Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fluid machines classification and working
Загружено:
Anonymous f1UCK4Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fluid machines classification and working
Загружено:
Anonymous f1UCK4Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fluid machines
Fluid machines are dynamic fluid machines that add (for pump) or extract (for turbines) flow
energy. The term pump is used when the working fluid is water or oil. The term compressor is
used when the working fluid is air/gas.
Classification of Fluid Machines
Fluid machines can be classified as:
Positive displacement machines Rotodynamic machines.
In positive displacement machines fluid is drawn into a finite space bounded by mechanical parts, then
sealed in it, and then forced out from space and the cycle is repeated. The flow is intermittent and
depends on the dimensions of the space (chamber), and speed or the pump. Gear pumps, vane pumps
are all positive displacement pumps.
In rotodynamic machines there is free passage between inlet and outlet of the machine
without intermittent sealing taking place. In these machines there is a rotor which is able to rotate
continuously and freely in the fluid. The transfer of energy is continuous which results in change of
pressure or momentum of the fluid. Centrifugal blower, centrifugal pumps and hydraulic turbines are
some examples of rotodynamic machines.
The two criteria, namely, the energy transfer and type of action, form the basis of
classification of hydraulic machines, as shown in Fig. 4.1. From the chart it can be seen that pumps and
compressors increase the energy of the fluid and may be positive displacement or rotodynamic. Fans are
always rotodynamic. Turbine does work and is rotodynamic.
Fluid machines
Further classification is based on flow and energy transfer. Fluid used as means of energy
transfer.
(a) Classification based on the geometry of flow path:
Radial flow; Axial flow; Mixed flow.
In radial flow the flow path is essentially radial with significant changes in radius. In axial flow
machines the flow path is nearly parallel to the machine centre line and the path does not change. In
mixed flow it is partly axial and partly radial.
(b) Fluid machines can use any of the following forms of energy
Heat energy (steam and gas turbines) Potential energy (hydraulic turbines) Kinetic energy (wind
mills)
In power producing machines work is done by the fluid flow and in power absorbing machines work is
done on the fluid to raise potential energy.
Centrifugal Pumps
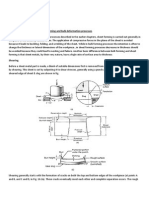
A single-stage centrifugal pump is shown in Fig . The rotating element is called the impeller which is
contained within the pump housing or casing. The shaft transfers mechanical energy to impeller which
must penetrate the casing, a system of bearings. Seals are required against the leakage of the fluid. Fluid
enters the machine nearly in axial direction at inlet through the eye of the impeller and leaves the
impeller radially out. Flow leaving the impeller is collected in a scroll or volute, which gradually
increases in area as fluid moves out through exit. The impeller has vanes to convey the fluid.
Fluid machines
Reciprocating pump : A reciprocating pump essentially consists of a piston moving to and fro in a
cylinder. The piston is driven by a crank powered by some prime mover such an electric motor, I C
engine or steam engine.
Gear Pump : These are used more often for oil pumping. Gear pumps consist of two identical mating
gears in a casing as shown in figure . The gears rotate as indicated in the sketch. Oil is trapped in the
space between the gear teeth and the casing.The oil is then carried from the lower pressure or
atmospheric pressure and is delivered at the pressure side. The two sides are sealed by the meshing
teeth in the middle. The maximum pressure that can be developed depends on the clearance and
viscosity of the oil.
Lobe Pump : This type is also popularly used with oil. The diagramatic sketch of a lobe pump is
shown in fig. This is a three lobed pump. Two lobe pump is also possible. The gear teeth are replaced by
lobes. Two lobes are arranged in a casing. As the rotor rotates, oil is trapped in the space between the
lobe and the casing and is carried to the pressure side. Helical lobes along the axis are used for smooth
Fluid machines
operation. Oil has to be filled before starting the pump. Lobe type of compressors are also in use.
The constant contact between the lobes makes a leak tight joint preventing oil leakage from the
pressure side.
Vane Pump : This is another popular type not only for oil but also for gases. A rotor is eccentrically
placed in the casing as shown in figure. The rotor carries sliding vanes in slots along the length. Springs
control the movement of the vanes and keep them pressed on the casing. Oil is trapped between the
vanes and the casing. As the rotor rotates the trapped oil is carried to the pressure side. The maximum
operating pressure is controlled by the back leakage.
Classification of turbines
(i) Impulse turbine (ii) Reaction Turbine.
