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
1 / 18
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
2 / 18
T061
A system dened to contain all of the air in a piston-cylinder device.
T009
A control surface (CS):
may be real or imaginary, at rest or in motion
may change its shape and size
neither contains matter nor occupies volume
has zero thickness and a property value at a point on the
boundary is shared by both the system and the surroundings.
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
T062
A system dened to contain all of the air that is initially in a tank that
is being lled.
3 / 18
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
4 / 18
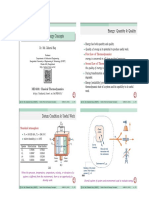
Control Mass (CM) or Closed System
Control Volume (CV) or Open System
T008
T078
T007
If a control surface is closed to mass ow, so that no mass can escape or
enter into the control volume, then it is called a Control Mass (CM)
or Closed system. Heat and work may cross the system boundary, but
the system contains the same amount of matter at all times.
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
5 / 18
Adiabatic System
T079
T082
When there is ow of mass through control surface, the system is
called a Control Volume (CV) or Open system.
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
6 / 18
Classication of Thermodynamic Systems
T083
T001
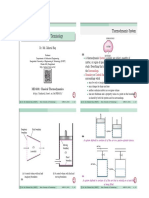
In Adiabatic system, the boundary is impermeable to heat.
An Isolated system is a special case of closed system that does not
interact in any way with its surroundings.
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
7 / 18
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
8 / 18
Macroscopic & Microscopic Views of Thermodynamics
State & Property
Thermodynamic systems can be studied from two points of view:
1
2
Microscopic approach or statistical thermodynamics
Macroscopic approach or classical thermodynamics
The microscopic approach recognizes that the system consists of
matter that is composed of countless, discrete molecules. Statistics
and probability theory are applied to deduce the macroscopic
behaviour or measurable quantities e.g. pressure, temperature etc.
In the macroscopic approach, the state of the system is described
by a relatively small set of characteristics that are called
properties e.g. mass, temperature, pressure and volume.
Macroscopic approach works well when the system is suciently
large such that it contains many molecules. For example, how
would you measure the temperature of such a system that consists
almost entirely of vacuum?
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
9 / 18
The condition of a system at any instant of time is called its state.
State at a given instant determines the properties of the system.
A property is a quantity whose numerical value depends on the
state but not on the history of the system. The origin of
properties include those
1
2
3
directly measurable
dened by laws of thermodynamics
dened by mathematical combinations of other properties.
Intensive properties are independent of the size or extent of the
system. Extensive properties depend on the size or extent of the
system. An extensive property is additive in the sense that its
value for the whole system is the sum of the values for its parts.
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
10 / 18
System boundary
E1, V1, T, P
Esystem = E1 + E2
Extensive Properties
Vsystem = V1 + V2 }
E2, V2, T, P
Tsystem = T1 = T2
} Intensive Properties
Psystem = P1 = P2
T012
Property
Mass
Volume
KE
PE
Total Energy
Internal Energy
Enthalpy
Entropy
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Extensive
m
V
1
mV 2
2
mgZ
E
U
H
S
Intensive
v
1 2
V
2
gZ
e
u
h
s
Basic Concepts & Terminology
Any property has a xed value in a give state in a given
equilibrium state, regardless of how the system arrives at the state.
Two states are identical if, and only if, the properties of the two
states are identical.
The change in the value of the property that occurs when a
system is altered from equilibrium state to another is always the
same, regardless of the process used to bring about the change.
ME 201 (2013)
11 / 18
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
12 / 18
Process & Cycle
Thermodynamic Equilibrium
A thermodynamic process is the succession of thermodynamic
states that a system passes through as it goes from an initial state
to a nal state.
A system in thermodynamic equilibrium simultaneously
satises the following stringent requirements:
A system process is said to go through a thermodynamic cycle
when the nal state of the process is the same as the initial state
of the process.
Mechanical Equilibrium: no unbalance forces acting on any part
of the system or the system as a whole.
Thermal Equilibrium: no temperature dierences between parts
of the system or between the system and the surrounding.
Chemical Equilibrium: no chemical reactions within the system
and no motion of any chemical species from one part to another
part of the system.
Once the system is in thermodynamic equilibrium and the
surroundings is kept unchanged, no motion will take place and no
work will be done.
T044
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
13 / 18
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
14 / 18
Categories of Thermodynamics Quantities
1
State functions: All properties are state functions.
Process or Path functions: quantities whose values depend on
the path of the process.
2
1
Z Z12 = Z
T038
T076
2
T077
During a quasi-static process, the system is at all time innitesimally
near a state thermodynamic equilibrium.
