Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Distillation Column Basics
Загружено:
Tejas PatelАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Distillation Column Basics
Загружено:
Tejas PatelАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
DISTILLATION COLUMN BASICS
The liquid mixture that is to be processed is known as the feed and this is introduced usually somewhere
near the middle of the column to a tray known as the feed tray. The feed tray divides the column into a
top (enriching or rectification) section and a bottom (stripping) section. The feed flows down the column
where it is collected at the bottom in the re-boiler.
Heat is supplied to the re-boiler to generate vapour. The source of heat input can be any suitable fluid
although in most chemical plants this is normally steam. !n refineries the heating source may be the
output streams of other columns. The vapour raised in the re-boiler is re-introduced into the unit at the
bottom of the column. The liquid removed from the re-boiler is known as the bottoms product or simply
bottoms.
The vapour moves up the column and as it exits the top of the unit it is cooled by a condenser. The
condensed liquid is stored in a holding vessel known as the reflux drum. "ome of this liquid is recycled
back to the top of the column and this is called the reflux. The condensed liquid that is removed from the
system is known as the distillate or top product.
Thus there are internal flows of vapour and liquid within the column as well as external flows of feeds and
product streams into and out of the column.
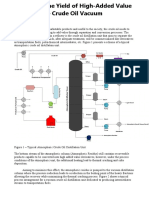
CRUDE DISTILLATION SYSTEM
The crude needs to be heated up before entering the fractionation column and this is done at first in a series of heat exchangers where
heat is taken from other process streams which require cooling before being sent to rundown. Heat is also exchanged against
condensing streams from the main column. Typically, the crude will be heated up in this way upto a temperature of 200 - 20
0
!,
before entering a furnace.
"s the raw crude oil arri#ing contains quite a bit of water and salt, it is normally sent for salt remo#ing first, in a
piece of equipment called a desalter. $pstream the desalter, the crude is mixed with a water stream, typically
about % - &' on feed. (ntense mixing takes place o#er a mixing #al#e and )optionally* as static mixer. The
desalter, a large liquid full #essel, uses an electric field to separate the crude from the water droplets. (t operates
best at +20 - +,0
0
!, hence it is con#eniently placed somewhere in the middle of the preheat train.
The role of a platformer is to pa#e the way for this by a process which reforms the molecules in low octane naphtha to produce a high
octane gasoline component. This is achie#ed by employing a catalyst with platinum as its acti#e compound- hence the name
.latformer. /or many refinery catalyst applications, a promoter is used, and in the platforming process, it is a chloride promoter which
stimulates the 0acidity0 of the catalyst and thereby the isomerisation reactions. 1ften, a bimetallic catalyst is used, i.e. in addition to the
platinum, a second metal, for instance 2henium is present on the catalyst. The main ad#antage is a higher stability under reforming
conditions. The disad#antage is that the catalyst becomes more sensiti#e towards poisons, process upsets and more susceptible to non-
optimum regenerations
PLATFORMING PROCESS
The main reactions of platforming process are as follows3
4ehydrogenation of naphthenes, yielding aromatics and hydrogen
4ehydro-isomerisation of alkyl cyclopentanes to aromatic and hydrogen
(somerisation of paraffins and aromatics
4ehydrocyclisation of paraffins to aromatics and hydrogen
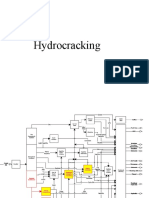
Hydrocracking of paraffins and naphthenes to ligher, saturated paraffins at the expense of hydrogen
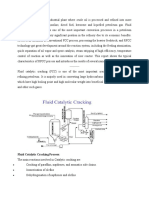
FCC Units (Catalytic cracking
Hot feed, together with some steam, is introduced at the bottom of the riser #ia special distribution no55les. Here it meets a stream of
hot regenerated catalyst from the regenerator flowing down the inclined regenerator standpipe. The oil is heated and #aporised by the
hot catalyst and the cracking reactions commence. The #apour, initially formed by #aporisation and successi#ely by cracking, carries
the catalyst up the riser at +0-20 m6s in a dilute phase. "t the outlet of the riser the catalyst and hydrocarbons are quickly separated in
a special de#ice. The catalyst )now partly deacti#ated by deposited coke* and the #apour then enter the reactor. The #apour passes
o#erhead #ia cyclone separator for remo#al of entrained catalyst before it enters the fractionator and further downstream equipment
for product separation. The catalyst then descends into the stripper where entrained hydrocarbons are remo#ed by in7ection of steam,
before it flows #ia the inclined stripper standpipe into the fluidised catalyst bed in the regenerator.
