Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Respiratory System Questions and Answers Bios
Загружено:
Chrispin Msofe0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
2K просмотров4 страницыRespiration meaning gas exchange is the process in which an organism absorbs from the environment gases necessary for its cellular metabolism and expels gases that are products of this metabolism. Gas exchange is fundamental for cellular respiration since the supplying of some reagents (oxygen) and the expelling of some products (e.g., carbon dioxide) of this chemical reaction depends on gas exchange. In beings from the kingdom Animalia the gas exchange may occur either by diffusion, tracheal respiration, cutaneous
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документRespiration meaning gas exchange is the process in which an organism absorbs from the environment gases necessary for its cellular metabolism and expels gases that are products of this metabolism. Gas exchange is fundamental for cellular respiration since the supplying of some reagents (oxygen) and the expelling of some products (e.g., carbon dioxide) of this chemical reaction depends on gas exchange. In beings from the kingdom Animalia the gas exchange may occur either by diffusion, tracheal respiration, cutaneous
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
2K просмотров4 страницыRespiratory System Questions and Answers Bios
Загружено:
Chrispin MsofeRespiration meaning gas exchange is the process in which an organism absorbs from the environment gases necessary for its cellular metabolism and expels gases that are products of this metabolism. Gas exchange is fundamental for cellular respiration since the supplying of some reagents (oxygen) and the expelling of some products (e.g., carbon dioxide) of this chemical reaction depends on gas exchange. In beings from the kingdom Animalia the gas exchange may occur either by diffusion, tracheal respiration, cutaneous
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
Respiratory System Questions and Answers
1. What is the difference between respiration meaning gas exchange and
cellular respiration?
Respiration meaning gas exchange is the process in which an organism
absorbs from the environment gases necessary for its cellular metabolism
and expels gases that are products of this metabolism. Cellular respiration
(aerobic or anaerobic) is the chemical reaction in which organic molecules
are degraded to make ATP molecules, the main energy source for the
metabolism.Gas exchange is fundamental for cellular respiration since the
supplying of some reagents (oxygen, in aerobic cellular respiration) and the
expelling of some products (e.g., carbon dioxide) of this chemical reaction
depends on gas exchange.
2. What is the chemical equation of the aerobic cellular respiration?
The chemical equation of the aerobic cellular respiration is the
following:C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 36 ADP + 36 P --> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 36 ATP
3. Considering the chemical equation of the aerobic cellular respiration
which molecules does the cell need and which molecules does it liberate in
the process?
Considering the chemical equation of the aerobic cellular respiration it is
observed that glucose and molecular oxygen are needed as reagents and
carbon dioxide and water are released. The process also spends ADP and
phosphate that turn into ATP.
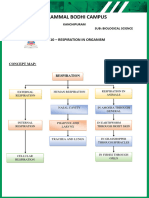
4. What are the different types of gas exchange that occur in animals?
In beings from the kingdom Animalia the gas exchange may occur either by
diffusion, tracheal respiration, cutaneous respiration, branchial respiration
or pulmonary respiration.
5. Oxygen comes from the environment and carbon dioxide in the end
returns to the environment. How do small animals solve the problem of
taking away and bringing these molecules from/to their cells? Why isn't
that solution possible for larger animals?
Small animals whose tissues make direct contact or are very close to the
environment, like cnidarians and poriferans, make gas exchange by
diffusion.Larger animals with cells without direct contact with the
environment or far from it need special gas transportation systems. In
these animals the respiratory and the circulatory systems play this role.
6. Beings from four phyla of the animal kingdom breath (do gas
exchange) by diffusion. Which are those phyla? How is this type of
respiration associated to features present in those animals?
The phyla of the animal kingdom whose beings do gas exchange by
diffusion are the poriferans, the cnidarians, the platyelminthes (flatworms)
and the nematodes (roundworms). This type of respiration in these beings
is possible because their tissues and cells are relatively close to the exterior.
7. Which animals make tracheal respiration? Is there a blood-like fluid that
participates in this process?
Insects and arachnids are the arthropod animals that make tracheal
respiration. In the body surface of these animals there are many orifices
called spiracles that communicate with small tubules, the tracheae, through
which air penetrates and carbon dioxide is expelled. The tracheae ramify
into tracheoles that reach all tissues of the animal.In the circulatory system
of insects the blood only transports nutrients; gases are independently
transported by the tracheal system.
8. What is the difference between respiration by diffusion and cutaneous
respiration? Does blood participate in cutaneous respiration?
Cutaneous respiration is not as simple as diffusion. In diffusion the gases
diffuse directly between the external environment and the cells. In
cutaneous respiration molecular oxygen penetrates through the skin and it
is collected by the blood circulation that then distributes the gas to the
tissues. Carbon dioxide is also collected from the tissues by the blood and
taken to the skin to be eliminated to the environment. So there is
important participation of blood in cutaneous respiration.
