Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Additional Mathematics F5 Probability Distribution
Загружено:
Fazlina MustafaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Additional Mathematics F5 Probability Distribution
Загружено:
Fazlina MustafaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Additional Mathematics F5 ~ Probability Distribution
D:Maths.Additional.19NormalDistributionF5_Normal.doc
1
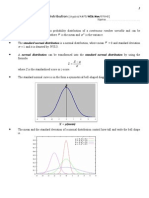
Skill 1 ~Normal Distribution: You should know .
~ is a probability distribution of continuous random variables (only quantities that can be measured).
~ is denoted by N(, o
2
) where = mean and o
2
= variance .
~ can be transformed into the standard normal distribution by using the formula,
X
Z
o
= , where Z ~ standard
score.
~ The standard normal curve, N(0, 1) is symmetrical about the vertical axis.
~ The area of the region bounded by the normal curve, X = a, V = b and the horizontal axis represents P(a X b),
that is the probability that a normal random variable has values between a and b.
~ The total area under the normal curve with horizontal axis is 1.
~ Graphs of Standard Normal Distribution:
Skill 1 : Calculate Probability (Area Under The Graph)
Type 1
Refer to the graph and table,
P(Z > 05) = 03085
If Z is a standard normal variable, find the value of the following.
(a) P(Z > 16) = (b) P(Z > 241) =
(c) P(Z > 1.835) = (d) P(Z > 0238) =
Type 2 (Reflection)
Refer to the graph and table,
P(Z < 05) = P(Z > 05)
= 03085
If Z is a standard normal variable, find the value of the following.
(a) P(Z < 11) = (b) P(Z < 152) =
(c) P(Z s 2.348) = (d) P(Z s 2.307) =
a
P(Z > a)
0
z
f(z)
a
0
z
f(z
)
b
a
P(a < Z< b)
a 0
z
f(z)
P(Z < a)
05
0
z
f(z)
P(Z > 05)
05
P(Z < 05)
0
z
f(z)
05
P(Z > 05)
0
z
f(z)
Additional Mathematics F5 ~ Probability Distribution
D:Maths.Additional.19NormalDistributionF5_Normal.doc
2
Type 3 (Deduction)
Refer to the graph and table,
P(05 < Z < 12) = P(Z > 05) P(Z > 12)
= 03085 01151
= 01934
If Z is a standard normal variable, find the value of the following.
(a) P(02 < Z < 21)
=
(b) P(132 s Z s 324)
=
(c) P(0352 < Z < 1984)
=
(d) P(0 < Z s 2.307)
=
(e) P( 325 < Z < 21)
=
(f) P( 2138 < Z < 0567)
=
Type 4 (Deduction)
Refer to the graph and table,
P(12 < Z < 05) = 1 P(Z > 05) P(Z < 12)
= 1 P(Z > 05) P(Z > 12)
= 1 03085 01151
= 05764
If Z is a standard normal variable, find the value of the following.
(a) P( 13 < Z < 15)
=
(b) P( 068 s Z s 217)
=
12 0
z
f(z)
P(12 < Z < 05)
12
05 0
z
f(z)
05
P(Z > 05)
0
z
f(z) P(Z < 12)
1
=
Reflection
=
05 12
0
z
f(z)
P(05 < Z < 12)
05
0
z
f(z)
P(Z > 05)
12
P(Z > 12)
0
z
f(z)
Additional Mathematics F5 ~ Probability Distribution
D:Maths.Additional.19NormalDistributionF5_Normal.doc
3
(c) P( 0752 < Z < 3001)
=
(d) P( 1.502 < Z s 2.100)
=
(e) P( 3842 < Z < 2123)
=
(f) P( 1238 < Z < 2142)
=
Skill 2 : Calculate z-value, Given the Probability P(Z > z)
Example:
Given P(Z > z) = 02266, find the z-value.
Refer to the table, P(Z > 075) = 02266 and then compare to the given statement,
Therefore, z = 075
Find the z-value of the following.