"ir is supplied to the regenerator by an air blower and distributed throughout the catalyst bed. The coke deposited is burnt off and the
regenerated catalyst passes down the regenerator standpipe to the bottom of the riser, where it 7oins the fresh feed and the cycle
recommences.
The flue gas )the combustion products* lea#ing the regenerator catalyst bed entrains catalyst particles. (n particular, it entrains 8fines8,
a fine dust formed by mechanical rubbing of catalyst particles taking place in the catalyst bed. 9efore lea#ing the regenerator, the flue
gas therefore passes through cyclone separators where the bulk of this entrained catalyst is collected and returned to the catalyst bed.
The /!! $nit can be a real margin impro#er for many refineries. (t is able to con#ert the residues into high #alue products like :.;,
9utylene, .ropylene and <ogas together with ;asoil. The /!! is also a start for chemical production )poly propylene*. <any /!!0s
ha#e 2 modes3 a <ogas mode and a ;asoil mode and /!!0s can be adapted to cater for the 2 modes depending on fa#ourabale
economic conditions. The only disad#antage of an /!! is that the products produced need to be treated )sulfur remo#al* to be on
specification. =ormally 2esidue /!!s act together with 2esidue Hydrocon#ersion .rocesses and Hydrocrackers in order to minimise
the product quality gi#e away and get a yield pattern that better matches the market specifications. >ia product blending, expensi#e
treating steps can be a#oided and the units prepare excellent feedstock for eachother3 desulfurised residue or hydrowax is excellent
/!! feed, while the /!! cycle oils are excellent Hydrocracker feed.
Вам также может понравиться
- Planning For Plant StartupДокумент91 страницаPlanning For Plant StartupGustavo Gonzalez ServaОценок пока нет
- Basic Instrumentation For Oil Gas Industries - Presentation - 29.08.10Документ101 страницаBasic Instrumentation For Oil Gas Industries - Presentation - 29.08.10Tejas Patel100% (5)
- Structural Steel Erection Best PracticesДокумент60 страницStructural Steel Erection Best Practicessudhakarballur92% (26)
- Two Step Spiral Pipe ManufacturingДокумент4 страницыTwo Step Spiral Pipe ManufacturingEagle SpiritОценок пока нет
- WellheadДокумент2 страницыWellheadRicardo Paz SoldanОценок пока нет
- MINDA Project ReportДокумент43 страницыMINDA Project ReportRupam10740100% (3)
- 117FK - Mineral Processing PDFДокумент8 страниц117FK - Mineral Processing PDFvenkiscribd444Оценок пока нет
- Fluid Catalytic Craking Unit (Fccu)Документ6 страницFluid Catalytic Craking Unit (Fccu)Nitin VarshneyОценок пока нет
- Quiz Mohd Rafiq Mohd ZubirДокумент11 страницQuiz Mohd Rafiq Mohd ZubirMohd RafiqОценок пока нет
- Catalytic Reforming PDFДокумент3 страницыCatalytic Reforming PDFAbey SamuelОценок пока нет
- 45 Naptha ReformingДокумент23 страницы45 Naptha ReformingJ MartínezОценок пока нет
- Transportation: EGEE 102 - Energy Conservation and Environmental ProtectionДокумент45 страницTransportation: EGEE 102 - Energy Conservation and Environmental ProtectionTanweer SalahОценок пока нет
- Aromatics Complex Project in Mangalore SezДокумент21 страницаAromatics Complex Project in Mangalore SezCОценок пока нет
- Main Parts of An EngineДокумент5 страницMain Parts of An EngineLuriz CadeliñaОценок пока нет
- JamnagarДокумент4 страницыJamnagarkatariamanojОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Catalytic ReformingДокумент32 страницыUnit 5 Catalytic ReformingStudy purposeОценок пока нет
- Motor Gasoline Analysis and SpecificationsДокумент4 страницыMotor Gasoline Analysis and SpecificationsFrançois LeroyОценок пока нет
