Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Four Types of Motherboards
Загружено:
Nard EspañolaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Four Types of Motherboards
Загружено:
Nard EspañolaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Four types of Motherboards
Today our class is about motherboard types and differences. we already discussed about
motherboard, which is the main circuit board and it interconnects the remaining parts
of computer.
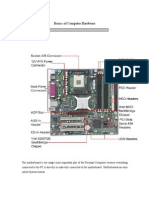
Totally we have 4 types of motherboards so far. They are XT, AT, Baby AT and ATX.
XT Motherboards:
XT Stands for eXtended Technology. These are all old model motherboard. In this motherboards, we find
old model processor socket LIF (Low Insertion Force) sockets, ram slots Dimms and ISA (Industry
Standards Architecture) slots, 12pin Power Connector and no ports.
They have slot type processors, Dimms memory modules, ISA slots for add-on card, and no ports. There
are connectors and add-on cards for ports.
Eg: Pentium-I, Pentium-MMX, Pentium -II and Pentium-II Processors.
AT Motherboards:
AT stands for Advanced Technology. Advanced Technology Motherboards have PGA (Pin Grid Array)
Socket, SD Ram slots, 20pin power connector PCI slots and ISA slots. we find the above components on
AT motherboards.
Eg: Pentium-III Processors
Baby AT Motherboards:
Baby AT Motherboards have the combination of XT and AT. They have both slot type processor sockets
and PGA processor sockets, SD Ram slots and DDR Ram slots, PCI slots and ISA slots, 12 Pin power
connector and 20Pin power connector and Ports.
Eg: Pentium-III and Pentium-IV
ATX Motherboards:
ATX stands for Advanced Technology eXtended. latest motherboards all are called as ATX motherboards.
designed by ATX form factor. In this motherboards, we find MPGA Processor Sockets, DDR Ram slots,
PCI slots, AGP slots, Primary and secondary IDE interfaces, SATA connectors, 20pin and 24 pin ATX
power connector and Ports.
Eg: Pentium-IV, Dual Core, Core 2 Duo, Quad Core, i3, i5 and i7 Processors.
Different types of Hard Disk Drive
Written By Admin on March 12, 2011 | Saturday, March 12, 2011
It is a non-volatile storage device which stores digitally encoded data on rapidly
rotating platters with magnetic surface.
Types of HDD :
1. IDE : Integrated Drive Electronics. IDE drives are also known as PATA drives(
Parallel advance technology attachment )
2. SATA : Serial advance technology attachment
3. SCSI : Small Computer System Interface. SCSI is pronounced as scuzzy.
4. SAS : Serial Attached SCSI
DE / PATA (Integrated Drive Electronics Drive / Parallel Advance Technology
Attachment Drive)
IDE/PATA Drives have usually 40 pins.
IDE/PATA Drives offer 133 MB/sec transfer rate.
It sends 8 bit data at a time.
PATA Cables are used to connect PATA HDD. Two drives can be connected in a
single pata cable. One as master and other as slave. The configuration of
master and slave is done by different combination of jumpers in the hdd.
SATA (Serial Advance Technology Attachment Drive)
SATA Drives have usually 7 pins, 4 pins in pair of two for sending and receiving
data and rest 3 pins are grounded.
SATA Drives offers generally 300MB/sec transfer rate.
It sends data bit by bit.
SATA Cables are used to connect SATA HDD. Only one drive can be connected in
a single sata cable.
SCSI (Small Computer System Interface Drive)
SCSI Drives have usually 50 to 68 pins.
SCSI Drive offers generally 640MB/sec transfer rate.
This drives are hot swappable.
SCSI cables are used to connect SCSI HDD. Maximum of 16 drives can be
connected in a single scsi cable. Each hdd have a 8 bytes hexadecimal code
known as WWN (worldwide name) for its identification in the cable.
SAS(Serial Attached SCSI Drive)
SAS Drives generally offers 805 MB/sec transfer rate.
This drives are hot swappable.
SAS Cables are used to connect SAS Drives. Maximum of 128 drives can be
connected in a single sas cable.
There are three types of power supply in common use:
AT used in older PCs
ATX used in more recent PCs
ATX V2 (also known as ATX12V) a newer type of power supply designed for the power
requirements of modern PCs. Generally speaking, you should be able use an ATX V2 PSU
with an older computer that had an ATX PSU. ATX V2 has a 24 pin connector going to the
motherboard, while ATX has a 20 pin connector, but as discussed below, you should be
able to work around this.