(a) P(Z > z) = 02546 (b) P(Z > z) = 065
(c) P(Z < z) = 00349 (d) P(Z s z) = 0852
(e) P(z < Z < 205) = 04320 (f) P(0.683 < Z < z) = 02370
(g) P(z < Z < 0.562) = 02620 (h) P( 2.32 < Z < z) = 03403
(i) P(z < Z < 0355) = 04786 (j) P( 1832 < Z < z) = 07494
(k) P(032 < Z < z) = 03477 (l) P(z < Z < 164) = 0975
Additional Mathematics F5 ~ Probability Distribution
D:Maths.Additional.19NormalDistributionF5_Normal.doc
4
Skill 3 : Conversion of x-value to z-value by using formula
Example:
Given x = 48, = 40, o = 8, find the z-value.
Therefore, z =
48 40
8
,
= 05
Convert the following x-values to z-values.
(a) x = 42, = 36, o = 5 (b) x = 30, = 40, o = 8
(c) x = 22, = 16, o = 3 (d) x = 12, = 16, o = 3
(e) x = 113, = 125, o
2
= 144 (f) x = 152, = 125, o
2
= 144
(g) x = 35, = 50, o
2
= 16 (h) x = 60, = 50, o
2
= 16
z =
X
o
Additional Mathematics F5 ~ Probability Distribution
D:Maths.Additional.19NormalDistributionF5_Normal.doc
5
Skill 4 : Conversion of z-value to x-value by using formula
Example:
Given z = 25, = 40, o = 8, find the z-value.
Therefore, x = (25)(8) + 40
= 60
Convert the following z-values to x-values.
(a) z = 135, = 18, o = 2 (b) z = 27, = 18, o = 2
(c) z = 2125, = 10, o = 2 (d) z = 215, = 30, o = 5
(e) z = 21, = 300, o
2
= 64 (f) z = 046, = 300, o
2
= 64
(g) z = 16, = 200, o
2
= 25 (h) z = 1, = 200, o
2
= 25
z =
X
o
X zo = +
Additional Mathematics F5 ~ Probability Distribution
D:Maths.Additional.19NormalDistributionF5_Normal.doc
6
Skill 5 : Problem Solving
Example:
The marks of a group of students in their Maths Test are normally distributed with a mean of 60 and a standard
deviation of 3. If a student is picked at random, find the probability that his mark is
(i) less than 57,
(ii) between 55 and 65.
Solution:
Given: mean, = 60
Standard deviation, o = 3
(i) P(less than 57) = P(X < 57)
= P z
| |
<
|
\ .
57 60
3
= P(z < 1)
= P(z > 1)
= 01587
(ii) P(between 55 and 65) = P(55 < X < 65)
= P z
| |
< <
|
\ .
55 60 65 60
3 3
= P( 1667 < z < 1667)
= 1 P(z < 1667) P(z > 1667)
= 1 P(z > 1667) P(z > 1667)
= 1 2(00478)
= 09044
Solve the following problems.
(a) A normal distribution has a mean of 30 and a standard deviation of 4. If X is the normal distribution variables,
find the value of
(i) P(X > 27) (ii) P(32 < X < 37)
z =
X
o
Identify from question
Type 2
Type 2 & 4
Additional Mathematics F5 ~ Probability Distribution
D:Maths.Additional.19NormalDistributionF5_Normal.doc
7
(b) The diameter of rotan rings produced by a factory are normally distributed with a mean of 4.5 cm and a standard
deviation of 0.5 cm. If a ring is chosen at random, find the probability that its diameter is
(i) longer than 4.7 cm, (ii) longer than 4.4 cm.
(c) The mass of soups produced by a factory are normally distributed with a mean of 140 g and a variance of 25 g.
If a soup is picked at random, find the probability that its mass is
(i) heavier than 145.5 g, (ii) between 138 g and 145 g.
Additional Mathematics F5 ~ Probability Distribution
D:Maths.Additional.19NormalDistributionF5_Normal.doc
8
Extra Work-out.
(a) A survey on the family income of the residents in Kampong A shows that their incomes are normally distributed
with a mean of RM1200 and a standard deviation of RM80.
(i) Calculate the percentage where the family income is less than RM1100.
(ii) If 30 families have an income of between RM1000 and RM1300, find the number of families involved.
