Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Particle Theory Worksheets
Загружено:
Shakila Shaki67%(3)67% нашли этот документ полезным (3 голоса)
2K просмотров6 страницMatter can be changed from one state to another by raising or lowering the temperature. The higher the temperature, the _____________ the particles move. 5) particles are _____________ to each other by forces that tend to hold the particles ____________.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документMatter can be changed from one state to another by raising or lowering the temperature. The higher the temperature, the _____________ the particles move. 5) particles are _____________ to each other by forces that tend to hold the particles ____________.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
67%(3)67% нашли этот документ полезным (3 голоса)
2K просмотров6 страницParticle Theory Worksheets
Загружено:
Shakila ShakiMatter can be changed from one state to another by raising or lowering the temperature. The higher the temperature, the _____________ the particles move. 5) particles are _____________ to each other by forces that tend to hold the particles ____________.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 6
SNC1
Particle Theory of Matter
What two experiments that suggested that matter is made of particles:
a) _____________ alcohol and water result in a combined volume that is _________
than the volumes of the original water and alcohol added together. This suggested that
different sized particles were combined and the __________ particles were fitting
_________
the larger particles.
b) When __________ and nitric acid are reacted together to make a new _______- coloured
substance. When this new substance was reacted with Aluminum, the __________ was
regenerated. This suggested that the particles of matter are not ____________ when
chemical reaction occur.
The Particle Theory
1) All matter is made of _____________.
2) Particles cannot be ____________ or _____________.
3) Particles are in a constant state of _______________.
4) The higher the temperature, the _____________ the particles move.
5) Particles are _____________ to each other by forces that tend to hold the particles ____________.
What can this theory explain?
A) Physical States of Matter: matter can be found in three states.
___________ _____________ ____________
shape: ___________ _____________ ____________
volume: ___________ _____________ ____________
Matter can be changed from one state to another by
raising or lowering the temperature. This is done by
adding or removing energy.
Changes that require adding energy (raising temp):
D ____________________________
E ____________________________
F ____________________________
Changes that require removing energy (lowering temp):
A ____________________________
B ____________________________
C ____________________________
How does the Particle Theory Explain These States:
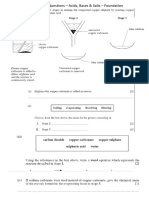
Particles in a: - gas are well separated with no regular arrangement.
- liquid are close together with no regular arrangement.
- solid are tightly packed, usually in a regular pattern.
Particles in a: - gas move freely in straight lines at high speeds and only change direction when they collide with another particle.
- liquid vibrate, move from place to place, and slide past each other.
- solid vibrate (jiggle) but generally do not move from place to place.
Liquids and solids are called condensed states because the particles are very close together,
so the substance cannot change volume much.
Liquids and gases are called fluid states because the particles can move from place to place,
so the substance can flow and change shape.
Some Characteristics of Gases, Liquids and Solids and the Microscopic Explanation for the Behavior
SOLID LIQUID GAS
retains a fixed volume and shape
particles locked into place
assumes the shape of the part of the
container which it occupies
particles can move/slide past one
another
assumes the shape and volume of
its container
particles can move past one
another
not easily compressible
little free space between particles
not easily compressible
little free space between particles
compressible
lots of free space between
particles
does not flow easily
particles cannot move or slide past
one another
flows easily
particles can move/slide past one
another
flows easily
particles can move past one
another
The particles do not move fast
enough to overcome the attractive
forces between particles. Particles
can vibrate back and forth, but the
forces always pull them back to their
original place.
Particles move fast enough to
partially overcome the attractive
forces. The lets them move past
each other, but they stay in contact
with each other.
The particles vibrate and move
about so fast that they break
away from each other and move
freely in space.
Questions
1) When we increase the temperature of a substance to change it from a solid to a liquid and then to a
gas, what does the extra energy do to the particles?
2) Some substances must be heated to a higher temperature to make them melt or evaporate than other
substances. What must be different about the particles in a substance that has a higher melting
temperature?
SNC1
Pure Substances and Mixtures
All matter can be divided into two categories based on (observable) evidence.
Observations:
a) When two substances are mixed, the new substance has different properties from the original substances.
These substances are called ____________________
Example: salt water tastes different from pure water and looks different from pure salt.
b) In addition, the properties are variable, depending on the proportions of the mixture.