9. Which animals make cutaneous respiration?
Terrestrial annelids and adult amphibians make cutaneous respiration (in
amphibians there is also pulmonary respiration).The thin skin and the need
for living in moist surrounds are typical features of these animals are.
10. What are branchiae? What are examples of animals that breath
through branchiae?
Branchiae, also known as gills, are small portions of richly vascularized
tissues internal or external to the body and in direct contact with the
surrounding water. The gills are organs that make gas exchange in aquatic
annelids, crustaceans, fishes and amphibian larvae (e.g., tadpoles).
Maktaba Huru Tz Sponsord by www.news4tyimeblog.com
Вам также может понравиться
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Learning Activity Sheet Q4 W1 v. 2Документ12 страницGENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Learning Activity Sheet Q4 W1 v. 2Pearl Lee MetiamОценок пока нет
- C7 RespirationДокумент18 страницC7 RespirationDharshiniОценок пока нет
- General Biology II Q4 Week 2Документ18 страницGeneral Biology II Q4 Week 2Rose MoselaОценок пока нет
- Laporan Praktikum RespirasiДокумент18 страницLaporan Praktikum Respirasisuryati rante tikuОценок пока нет
- Ratification Page: Djumarirmanto S.PD Nurfitrah Aulia Ayub ID.1214441027Документ26 страницRatification Page: Djumarirmanto S.PD Nurfitrah Aulia Ayub ID.1214441027ummu prtiwiОценок пока нет
- CH 10-RespirationДокумент10 страницCH 10-RespirationMushtaqAnsariОценок пока нет
- Gas ExchangeДокумент18 страницGas ExchangemiatamayoqtОценок пока нет
- Respiration: Raja Fayaz AliДокумент12 страницRespiration: Raja Fayaz AliSuchitra SharmaОценок пока нет
- BiologyДокумент23 страницыBiologysammyusophОценок пока нет
- Ratification Page: Djumarirmanto, S.PD Suciati Nurdin ID: 1314140006Документ17 страницRatification Page: Djumarirmanto, S.PD Suciati Nurdin ID: 1314140006nurhikmah abbasОценок пока нет
- Breathing and Exchange: of GasesДокумент10 страницBreathing and Exchange: of GaseshellohelloworldОценок пока нет
- General Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PДокумент26 страницGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PTipsy MonkeyОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Breathing and RespirationДокумент8 страницDifference Between Breathing and RespirationpreethaОценок пока нет
- Biology Lecture NotesДокумент56 страницBiology Lecture NotesMaisonette MichОценок пока нет
- Animal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Документ19 страницAnimal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Abhishek Singh ChandelОценок пока нет
- Pastel Illustration Computer UI English Class Education PresentationДокумент30 страницPastel Illustration Computer UI English Class Education PresentationElaiza marie VenusОценок пока нет
- RespirationДокумент9 страницRespirationpriya.kesharwani0557Оценок пока нет
- Respiratory: Keyword: Respiration, Respiratory, OxygenДокумент8 страницRespiratory: Keyword: Respiration, Respiratory, Oxygensiti syahirahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 30 AnswersДокумент8 страницChapter 30 AnswersJuan SandovalОценок пока нет
- Gas ExchangeДокумент12 страницGas ExchangeJerwin GarnaceОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 Gas Exchange and Transportcirculation in Plants and AnimalsДокумент13 страницLesson 2 Gas Exchange and Transportcirculation in Plants and AnimalsMonica QuiambaoОценок пока нет
- 18 OCTOBER, 2021 Monday. Biology Respiratory SystemsДокумент9 страниц18 OCTOBER, 2021 Monday. Biology Respiratory SystemsOyasor Ikhapo AnthonyОценок пока нет
- Science 8 Iii Partial 4 and Study GuieДокумент5 страницScience 8 Iii Partial 4 and Study GuieHector PeñateОценок пока нет
- Introduction BreathingДокумент6 страницIntroduction BreathingJIENASHENIE NAIR A/P SURESH MoeОценок пока нет
- Gaseous Exchange: Short Question AnswersДокумент5 страницGaseous Exchange: Short Question AnswersNadeem ArainОценок пока нет
- General Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PДокумент25 страницGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PSyrine Myles Sullivan100% (2)