- Compatibility With Plastics and Elastomers: TitleДокумент2 страницыCompatibility With Plastics and Elastomers: TitleashrafОценок пока нет
- Hydrotreating Amine Treating & Sulphur Recovery: PetroДокумент8 страницHydrotreating Amine Treating & Sulphur Recovery: PetroIlham HakimОценок пока нет
- Performance Analysis of Reciprocating Refrigerant CompressorДокумент6 страницPerformance Analysis of Reciprocating Refrigerant CompressorIjsrnet EditorialОценок пока нет
- Packinox Catalytic ReformingДокумент2 страницыPackinox Catalytic Reformingzohaib_farooqОценок пока нет
- Benzene, Xylene, Toluene (BTX) 2018Документ10 страницBenzene, Xylene, Toluene (BTX) 2018Matthew SantawОценок пока нет
- 09 Gasoline UpgradingДокумент63 страницы09 Gasoline UpgradingLượng NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Reforming Process - Catalyst Advancement: A Presentation OnДокумент23 страницыReforming Process - Catalyst Advancement: A Presentation OnSiddharth Sharma100% (1)
- Process of Refinery: Chapter-1Документ43 страницыProcess of Refinery: Chapter-1veena0602Оценок пока нет
- BXPДокумент53 страницыBXPkaranx16Оценок пока нет
- Hydrodesulfurization Often Abbreviated To HDSДокумент16 страницHydrodesulfurization Often Abbreviated To HDSigor0104100% (1)
- 27 UnionfiningДокумент2 страницы27 Unionfiningali11111Оценок пока нет
- HydrocrackingДокумент25 страницHydrocrackingJoprince PrincipioОценок пока нет
- CRU PresentationДокумент18 страницCRU PresentationManish KalraОценок пока нет
- Petroleum RefiningДокумент51 страницаPetroleum RefiningChalsawivelaОценок пока нет
- Petrochemicals: Petrochemicals Are Chemical Products Made From TheДокумент3 страницыPetrochemicals: Petrochemicals Are Chemical Products Made From TheRaj Sunil KandregulaОценок пока нет
- The Structure of The Indian Petrochemical IndustryДокумент56 страницThe Structure of The Indian Petrochemical IndustryAshwin RamayyagariОценок пока нет
- Environmental Aspects of Petroleum RefiningДокумент5 страницEnvironmental Aspects of Petroleum RefiningvsrslmОценок пока нет
- Questions Bank Summary Crude Oil Pumping StationsДокумент31 страницаQuestions Bank Summary Crude Oil Pumping StationsAkol AganyОценок пока нет
- Refining ProcessДокумент15 страницRefining Processtechy TalksОценок пока нет
- Upgrade HDK Resid HP 2008-EnglishДокумент6 страницUpgrade HDK Resid HP 2008-Englishsaleh4060Оценок пока нет
- MRPLДокумент44 страницыMRPLNeha IsaacОценок пока нет
- PRPC NoteДокумент61 страницаPRPC NoteRohan MehtaОценок пока нет
- Petroleum Refining Crude Oil Refining Processes PDFДокумент6 страницPetroleum Refining Crude Oil Refining Processes PDFJAPAN NANAVATI0% (1)
- Introduction To Inviromental Control in Refining IndustryДокумент34 страницыIntroduction To Inviromental Control in Refining IndustryAmer ShaierОценок пока нет
- JamnagarДокумент3 страницыJamnagarkallurisuryaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3: Petroleum Refining Overview: 3.1 Crude OilДокумент66 страницLecture 3: Petroleum Refining Overview: 3.1 Crude OilKumar AyushОценок пока нет
- Refining Margin Supplement OMRAUG 12SEP2012Документ30 страницRefining Margin Supplement OMRAUG 12SEP2012Won JangОценок пока нет
- Gasoline PropertiesДокумент6 страницGasoline PropertiesbahadorОценок пока нет
- Hydrocracking: P A R T 7Документ22 страницыHydrocracking: P A R T 7Bharavi K SОценок пока нет
- Column InternalsДокумент15 страницColumn InternalsOlman VargasОценок пока нет
- New Hydroprocessing Approaches To Increase Petrochemicals Production Rev 4Документ11 страницNew Hydroprocessing Approaches To Increase Petrochemicals Production Rev 4nishilgeorgeОценок пока нет