Example: water tastes saltier and has a higher density if more salt is added to the same amount of water.
c) Mixtures can be un-mixed (separated) by different physical processes:
i) evaporation
ii) ____________________
iii) ____________________
iv) ____________________
d) When mixtures are separated by physical processes into simpler substances, one eventually produces,
substances that cannot be further broken down into simpler substances.
These new substances have physical properties that are not variable (the same in different samples).
These types of substances are called _________________ substances.
Example: salt water can be distilled (the water is evaporated off and recondensed to a pure liquid)
into water and salt. The water and salt have the same basic properties each time you do this.
In addition, water and salt cannot be un-mixed into any other substances.
Therefore: salt and water must NOT be mixtures.
SUMMARY: all substances can be placed into one of two categories:
A) Pure Substances: properties are same from one sample to another.
cannot be separated down into other substances by mechanical means.
B) Mixtures: properties are variable from one sample to another.
can be separated into other substances by mechanical means.
Given that samples of pure substances always have the same properties, where as mixtures have
variable properties (density, viscosity...) suggests an explanation based on the particle theory of matter.
3) How might the theory explain this?
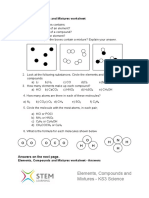
4) Classify the following substance into pure substances (PS) or mixtures (M).
a) Air b) Oxygen c) Sugar d) chocolate chip cookies
e) sugar water f) syrup g) water h) aluminum foil
i) copper wire j) dusty air j) wet sand k) muddy water
How does Particle Theory of Matter explain the difference between mixtures and pure substances?
1) Observation
Pure substances: ___________ properties; cannot be ___________ separated into other substances.
Mixtures: __________ properties, can be ____________ separated into other substances.
Explanation
Pure Substance: only one type of particle is present.
- the properties must be consistent because the same type of particle is present in each case
- the substances cannot be physically separated because any particles that are removed are the
same as the ones that are left behind.
Mixture: at least two types of particles are present.
- the different particles can be in any ratio, so the properties of the mixture are variable.
- the substances can be physically separated because the different particle types can be
separated from each other.
(one particle type may evaporate at a lower temperature, for example)
5) Which of the following substances are mixtures and which are mixtures?
A) ___________ B) ___________ C) ___________ D) ___________ E) ___________
6) Which two substances would have to be mixed to get substance D?
7) a) If substances C and D were to be separated, would you get the same pure substances?
b) What is different about substances C and D?
8) a) What is different about the particles in substance B compared to the other 4 substances?
b) Why is substance B a pure substance?
SNC1
Elements and Compounds: Two Types of Pure Substance
Observation
Pure substances can be combined in certain ways to produce new substances that also are uniform and
consistent in their properties.
- these new substances also must be pure substances!
- since they are made by compounding other pure substances together, they are called ____________
- the processes that we use to make these new substances are called ___________ changes.
We know that pure substances have only one type of particle.
We also know that in chemical changes, the reacting particles (atoms) are not destroyed, because we
can get them back in subsequent chemical changes.
Explanation
The particles in a chemical reaction must fuse together to form a compound particle.
They must do this in a particular ratio:
-the properties of a compound always are the _____________,
- so the compound particles always must be the ______________.
How do we know that a new substance is created?
How do we identify substances in the first place?
We look at __________________ properties.
Examples:
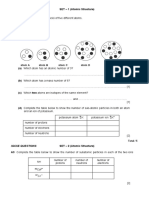
One of the best of these for identifying substances is: ________________
This property is determined by the ______ of the particles and how _________ they are together.
Density: D =
If volume is measured in mL and mass is measured in grams, the units for density are: __________
Question: can we verify that density really is a property that can be used to identify substances. For
example, Aluminum, steel, and Silver are all shiny, grey metals. Can we use density to tell them
apart?
To find out, we will perform a: _________________
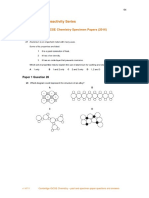
Chemical and Physical Changes
Physical Changes:
These are processes that combine substances into mixtures, separate mixtures, and change the object
properties of substances. In other words, the change does not alter the particles.
e.g.: mix sand and water, chop potatoes, break a coffee mug,
evaporate salt water to make pure salt and pure water,
freeze water (any change in state).
Physical changes cause different types of particles to mix or separate.
In a physical change, no new substances are made.