(b) The age of the residents in a town are normally distributed with a mean of 45 years old and a variance of 36
years old.
(i) If a resident is chosen at random, find the probability that he/she is more than 50 years old.
(ii) If there are 60 000 residents in the town, estimate the number of residents whose age are more than 50
years old.
Additional Mathematics F5 ~ Probability Distribution
D:Maths.Additional.19NormalDistributionF5_Normal.doc
9
(c) During a test, the score obtained by 50 000 candidates are normally distributed with a mean of 45 and a
standard deviation of 8.
(i) If the excellent score is 60 and above, estimate the number of excellent candidates.
(ii) If 15% of the candidates failed in their test, estimate the minimum score required to get a pass.
(d) 500 students in a school took a Mathematics test. The marks obtained are normally distributed with mean 55 and
standard deviation 10.
(i) If the passing mark is 40, what is the probability that a student chosen at random will pass the test?
(ii) Find the number of pupils who will pass the test if the passing mark is 40.
(iii) If 15% of the students pass the test with grade A, find the minimum mark required to obtain grade A in the
test.
Вам также может понравиться
- Special Continuous Probability Distributions Normal Distribution IIДокумент24 страницыSpecial Continuous Probability Distributions Normal Distribution IIAyush BhadauriaОценок пока нет
- Practice Question Lectures 41 To 45 MoreДокумент14 страницPractice Question Lectures 41 To 45 MoreStefanie FerminОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 QS (PC)Документ17 страницChapter 4 QS (PC)SEOW INN LEEОценок пока нет
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- 2010 JJC Prelim P2 SolutionsДокумент12 страниц2010 JJC Prelim P2 Solutionsnothingtodo1992Оценок пока нет
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Practice Question Lectures 41 To 45 MoreДокумент14 страницPractice Question Lectures 41 To 45 MoreSyed Ali HaiderОценок пока нет
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageОт EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageОценок пока нет
- 2.3 Probability DistributionsДокумент41 страница2.3 Probability DistributionsPatricia Nicole BautistaОценок пока нет
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)От EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Оценок пока нет
- MJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2Документ11 страницMJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 2jimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОт EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesОценок пока нет
- Normal DistributionsДокумент10 страницNormal DistributionsCikgu Zaid IbrahimОценок пока нет
- CHP 8.2 Normal (Mon) W26Документ8 страницCHP 8.2 Normal (Mon) W26Bid HassanОценок пока нет
- U U U U: Be The Statement ThatДокумент9 страницU U U U: Be The Statement Thatnothingtodo1992Оценок пока нет
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsДокумент10 страницNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Applied Statistics: Normal DistributionДокумент13 страницApplied Statistics: Normal Distributioniiyousefgame YTОценок пока нет
- YJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Solutions Paper 2Документ9 страницYJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Solutions Paper 2sfrr07Оценок пока нет
- Nyjc h2 Math p2 SolutionДокумент11 страницNyjc h2 Math p2 SolutionjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Taburan Normal: Kebarangkalian Dan Penyelesaian MasalahДокумент84 страницыTaburan Normal: Kebarangkalian Dan Penyelesaian MasalahMuhammad IzzatОценок пока нет
- S. No Questions Solutions Sol: 1 (B) : Poornima University. For Any Query, Contact Us At: 8875666617,18Документ6 страницS. No Questions Solutions Sol: 1 (B) : Poornima University. For Any Query, Contact Us At: 8875666617,18Vaibhav SinghОценок пока нет
- Normal Distribution Notes & Exam Type QstnsДокумент18 страницNormal Distribution Notes & Exam Type QstnsMartin CarlОценок пока нет
- STATS GP1 Assessment2Документ24 страницыSTATS GP1 Assessment2NUR AININ SOFIYA OMARОценок пока нет