- 112 Refinery Overview ChevronДокумент2 страницы112 Refinery Overview Chevronupender345Оценок пока нет
- Advanced Catalytic Olefins ACO First Commercial Demonstration Unit Begins OperationsДокумент12 страницAdvanced Catalytic Olefins ACO First Commercial Demonstration Unit Begins OperationsmakhadermfОценок пока нет
- Vis BreakingДокумент21 страницаVis BreakingAhmed Hassan RashedОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen: The "Forever Fuel" That We Can Never Run Out ofДокумент26 страницHydrogen: The "Forever Fuel" That We Can Never Run Out ofSunil AroraОценок пока нет
- Catalytic Reforming - 2Документ31 страницаCatalytic Reforming - 2adityarajchikkalaОценок пока нет
- HydrocrackingДокумент33 страницыHydrocrackingNikita SeleznevОценок пока нет
- Selection of Technologies For Gas Plant NaturalДокумент15 страницSelection of Technologies For Gas Plant NaturaljxlОценок пока нет
- Petrochemicals RSOC 2Документ33 страницыPetrochemicals RSOC 2Sarhad AhmedОценок пока нет
- The Secretariat: Information Ce NterДокумент8 страницThe Secretariat: Information Ce NterAmeya KannamwarОценок пока нет
- Honeywell Uop FCC Related Processes DatasheetДокумент4 страницыHoneywell Uop FCC Related Processes Datasheetduraid ahmadОценок пока нет
- Bp-Uop Cyclar Process: Lubo ZhouДокумент10 страницBp-Uop Cyclar Process: Lubo ZhouBharavi K SОценок пока нет
- Oil Price Trends in India and Its DeterminentsДокумент16 страницOil Price Trends in India and Its DeterminentsDeepthi Priya BejjamОценок пока нет
- Fluid Catalytic Cracking of Heavy (Residual) Oil Fractions A Review PDFДокумент21 страницаFluid Catalytic Cracking of Heavy (Residual) Oil Fractions A Review PDFMmediong UdofiaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 Conversion and Characterisation - IITB - 2022Документ35 страницLecture 3 Conversion and Characterisation - IITB - 2022J JayaОценок пока нет
- Continuous Distillation: Navigation SearchДокумент9 страницContinuous Distillation: Navigation SearchSunil ShaОценок пока нет
- Petrochemical Technology (Interview)Документ23 страницыPetrochemical Technology (Interview)Ohol Rohan BhaskarОценок пока нет
- 6 UOP. Honeywel Egypt - Technologies For Distillate Production - Hydrocracking - E SvenssonДокумент17 страниц6 UOP. Honeywel Egypt - Technologies For Distillate Production - Hydrocracking - E SvenssonCamilo inversionesОценок пока нет
- Fluid Catalytic Cracking ProcessДокумент3 страницыFluid Catalytic Cracking ProcessMinh Tuấn PhạmОценок пока нет
- Electrode CalculationДокумент2 страницыElectrode CalculationTejas PatelОценок пока нет
- Elec Workflow PDFДокумент1 страницаElec Workflow PDFTejas Patel100% (1)
- IELTS TutorialДокумент2 страницыIELTS TutorialTejas PatelОценок пока нет
- Welcome To Presentation On: Pipe Support Systems & Piping FlexibilityДокумент67 страницWelcome To Presentation On: Pipe Support Systems & Piping Flexibilitysids8292% (24)
- Peaking BandingДокумент2 страницыPeaking Bandingsetak100% (4)
- Edexcel Higher Fluid Mechanics H1 Unit 8 NQF Level 4 Outcome 2 Viscosity Tutorial 2 - The Viscous Nature of FluidsДокумент10 страницEdexcel Higher Fluid Mechanics H1 Unit 8 NQF Level 4 Outcome 2 Viscosity Tutorial 2 - The Viscous Nature of FluidsTejas PatelОценок пока нет
- Concepts of Pipe Stress AnalysisДокумент54 страницыConcepts of Pipe Stress AnalysisTejas Patel100% (12)
- Pipe Solutions LTD - Technical Reference Guide - Thermal Pipe ExpansionДокумент28 страницPipe Solutions LTD - Technical Reference Guide - Thermal Pipe Expansionrebecca991027Оценок пока нет