Chemical Changes: (chemical reactions)
These are processes that change pure substances into other pure substances. This is the key criterion,
a substance that was not present in the sample before the process starts must be present at the end of
the process. The particles of the substance are themselves changed.
e.g.: cooking food, digesting food, burning anything.
Chemical changes cause particles to join or separate to make new types of particle.
A new type of particle means a new substance.
How do you tell if a process is a chemical change or a physical change?
A) Identify a new substance. This can be time consuming, but it is the only certain way.
- look for new ______________________. (examples: _______________________________)
- look for new chemical _______________
- types of chemical reactions that the substance will take part in
- reacts with oxygen (combustion)
- reacts with water
- reacts with acids or bases
B) There are some clues that suggest that a chemical change has occurred:
i) large amounts of _________ are released or absorbed (sample gets _______ or _________)
example: _______________________________________
ii) a permanent ___________ change occurs
example: _______________________________________
iii) a new _________ is produced
example: _______________________________________
iv) a _________ is created (___________ or fizzing)
example: _______________________________________
v) a solid ____________ is made (when solutions are mixed)
example: _______________________________________
vi) the process is difficult to _____________
example: _______________________________________
None of these clues is fool-proof. Write down one exception for each of the clues.
i) water freezes ii) paint dries
iii) melt plastic and you start to smell it iv) water boils (it is still water, just in the gas state)
v) salt precipitates when salt water evaporates vi) a coffee mug breaks
Вам также может понравиться
- IGCSE Science WorksheetsДокумент103 страницыIGCSE Science WorksheetsYoshua Yanottama89% (9)
- Pollination Unit Test PDFДокумент7 страницPollination Unit Test PDFapi-463869656Оценок пока нет
- IGCSE Reproduction in Plants WsДокумент4 страницыIGCSE Reproduction in Plants WsAnand Kumar ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Atoms and Elements Worksheet 1 Year 1 ScienceДокумент10 страницAtoms and Elements Worksheet 1 Year 1 SciencemizterdeeОценок пока нет
- Magnetism - Science Year 8Документ15 страницMagnetism - Science Year 8b_syiera100% (7)
- 04-Using AudacityДокумент7 страниц04-Using AudacityShakila Shaki100% (1)
- States of Matter Worksheet For STEДокумент2 страницыStates of Matter Worksheet For STECaryl Ann C. Sernadilla100% (1)
- Revision Grade 7 Worksheet - Metals and Non - MetalsДокумент2 страницыRevision Grade 7 Worksheet - Metals and Non - MetalsChandrashekhar Patil100% (3)
- Compound and Mixture Worksheet 1Документ4 страницыCompound and Mixture Worksheet 1quinzhang100% (1)
- WORKSHEET ON REACTIVITY SERIES ANSWERSДокумент1 страницаWORKSHEET ON REACTIVITY SERIES ANSWERSКуаныш Жанадил100% (3)
- Separation Techniques WorksheetДокумент2 страницыSeparation Techniques WorksheetBrianMarBeltran100% (3)
- Basic Electricity Questions IGCSEДокумент11 страницBasic Electricity Questions IGCSEFan Xin Foo100% (1)
- Atoms and Molecules WorksheetДокумент1 страницаAtoms and Molecules WorksheetBank Yossy Woluslawe60% (5)
- Unit 2 Acids Bases Salts Past QuestionsДокумент49 страницUnit 2 Acids Bases Salts Past QuestionsDwiyasa Irin100% (2)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- IGCSE Atoms Elements and CompoundsДокумент35 страницIGCSE Atoms Elements and CompoundsMatthew KirkОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 1 (Micro-Organisms)Документ6 страницWorksheet 1 (Micro-Organisms)taqi razaОценок пока нет
- Challenge 8 AnswersДокумент26 страницChallenge 8 Answerssalman hashmii100% (1)
- Cell Revision WorksheetДокумент3 страницыCell Revision WorksheetCally Chew100% (3)
