Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis
Загружено:
Jhon Jerric Pante AguinaldoАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis
Загружено:
Jhon Jerric Pante AguinaldoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
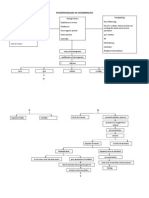
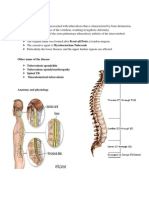
III.
Pathophysiology of Osteomyelitis
External fixation device
Foley catheter
Cerebral or peripheral IV line
Trauma to long bones
Contagious infection
Direct inoculation
- stab or puncture to long bones
mode of entrance for microorganism
(staphylococcus aureus streptococcus group ! streptococcuc Escherchia coli"
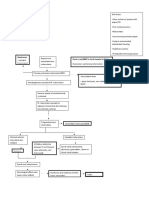
Infection
(presence of microorganism"
Inflammatory and immunologic response
Infection spreads through bone vie puss
formation
Vol#mann$s and %aversion canals edema
Vascular
congestion
pain
Vascular occlusion
!one necrosis and ischemia
Ischemia allo&s necrotic bone to
separate from living bone
formation of se'uestra
se'uestra enlarged spreading to&ard
and breading the cortex
forming subperiosteal abcess
interfered vascular supply
bone dies and become inert
central residual remains as se'uestrum composed of cancellous
or cortical bone or combination
ne& bone is formed and forming an encasement
around the se'uestrum
poc#ets of infection are &alled off in &hich
organism lie dormant for long period
chronic sinuses may form and reach the surface and drain
channels become plugged and remains closed until the
pressure of the puss builds up and causes the sinuses
to reopen and reach the surface through ne& channels
(chronic osteomyelitis)
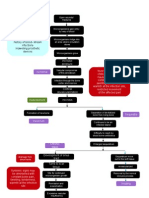
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Infection of the bone starts from the entry of the causative agent ((taphylococcus
aureus )roteus )seudomanas E* Coli"* These microorganisms typically find a culture
site in a hematoma from a recent trauma or in a &ea#ened area such as the site of local
infection and spread directly to bone* The microorganisms lodge into an area &here they
&ill gro& and multiply* They &ill travel to the bone by the bloodstream and may travel to
different parts of the body* This &ill no& cause bone inflammation &hich is the initial
response to infection* +fter , or - days thrombosis of the blood vessels occurs in the
area resulting in ischemia &ith bone necrosis* The lumen of the blood vessels &ill
decrease hence causes increase in the pressure on the affected part* +s the organisms
gro& and form pus &ithin the bone tension builds &ithin the rigid medullary cavity and
under the periosteum and may spread into ad.acent soft tissue and .oints forcing pus
through the haversian canals* /nless the infective process is treated promptly bone
abscess form* The resulting abscess cavity contains dead one tiss!e (se'uestrum" &hich
does not easily li'uefy and drain* It also deprives the bone of its blood supply and
eventually may cause necrosis0 hence it stimulates the periosteum to create a ne& bone
(involucrum" &hich surrounds the se'uestrum*
The se'uestrum detaches and &or#s its &ay out through an abscess or the
sinuses* (eparation of dead tissue from living bone may also occur* This &ill no&
develop a sinus tract &hich could eventually turns to scar*
Вам также может понравиться
- Osteomyelitis, PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыOsteomyelitis, Pathophysiology4kscribdОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of OsteomyelitisДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of OsteomyelitisKeith Madarang100% (2)
- Predisposing Factors and Stages of OsteomyelitisДокумент1 страницаPredisposing Factors and Stages of OsteomyelitisKim Enrico JumarangОценок пока нет
- Common Cause or Etiology of Pott's DiseaseДокумент5 страницCommon Cause or Etiology of Pott's DiseaseStan Aves GarciaОценок пока нет
- Osteomyelitis Pathophysiology: Modifiable, Non-Modifiable FactorsДокумент1 страницаOsteomyelitis Pathophysiology: Modifiable, Non-Modifiable FactorsJohara Mae De RamaОценок пока нет
- Patho of Pott's DiseaseДокумент2 страницыPatho of Pott's DiseaseIris Balino100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of OsteomyelitisДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Osteomyelitissorryandreosayanisalreadytaken100% (1)
- OsteomyelitisДокумент7 страницOsteomyelitis4kscribd100% (1)
- Pott's DiseaseДокумент8 страницPott's DiseaseLorebell100% (2)
- NCP - OsteosarcomaДокумент5 страницNCP - OsteosarcomaNelson Lacsamana100% (1)
- HNP Case Scenario For Case StudyДокумент2 страницыHNP Case Scenario For Case StudyDeinielle Magdangal RomeroОценок пока нет
