Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Assignment 22
Загружено:
Sakshi BachhetyАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Assignment 22
Загружено:
Sakshi BachhetyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Physics 121.
6 2007/2008
Assignment 22
This assignment is for practice only. It does not need to be submitted.
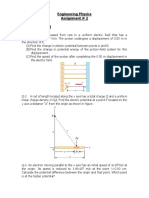
1. Chapter 28, Problem 23. In the circuit of
Figure P28.23, determine the current in
each resistor and the voltage across the
200- resistor.
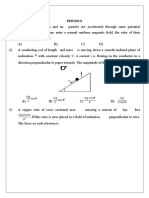
2. Someone has labelled the currents in each
branch of the circuit as shown. Which one of
the following is a correct equation?
I
2
I
1
I
3
I
5
I
4
I
6
(A) I
1
+I
3
=I
5
(B) I
4
+I
3
=I
2
(C) I
2
+I
1
=I
6
(D) I
6
+I
4
=I
5
(E) I
2
+I
4
=I
3
3. Chapter 33, Problem 2. (a) What is the resistance of a lightbulb that uses an
average power of 75.0 W when connected to a 60.0-Hz power source having a
maximum voltage of 170 V? (b) What If? What is the resistance of a 100-W
bulb?
4. The figure shows three lamps connected
to a 120-V AC (rms) household supply
voltage. Lamps 1 and 2 have 150-W
bulbs; lamp 3 has a 100-W bulb. Find the
rms current and resistance of each bulb.
5. A typical galvanometer, which requires a current of 1.50 mA for full-scale
deflection and has a resistance of 75.0 , may be used to measure currents of
much greater values. To enable an operator to measure large currents without
damage to the galvanometer, a relatively small shunt resistor is wired in parallel
with the galvanometer. Most of the current then goes through the shunt resistor.
Calculate the value of the shunt resistor that allows the galvanometer to be used to
measure a current of 1.00 A at full-scale deflection. (Suggestion: use Kirchhoffs
rules.)
6. An electron is moving toward the North in a region of space where there is a
magnetic field which is pointing vertically downward. In which direction is the
magnetic force on the electron?
(A) Down
(B) Up
(C) North
(D) South
(E) East
(F) West
7. Chapter 29, Problem 2. Consider an electron near the Earths equator [where the
magnetic field is directed toward the North]. In which direction does it tend to
deflect [due to the magnetic force] if its velocity is directed (a) downward,
(b) northward, (c) westward, or (d) south-eastward?
8. Chapter 29, Problem 4. A proton travels with a speed of 3.00 10
6
m/s at an
angle of 37.0 with the direction of a magnetic field of 0.300 T in the +y direction.
What are (a) the magnitude of the magnetic force on the proton and (b) its
acceleration?
9. Chapter 29, Problem 8. An electron in a uniform electric and magnetic field has
a velocity of 1.20 10
4
m/s (in the positive x direction), and an acceleration of
2.00 10
12
m/s
2
(in the positive z direction). If the electric field has a magnitude
of 20.0 N/C (in the positive z direction), what can you determine about the
magnetic field in the region? What can you not determine?
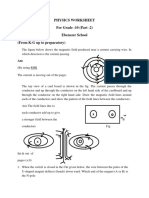
10. A conductor suspended by two flexible wires,
as shown in figure, has a mass per unit length
of 0.040 0 kg/m. What current must exist in the
conductor in order for the tension in the
supporting wires to be zero when the magnetic
field is 3.60 T into the page? What is the
required direction for the current?
11. Chapter 29, Problem 34. A current of 17.0 mA is maintained in a single circular
loop of 2.00 m circumference. A magnetic field of 0.800 T is directed parallel to
the plane of the loop. (a) Calculate the magnetic moment of the loop. (b) What is
the magnitude of the torque exerted by the magnetic field on the loop?
12. A singly charged positive ion has a mass of 3.20 10
26
kg. After being
accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 833 V, the ion enters a
magnetic field of 0.920 T along a direction perpendicular to the direction of the
field. Calculate the radius of the path of the ion in the field.
13. Chapter 29, Problem 17. A velocity selector consists of electric and magnetic
fields described by the expressions k E
E =
r
and j B
B =
r
, with B =15.0 mT. Find
the value of E such that a 750-eV electron moving along the positive x axis is
undeflected.
14. Chapter 29, Problem 19. Consider the mass spectrometer shown schematically
in Figure 29.13. The magnitude of the electric field between the plates of the
velocity selector is 2 500 V/m, and the magnetic field in both the velocity selector
and the deflection chamber has a magnitude of 0.035 0 T. Calculate the radius of
the path for a singly charged ion having a mass m =2.18 10
26
kg.
15. A charge can move through a region where there is a magnetic field B and not
experience a force by
(A) travelling very quickly.
(B) travelling parallel to B.
(C) travelling perpendicular to B.
(D) travelling very slowly.