- Gas ChangeДокумент20 страницGas ChangeBleebs CreigsОценок пока нет
- Module 10Документ8 страницModule 10Jamille Nympha C. BalasiОценок пока нет
- Chennai Public School: NotesДокумент10 страницChennai Public School: Notesrishabh mohantyОценок пока нет
- Q4 STEM General Biology 2 Week 3Документ4 страницыQ4 STEM General Biology 2 Week 3ralphОценок пока нет
- The Respiratory System-11 By:-Dr. Hazim AL-RawiДокумент12 страницThe Respiratory System-11 By:-Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDrAli Al-FendiОценок пока нет
- General Biology II q4 Week 2Документ26 страницGeneral Biology II q4 Week 2Educhamp Learning CenterОценок пока нет
- Class 10 - Science - Life ProcessesДокумент14 страницClass 10 - Science - Life ProcessesNaitik sethiaОценок пока нет
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- NegOr Q4 GenBio2 SLKWeek2 v2Документ22 страницыNegOr Q4 GenBio2 SLKWeek2 v2albazeervaОценок пока нет
- Biology U2Документ10 страницBiology U2Alima IqbalОценок пока нет
- Biology Homework Dwi Oktavianto Makdasari X-AДокумент15 страницBiology Homework Dwi Oktavianto Makdasari X-ADwiОценок пока нет
- MLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsДокумент4 страницыMLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDivyanshi BansalОценок пока нет
- Respiratory System NotesДокумент4 страницыRespiratory System NotesFlare FlareonОценок пока нет
- Spyros Filippas A4 Biology Term ProjectДокумент12 страницSpyros Filippas A4 Biology Term Projectpipis pipasОценок пока нет
- Sistem RespirasiДокумент26 страницSistem RespirasiAnnida LegiОценок пока нет
- Gas Exchange in Plants and AnimalsДокумент7 страницGas Exchange in Plants and AnimalsMarvin MelisОценок пока нет
- Laporan Praktikum Fishew RespirasiДокумент9 страницLaporan Praktikum Fishew RespirasiputriajengsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - Life ProcessesДокумент8 страницChapter 6 - Life ProcessesManvendra Shah (B18EE026)Оценок пока нет
- RespirationДокумент5 страницRespirationDivyansh SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Respiration NotesДокумент7 страницRespiration NotesKrishna SharmaОценок пока нет
- Life Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFДокумент4 страницыLife Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshОценок пока нет
- CH 6 E - Notes RespirationДокумент5 страницCH 6 E - Notes RespirationRajvir tradaОценок пока нет
- NCERT - Sol - Life ProcessesДокумент11 страницNCERT - Sol - Life ProcessesRagini BaghelОценок пока нет
- Life ProcessesДокумент7 страницLife ProcesseskrithicktcrОценок пока нет
- Part 2 Gas Exchange and The Respiratory SystemДокумент16 страницPart 2 Gas Exchange and The Respiratory Systemrongelandrew.gilbolingoОценок пока нет
- Oxygen 6-Vise o DisanjuДокумент12 страницOxygen 6-Vise o DisanjuSnezana JosicОценок пока нет
- Notes RespirationДокумент6 страницNotes Respirationakheel7353Оценок пока нет
- Class X Physics NCERT Solution by NTSE GuruДокумент6 страницClass X Physics NCERT Solution by NTSE GuruNTSE GuruОценок пока нет
- Biolab 2Документ3 страницыBiolab 2diemtruc414Оценок пока нет
- The Respiratory System: Cellular Respiration ATPДокумент15 страницThe Respiratory System: Cellular Respiration ATPAajy BgavaharОценок пока нет
- Grade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsДокумент22 страницыGrade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsJanardhanОценок пока нет
- Life Processes Questions Q1Документ15 страницLife Processes Questions Q1Geeta ReddyОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Gas ExchangeДокумент19 страницRespiratory Gas ExchangeRahul MeenaОценок пока нет
- Coordination and Response BiologyДокумент2 страницыCoordination and Response BiologyChrispin MsofeОценок пока нет
- The Slave Trade in East Africa. HistoryДокумент6 страницThe Slave Trade in East Africa. HistoryChrispin MsofeОценок пока нет
- Factors For The Growth of African Nationalism HistoryДокумент8 страницFactors For The Growth of African Nationalism HistoryChrispin Msofe93% (14)
- Physics 4 O LevelДокумент3 страницыPhysics 4 O LevelChrispin Msofe100% (1)