- Fractures, PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаFractures, Pathophysiology4kscribdОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of FractureДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of FractureVenus Tagaan UcatОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology OsteosarcomaДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology OsteosarcomaVernadeth Dumagat50% (2)
- PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаPathophysiologyRj MagpayoОценок пока нет
- Potts Disease Case AnalysisДокумент5 страницPotts Disease Case AnalysisAdrian MallarОценок пока нет
- NCP PottsДокумент3 страницыNCP PottsFenie Jane Quinlat LapastoraОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of OsteosarcomaДокумент5 страницPathophysiology of Osteosarcomafanvicfay100% (9)
- Cholecystitis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Документ4 страницыCholecystitis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Jorie RocoОценок пока нет
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMaДокумент1 страницаPATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMakyawОценок пока нет
- Potts DiseaseДокумент3 страницыPotts DiseasePaul Stephen PinedaОценок пока нет
- Gout Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentДокумент17 страницGout Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentPaulette Olisco0% (1)
- Patho Pott's DseДокумент2 страницыPatho Pott's Dsexai_teovisioОценок пока нет
- Case Study About Pott's DiseaseДокумент7 страницCase Study About Pott's Diseasebhy18190% (1)
- Paget's Disease of The BoneДокумент9 страницPaget's Disease of The BonePam RomeroОценок пока нет
- PYOMYOSITISДокумент6 страницPYOMYOSITISChristine CoridoОценок пока нет
- Case Study - Pott's Disease (Final)Документ38 страницCase Study - Pott's Disease (Final)Raymund Christopher Dela Peña60% (5)
- Pathophysiology of FractureДокумент4 страницыPathophysiology of FractureLemuel GuevarraОценок пока нет
- Osteomyelitis HandoutДокумент4 страницыOsteomyelitis HandoutJazzmin Angel ComalingОценок пока нет
- Rabies PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаRabies PathophysiologyMichael Urrutia100% (1)
- Pott's DiseaseДокумент17 страницPott's DiseaseRheegell Ellar-Fuertes100% (1)
- Tetanus PathoДокумент3 страницыTetanus PathoElisha Gine AndalesОценок пока нет
- Group 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERДокумент1 страницаGroup 3 Pathophysiology-of-BREAST-CANCERArisa VijungcoОценок пока нет
- OsteomyelitisДокумент47 страницOsteomyelitisArmand Al HaraaniОценок пока нет
- (Brand Name) & Date Ordered General Class and Family Specific IndicationДокумент2 страницы(Brand Name) & Date Ordered General Class and Family Specific IndicationNicole Grace VillegasОценок пока нет
- Pa Tho Physiology of Open FractureДокумент2 страницыPa Tho Physiology of Open FracturegiffersonbОценок пока нет
- Casestudy OsteomyelitisДокумент52 страницыCasestudy OsteomyelitisMJ Amarillo84% (19)
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыPost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology FracturesДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology FracturesSewyel Garburi71% (7)
- Pathophysiology of TetanusДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of TetanusAnitha SuprionoОценок пока нет
- FractureДокумент7 страницFractureirene joy100% (2)
- Casestudy Pott's DiseaseДокумент36 страницCasestudy Pott's DiseaseyasiraОценок пока нет
- OSTEOSARCOMAДокумент5 страницOSTEOSARCOMALorebell75% (4)
- Potts Disease Case Study OLGCДокумент15 страницPotts Disease Case Study OLGChomermanlapaz100% (2)
- Schematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and TuberculosisДокумент1 страницаSchematic Diagram Pathophysiology (Book-Based) COPD and Tuberculosispragna novaОценок пока нет
- Potts DiseaseДокумент5 страницPotts Diseasemyla-elmarie100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Potts DiseaseДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Potts DiseaseJoanna Marie M. dela Cruz100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Appendicitis: Causes and SymptomsДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Appendicitis: Causes and SymptomsSherry Mae Rizza GonzalesОценок пока нет
- PyomyositisДокумент17 страницPyomyositisiluvmypoopoo22100% (1)
- Bone InfectionsДокумент22 страницыBone InfectionsOmar MustafaОценок пока нет
- Pathogenesis of Post Traumatic OsteomyelitisДокумент5 страницPathogenesis of Post Traumatic OsteomyelitisChan Zhi KangОценок пока нет
- OSTEOMYELITISДокумент5 страницOSTEOMYELITISArafat Masud Niloy100% (1)
- Infections of The Bone Dr. Mehzabin AhmedДокумент14 страницInfections of The Bone Dr. Mehzabin AhmednhemieОценок пока нет
- Gambar. 2.1. Osteomielitis HematogenДокумент13 страницGambar. 2.1. Osteomielitis HematogenTri Wahyu SaptamiОценок пока нет