Youll find a very useful article about ATX and ATX V2 power supplies here.
Types of RAM: How to Identify and their Specifications
by Bryce Whitty
There are many different types of RAM which have appeared over the years and it is often difficult
knowing the difference between them both performance wise and visually identifying them. This article
tells a little about each RAM type, what it looks like and how it performs.
FPM RAM
FPM RAM, which stands for Fast Page Mode RAM is a type of Dynamic RAM (DRAM). The term "Fast
Page Mode" comes from the capability of memory being able to access data that is on the same page
and can be done with less latency. Most 486 and Pentium based systems from 1995 and earlier use FPM
Memory.
FPM RAM
EDO RAM
EDO RAM, which stands for "Extended Data Out RAM" came out in 1995 as a new type of memory
available for Pentium based systems. EDO is a modified form of FPM RAM which is commonly referred to
as "Hyper Page Mode". Extended Data Out refers to fact that the data output drivers on the memory
module are not switched off when the memory controller removes the column address to begin the next
cycle, unlike FPM RAM. Most early Penitum based systems use EDO.
EDO RAM
SDRAM
SDRAM , which is short for Synchronous DRAM is a type of DRAM that runs in synchronization with the
memory bus. Beginning in 1996 most Intel based chipsets began to support SDRAM which made it a
popular choice for new systems in 2001.
SDRAM is capable of running at 133MHz which is about three times faster than FPM RAM and twice as
fast as EDO RAM. Most Pentium or Celeron systems purchased in 1999 have SDRAM.
SD RAM
DDR RAM
DDR RAM, which stands for "Double Data Rate" which is a type of SDRAM and appeared first on the
market around 2001 but didnt catch on until about 2001 when the mainstream motherboards started
supporting it. The difference between SDRAM and DDR RAM is that instead of doubling the clock rate it
transfers data twice per clock cycle which effectively doubles the data rate. DDRRAM has become
mainstream in the graphics card market and has become the memory standard.
DDR RAM
DDR2 RAM
DDR2 RAM, which stands for "Double Data Rate 2" is a newer version of DDR which is twice as fast as
the original DDR RAM. DDR2RAM came out in mid 2003 and the first chipsets that supported DDR2
came out in mid 2004. DDR2 still is double data rate just like the original DDR however DDR2-RAM has
modified signaling which enables higher speeds to be achieved with more immunity to signal noise and
cross-talk between signals.
DDR2 RAM
RAMBUS (RIMM) RAM
RAMBUS RDRAM is a type of ram of its own, it came out in 1999 and was developed from traditional
DRAM but its architecture is totally new. The RAMBUS design gives smarter access to the ram meaning
that units can prefetch data and free some CPU work. The idea behind RAMBUS RAM is to get small
packets of data from the RAM, but at very high clock speeds. For example, SD RAM can get 64bit of
information at 100MHz where RAMBUS RAM would get 16bits of data at 800MHz. RIMM ram was
generally unsuccessful as Intel had a lot of problems with the RAM timing or signal noise. RD RAM did
make an appearance in the Sony Playstation 2 and the Nintendo 64 game consoles.
RD RAM
Single Core CPUs
Single core CPUs are the oldest type of computer CPU available and initially this was the
only type of CPU that could be used in computers. Single core CPUs can only start one
operation at a time, so they were not very good at multi-tasking. This meant that there were
noticeable decreases in performance whenever more than one application was running.
Although only one operation could be started at a time, another one could be activated
before the first one was finished but with each new operation the computer would run more
slowly. Performance on these types of CPUs were largely dependent on their clock speeds,
which was a measurement of their power.
Dual Core CPUs
A dual core CPU is a single CPU that has two cores and thus functions like two CPUs in one.
Unlike single core CPUS where the processor had to switch back and forth between different
sets of data streams if more than one operation was running, dual core CPUs can handle
multitasking much more efficiently. To make the most of a dual core CPU, both the
operating system and the programs running on it must have special code called SMT
(simultaneous multi-threading technology) written into it. Dual core CPUs are faster than
single core ones but not as fast the quad core CPUs that have superseded them.