(E) travelling in a circle.
16. A circular flat coil of N turns and enclosed area A, carrying a current I, is placed
in a uniform magnetic field, of magnitude B, so that the line perpendicular to the
plane of the coil is parallel to the direction of the magnetic field. The torque on
the coil is
(A) zero
(B) NIBA
(C) NBA
(D) IBA
(E) None of the above.
Вам также может понравиться
- Magnetic Levitation Force CalculationДокумент4 страницыMagnetic Levitation Force Calculationbenimana cedricОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 5Документ4 страницыTutorial 5Wan HafizaОценок пока нет
- Asas 1 Preparation Lev 12Документ3 страницыAsas 1 Preparation Lev 12tiarans703Оценок пока нет
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsДокумент5 страницMagnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism - Class 12 QuestionsBug LordОценок пока нет
- Class 12 - HY2 - RevisionДокумент6 страницClass 12 - HY2 - RevisionSam SolomonОценок пока нет
- MovingChargesMagnetismДокумент4 страницыMovingChargesMagnetismSheena RizviОценок пока нет
- Class 12 - HY2 - RevisionДокумент6 страницClass 12 - HY2 - RevisionSam SolomonОценок пока нет
- HomeWork 06Документ6 страницHomeWork 06Christian PaulОценок пока нет
- Question 961019Документ11 страницQuestion 961019rajaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 6@HiLCoEДокумент4 страницыWorksheet 6@HiLCoEAbraham DamtewОценок пока нет
- CH 4-MCM-WSДокумент8 страницCH 4-MCM-WSmmkishore067Оценок пока нет
- Spty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFДокумент14 страницSpty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFyeateshwarriorОценок пока нет
- QuestionДокумент5 страницQuestionlingkamkitОценок пока нет
- G12 Phy Pa2 Q.PДокумент8 страницG12 Phy Pa2 Q.PnjragavendaraОценок пока нет
- Advanced Physics ReviewДокумент3 страницыAdvanced Physics ReviewalОценок пока нет
- Ch29-PHYS 205-Problems To Solve in Class-Magnetic-FieldsДокумент2 страницыCh29-PHYS 205-Problems To Solve in Class-Magnetic-FieldsAllyson OffreyОценок пока нет
- Assignment#2, Potential, Capacitors, Magnetic Force and FieldДокумент5 страницAssignment#2, Potential, Capacitors, Magnetic Force and FieldBilal KhalidОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Induction ProblemsДокумент2 страницыElectromagnetic Induction ProblemsSharath MysoreОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Induction ExplainedДокумент35 страницElectromagnetic Induction ExplainedabhinashОценок пока нет
- Tutorial: Chapter 22, Problem 03Документ4 страницыTutorial: Chapter 22, Problem 03tonyformedОценок пока нет
- EP Assignment Spring 2015 PDFДокумент6 страницEP Assignment Spring 2015 PDFanon_429934438Оценок пока нет
- Magnetism Tutorial with Physics Problems and FiguresДокумент3 страницыMagnetism Tutorial with Physics Problems and FiguresjessycaОценок пока нет
- Electricity & Magnetism Tutorial III & IVДокумент7 страницElectricity & Magnetism Tutorial III & IVsachini weesingheОценок пока нет
- Emi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Документ6 страницEmi Assignment (Nitin M Sir)Kenny RuizОценок пока нет
- Jee Main - CPT - IДокумент31 страницаJee Main - CPT - IMohammed Aftab Ahmed0% (1)
- E2T2 Practice Problems – Magnetic Fields and InductionДокумент12 страницE2T2 Practice Problems – Magnetic Fields and InductionAatishImrozОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Electromagnetic FieldДокумент5 страницChapter 1 - Electromagnetic Fieldhoangkhanhvn8Оценок пока нет
- Ninety - Nine Percent of All Failures Come From The People Who Have The Habit of Making ExcusesДокумент7 страницNinety - Nine Percent of All Failures Come From The People Who Have The Habit of Making ExcusesAryan MurghaiОценок пока нет
- 2.short Answer Type IIДокумент3 страницы2.short Answer Type IIJohn WickОценок пока нет
- Physics 2004 Set 1: Subjective TestДокумент36 страницPhysics 2004 Set 1: Subjective TestAkshit ChanderОценок пока нет
- Magnetics MCQs and AnswersДокумент4 страницыMagnetics MCQs and AnswersRohit YadavОценок пока нет
- Assignment Electricity and Mag.Документ3 страницыAssignment Electricity and Mag.Hafiz IkramaОценок пока нет
- Book 1 Complete Test 2024Документ5 страницBook 1 Complete Test 2024lukkuyadav050Оценок пока нет
- Classroom Assignment 6 With AnswersДокумент3 страницыClassroom Assignment 6 With AnswersBishoy EmileОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 8Документ2 страницыTutorial 8yhbarakat11Оценок пока нет
- Physics Sample PaperДокумент4 страницыPhysics Sample Papermanishpant1Оценок пока нет
- Assignment On EMIДокумент6 страницAssignment On EMIewrОценок пока нет
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Документ6 страницPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024xkryxxzОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Sheet 5Документ3 страницыTutorial Sheet 5Abraham KabweОценок пока нет
- Model Question Paper for Class XII Physics Half Yearly ExamДокумент6 страницModel Question Paper for Class XII Physics Half Yearly ExamSoumya KhatriОценок пока нет