- Worksheet On The Reactivity SeriesДокумент2 страницыWorksheet On The Reactivity SeriesPramudith LiyanageОценок пока нет
- The Reactivity SeriesДокумент25 страницThe Reactivity SeriesFatema KhatunОценок пока нет
- Worksheet - States of MatterДокумент2 страницыWorksheet - States of MatterDivya Pritam100% (1)
- Worksheet Elements Compounds Mixtures ks3Документ4 страницыWorksheet Elements Compounds Mixtures ks3eric sivanesh0% (1)
- Separation Techniques WS 1 - Chromatography, Distillation & MoreДокумент6 страницSeparation Techniques WS 1 - Chromatography, Distillation & MoreKhondokar Tarakky0% (1)
- 2 The Life CycleДокумент12 страниц2 The Life Cycleرحال الزمانОценок пока нет
- IGCSE chemistry: Preparation and reactions of saltsДокумент4 страницыIGCSE chemistry: Preparation and reactions of saltsNayeemAhmed67% (3)
- AQA GCSE Computer Science Exam QuestionsДокумент43 страницыAQA GCSE Computer Science Exam QuestionsLuxman Satchi100% (6)
- Grade 8 Physics WorksheetДокумент6 страницGrade 8 Physics Worksheetsanathd67% (18)
- Key Neutron Proton: Igcse Questions Set - 1 (Atomic Structure)Документ25 страницKey Neutron Proton: Igcse Questions Set - 1 (Atomic Structure)Faria Tahsin100% (2)
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Документ66 страницIGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Antonia Putri Sri Nova YolandhaОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseОценок пока нет
- Respiration WorksheetДокумент5 страницRespiration WorksheetFendy Hamid67% (6)
- Elements, Compounds, Mixtures WorksheetДокумент6 страницElements, Compounds, Mixtures WorksheetAlvianica Nanda Utami100% (1)
- Notes Ws Phase Diagram Vapor Pressure KeyДокумент4 страницыNotes Ws Phase Diagram Vapor Pressure KeyVanessa JabagatОценок пока нет
- Igcse Chemistry Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Ans1Документ26 страницIgcse Chemistry Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Ans1Es Lim75% (4)
- Metal and Oxygen WorksheetДокумент2 страницыMetal and Oxygen WorksheetFaridah Shazlina100% (2)
- Separation Techniques WorksheetДокумент2 страницыSeparation Techniques Worksheetmarleigh75% (4)
- KS3 Blood Circulation TESTДокумент4 страницыKS3 Blood Circulation TESTA.K Mon100% (1)
- MYP Biology Booklet # 3 Grade9 - MS1Документ27 страницMYP Biology Booklet # 3 Grade9 - MS1Aref Dahabrah100% (1)
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions RespirationОт EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions RespirationРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Elements-Compounds and Mixtures WorksheetДокумент2 страницыElements-Compounds and Mixtures WorksheetAG100% (3)
- IGCSE Chemistry past paper questions and answersДокумент14 страницIGCSE Chemistry past paper questions and answersVirti Desai100% (1)
- 2015 06 SPE Facilities Savvy Separator Series Part 1Документ6 страниц2015 06 SPE Facilities Savvy Separator Series Part 1Didik WahyudiОценок пока нет
- PD CEN-TR 13932 Rotodynamic PumpsДокумент28 страницPD CEN-TR 13932 Rotodynamic PumpsMericОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry Note (9-1) On States of MatterДокумент4 страницыIGCSE Chemistry Note (9-1) On States of MatterMd. Saif Ullah Bari100% (3)
- Atomic Structure Past Paper QuestionsДокумент7 страницAtomic Structure Past Paper QuestionsOshan Dissanayake50% (2)
- Metals and Nonmetals Worksheet PDFДокумент5 страницMetals and Nonmetals Worksheet PDFDesmarie CastilloОценок пока нет
- Science Test BookДокумент3 страницыScience Test Bookayush sonar100% (1)
- Separation Techniques WorksheetДокумент2 страницыSeparation Techniques WorksheetyuniОценок пока нет
- 8 States of MatterДокумент4 страницы8 States of Matterrashmi_harryОценок пока нет
- 7 Classification and Variation - QueДокумент11 страниц7 Classification and Variation - Querashmi_harry100% (4)
- Worksheet On Elements, Compounds, MixturesДокумент6 страницWorksheet On Elements, Compounds, Mixturesnettexts100% (4)
- Elements Compounds Mixtures WKSTДокумент5 страницElements Compounds Mixtures WKSTAmanda ClayОценок пока нет