- Wasichana Shule ZoteДокумент544 страницыWasichana Shule ZoteSirbus Gents100% (1)
- Biology For Form II-IV NotesДокумент28 страницBiology For Form II-IV NotesChrispin MsofeОценок пока нет
- Biology For Form II-IV NotesДокумент28 страницBiology For Form II-IV NotesChrispin MsofeОценок пока нет
- The Umrao (Solar Quote)Документ3 страницыThe Umrao (Solar Quote)Seema solar EnterprisesОценок пока нет
- Jacques Cousteau: Jacques Cousteau, in Full Jacques-Yves Cousteau, (BornДокумент4 страницыJacques Cousteau: Jacques Cousteau, in Full Jacques-Yves Cousteau, (BornanguesanОценок пока нет
- Sample Problem Series of 10 Evaporators Multiple Equipment Non Reactive System PDFДокумент2 страницыSample Problem Series of 10 Evaporators Multiple Equipment Non Reactive System PDFPytharix CaineОценок пока нет
- Development Control Rules - CMDA: The Main Divisions of DCRДокумент10 страницDevelopment Control Rules - CMDA: The Main Divisions of DCReshОценок пока нет
- Uttar PradeshДокумент24 страницыUttar PradeshharhelОценок пока нет
- Theoretical Framework: The Methodological Framework Emerges From The Conceptual FrameworkДокумент6 страницTheoretical Framework: The Methodological Framework Emerges From The Conceptual FrameworkBenz Andrew RegisОценок пока нет
- 3999WS-Zink Spray 80 81GB-EnДокумент11 страниц3999WS-Zink Spray 80 81GB-Enhvdb72Оценок пока нет
- Water Resource Systems Planning and Management Daniel P. Loucks & Eelco Van BeekДокумент69 страницWater Resource Systems Planning and Management Daniel P. Loucks & Eelco Van BeekM Shahid0% (1)
- Sewage Treatment PlantДокумент99 страницSewage Treatment PlantSubramoniam Marine100% (4)
- Pr6Tek: Material Safety Data Sheet Product IdentificationДокумент4 страницыPr6Tek: Material Safety Data Sheet Product IdentificationNugroho100% (1)
- Storm Water Pump StationДокумент6 страницStorm Water Pump StationНемања КараклајићОценок пока нет
- SEEPW 2007 Engineering BookДокумент319 страницSEEPW 2007 Engineering BookMihaiОценок пока нет
- Atlas Copco ZT55Документ14 страницAtlas Copco ZT55benlineyОценок пока нет
- Approval From Colombo Municipal CouncilДокумент4 страницыApproval From Colombo Municipal CouncilkamaldeshapriyaОценок пока нет
- CG-PRC017-EN - 01012011 UltimoДокумент56 страницCG-PRC017-EN - 01012011 UltimobyronchqОценок пока нет
- Basic Guide To Calculating Falls and Gradients For Drainage - Basic Guide To Calculating Falls and Gradients For Drainage - Wyre CouncilДокумент6 страницBasic Guide To Calculating Falls and Gradients For Drainage - Basic Guide To Calculating Falls and Gradients For Drainage - Wyre Councilvenkateswara rao pothinaОценок пока нет
- Queensland Urban Drainage Manual PDFДокумент459 страницQueensland Urban Drainage Manual PDFAnthony Nguyen89% (9)
- Daftar SIMAK MEPДокумент6 страницDaftar SIMAK MEPRicky PrabowoОценок пока нет
- Pre-Excavation Grouting in Hard Rock Tunnelling PDFДокумент58 страницPre-Excavation Grouting in Hard Rock Tunnelling PDFTony ChanОценок пока нет
- Paper 2 Stator Water SystemДокумент34 страницыPaper 2 Stator Water SystemLakshmi Narayan100% (1)
- Spill ResponseДокумент10 страницSpill ResponseLittle Holland Pty Ltd100% (1)
- Englefield Electronic Bidet SeatДокумент1 страницаEnglefield Electronic Bidet SeatjeffОценок пока нет
- Test - WASH PM Assistant - TemplateДокумент6 страницTest - WASH PM Assistant - Templatealgodami100% (5)
- Christine - MBARI Biogeochemical LessonДокумент10 страницChristine - MBARI Biogeochemical LessonMelissa NatashaОценок пока нет
- BBA - Under Floor HeatingДокумент8 страницBBA - Under Floor HeatingPaul KwongОценок пока нет
- Baseline TOR FinalДокумент12 страницBaseline TOR FinalAsnakew LegesseОценок пока нет
- ESS 4 StandardДокумент7 страницESS 4 StandardLineth DomingoОценок пока нет
- Ma Offs Plarm Ad Accts in TheДокумент8 страницMa Offs Plarm Ad Accts in ThePedro Paulo CordeiroОценок пока нет
- Brief Directions For The Use of Biodynamic Sprays 500, 501 and 508Документ3 страницыBrief Directions For The Use of Biodynamic Sprays 500, 501 and 508budhistsluvcopyrightОценок пока нет
- PLAXIS 2D 2017 Tutorial Lesson07Документ13 страницPLAXIS 2D 2017 Tutorial Lesson07Boni TamaОценок пока нет