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
15 / 18
dy = y2 y1 = y
dy = 0
T013
State function
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Path function
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
16 / 18
Conservation of Mass
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
Two systems with thermal equilibrium with a third are in thermal
equilibrium with each other.
T051
mcv ,t + min = mcv ,t +t + mout
mcv ,t +t mcv ,t = min mout
mcv ,t +t mcv ,t
t
dmcv
dt
min mout
t
= min mout
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
: if t 0
dmcv
dt
(BUET)
in
T356
min
out
mout
Basic Concepts & Terminology
T002
T045
ME 201 (2013)
17 / 18
c
Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq
(BUET)
Basic Concepts & Terminology
ME 201 (2013)
18 / 18
Вам также может понравиться
- ME201 - BasicsДокумент5 страницME201 - Basicsiftekher khanОценок пока нет
- ME203 2 BasicsДокумент5 страницME203 2 Basicsabdullah2110154Оценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Engg ThermodynamicsДокумент47 страницUnit 1 Engg Thermodynamicsvenkat_mie1080Оценок пока нет
- ME203 BasicsДокумент5 страницME203 BasicsDurjoy Kumar PaulОценок пока нет
- Engineering Thermodynamics 1 THRM1001: Basic Concepts and DefinitionsДокумент50 страницEngineering Thermodynamics 1 THRM1001: Basic Concepts and DefinitionsTashi BestОценок пока нет
- ENGG111-Thermal Engineering and Thermal Power Plants-BSTДокумент14 страницENGG111-Thermal Engineering and Thermal Power Plants-BSTJay Prakash MandalОценок пока нет
- (5285) Sheet Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry TH eДокумент42 страницы(5285) Sheet Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry TH eboom rangОценок пока нет
- Introduction To ThermodynamicsДокумент65 страницIntroduction To ThermodynamicsNafisa AnikaОценок пока нет
- ME 265 Lecture Slides 1b (Introduction)Документ27 страницME 265 Lecture Slides 1b (Introduction)Leslie Owusu MensahОценок пока нет
- Bme A 1 DtuДокумент36 страницBme A 1 DtuChadОценок пока нет
- (22051) Sheet 0 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry TH and Ex BДокумент120 страниц(22051) Sheet 0 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry TH and Ex Bjust danceОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics 3.1.1 Characteristics of ThermodynamicsДокумент9 страницThermodynamics 3.1.1 Characteristics of ThermodynamicsSaheera HazarikaОценок пока нет
- 5.et Unit 1Документ20 страниц5.et Unit 1Deepak MisraОценок пока нет
- Unit 2: Basic ThermodynamicsДокумент18 страницUnit 2: Basic ThermodynamicsAmar ZalleeОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics IntroductionДокумент61 страницаThermodynamics IntroductionagarwaldivyangОценок пока нет
- Unit II. First Law of Thermodynamics: Summary and Key ConceptsДокумент3 страницыUnit II. First Law of Thermodynamics: Summary and Key ConceptsfrendОценок пока нет
- 062 - ME8391, ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Notes PDFДокумент136 страниц062 - ME8391, ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Notes PDFKishan RaushanОценок пока нет
- Concepts and Definitions 2022Документ49 страницConcepts and Definitions 2022NIRUPAN KARKIОценок пока нет
- Advanced Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (Cheg6121) : Review of Basic ThermodynamicsДокумент74 страницыAdvanced Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (Cheg6121) : Review of Basic ThermodynamicsetayhailuОценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ30 страницModule 1Sagar N GowdaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of ThermodynamicsДокумент12 страницChapter 1: Basic Concepts of ThermodynamicsarunyogОценок пока нет
- ET GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-1 05102019071650AMДокумент13 страницET GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-1 05102019071650AMSatyam SinghОценок пока нет
- Engineering Thermodynamics 2 MarksДокумент16 страницEngineering Thermodynamics 2 MarksProf.S.Y PawarОценок пока нет