In the case of impulse turbine all the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy in the nozzles. The
impulse provided by the jets is used to turn the turbine wheel. The pressure inside the turbine is
atmospheric. This type is found suitable when the available potential energy is high and the flow
available is comparatively low. Some people call this type as tangential flow units.
In reaction turbines the available potential energy is progressively converted in the turbines rotors and
the reaction of the accelerating water causes the turning of the wheel.These are again divided into
radial flow, mixed flow and axial flow machines. Radial flow machines are found suitable for moderate
levels of potential energy and medium quantities of flow. The axial machines are suitable for low levels
of potential energy and large flow rates.
Pelton Wheel : Pelton wheel is an impulse turbine. It is driven by a single jet which lies in the plane
of runner. A high velocity jet prossesing kinetic energy strikes the bucket in succession. The water takes
nearly I 80 turn inside the buckets. The water falls into the tail race.
Francis Turbine : Francis turbine is a reaction turbine shown in Fig. Water enters
circumferentially through turbine casing. It enters from the outer periphery of guide vanes and flows
Fluid machines
into runner. It flows down the rotor radially and leaves axially. Water leaving the runner flows through a
diffuser known as draft tube before entering the tail race.
Kaplan Turbine : Kaplan turbine is a reaction turbine shown in Fig. The water from the spiral casing
enters guide blades similar to Francis. The Kaplan turbine consists of an axial flow runner with 4 to 6
blades of an airfoil section. In this turbine both guide vanes and moving blades are adjustable and
therefore high efficiency can be obtained.
Вам также может понравиться
- Machine tools and digital manufacturing questionsДокумент3 страницыMachine tools and digital manufacturing questionsAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Machine tools and digital manufacturing questionsДокумент3 страницыMachine tools and digital manufacturing questionsAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Metallurgy and Material Science Fracture, Composites, Ceramics, Super Alloys, Smart MaterialsДокумент1 страницаMetallurgy and Material Science Fracture, Composites, Ceramics, Super Alloys, Smart MaterialsAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Smoothies For Optimum HealthДокумент192 страницыSmoothies For Optimum HealthAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Metrology &machine Tools Nov 2006adДокумент2 страницыMetrology &machine Tools Nov 2006adAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Manufacturing Process Btech MG University QP SolvedДокумент24 страницыManufacturing Process Btech MG University QP SolvedAnonymous f1UCK4100% (2)
- Introduction To Sustainable ManufacturingДокумент24 страницыIntroduction To Sustainable ManufacturingAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Designproject, Comprehensiveexam, Seminarprojectpdf PDFДокумент2 страницыDesignproject, Comprehensiveexam, Seminarprojectpdf PDFAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Designproject, Comprehensiveexam, Seminarprojectpdf PDFДокумент2 страницыDesignproject, Comprehensiveexam, Seminarprojectpdf PDFAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Heap Leaching OF MetalsДокумент60 страницHeap Leaching OF MetalsAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) 5x Less Effective Than Steady State CardioДокумент5 страницHigh Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) 5x Less Effective Than Steady State CardioAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- CE 2 Materials Testing LaboratoryДокумент1 страницаCE 2 Materials Testing LaboratoryAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) 5x Less Effective Than Steady State CardioДокумент5 страницHigh Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) 5x Less Effective Than Steady State CardioAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Industrial Safety Ele - IVДокумент7 страницIndustrial Safety Ele - IVAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Sheet Metal FormingДокумент11 страницSheet Metal FormingAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- WeldДокумент10 страницWeldAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- WeldingДокумент17 страницWeldingAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Machines LaboratoryДокумент27 страницHydraulic Machines LaboratoryAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- WeldingДокумент17 страницWeldingAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Rollingsidharta FrontmatterДокумент24 