- PHYSICS (Theory) ExamДокумент5 страницPHYSICS (Theory) ExamKapil BakshiОценок пока нет
- MCQ Magnetic Fields and ForcesДокумент11 страницMCQ Magnetic Fields and ForcesMaha TharwatОценок пока нет
- Part Xxvii - Magnetic Fields & Forces-Set 2Документ8 страницPart Xxvii - Magnetic Fields & Forces-Set 2apostolos efstathiouОценок пока нет
- Physics II ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSОценок пока нет
- Physics Worksheet For Grade - 10 (Part - 2) Ebenezer School (From K-G Up To Preparatory)Документ6 страницPhysics Worksheet For Grade - 10 (Part - 2) Ebenezer School (From K-G Up To Preparatory)YishakОценок пока нет
- Unit 7 ExercisesДокумент6 страницUnit 7 ExercisesBao Hoang LeОценок пока нет
- HY - Class XII - 2015-2016 - Class XII - 2016-2017Документ3 страницыHY - Class XII - 2015-2016 - Class XII - 2016-2017Rijty SagartonОценок пока нет
- (Theory) VCBE/PO1/A/12: Sample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - PhysicsДокумент6 страниц(Theory) VCBE/PO1/A/12: Sample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - PhysicsNithin BalanОценок пока нет
- 4 QP Electromagnetic Induction 3.Документ8 страниц4 QP Electromagnetic Induction 3.Muzna AlshahwarziОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15 ProblemsДокумент7 страницChapter 15 ProblemsekojantiОценок пока нет
- Test1 16FДокумент8 страницTest1 16FJasper LuОценок пока нет
- Ee1 Ece 500Документ7 страницEe1 Ece 500Karen Gale A. Lodia - AlarconОценок пока нет
- Xam Idea Previous Years Question Papers 2008-2012Документ419 страницXam Idea Previous Years Question Papers 2008-2012Mohammed Farhad77% (13)
- Physic 12 Sample PaperДокумент5 страницPhysic 12 Sample PaperDeep ChovatiyaОценок пока нет
- Principles and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsОт EverandPrinciples and Practices of Molecular Properties: Theory, Modeling, and SimulationsОценок пока нет
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyОт EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyОценок пока нет
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsОт EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Respectively. If B Maintains A Constant Speed, While A: Figure 1Документ1 страницаRespectively. If B Maintains A Constant Speed, While A: Figure 1Ashish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Prob90 2Документ1 страницаProb90 2Ashish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Relative VelocityДокумент4 страницыRelative VelocityAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Online T Est Dashboard: Test Id: Test7 Home (Userhome - PHP) View Results (Viewresults - PHP? Test - Id Test7)Документ10 страницOnline T Est Dashboard: Test Id: Test7 Home (Userhome - PHP) View Results (Viewresults - PHP? Test - Id Test7)Ashish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- E4 QuestionsДокумент10 страницE4 QuestionsAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- GujCET Physics 2010Документ5 страницGujCET Physics 2010Ashish Awasthi50% (2)
- Prob90 2Документ1 страницаProb90 2Ashish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Polar CoordinatesДокумент3 страницыPolar Coordinatesvxa_victorОценок пока нет
- BPhO Paper2 2007 QPДокумент10 страницBPhO Paper2 2007 QPAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Maxwell's Equations Magnetism and MatterДокумент19 страницMaxwell's Equations Magnetism and MatterAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- E4 QuestionsДокумент10 страницE4 QuestionsAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics Practice Probs 1Документ2 страницыElectrostatics Practice Probs 1Ashish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- EM WavesДокумент20 страницEM WavesAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Magnetic FieldsДокумент13 страницMagnetic FieldsAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Photons and Matter WavesДокумент12 страницPhotons and Matter WavesAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- ImagesДокумент16 страницImagesAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics Practice Probs 1Документ2 страницыElectrostatics Practice Probs 1Ashish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Induction and InductanceДокумент24 страницыInduction and InductanceAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- EM Oscillations and ACДокумент19 страницEM Oscillations and ACAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- GUJCET CapacitorsДокумент12 страницGUJCET CapacitorsAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Gentoo Linux DocumentationДокумент5 страницGentoo Linux DocumentationAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- CRR SLRДокумент14 страницCRR SLRSharanyan IyengarОценок пока нет
- ErodicityДокумент2 страницыErodicityAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет
- ShazyДокумент1 страницаShazyAshish AwasthiОценок пока нет