- Engineering Principles-Feng 123 Lecture Notes Volume 2: BY Ing. Sahr T. NyallomaДокумент12 страницEngineering Principles-Feng 123 Lecture Notes Volume 2: BY Ing. Sahr T. NyallomaAlbert LappiaОценок пока нет
- Topic 1: BMM 2513 Thermodynamics 1Документ48 страницTopic 1: BMM 2513 Thermodynamics 1Harriz SynysterОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics: Unit - 1Документ54 страницыThermodynamics: Unit - 1winny roboticsОценок пока нет
- 4.1 Eng. Thermo PDFДокумент66 страниц4.1 Eng. Thermo PDFCHOON CHEAK YOKОценок пока нет
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Lecture Notes PDFДокумент139 страницMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Lecture Notes PDFvenkat_mie1080100% (2)
- ME 266 Lecture 1 (Introduction-Basic Concepts)Документ30 страницME 266 Lecture 1 (Introduction-Basic Concepts)Akoto BlessОценок пока нет
- Iit-Jee Syllabus: Chemical EnergeticsДокумент1 страницаIit-Jee Syllabus: Chemical EnergeticsPawan BabelОценок пока нет
- Engineering Thermodynamics 2 MarksДокумент16 страницEngineering Thermodynamics 2 MarksSanjeev PawarОценок пока нет
- Compact Heat Exchangers Selection Application Design and EvaluationДокумент18 страницCompact Heat Exchangers Selection Application Design and EvaluationLailatul QidsiyahОценок пока нет
- Concepts and Definitions-: - Today's Objectives: In-Class ActivitiesДокумент34 страницыConcepts and Definitions-: - Today's Objectives: In-Class ActivitiesMbangue lango patrick manuelОценок пока нет
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals: Mechanical EngineeringДокумент51 страницаKing Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals: Mechanical EngineeringAlex Ceballos ZavaletaОценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент30 страницThermodynamicsNeha Kaur SinhaОценок пока нет
- Lecture1 ThermodynamicsДокумент19 страницLecture1 Thermodynamicsshawon_darkОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ9 страницChapter 1maheshluintelОценок пока нет
- Thermo 1Документ24 страницыThermo 1mustafemohamedaden08Оценок пока нет
- Basic Concet of ThermodynamicsДокумент18 страницBasic Concet of ThermodynamicsSachin ChaturvediОценок пока нет
- Mod1A Basics of ME ThermoДокумент98 страницMod1A Basics of ME ThermoGauthamanОценок пока нет
- AEAS 207 Lec 1Документ44 страницыAEAS 207 Lec 1Samin Yaser AhmedОценок пока нет
- TD NotesДокумент69 страницTD NotesAnil ThotaОценок пока нет
- 6 Thermodynamics - TextbooksДокумент86 страниц6 Thermodynamics - Textbooksmansoorshaik1991Оценок пока нет
- Ambo University: Regulation and ControlДокумент20 страницAmbo University: Regulation and ControlFikadu EshetuОценок пока нет
- Pamphlet PDFДокумент68 страницPamphlet PDFomah khemikalОценок пока нет
- CCTD101B Notes 1 - Basic Concepts and DefinitionsДокумент10 страницCCTD101B Notes 1 - Basic Concepts and DefinitionsShan ShanzОценок пока нет
- Engineering ThermodynamicsДокумент30 страницEngineering ThermodynamicsAddisu DagneОценок пока нет
- Basic ThermodynamicДокумент33 страницыBasic ThermodynamicLaxmikanth GurumurthyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ7 страницLecture 2AsalinaОценок пока нет
- 03 06 at Basic Concepts and DefinitionsДокумент33 страницы03 06 at Basic Concepts and DefinitionsMuhammad ArslanОценок пока нет
- TD PPT (Ame003) (18 19 16)Документ232 страницыTD PPT (Ame003) (18 19 16)deepak kantipudiОценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент98 страницThermodynamicsGuruKPO100% (9)
- Lecture 1Документ23 страницыLecture 1Melkiyas DiribaОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics: Why Do We Need To Study Thermodynamics?Документ56 страницThermodynamics: Why Do We Need To Study Thermodynamics?PE9001 AarthiОценок пока нет
- Name: Subject:: Kush Patel Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 20BCH029Документ9 страницName: Subject:: Kush Patel Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 20BCH029Kush PatelОценок пока нет
- Getting Started: Introductory Concepts and DefinitionsДокумент26 страницGetting Started: Introductory Concepts and DefinitionsSantiago Cardona ArroyaveОценок пока нет