страницыRollingsidharta FrontmatterAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Metallurgy and Material ScienceДокумент1 страницаMetallurgy and Material ScienceAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Materials and ManufacturingДокумент50 страницMaterials and ManufacturingAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Shell Metal FormingДокумент36 страницShell Metal FormingAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Materials and ManufacturingДокумент50 страницMaterials and ManufacturingAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Gas Dynamics Question PaerДокумент1 страницаGas Dynamics Question PaerAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Fluid Machine Lab ManualДокумент0 страницFluid Machine Lab ManualBalvinder100% (2)
- Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionДокумент2 страницыGas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Gun DiodeДокумент17 страницGun DioderamyarakiОценок пока нет
- Casting and Foundry TechnologyДокумент52 страницыCasting and Foundry TechnologyAnonymous f1UCK4Оценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics Hydraulics Lab ManualДокумент24 страницыFluid Mechanics Hydraulics Lab Manualsawmag123Оценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Fire Pump Sizing Seminar HandoutДокумент18 страницFire Pump Sizing Seminar Handouthitokiri_knivesОценок пока нет
- Accepted Manuscript: Renewable EnergyДокумент38 страницAccepted Manuscript: Renewable EnergyPrivateОценок пока нет
- NCID MEP Trade Colour Code - R2 With CompareДокумент2 страницыNCID MEP Trade Colour Code - R2 With CompareWun Na ThuzarОценок пока нет
- ICAER 2015 Compendium Final PDFДокумент2 090 страницICAER 2015 Compendium Final PDFadithya333Оценок пока нет
- 180K 10K PSI NITROGEN PUMPДокумент3 страницы180K 10K PSI NITROGEN PUMParez muhammedОценок пока нет
- SPM 097Документ2 страницыSPM 097Benito CelestinОценок пока нет
- FirmsДокумент1 страницаFirmsSan ThiyaОценок пока нет
- Bomba Neumatica Milton RoyДокумент8 страницBomba Neumatica Milton RoyGuillermo de la Fuente SantiagoОценок пока нет
- 12V 100ah 12V 115ah Solar Series: Technical Dimensions (MM)Документ3 страницы12V 100ah 12V 115ah Solar Series: Technical Dimensions (MM)Houssine ZaïmiОценок пока нет
- Fuel Cells and MHD GenerationДокумент52 страницыFuel Cells and MHD Generationsubbu2051Оценок пока нет
- Aurora Fire Pump SpecsДокумент16 страницAurora Fire Pump SpecsJosé Martín Meza CabillasОценок пока нет
- 04 PPP TTE API 570 Piping InspnДокумент35 страниц04 PPP TTE API 570 Piping InspnRavindra S. Jivani100% (8)
- LV 2000LowVolumeДокумент2 страницыLV 2000LowVolumeDian MiauОценок пока нет
- 17V10 Johnson How To Collect Form and Ship SulfurДокумент43 страницы17V10 Johnson How To Collect Form and Ship SulfurabderrahimnОценок пока нет
- Conventional Power GenerationДокумент74 страницыConventional Power GenerationAlexandru DobosОценок пока нет
- ATEX 95 Compliant Air-Handling Units for Hazardous AreasДокумент4 страницыATEX 95 Compliant Air-Handling Units for Hazardous AreasLeed ENОценок пока нет
- MEC7110: Solar Energy TechnologyДокумент3 страницыMEC7110: Solar Energy TechnologyNkugwa Mark WilliamОценок пока нет
- Two-Stage Compression Centrifugal Chiller: Model RTGC SeriesДокумент6 страницTwo-Stage Compression Centrifugal Chiller: Model RTGC SeriesOM Eksperlik HizmetleriОценок пока нет
- New Stator Core Manufacturing ConceptsДокумент22 страницыNew Stator Core Manufacturing ConceptsL Mahender ReddyОценок пока нет
- BSRIA-Check List - Cold WaterДокумент3 страницыBSRIA-Check List - Cold WaterSawar NaheelОценок пока нет
- Exchanger Selection & Design in An LPG Recovery UnitДокумент27 страницExchanger Selection & Design in An LPG Recovery UnitjamestppОценок пока нет
- HSPE-144M M6 HC Bifacial 450W Rev.00Документ2 страницыHSPE-144M M6 HC Bifacial 450W Rev.00Alejandro Holguin QuinteroОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 9Документ4 страницыTutorial 9Jyoti Krishna PandaОценок пока нет
- Alcorcon Fluid Machineries ReviewerДокумент14 страницAlcorcon Fluid Machineries Revieweresto_domingo100% (1)
- DLN Combustion Systems ExplainedДокумент49 страницDLN Combustion Systems ExplainedSahariar Bin Shafique100% (1)
- 09-014 Oil in Turbocharger and Air PipingДокумент6 страниц09-014 Oil in Turbocharger and Air PipingVictor MontesdeocaОценок пока нет
- A. M. Buri Steam Power Plant Having A Forced Flow Steam Generator Filed May 28, 1956Документ4 страницыA. M. Buri Steam Power Plant Having A Forced Flow Steam Generator Filed May 28, 1956Anonymous KzJcjGCJbОценок пока нет
- Magneto Hydro Dynamic Generators: A Solution For Future Energy CrisisДокумент7 страницMagneto Hydro Dynamic Generators: A Solution For Future Energy CrisisZipronОценок пока нет