- AP ECON 2500 Session 4Документ18 страницAP ECON 2500 Session 4Thuỳ DungОценок пока нет
- ch06 Mah2Документ88 страницch06 Mah2Ahadul Hoque NavidОценок пока нет
- 01-Stat2 Exercise Set 1 SolutionДокумент6 страниц01-Stat2 Exercise Set 1 SolutionVivek PoddarОценок пока нет
- JJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsДокумент14 страницJJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- MTH 2003 Sample Final DДокумент9 страницMTH 2003 Sample Final DCTLОценок пока нет
- Normal DistributionДокумент10 страницNormal DistributionJohan GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Applied Statistics: Normal DistributionДокумент11 страницApplied Statistics: Normal Distributioniiyousefgame YTОценок пока нет
- Msqe Pea 2016Документ11 страницMsqe Pea 2016blahblahОценок пока нет
- Normal Distribution StatisticsДокумент18 страницNormal Distribution StatisticsNOMAN SHEHZADОценок пока нет
- Topics To Be Covered:: Assignment# 2Документ7 страницTopics To Be Covered:: Assignment# 2Rimsha ShiekhОценок пока нет
- 2949 (29-01-12) LASS XII - AG-7cbseДокумент5 страниц2949 (29-01-12) LASS XII - AG-7cbseVarsha DangeОценок пока нет
- Iit Jee 2004 Screening MathsДокумент10 страницIit Jee 2004 Screening MathsRahul BadwaikОценок пока нет
- Qesemacademy Math Social ModelДокумент11 страницQesemacademy Math Social ModelBerihun TsegayeОценок пока нет
- CJC h2 Math p2 SolutionДокумент14 страницCJC h2 Math p2 SolutionjimmytanlimlongОценок пока нет
- Vidyalankar Vidyalankar Vidyalankar Vidyalankar: Advanced Engineering MathematicsДокумент16 страницVidyalankar Vidyalankar Vidyalankar Vidyalankar: Advanced Engineering MathematicsPooja JainОценок пока нет
- Leep 214Документ23 страницыLeep 214Koyal Gupta100% (1)
- Actl 20025101 Finalexamsolutions 2006Документ15 страницActl 20025101 Finalexamsolutions 2006柯颖Оценок пока нет
- Practice Questions Lecture 39-41Документ5 страницPractice Questions Lecture 39-41Random Fun clipsОценок пока нет
- WBJEE 2014 Mathematics Question Paper With SolutionsДокумент20 страницWBJEE 2014 Mathematics Question Paper With SolutionsLokesh Kumar0% (2)
- FIITJEE Solutions To: IIT - JEE - 2009Документ10 страницFIITJEE Solutions To: IIT - JEE - 2009gautham28Оценок пока нет
- Notes and Formulae MathematicsДокумент9 страницNotes and Formulae MathematicsNurAinKhalidОценок пока нет
- IIT-JEE 2004 Mains Questions & Solutions - Maths - Version 2 (The Questions Are Based On Memory)Документ15 страницIIT-JEE 2004 Mains Questions & Solutions - Maths - Version 2 (The Questions Are Based On Memory)AlokShuklaОценок пока нет
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsДокумент6 страницIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsSayan Kumar KhanОценок пока нет
- Practice Question of Lecture 41 To 45 UpdatedДокумент5 страницPractice Question of Lecture 41 To 45 UpdatedAhmad DurraniОценок пока нет
- Ex ContinuousprobДокумент19 страницEx Continuousprobabed311Оценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент489 страницUntitledchanti489Оценок пока нет
- Bivariate Normal 1 With Answers PDFДокумент22 страницыBivariate Normal 1 With Answers PDFdОценок пока нет
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryДокумент9 страницNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometrySharmini RajagopalОценок пока нет
- Formula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasДокумент9 страницFormula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasPurawin Subramaniam100% (11)
- Topic 6Документ30 страницTopic 6Zienab AhmedОценок пока нет
- P P (Red Ball) 3/5, Which Remains Constant From Trial To TrialДокумент10 страницP P (Red Ball) 3/5, Which Remains Constant From Trial To Trialrohitrgt4uОценок пока нет
- Complex NumbersДокумент126 страницComplex NumbersHubert SemenianoОценок пока нет