- Due To The Sharp Bending of The Vessels in The Metaphysic and Also by The Hematoma Formed After InjuryДокумент6 страницDue To The Sharp Bending of The Vessels in The Metaphysic and Also by The Hematoma Formed After InjuryBashar EbrahimОценок пока нет
- Disorders of Bone II-2Документ59 страницDisorders of Bone II-2Guhan DergОценок пока нет
- OSTEOMYELITISДокумент4 страницыOSTEOMYELITISGanah PeterОценок пока нет
- Script Case PressДокумент7 страницScript Case PressMa. Gina DerlaОценок пока нет
- OsteomyelitisДокумент41 страницаOsteomyelitisArumpaavai PugazhiniОценок пока нет
- Patho (Osteomyelitis)Документ2 страницыPatho (Osteomyelitis)sidaveОценок пока нет
- Urinary Tract Infection in The ElderlyДокумент18 страницUrinary Tract Infection in The ElderlyNicky AlexandraОценок пока нет
- Annex K Basic DOH PEME Package - Rev 02Документ5 страницAnnex K Basic DOH PEME Package - Rev 02Kurt Ronald SanJuan EstebanОценок пока нет
- Quiz Blood Born Pathogen Refresher Mix Quiz Non ECU Employees and Students and Temporary StaffДокумент4 страницыQuiz Blood Born Pathogen Refresher Mix Quiz Non ECU Employees and Students and Temporary Staffvipin khatriОценок пока нет
- Leishmania tropica Causes Different Forms of LeishmaniasisДокумент2 страницыLeishmania tropica Causes Different Forms of LeishmaniasisJeddhie MoraОценок пока нет
- PhlebotomyДокумент24 страницыPhlebotomyERSKINE LONEYОценок пока нет
- CRISPR HandbookДокумент14 страницCRISPR HandbookLina Tadeo Fabián100% (2)
- Cholera: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleДокумент17 страницCholera: Click To Edit Master Subtitle Stylegirlygirl10Оценок пока нет
- Lab InvestigationsДокумент25 страницLab Investigationsbadar_aq100% (1)
- Cornell StatementДокумент4 страницыCornell StatementNews10NBCОценок пока нет
- Home Remedies Using Onion Prophet666Документ2 страницыHome Remedies Using Onion Prophet666Hussainz AliОценок пока нет
- With Alcohol-Based Formulation With Soap and WaterДокумент1 страницаWith Alcohol-Based Formulation With Soap and WaterRevina AmaliaОценок пока нет
- Andalas University Faculty Of Nursing Guide To COVID-19 PreventionДокумент1 страницаAndalas University Faculty Of Nursing Guide To COVID-19 PreventionHahahahaОценок пока нет
- Triacid N PI enДокумент2 страницыTriacid N PI enkashif raoОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Arterial Pressure TestingДокумент22 страницыPulmonary Arterial Pressure Testingeven24Оценок пока нет
- Measles MorbiliДокумент16 страницMeasles MorbiliRegyna SusantiОценок пока нет
- Microbiology and Parasitology #1Документ11 страницMicrobiology and Parasitology #1Judy BaguiwenОценок пока нет
- Asessment of Mother's Practice Towards Child Vaccination and Its Associated Factors With Child Vaccination inДокумент24 страницыAsessment of Mother's Practice Towards Child Vaccination and Its Associated Factors With Child Vaccination inMinlik-alew Dejenie100% (6)
- Communicable Disease ControlДокумент20 страницCommunicable Disease ControlAlison ArellanoОценок пока нет
- Expanded Immunization Program EpiДокумент22 страницыExpanded Immunization Program EpiGirome BairaОценок пока нет
- TRICHOMONIASISДокумент14 страницTRICHOMONIASISAuddrey Tan100% (1)
- Chronic Pelvic Pain Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент48 страницChronic Pelvic Pain Diagnosis and TreatmentFeruza SultanmuratovaОценок пока нет
- Phytochemical Screening and Antibacterial Activities of Vernonia Ambigua, Vernonia Blumeoides and Vernonia Oocephala (Asteraceae)Документ7 страницPhytochemical Screening and Antibacterial Activities of Vernonia Ambigua, Vernonia Blumeoides and Vernonia Oocephala (Asteraceae)linubinoiОценок пока нет
- Fungal Structures for Nutrient AbsorptionДокумент2 страницыFungal Structures for Nutrient AbsorptionSajjad Hossain Shuvo100% (1)
- 10 Reasons Smoking Is Bad For YouДокумент6 страниц10 Reasons Smoking Is Bad For YouYuNa YoshinoyaОценок пока нет
- Bioprotexion Manual Virocid VirocidДокумент9 страницBioprotexion Manual Virocid Virocidabd el rhman gamalОценок пока нет
- Parivarik Mahila Lok AdalatДокумент19 страницParivarik Mahila Lok Adalatabhimanyu5001Оценок пока нет
- Amazing Sanitary Napkin Relieves Infection, Stress with 6,070 Negative IonsДокумент6 страницAmazing Sanitary Napkin Relieves Infection, Stress with 6,070 Negative Ionsrostenec100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S209379112300063X MainДокумент8 страниц1 s2.0 S209379112300063X Mainshoshanasingh52Оценок пока нет
- Mcr-Prs Lec Chapter14 (Word Format)Документ4 страницыMcr-Prs Lec Chapter14 (Word Format)Ali UyОценок пока нет
- Aerosol Generating Medical ProceduresДокумент6 страницAerosol Generating Medical Proceduresdhira anindita100% (1)