- Piping Material Specification-GeneralДокумент15 страницPiping Material Specification-GeneralTejas PatelОценок пока нет
- Plot Plan & Equipment LayoutДокумент6 страницPlot Plan & Equipment LayoutTejas PatelОценок пока нет
- Steel ConnectionsДокумент56 страницSteel ConnectionsTejas Patel94% (16)
- Piping Design Guide-Vertical DrumsДокумент9 страницPiping Design Guide-Vertical DrumsTejas PatelОценок пока нет
- Reference PointДокумент3 страницыReference PointTejas PatelОценок пока нет
- Butt Fusion ParametersДокумент9 страницButt Fusion ParametersarkadjyothiprakashОценок пока нет
- A Study On The Specific Rate of Breakage of Cement MaterialsДокумент7 страницA Study On The Specific Rate of Breakage of Cement MaterialshamidОценок пока нет
- Basf Petronas Chemicals SDN BHD: BPC Hibiscus Infrastructure & Utility Upgrading ProjectДокумент24 страницыBasf Petronas Chemicals SDN BHD: BPC Hibiscus Infrastructure & Utility Upgrading ProjectjonedОценок пока нет
- TCN 02 c1476 Vol If TCC CML RevДокумент27 страницTCN 02 c1476 Vol If TCC CML RevghostamirОценок пока нет
- PSI Wall SleevesДокумент8 страницPSI Wall SleevespicottОценок пока нет
- Phys 371: Materials Physics Introduction To Materials Science)Документ27 страницPhys 371: Materials Physics Introduction To Materials Science)Sary KilanyОценок пока нет
- Rotational Moulding Design GuideДокумент14 страницRotational Moulding Design Guidesushant3240Оценок пока нет
- Conexiones Electricas Entre Materiales DistintosДокумент20 страницConexiones Electricas Entre Materiales DistintosJose GutierrezОценок пока нет
- List of Welding ProcessesДокумент4 страницыList of Welding ProcessesspahicdaniloОценок пока нет
- Logistics Services SindhuДокумент86 страницLogistics Services SindhubandichaituОценок пока нет
- Civil Engineering Seminar Topics - Geopolymeric Building Materials by Synergetic Utilisation of Industrial WastesДокумент10 страницCivil Engineering Seminar Topics - Geopolymeric Building Materials by Synergetic Utilisation of Industrial WastesfasilvkdОценок пока нет
- Canusa Pipeline Repair Products Installation GuideДокумент2 страницыCanusa Pipeline Repair Products Installation GuideLewoski100% (1)
- ZH 05Документ2 страницыZH 05billalaxmanОценок пока нет
- TS en 10120 - 2010Документ12 страницTS en 10120 - 2010Çağlar EbeperiОценок пока нет
- STI 8130 Data SheetДокумент2 страницыSTI 8130 Data SheetJMAC SupplyОценок пока нет
- Kanban in JitДокумент12 страницKanban in JitHimanshu SeerviОценок пока нет
- Preferred Tol and FitsДокумент9 страницPreferred Tol and Fitsananda_beloshe75Оценок пока нет
- Bulk Deformation ProcessДокумент67 страницBulk Deformation ProcessJith ViswaОценок пока нет
- Maharashtra Industries Directory PDFДокумент2 страницыMaharashtra Industries Directory PDFmanisha50% (2)
- TR - Heat TreatmentДокумент48 страницTR - Heat TreatmentAMIT PRAJAPATIОценок пока нет
- 6004 0100 ALE 0000 SH 0004 Up Dated Preferred Subcontractor List (04!02!15)Документ23 страницы6004 0100 ALE 0000 SH 0004 Up Dated Preferred Subcontractor List (04!02!15)romahi0% (1)
- Matdan BCS Series CatalogДокумент2 страницыMatdan BCS Series Catalogsatheez3251Оценок пока нет
- 18 Service Experience Me Gi EnginesДокумент61 страница18 Service Experience Me Gi EnginesCharalampos Soultatis100% (2)
- Hebbec PDFДокумент15 страницHebbec PDFCHAVEZ26Оценок пока нет
- Timber Frame NSAI AgrementДокумент22 страницыTimber Frame NSAI Agrementanthonyquinn500Оценок пока нет
- Fabric Defects & InspectionДокумент23 страницыFabric Defects & InspectionYogesh SharmaОценок пока нет