Quad Core CPUs
Quad Core CPUs are a further refinement of the multi-core CPU design and features four
cores on a single CPU. Just as dual core CPUs could split the workload between two cores,
quad cores allows for even greater multitasking. This doesn't mean that a single operation
will be four times faster however, and unless the programs and applications running on it
has SMT code, the speed increase will not be so noticeable. These types of CPUs are useful
for people that need to run a lot of different programs at the same time as well as gamers, as
there are games like the Supreme Commander series that are optimized for multi-core
CPUs.
Read more : http://www.ehow.com/list_6966558_types-computer-cpu.html
Вам также может понравиться
- Nintendo DS Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #14От EverandNintendo DS Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #14Оценок пока нет
- The Motherboard: Basics of Computer HardwareДокумент34 страницыThe Motherboard: Basics of Computer Hardwareprashanth2222Оценок пока нет
- Intro To It Hardware1Документ32 страницыIntro To It Hardware1tprastyanaОценок пока нет
- A+ Cert Chapter 1 MiscДокумент4 страницыA+ Cert Chapter 1 Misc123456Оценок пока нет
- Random Access MemoryДокумент19 страницRandom Access MemoryOrlando FelixОценок пока нет
- Different RAM Types and Its UsesДокумент8 страницDifferent RAM Types and Its Usesdanielle leigh100% (6)
- Selecting Criteria of A MotherboardДокумент3 страницыSelecting Criteria of A MotherboardDa NishОценок пока нет
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsДокумент98 страницFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and Peripheralsjuliet brusola100% (1)
- Netking: Ahsan Jameel KhanДокумент20 страницNetking: Ahsan Jameel KhanIshq Ek BaarОценок пока нет
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsДокумент78 страницFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsVencent BuellОценок пока нет
- Computer Hardware: Intel AMD Dual CoreДокумент6 страницComputer Hardware: Intel AMD Dual CoreanishklОценок пока нет
- BY: For:: Ahmad Khairi HalisДокумент19 страницBY: For:: Ahmad Khairi HalisKhairi B HalisОценок пока нет
- 1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorДокумент12 страниц1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorTuesept Anne Vargas UrgenteОценок пока нет
- Different RAM Types and Its UsesДокумент3 страницыDifferent RAM Types and Its Usessinu66Оценок пока нет
- Computer ComponentsДокумент32 страницыComputer ComponentsJSPAMoreОценок пока нет
- The Devices Which Are Necessary To Assemble A ComputerДокумент31 страницаThe Devices Which Are Necessary To Assemble A ComputerStanley VijayakumarОценок пока нет
- Katani Kalan, Ludhiana: Project Report On Computer HardwareДокумент33 страницыKatani Kalan, Ludhiana: Project Report On Computer HardwareVijayinder Singh PatialОценок пока нет
- BIOS InstallationДокумент5 страницBIOS InstallationArif ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Computer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsДокумент29 страницComputer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsRajendra PatilОценок пока нет
- 27 Main Parts of Motherboard and Its FunctionДокумент30 страниц27 Main Parts of Motherboard and Its FunctionAngelica CarbonquilloОценок пока нет
- Parts of A Computer System Unit (Components)Документ31 страницаParts of A Computer System Unit (Components)Anonymous PcPkRpAKD5Оценок пока нет
- Motherboard and Other PartsДокумент32 страницыMotherboard and Other PartsJom's Mijares100% (1)
- CSS8Документ3 страницыCSS8Chelsea EriveОценок пока нет
- A+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationДокумент40 страницA+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationLindasharon AwourОценок пока нет
- Different RAM Types and Its Uses: IntroДокумент6 страницDifferent RAM Types and Its Uses: Introkittu423Оценок пока нет
- BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) : RAM DDRДокумент3 страницыBIOS (Basic Input/Output System) : RAM DDRsnag07Оценок пока нет