- Rates of Reaction WorksheetДокумент2 страницыRates of Reaction WorksheetSyuhadaratul Ainy100% (2)
- Revision Worksheet Chapter Heat ANSWER KEYДокумент5 страницRevision Worksheet Chapter Heat ANSWER KEYshamshadОценок пока нет
- Operating instructions for axially split volute casing pumpДокумент38 страницOperating instructions for axially split volute casing pumpjoseantoniomontielОценок пока нет
- Daily Test Chapter Adaptation and EcosystemДокумент4 страницыDaily Test Chapter Adaptation and EcosystemVita Faridiana100% (1)
- Aqa Gcse Computer Science (8520) : Knowledge OrganisersДокумент45 страницAqa Gcse Computer Science (8520) : Knowledge OrganisersShakila Shaki100% (1)
- IT TG Graphics Creation 9626Документ39 страницIT TG Graphics Creation 9626Shakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Chemistry Notes: Organic CompoundsДокумент7 страницIGCSE Chemistry Notes: Organic CompoundsFasih AhmadОценок пока нет
- 9626 AICE Information Technology Student Learner GuideДокумент27 страниц9626 AICE Information Technology Student Learner Guideiman alhadarОценок пока нет
- 9626 AICE Information Technology Student Learner GuideДокумент27 страниц9626 AICE Information Technology Student Learner Guideiman alhadarОценок пока нет
- 9626 AICE Information Technology Student Learner GuideДокумент27 страниц9626 AICE Information Technology Student Learner Guideiman alhadarОценок пока нет
- WS 4 IG I Chemistry BEHAVIOUR OF METALSДокумент7 страницWS 4 IG I Chemistry BEHAVIOUR OF METALSRaj MalkanОценок пока нет
- 7C2 Changes of State WorksheetДокумент1 страница7C2 Changes of State Worksheetmisskentjones100% (1)
- Gas Exchange WorksheetДокумент2 страницыGas Exchange Worksheetnoddy_noddy100% (1)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BUSINESS 9609/11Документ4 страницыCambridge International AS & A Level: BUSINESS 9609/11Shakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- Unit1-1 7 1-OperatingSystemsДокумент7 страницUnit1-1 7 1-OperatingSystemsShakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- Unit1 1.3 StorageДокумент7 страницUnit1 1.3 StorageShakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- (WH) - With Held For Further Verification of DocumentsДокумент1 страница(WH) - With Held For Further Verification of DocumentsKANTHAVEL TОценок пока нет
- Computer ApplicationsДокумент1 страницаComputer Applicationschirag chawlaОценок пока нет
- Unit2 2.6.1 TheBinaryNumberSystemДокумент12 страницUnit2 2.6.1 TheBinaryNumberSystemShakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- Theory BookletДокумент88 страницTheory BookletMichael FarajianОценок пока нет
- Study Guide: IGCSE and AS/A2 Level 2017 - 2018Документ45 страницStudy Guide: IGCSE and AS/A2 Level 2017 - 2018Shakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- Study Guide: IGCSE and AS/A2 Level 2017 - 2018Документ45 страницStudy Guide: IGCSE and AS/A2 Level 2017 - 2018Shakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- Physics GCE SampleДокумент49 страницPhysics GCE Samplesaif-100% (1)
- Computer Applications IX OnlyДокумент7 страницComputer Applications IX OnlyDev Printing SolutionОценок пока нет
- SF TF: Layout Second Floor Layout Third FloorДокумент2 страницыSF TF: Layout Second Floor Layout Third FloorShakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент5 страницChemistry Multiple Choice QuestionsShakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- Learner Guide: Cambridge IGCSE /cambridge IGCSE (9-1) Computer Science 0478 / 0984Документ25 страницLearner Guide: Cambridge IGCSE /cambridge IGCSE (9-1) Computer Science 0478 / 0984Shakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- Supplementary Multiple-Choice Answer Sheet: Example InstructionsДокумент1 страницаSupplementary Multiple-Choice Answer Sheet: Example Instructionsyug tilvaОценок пока нет
- Study Guide: IGCSE and AS/A2 Level 2017 - 2018Документ45 страницStudy Guide: IGCSE and AS/A2 Level 2017 - 2018Shakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- 1.5 Impact of Emerging Technologies-2Документ9 страниц1.5 Impact of Emerging Technologies-2Sam ManОценок пока нет