- Basics of Thermodynamics: GE Oil & GasДокумент21 страницаBasics of Thermodynamics: GE Oil & GasArzymanОценок пока нет
- Engineering Thermodynamics NotesДокумент106 страницEngineering Thermodynamics NotesOnline EarnОценок пока нет
- Review of Heat Transfer & Fluid Flow Modes of Heat Transfer: Dr. Md. Zahurul HaqДокумент7 страницReview of Heat Transfer & Fluid Flow Modes of Heat Transfer: Dr. Md. Zahurul Haqmz_haqОценок пока нет
- HRSG: Pinch Point Analysis: Dr. Md. Zahurul HaqДокумент2 страницыHRSG: Pinch Point Analysis: Dr. Md. Zahurul Haqmz_haqОценок пока нет
- Course Outline ME 307: SyllabusДокумент1 страницаCourse Outline ME 307: Syllabusmz_haqОценок пока нет
- ME 307: Heat Transfer Equipment Design: (Arpachi-Ex-7.9)Документ5 страницME 307: Heat Transfer Equipment Design: (Arpachi-Ex-7.9)mz_haqОценок пока нет
- ME 307: Heat Transfer Equipment DesignДокумент9 страницME 307: Heat Transfer Equipment Designmz_haqОценок пока нет
- Heat Exchangers: Applications & Classifications Applications of Heat ExchangersДокумент5 страницHeat Exchangers: Applications & Classifications Applications of Heat Exchangersmz_haqОценок пока нет
- HX: Effective NTU Method Ǫ - NTU Method: LN ExpДокумент5 страницHX: Effective NTU Method Ǫ - NTU Method: LN Expmz_haqОценок пока нет
- ME6101 ExergyДокумент9 страницME6101 Exergymz_haqОценок пока нет
- ME6101 EntropyДокумент8 страницME6101 Entropymz_haqОценок пока нет
- HX: Energy Balance and LMTD MethodДокумент5 страницHX: Energy Balance and LMTD Methodmz_haqОценок пока нет
- IJPGC2003-40143: Developing Turbulence On The Propagation of Flames in Methane-Air PremixtureДокумент7 страницIJPGC2003-40143: Developing Turbulence On The Propagation of Flames in Methane-Air Premixturemz_haqОценок пока нет
- 01 Matplotlib PDFДокумент9 страниц01 Matplotlib PDFmz_haqОценок пока нет
- HT2003 47484Документ8 страницHT2003 47484mz_haqОценок пока нет
- Icope03 DraftДокумент6 страницIcope03 Draftmz_haqОценок пока нет
- ME6101 FirstLawДокумент7 страницME6101 FirstLawmz_haqОценок пока нет
- ME6101 BasicsДокумент5 страницME6101 Basicsmz_haqОценок пока нет
- ME6101 CombustionДокумент4 страницыME6101 Combustionmz_haqОценок пока нет
- ME6101 BasicsДокумент5 страницME6101 Basicsmz_haqОценок пока нет
- ME 201 SecondLawДокумент6 страницME 201 SecondLawmz_haqОценок пока нет
- Hybrid 4Документ3 страницыHybrid 4mz_haqОценок пока нет
- Hybrid Vehicles, Electric Vehicles, Fuel Cell Electric VehiclesДокумент10 страницHybrid Vehicles, Electric Vehicles, Fuel Cell Electric Vehiclesmz_haqОценок пока нет
- ME 6101 OutlineДокумент1 страницаME 6101 Outlinemz_haqОценок пока нет
- Hybrid VehiclesДокумент16 страницHybrid Vehiclesmz_haqОценок пока нет
- Hybrid VehiclesДокумент16 страницHybrid Vehiclesmz_haqОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Studies of Premixed Combustion (PHD Thesis)Документ211 страницFundamental Studies of Premixed Combustion (PHD Thesis)mz_haqОценок пока нет
- EE&C Technologies For Textile/Garments/Steel Sector: Dr. Md. Zahurul HaqДокумент21 страницаEE&C Technologies For Textile/Garments/Steel Sector: Dr. Md. Zahurul Haqmz_haqОценок пока нет
- 1 5302 711 Mo LGW523 GBДокумент110 страниц1 5302 711 Mo LGW523 GBNeznanog Junaka Sest VranjeОценок пока нет
- ProcICGET13 HaqДокумент4 страницыProcICGET13 Haqmz_haqОценок пока нет
- The Concept of Exergy and Energy Quality - Truls GundersenДокумент26 страницThe Concept of Exergy and Energy Quality - Truls Gundersenuser_account100% (1)
- Tikz TutorialДокумент34 страницыTikz Tutorialmz_haq100% (1)
- Eacsb PDFДокумент297 страницEacsb PDFTai ThomasОценок пока нет
- DTR FormДокумент1 страницаDTR FormSharlene Mae DeJesus AbreraОценок пока нет
- Job Order ContractДокумент1 страницаJob Order ContractPaulo Abenio Escober100% (1)
- Juz AmmaДокумент214 страницJuz AmmaIli Liyana Khairunnisa KamardinОценок пока нет
- George F. Nafziger, Mark W. Walton-Islam at War - A History - Praeger (2008)Документ288 страницGeorge F. Nafziger, Mark W. Walton-Islam at War - A History - Praeger (2008)موسى رجب100% (2)