- ReportДокумент8 страницReportapi-3734554100% (1)
- IT Workshop Lab Manual PDFДокумент166 страницIT Workshop Lab Manual PDFAnusha KakumanuОценок пока нет
- Units (CPU), Expansions Slots and Random-Access Memory (RAM)Документ6 страницUnits (CPU), Expansions Slots and Random-Access Memory (RAM)Jonathan ScottОценок пока нет
- Drives Are Storage MediaДокумент13 страницDrives Are Storage MediaKartik AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Basic Parts of Mother Board: Function and Uses EIDE ConnectorsДокумент5 страницBasic Parts of Mother Board: Function and Uses EIDE ConnectorsAudrey Kristina MaypaОценок пока нет
- 1 - Firewire HeaderДокумент4 страницы1 - Firewire HeaderVishnu TejaОценок пока нет
- Motherboard Parts (Explained)Документ1 страницаMotherboard Parts (Explained)maryОценок пока нет
- Central Processing UnitДокумент5 страницCentral Processing UnitVaishali WaghОценок пока нет
- Motherboard: The CPUДокумент10 страницMotherboard: The CPU000pssОценок пока нет
- Lab ManualДокумент24 страницыLab ManualAhmar KhanОценок пока нет
- CHMA Unit - VДокумент25 страницCHMA Unit - VSayyan Shaikh100% (1)
- Parts of A MotherboardДокумент9 страницParts of A Motherboardraze techОценок пока нет
- MaintenaceДокумент90 страницMaintenaceGashaw GetanehОценок пока нет
- Parts of A MotherboardДокумент4 страницыParts of A MotherboardPamieDyОценок пока нет
- Hardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519Документ46 страницHardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519crecbhoomi21Оценок пока нет
- Different Types of RAM FPM RamДокумент2 страницыDifferent Types of RAM FPM RamJayson RegayaОценок пока нет
- Intel Ted Hoff Instructions Hardware Software Pentium CPU Socket Motherboard Heat SinkДокумент12 страницIntel Ted Hoff Instructions Hardware Software Pentium CPU Socket Motherboard Heat SinkHaris QurashiОценок пока нет
- What Is Computer?: Bits For TransmissionДокумент122 страницыWhat Is Computer?: Bits For TransmissionHenson JoyОценок пока нет
- IEEE 1394 PortДокумент4 страницыIEEE 1394 PortPRincess ScarLetОценок пока нет
- Lesson 02 - Main Parts of ComputerДокумент22 страницыLesson 02 - Main Parts of ComputerDummy AccountОценок пока нет
- What Is HardwareДокумент8 страницWhat Is HardwareMatthew CannonОценок пока нет
- Into To Comp SysДокумент80 страницInto To Comp SysMaica BaldonadoОценок пока нет
- Lab2 - Hardware-2Документ24 страницыLab2 - Hardware-2Mohammed AlobaidyОценок пока нет
- Slots and PortsДокумент7 страницSlots and Portsdaniyalshakeel573Оценок пока нет
- MOBO Basic PartsДокумент17 страницMOBO Basic PartsJohara Mundas DiocolanoОценок пока нет
- Difference Betweew Celeron and PentiumДокумент3 страницыDifference Betweew Celeron and PentiumAkash RuhilОценок пока нет
- Motherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryДокумент8 страницMotherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryJhay Consolacion WalkerОценок пока нет
- PC Hardware Interview Questions-1Документ10 страницPC Hardware Interview Questions-1ShaneVaz100% (1)
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionДокумент14 страницIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- Notes On System Memory & BiosДокумент9 страницNotes On System Memory & BiosHenson JoyОценок пока нет
- It Os Etmnr2Документ11 страницIt Os Etmnr2diljithdinesh1501Оценок пока нет
- Parts of A Computer With Their FunctionsДокумент19 страницParts of A Computer With Their FunctionsJaried SumbaОценок пока нет
- How Motherboard WorksДокумент12 страницHow Motherboard Worksrez hablo100% (1)
- Farm ImplementsДокумент8 страницFarm ImplementsNard EspañolaОценок пока нет
- Auto E-Class Record 2019Документ67 страницAuto E-Class Record 2019Nard EspañolaОценок пока нет
- Graduation Program LayoutДокумент6 страницGraduation Program LayoutNard EspañolaОценок пока нет
- Chinese TraditionsДокумент2 страницыChinese TraditionsNard EspañolaОценок пока нет
- African TraditionsДокумент3 страницыAfrican TraditionsNard EspañolaОценок пока нет
- Four Types of MotherboardsДокумент12 страницFour Types of MotherboardsNard EspañolaОценок пока нет