- Coordinate GeometryДокумент19 страницCoordinate GeometryFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Graph OA - Object Move With Constant Speed Graph AB - Object Is Not MovingДокумент8 страницGraph OA - Object Move With Constant Speed Graph AB - Object Is Not MovingFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- SMK Seri Rompin 26810 Kuala Rompin Peperiksaan Penilaian 3 Tingkatan 4 2014Документ2 страницыSMK Seri Rompin 26810 Kuala Rompin Peperiksaan Penilaian 3 Tingkatan 4 2014Fazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Modul 1 Asas NomborДокумент3 страницыModul 1 Asas NomborFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Solve The Equation - Selesaikan Persamaan (3 Marks/markah) Answer/JawapanДокумент11 страницSolve The Equation - Selesaikan Persamaan (3 Marks/markah) Answer/JawapanFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Slot 1: Matrices Mathematical ReasoningДокумент1 страницаSlot 1: Matrices Mathematical ReasoningFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Reasoning AnswerДокумент3 страницыMathematical Reasoning AnswerFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Kebarangkalian Hujung Atas Q Bagi Taburan NormalДокумент4 страницыKebarangkalian Hujung Atas Q Bagi Taburan NormalFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Jadual KebarangkalianДокумент1 страницаJadual KebarangkalianFazlina Mustafa100% (1)
- Which Graph Represent y - 3x - 5 ? A.: Rajah 1 Menunjukkan Satu Garis Lurus JKДокумент3 страницыWhich Graph Represent y - 3x - 5 ? A.: Rajah 1 Menunjukkan Satu Garis Lurus JKFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Set K2Документ7 страницSet K2Fazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- 1 2 Given That N (G H) 4, N (G) 15 and N (H) 12, Find N (G H)Документ3 страницы1 2 Given That N (G H) 4, N (G) 15 and N (H) 12, Find N (G H)Fazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- StatisticsДокумент11 страницStatisticsFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Selesaikan Persamaan Kuadratik Selesaikan Persamaan Kuadratik BerikutДокумент4 страницыSelesaikan Persamaan Kuadratik Selesaikan Persamaan Kuadratik BerikutFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Quadratic Expression1Документ1 страницаQuadratic Expression1Fazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Mind Map VectorДокумент1 страницаMind Map VectorFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Modul Matematik Tambahan Form 5 (JPNP)Документ110 страницModul Matematik Tambahan Form 5 (JPNP)Fazlina Mustafa0% (1)
- Formulae Given in ExamДокумент2 страницыFormulae Given in ExamFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Vectors N TrigoДокумент20 страницVectors N TrigoFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ24 страницыChapter 6Fazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Scalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature andДокумент10 страницScalar Quantity, Such As Area, Volume, Mass, Temperature andFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Up1 f5 SMKSR 2014 k1 SkemaДокумент6 страницUp1 f5 SMKSR 2014 k1 SkemaFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Modul Matematik Tambahan Form 4 JPNPДокумент162 страницыModul Matematik Tambahan Form 4 JPNPFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- 19ProbablityDistributionsF5 BinomialДокумент6 страниц19ProbablityDistributionsF5 BinomialFazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Vectors (PPD)Документ11 страницVectors (PPD)Fazlina MustafaОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three MultipleДокумент15 страницChapter Three MultipleabdihalimОценок пока нет
- Q4 TOS Math 7Документ1 страницаQ4 TOS Math 7MorilleОценок пока нет
- Syllabus Statistics For Mechanical EngineeringДокумент1 страницаSyllabus Statistics For Mechanical Engineeringdfsdfsdfdf4646545Оценок пока нет
- 1.3 Measure of Variability and PositionДокумент47 страниц1.3 Measure of Variability and PositionShyla Patrice DantesОценок пока нет
- Forecasting 1Документ27 страницForecasting 1Abhishek KumarОценок пока нет
- LSS BB Body of KnowledgeДокумент5 страницLSS BB Body of KnowledgeVigneshОценок пока нет
- Normal Distribution: Statistics and Probability Topic #4Документ18 страницNormal Distribution: Statistics and Probability Topic #4Diama, Hazel Anne B. 11-STEM 9Оценок пока нет