- 96boards Iot Edition: Low Cost Hardware Platform SpecificationДокумент15 страниц96boards Iot Edition: Low Cost Hardware Platform SpecificationSapta AjieОценок пока нет
- Huge Filing Bill WhiteДокумент604 страницыHuge Filing Bill WhiteBen SellersОценок пока нет
- Notice: Agency Information Collection Activities Proposals, Submissions, and ApprovalsДокумент1 страницаNotice: Agency Information Collection Activities Proposals, Submissions, and ApprovalsJustia.comОценок пока нет
- Solvency PPTДокумент1 страницаSolvency PPTRITU SINHA MBA 2019-21 (Kolkata)Оценок пока нет
- Save Clay Court OpinionДокумент12 страницSave Clay Court OpinionWNDUОценок пока нет
- What Is Cybercrime?Документ3 страницыWhat Is Cybercrime?JoshuaFrom YTОценок пока нет
- 8 Soc - Sec.rep - Ser. 123, Unempl - Ins.rep. CCH 15,667 Alfred Mimms v. Margaret M. Heckler, Secretary of The Department of Health and Human Services, 750 F.2d 180, 2d Cir. (1984)Документ8 страниц8 Soc - Sec.rep - Ser. 123, Unempl - Ins.rep. CCH 15,667 Alfred Mimms v. Margaret M. Heckler, Secretary of The Department of Health and Human Services, 750 F.2d 180, 2d Cir. (1984)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- 2-Samonte Vs de La SalleДокумент1 страница2-Samonte Vs de La SalleLove EsmeroОценок пока нет
- PO-12 - F - 06 1 PA GE 2/ NU MPA GES 2: Învăţământ UniversitarДокумент3 страницыPO-12 - F - 06 1 PA GE 2/ NU MPA GES 2: Învăţământ UniversitarElena FilipОценок пока нет
- Strategic Litigation Impacts, Insight From Global ExperienceДокумент144 страницыStrategic Litigation Impacts, Insight From Global ExperienceDhanil Al-GhifaryОценок пока нет
- Credit, Background, Financial Check Disclaimer2Документ2 страницыCredit, Background, Financial Check Disclaimer2ldigerieОценок пока нет
- Lesson 25 The Fruits of Manifest Destiny StudentДокумент31 страницаLesson 25 The Fruits of Manifest Destiny StudentGabriel BalderramaОценок пока нет
- Processes To Compel AppearanceДокумент34 страницыProcesses To Compel AppearanceNayem Miazi100% (2)
- Tom Jones - : A Fighter For Freedom and Working PeopleДокумент44 страницыTom Jones - : A Fighter For Freedom and Working PeopleAramОценок пока нет
- Dokumenti/ Këshilli I Europës Tregon Pse U Refuzuan Kandidatët e Qeverisë Shqiptare Për Gjyqtar Në StrasburgДокумент4 страницыDokumenti/ Këshilli I Europës Tregon Pse U Refuzuan Kandidatët e Qeverisë Shqiptare Për Gjyqtar Në StrasburgAnonymous pPe9isQYcSОценок пока нет
- Shay Eshel - The Concept of The Elect Nation in Byzantium (2018, Brill) PDFДокумент234 страницыShay Eshel - The Concept of The Elect Nation in Byzantium (2018, Brill) PDFMarko DabicОценок пока нет
- 2020 Omnibus AffidavitДокумент1 страница2020 Omnibus AffidavitJAKE FRANCIS LUMBRESОценок пока нет
- Water Quality Categorization Using WQI in Rural Areas of Haridwar, IndiaДокумент16 страницWater Quality Categorization Using WQI in Rural Areas of Haridwar, IndiaESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and ConservaionОценок пока нет
- File Converter: +200 Formats Supported Data SecurityДокумент3 страницыFile Converter: +200 Formats Supported Data SecurityNPp8grciaОценок пока нет
- Shah Abdul Latif University, Khairpur: ST NDДокумент9 страницShah Abdul Latif University, Khairpur: ST NDsaqib maharОценок пока нет
- Renter Information Rental Information Charge Information: Biswadeep Das Time ChargesДокумент1 страницаRenter Information Rental Information Charge Information: Biswadeep Das Time ChargesBiswadeep DasОценок пока нет
- DL Services GhashyamДокумент2 страницыDL Services GhashyamGhanshyam ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- MCQ On Guidance Note CAROДокумент63 страницыMCQ On Guidance Note CAROUma Suryanarayanan100% (1)
- Sony SBS Flyer 03Документ2 страницыSony SBS Flyer 03rehman0084Оценок пока нет
- 1788-10 Series 310 Negative Pressure Glove Box ManualДокумент10 страниц1788-10 Series 310 Negative Pressure Glove Box Manualzivkovic brankoОценок пока нет