- Four Types of MotherboardsДокумент12 страницFour Types of MotherboardsNard EspañolaОценок пока нет
- Hukbalahap: March 16, 2019 Godwin M. Rarama Readings in The Philippine History Seat No. 35Документ2 страницыHukbalahap: March 16, 2019 Godwin M. Rarama Readings in The Philippine History Seat No. 35Godwin RaramaОценок пока нет
- Witness Affidavit of Emeteria B, ZuasolaДокумент4 страницыWitness Affidavit of Emeteria B, ZuasolaNadin MorgadoОценок пока нет
- Questionnaire Exercise: Deals Desk Analyst Please Answer Below Questions and Email Your Responses Before First Technical Round of InterviewДокумент2 страницыQuestionnaire Exercise: Deals Desk Analyst Please Answer Below Questions and Email Your Responses Before First Technical Round of InterviewAbhinav SahaniОценок пока нет
- Novozymes IPRДокумент19 страницNovozymes IPRthereisaneedОценок пока нет
- Sustainable Project Management. The GPM Reference Guide: March 2018Документ26 страницSustainable Project Management. The GPM Reference Guide: March 2018Carlos Andres PinzonОценок пока нет
- TEMI880&850 Manual (Eng)Документ122 страницыTEMI880&850 Manual (Eng)Mihir PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Calculate PostageДокумент4 страницыCalculate PostageShivam ThakurОценок пока нет
- Lets Talk About Food Fun Activities Games Oneonone Activities Pronuncia - 1995Документ1 страницаLets Talk About Food Fun Activities Games Oneonone Activities Pronuncia - 1995IAmDanaОценок пока нет
- Manual de Colisión Mazda 626 1986-1987Документ9 страницManual de Colisión Mazda 626 1986-1987mark rueОценок пока нет
- Bidding Process in Infrastructure ProjectsДокумент44 страницыBidding Process in Infrastructure ProjectsRajesh Chowdary Chintamaneni100% (2)
- LSM - Neutral Axis Depth CalculationДокумент2 страницыLSM - Neutral Axis Depth CalculationHimal KafleОценок пока нет
- Ps 6013 Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Symbology Method, Usage and Definitions 2013-08-01 (G)Документ18 страницPs 6013 Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Symbology Method, Usage and Definitions 2013-08-01 (G)maheshmbelgaviОценок пока нет
- C TKP3 SMQДокумент11 страницC TKP3 SMQDavid Tovar cruzОценок пока нет
- 13 DocumentsДокумент38 страниц13 DocumentsPoorClaresBostonОценок пока нет
- Openness and The Market Friendly ApproachДокумент27 страницOpenness and The Market Friendly Approachmirzatouseefahmed100% (2)
- Rosmary PollockДокумент4 страницыRosmary PollockhbОценок пока нет
- Business Opportunity Identification and SelectionДокумент15 страницBusiness Opportunity Identification and SelectionAnonymous 3H6fFBmОценок пока нет
- The Man Who Knew Too Much: The JFK Assassination TheoriesДокумент4 страницыThe Man Who Knew Too Much: The JFK Assassination TheoriesedepsteinОценок пока нет
- Drafting Foundation PlanДокумент24 страницыDrafting Foundation Planerol bancoroОценок пока нет
- Name - Hiral Baid Class - 12 C Subject - Commerce Project 1 - Swot Analysis and Consumer ProtectionДокумент21 страницаName - Hiral Baid Class - 12 C Subject - Commerce Project 1 - Swot Analysis and Consumer Protectionhiral baidОценок пока нет
- Marine Products: SL-3 Engine ControlsДокумент16 страницMarine Products: SL-3 Engine ControlsPedro GuerraОценок пока нет
- Case Study On DominoДокумент7 страницCase Study On Dominodisha_pandey_4Оценок пока нет
- OpenShift Container Platform-4.6-Installing On vSphere-en-USДокумент189 страницOpenShift Container Platform-4.6-Installing On vSphere-en-USChinni MunniОценок пока нет
- A033Документ24 страницыA033PRANAV GOYALОценок пока нет
- BIR Form 2307Документ20 страницBIR Form 2307Lean Isidro0% (1)
- 20 X 70Документ102 страницы20 X 70MatAlengОценок пока нет
- Duraguard MsdsДокумент1 страницаDuraguard MsdsSantosh Kumar GoudaОценок пока нет
- Magnetic Properties of MaterialsДокумент10 страницMagnetic Properties of MaterialsNoviОценок пока нет
- Sfa 5.22 PDFДокумент36 страницSfa 5.22 PDFLuis Evangelista Moura PachecoОценок пока нет
- List of TCP and UDP Port NumbersДокумент44 страницыList of TCP and UDP Port NumbersElvis JavierОценок пока нет