- 1.1.2 Types of ProcessorДокумент6 страниц1.1.2 Types of ProcessorShakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- IGCSE Worksheet - Networking BasicsДокумент11 страницIGCSE Worksheet - Networking BasicsShakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- Question Paper Computer SystemsДокумент24 страницыQuestion Paper Computer SystemsShakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- 9608 Example Candidate Responses Paper 3 (For Examination From 2016)Документ71 страница9608 Example Candidate Responses Paper 3 (For Examination From 2016)Shakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- 1.1.2 Types of ProcessorДокумент6 страниц1.1.2 Types of ProcessorShakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- 1.2.1 Systems SoftwareДокумент8 страниц1.2.1 Systems SoftwareShakila ShakiОценок пока нет
- Physics Session 2018 19 Term Wise SyllabusДокумент12 страницPhysics Session 2018 19 Term Wise SyllabusEASY TECHSОценок пока нет
- F. Huang - Engineering ThermodynamicsДокумент52 страницыF. Huang - Engineering ThermodynamicsHectorCabz100% (1)
- 5208Документ53 страницы5208Aditya ParabОценок пока нет
- Engineering Thermodynamics Worksheet AnalysisДокумент13 страницEngineering Thermodynamics Worksheet Analysisroba angasuОценок пока нет
- Installation, Operation, and Maintenance Manual: 80 Series PumpДокумент29 страницInstallation, Operation, and Maintenance Manual: 80 Series PumpFelipe Ignacio PaillavilОценок пока нет
- PDL FOR Emergency Procedure Guide - 170713 PDFДокумент2 страницыPDL FOR Emergency Procedure Guide - 170713 PDFmalisolangiОценок пока нет
- 1st Quarter Test Science 3 2022-2023 RagyДокумент2 страницы1st Quarter Test Science 3 2022-2023 RagyAnn GeluaОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Secondary Refining Slag Parameters WitДокумент11 страницAnalysis of Secondary Refining Slag Parameters WitAbhinandan ChatterjeeОценок пока нет
- Grasso: Ammonia Liquid Chiller Series FX PP, LP, VP 200 - 6000 KWДокумент65 страницGrasso: Ammonia Liquid Chiller Series FX PP, LP, VP 200 - 6000 KWManuel MartinezОценок пока нет
- Grammar Review 10. Conditional Sentences 1Документ4 страницыGrammar Review 10. Conditional Sentences 1thanh haОценок пока нет
- Phenomena: A Concise Guide to Macroscopic, Microscopic, and Molecular PhenomenaДокумент8 страницPhenomena: A Concise Guide to Macroscopic, Microscopic, and Molecular PhenomenaNitesh ChauhanОценок пока нет
- II Semester Physics Lab ManualДокумент45 страницII Semester Physics Lab ManualSivalingam Dinesh100% (3)
- Nitoproof WB Primer PDFДокумент2 страницыNitoproof WB Primer PDFSun Ny0% (1)
- Speed of Sound ExperimentДокумент3 страницыSpeed of Sound ExperimentJaneille ScottОценок пока нет
- AICS Chemistry Modules OverviewДокумент53 страницыAICS Chemistry Modules OverviewAshley Marie TrajadaОценок пока нет
- HT64-132 系列流量计完工图Документ14 страницHT64-132 系列流量计完工图Kunpeng ZhouОценок пока нет
- E PT124B-3051DRДокумент3 страницыE PT124B-3051DRboroumandОценок пока нет
- Chem HelpДокумент29 страницChem HelpRobyn KentОценок пока нет
- E-501A/B Shell Pressure Relief Valve Data SheetДокумент18 страницE-501A/B Shell Pressure Relief Valve Data Sheetanamaria ursuОценок пока нет
- Crosby Series BP Omni-TrimДокумент16 страницCrosby Series BP Omni-TrimSilvio CalviОценок пока нет
- All Flowmeter Basics PDFДокумент1 страницаAll Flowmeter Basics PDFAtharva PathakОценок пока нет
- OLGA 7 Offshore Low ResДокумент16 страницOLGA 7 Offshore Low Resruben'sОценок пока нет
- Caracteristicas Normas ASME B31Документ3 страницыCaracteristicas Normas ASME B31darthneoОценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент182 страницыFluid Mechanicsreddy331Оценок пока нет
- Dicet Flow Module 1Документ27 страницDicet Flow Module 1Julius ChavezОценок пока нет
- Hermetic Pumpen Canned Motor Pumps Catalogue For Model CN - CNF - CNKДокумент16 страницHermetic Pumpen Canned Motor Pumps Catalogue For Model CN - CNF - CNKADITYA_PATHAKОценок пока нет