- Data Set 1. The Class Levels of A Simple Random Sample of Students Are As FollowsДокумент6 страницData Set 1. The Class Levels of A Simple Random Sample of Students Are As FollowsEhron RiveraОценок пока нет
- A Study of Train Dwelling Time at The Hong Kong Mass Transit Railway SystemДокумент11 страницA Study of Train Dwelling Time at The Hong Kong Mass Transit Railway SystemNguyễn Phạm Kiến MinhОценок пока нет
- Characterising and Displaying Multivariate DataДокумент15 страницCharacterising and Displaying Multivariate DataR. Shyaam PrasadhОценок пока нет
- hw02 DescriptionДокумент4 страницыhw02 DescriptionCan KurtulanОценок пока нет
- Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011 Arbogast 613 20Документ8 страницAm. J. Epidemiol. 2011 Arbogast 613 20Amelia Yunira PratiwiОценок пока нет
- Mathematics For Machine LearningДокумент134 страницыMathematics For Machine LearningDaria GodorozhaОценок пока нет
- Interpretasi DiskriminanДокумент4 страницыInterpretasi DiskriminanDaffa Grawira JyestaОценок пока нет
- Different Question: Conduct The 5-Step Test For This ExerciseДокумент6 страницDifferent Question: Conduct The 5-Step Test For This ExerciseTun TaiОценок пока нет
- Sas Notes Module 4-Categorical Data Analysis Testing Association Between Categorical VariablesДокумент16 страницSas Notes Module 4-Categorical Data Analysis Testing Association Between Categorical VariablesNISHITA MALPANI100% (1)
- Statistics and Probability Lecture 12Документ6 страницStatistics and Probability Lecture 12john christian de leon0% (2)
- Linear Regression Analysis: Gaurav Garg (IIM Lucknow)Документ96 страницLinear Regression Analysis: Gaurav Garg (IIM Lucknow)Sakshi JainОценок пока нет
- Doomsday ArgumentДокумент13 страницDoomsday Argumentpatty444Оценок пока нет
- StatisticsДокумент4 страницыStatisticsJohn Lou Caray100% (1)
- Sampling DistributionsДокумент92 страницыSampling DistributionsSandeep KumarОценок пока нет
- Procedure of Selecting A Simple Random SampleДокумент1 страницаProcedure of Selecting A Simple Random SampleNoorkey adenОценок пока нет
- One Sample T Test ThesisДокумент6 страницOne Sample T Test Thesisjmvnqiikd100% (2)
- Geostatistical Mineral Resource Estimation: AMEC Advantage TrainingДокумент8 страницGeostatistical Mineral Resource Estimation: AMEC Advantage TrainingPatricia Del Carmen Guevara VasquezОценок пока нет
- Nama: Syafitri Putri Gusasi (2100032) Kelas: A - Akuntansi Mata Kuliah: Statistika Dan Analisis Data 1. AДокумент9 страницNama: Syafitri Putri Gusasi (2100032) Kelas: A - Akuntansi Mata Kuliah: Statistika Dan Analisis Data 1. ASYAFITRI PUTRIОценок пока нет
- Modeling Ordinal Categorical Data (Agresti)Документ71 страницаModeling Ordinal Categorical Data (Agresti)Davide RadiceОценок пока нет
- Question #1: Ms FinanceДокумент5 страницQuestion #1: Ms Financezungetsu100% (1)
- Cda1q - zEQomQNav8xCKJjA - Inferential and Predictive Statistics For Business - Mod 1 PDFДокумент147 страницCda1q - zEQomQNav8xCKJjA - Inferential and Predictive Statistics For Business - Mod 1 PDFreshma thomasОценок пока нет
- FIX Exam ScoresДокумент1 страницаFIX Exam ScoresAhmad Choirul AnamОценок пока нет
- Data Hujan Harian 01 (MM) Propinsi: Jawa Tengah KABUPATEN: Kota Semarang Tahun: 1984Документ35 страницData Hujan Harian 01 (MM) Propinsi: Jawa Tengah KABUPATEN: Kota Semarang Tahun: 1984Arief HermawanОценок пока нет
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)От EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Оценок пока нет
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsОт EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.От EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeОт EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeОт EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersОт EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormОт EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryОт EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingОт EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldОт EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (80)
- ParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)От EverandParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)Оценок пока нет